Search results
Search for "recycling" in Full Text gives 160 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Synthesis of diaryl phosphates using phytic acid as a phosphorus source
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2026, 22, 213–223, doi:10.3762/bjoc.22.15
- esterification with alcohols using sustainable biomass-derived phytic acid as a phosphorus source (Figure 2E). This approach can facilitate the development of environmentally friendly phosphate ester production as well as phosphorus recovery and recycling techniques. To date, the preparation of phosphate esters
Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of selenium-containing atropisomers via C–Se bond formations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2447–2455, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.186
- pathway. In both pathways, the active chiral rhodium catalyst is regenerated through a silver salt-mediated recycling, with Ag–SePh being formed as a byproduct (Scheme 2). 2. Catalytic atroposelective synthesis of selenium-containing atropisomers by spontaneous selenosulfonylation of alkynes Vinyl
Synthesis of β-ketophosphonates through aerobic copper(II)-mediated phosphorylation of enol acetates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1192–1200, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.96
- -centered radical from diisopropyl H-phosphonate (2a). In addition, the anion affects the redox properties of the copper ion, and thus the optimal choice is important to achieve both sufficient oxidative properties and catalyst recycling by reoxidation with O2. The employment of Mn(acac)3 and FeCl3, which
- ) sulfate under an argon atmosphere afforded 3a in 33% yield. These results indicate, that copper(II) at high loading is capable of oxidizing H-phosphonate even in inert conditions [72]; however, a balanced concentration of oxygen in the reaction mixture is required for recycling of copper catalyst and
Gold extraction at the molecular level using α- and β-cyclodextrins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1116–1125, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.89

- subsection, has sparkled the interest for industrial applications ranging from the recycling of gold-bearing e-waste [41] to the isolation of gold from mining sites. In 2014, a new company, Cycladex, was funded by Sir Fraser Stoddart and Dr. Roger Pettman with the mission of conducting eco-friendly mining of
- can yield 150 grams or more of gold, according to a study conducted in Japan in 2008 by recycling companies [50]. It is important, however, that the gold extraction method for e-waste sources is affordable in order to hold up the interest in the recovery, separation, and recycling of these materials
- saturated solution of β-CD and DBC at 0.1% (v/v) and stirred for five minutes to ensure maximal gold precipitation. Conversion of the [AuBr4]− anions trapped in the co-precipitate to gold metal was done by adding a reducing solution of N2H4·H2O. The process further allowed recycling β-CD from the solution
Effect of substitution position of aryl groups on the thermal back reactivity of aza-diarylethene photoswitches and prediction by density functional theory
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 242–252, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.16
- reaction mixture was neutralized by HCl aqueous solution, extracted with ether, washed with brine, dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using n-hexane and ethyl acetate 8:2 and recycling HPLC using chloroform as the
- concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using n-hexane and ethyl acetate 8:2 and recycling HPLC using chloroform as the eluent to give 0.68 g of I1 in 56% yield. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, TMS) δ = 2.09 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.46 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.27 (s, 1H, aromatic H
- quench the reaction. The reaction mixture was neutralized by an aqueous HCl solution, extracted with ether, washed with brine, dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated in vacuo. The crude product was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using n-hexane and ethyl acetate 8:2 and recycling
Cu(OTf)2-catalyzed multicomponent reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 122–145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.7
- -workers in 2003 (Scheme 13) [28]. Working in acetonitrile at room temperature, very high yields were obtained with recycling of the catalyst with negligible loss of activity. The reaction is successful also by operating it in ethanol as a solvent under microwave irradiation [29]. More recently, the
5th International Symposium on Synthesis and Catalysis (ISySyCat2023)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2704–2707, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.227

- organocatalyst for the gram-scale enantioselective synthesis of (S)-baclofen”, an interesting approach to recycling the very useful cinchona squaramide organocatalysts was described. This approach involved functionalization of the organocatalyst with a lipophilic linker (octadecyl side chains), resulting in a
Electrochemical allylations in a deep eutectic solvent
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2217–2224, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.189
- time, electrosynthesis requires a solvent and a supporting electrolyte in order for current to pass through the reaction. These are effectively consumable reagents unless a convenient means of recycling can be developed. As part of our interest in unusual solvents and electrochemistry, we explored the
- used, offering an interesting new option for electrochemical allylations. Keywords: allylation; electrosynthesis; eutectic solvent; recycling; tin; Introduction The last several years have witnessed a tremendous resurgence of interest in electrochemistry in the area of organic synthesis [1]. While
- limitation by using electrochemistry with catalytic amounts of metal or perhaps by recovering and recycling the metal with a recyclable solvent was the goal motivating this project. With this as a background, we undertook an investigation of electrochemical allylation in DES. Results and Discussion While
Factors influencing the performance of organocatalysts immobilised on solid supports: A review
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2129–2142, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.183

- applications in organic chemistry. Keywords: asymmetric synthesis; catalyst recycling; heterogenisation; organocatalysis; solid support; Introduction Organocatalysts are small molecules that do not contain a metal atom in the reaction centre and are able to increase the speed of reactions. They have proven
- MacMillan were awarded the Nobel Prize in 2021 for the development of asymmetric organocatalysis [6]. To date, industrial companies have used a number of asymmetric organocatalytic processes to synthesise pharmaceuticals and fine chemicals on large scales [7]. Catalyst recycling is key from both an economic
- fine chemical and pharmaceutical industries [9]. The limitation of homogeneous catalysts, however, is their complex, time-consuming and energy-intensive recovery and subsequent recycling. Therefore, synthetic modification of catalysts is a commonly used method to aid their recovery. Obstacles to the
Efficacy of radical reactions of isocyanides with heteroatom radicals in organic synthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2114–2128, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.182
- aware of resource recycling, and promote the use of natural energy [16]. The following three methods are generally used to generate heteroatom radicals (E•) (Scheme 1). In method 1, E• is generated by hydrogen abstraction from E–H by cyanoisopropyl radicals generated by thermal decomposition of 2,2
The Groebke–Blackburn–Bienaymé reaction in its maturity: innovation and improvements since its 21st birthday (2019–2023)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1839–1879, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.162

- , respectively. For further investigations, however, CALB was chosen due to its lower cost and easier availability. Optimization of enzyme loading and substrate ratios increased the yield up to 91%. Immobilization of the enzyme on silica particles was not detrimental to the yield, but allowed enzyme recycling
Synthesis of polycyclic aromatic quinones by continuous flow electrochemical oxidation: anodic methoxylation of polycyclic aromatic phenols (PAPs)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1746–1757, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.153
- trap the phenoxonium cation formed in the oxidation as an acetal, that later were hydrolysed to the quinone. Formation of hydrogen gas as the cathode reaction caused challenges in the flow cell and were overcome by recycling the reaction mixture through the cell at increased flow rate several times
- estitmation of the HOMO/LUMO energies to shed more light on this transformation. The easy separation of the supporting electrolyte from the product will allow recycling and makes this a green transformation. Keywords: acetal formation; cyclic voltammetry; flow electrochemistry; green oxidation; polycyclic
- cations B and C which have only one Clar sextet with two alternative positions. Conclusion The electrochemical oxidation of polycyclic aromatic phenols to quinones represents a green alternative to chemical oxidants. Hydrogen gas evolution can be handled by recycling of the reaction mixture through the
Chemo-enzymatic total synthesis: current approaches toward the integration of chemical and enzymatic transformations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1693–1712, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.151
- for methyl malonyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA in the enzymatic conversions. After careful and systematic optimization of the reaction conditions, such as the stoichiometry of the PKS modules and pH, along with the application of a NADPH recycling system, JuvEIV/JuvEV-catalyzed enzymatic conversions of 77–79
Methyltransferases from RiPP pathways: shaping the landscape of natural product chemistry
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1652–1670, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.147
- system and must be prepared beforehand. The incorporation of unnatural amino acids by the ribosome is less efficient and leads to incomplete translation, resulting in shunt products. Additionally, ribosome recycling efficiency and synthesis of full length proteins declines with length of the primary
Synthesis of cyclic β-1,6-oligosaccharides from glucosamine monomers by electrochemical polyglycosylation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1421–1427, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.124
- was further washed with aqueous 1 M HCl solution and dried over Na2SO4. Then, the solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the crude product (220 mg) was purified with recycling preparative gel permeation chromatography equipped with two series-connected JAIGEL-2HH columns (eluent: CHCl3, flow
Evaluation of the enantioselectivity of new chiral ligands based on imidazolidin-4-one derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 684–691, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.62
- catalytic arrangements of the most enantioselective catalysts, including anchoring on polystyrene beads [8][9], magnetic nanoparticles [10], or block copolymers composed of PEG-poly(Glu) [11]. These modifications have facilitated the recycling of the catalysts, offering numerous advantages, including
Green and sustainable approaches for the Friedel–Crafts reaction between aldehydes and indoles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 379–426, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.36
1-Butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate as suitable solvent for BF3: the case of alkyne hydration. Chemistry vs electrochemistry
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1966–1981, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.147
- pollutants. This also facilitates their recovery and recycling. Furthermore, they generally exhibit low flammability, high thermal and chemical stability, good thermal and electrical conductivity, together with the ability to solubilize organic and inorganic compounds of different polarity [78][79][80][81
- hexafluorophosphate (BMIm-PF6) as co-solvent with methanol and water to allow recycling of a phosphine-based Au(I) complex, as an efficient catalytic system for the hydration of terminal alkynes [87]. Moreover, the interesting properties of ILs have also been exploited to synthesize new solid polymeric catalysts for
- starting or stopping the electrolysis, 3) the absence of fuming, most probably due to the ability of the IL to stabilize the Lewis acid, 4) reduced sensitivity to moisture, due to the protective action of the IL, and 5) the possibility of recycling the same sample of IL for subsequent reaction cycles. In
Controlling the reactivity of La@C82 by reduction: reaction of the La@C82 anion with alkyl halide with high regioselectivity
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1858–1866, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.138

- -electron reduction of Gd@C2v-C82 for the addition reaction to occur at room temperature [22]. Supporting Information File 1, Figure S1 depicts the three HPLC separation steps including recycling for the isolation. The matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI–TOF) mass spectra of 2a
A novel recyclable organocatalyst for the gram-scale enantioselective synthesis of (S)-baclofen
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1811–1824, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.133

- , application, and recycling of a new lipophilic cinchona squaramide organocatalyst. The synthesized lipophilic organocatalyst was applied in Michael additions. The catalyst was utilized to promote the Michael addition of cyclohexyl Meldrum’s acid to 4-chloro-trans-β-nitrostyrene (quantitative yield, up to 96
- long and expensive process. Therefore, for sustainable application, the cost-efficient recovery and reuse of organocatalysts are critical issues. Fortunately, a wide range of recycling options are known in the literature, often based on liquid–solid phase separation [14]. Catalyst recycling can be
- flow systems. Accordingly, the main recycling methods rely on the immobilization of catalysts on heterogeneous supports, however, this could often lead to the deterioration of activity and/or selectivity [27]. A possible solution to avoid these drawbacks is the heterogenization of the catalyst after a
A series of perylene diimide cathode interlayer materials for green solvent processing in conventional organic photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1620–1629, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.119

- Organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices for energy harvesting or light recycling are of interest due to their low cost, fabrication via layer-by-layer printing, flexibility, and low carbon footprint [1][2]. Due to the processability of organic materials used in OPVs, the large-scale manufacturing of such
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
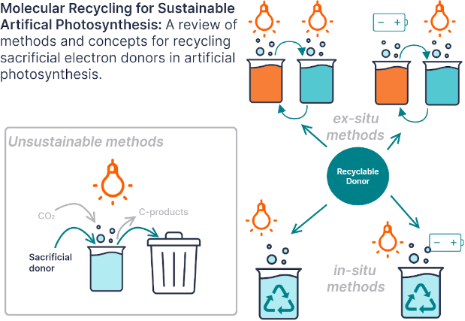
- Grace A. Lowe van ’t Hoff Institute for Molecular Sciences (HIMS), Universiteit van Amsterdam (UvA), Science Park 904, Amsterdam, 1098 XH, The Netherlands 10.3762/bjoc.19.88 Abstract This review surveys advances in the literature that impact organic sacrificial electron donor recycling in
- highlights photo- and electrochemical methods for recycling amines and NADH analogues that can be used as electron donors in artificial photosynthesis. Important properties of sacrificial donors and recycling strategies are also discussed. Compounds from other fields, such as redox flow batteries and
- challenging in these scenarios. There is currently a steadily growing body of research investigating recycling of sacrificial electron donors. Meanwhile, advances in other fields have resulted in a vast array of alternative redox mediators and recyclable electron donors to explore. Sacrificial donors have
Photoredox catalysis harvesting multiple photon or electrochemical energies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1055–1145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.81
- ), where the electrochemical and photochemical steps are intimately involved within the same catalytic cycle, as subsequent steps. This broadly separates into two subcategories, “radical ion e-PRC” (Figure 2, right) and “recycling e-PRC”. Radical ion e-PRC typically implicates electrogenerated radical ion
- doublet states which are photoexcited to yield super-oxidants or super-reductants while recycling e-PRC involves the turnover of a ‘standard’ (typically closed-shell) photoredox catalyst (PC) by means of anodic oxidation or cathodic reduction [28][29]. Furthermore, a series of new protocols using
A new oxidatively stable ligand for the chiral functionalization of amino acids in Ni(II)–Schiff base complexes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 566–574, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.41

- )) and includes a chiral auxiliary, an amino acid, and a bifunctional linker capable to arrange the components in the Schiff base complex. Such templates provide a significant C–H acidity at the α-amino acid carbon and a possibility for recycling of the chiral auxiliaries (for reviews see [5][14][15][16
Inline purification in continuous flow synthesis – opportunities and challenges
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1720–1740, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.182

- solution to avoid particles in the chromatography system [37][124]. In relation to nanofiltration, several devices equipped with specific membranes have been reported. Hessel and co-workers published a detailed review about inline recycling and separation of homogeneous catalysts, which contains a detailed
- biocatalysts in view of recycling. This will likely see applications for generating small volume drugs or other high value entities where fast access to a high quality product is key, or where the isolation and handling of intermediates is not viable due to their properties. Thus, it can be concluded that many

















































































































































































































































































































































































































































