Search results
Search for "vesicles" in Full Text gives 74 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Effect of a photoswitchable rotaxane on membrane permeabilization across lipid compositions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2498–2512, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.192

- modulate membrane permeability in large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) of varying lipid compositions. Upon photoisomerization, the rotaxane significantly enhanced the release of the hydrophilic dye sulforhodamine B in vesicles composed of EYPC/Chol 8:2, with release increasing from 29% (non-irradiated) to 59
- photochemical process occurs, which triggers the release from only the vesicles containing EYPC. These findings underscore the significance of both the physical and chemical properties of the bilayer in enabling effective light-triggered cargo release through rotaxane activation. Keywords: lipid membrane
- permeabilization in bilayers of varying rigidity and whether membrane phase influences its photoswitching behavior. To address these questions, we investigated the light-induced switching of rotaxane 1 in large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs) composed of lipids representative of distinct membrane phases. Membrane
Rotaxanes with integrated photoswitches: design principles, functional behavior, and emerging applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2345–2366, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.179

- shuttling motion along a 3.2 nm axle between two BAA recognition sites in acetonitrile solution. The behavior of this rotaxane was investigated in lipid bilayers of large and giant vesicles. Remarkably, the photoisomerization of the azobenzene units enabled modulation of the rotaxane's interaction with the
- lipid membrane, leading to reversible changes in giant lipid vesicles. In the trans isomer, the membrane tension decreased, resulting in deformation and pronounced membrane undulations. Isomerization to the cis form increased membrane tension, causing vesicle contraction. Molecular dynamics simulations
- for drug delivery, therapeutics, and various biotechnological applications [85][86][87][88]. As a proof of principle, this rotaxane was used to trigger the light-induced release of hydrophilic cargo from large vesicles, highlighting its potential as a platform for controlled drug delivery. Recently
Research progress on calixarene/pillararene-based controlled drug release systems
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1757–1785, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.139

- vesicles, micelles and nanoparticles, overcoming the difficulties in modifying cyclodextrin and cucurbituril. These features make CAs and PAs promising candidates for stimulus responsive drug release systems [46]. Their structural diversity and functional designability offer broad prospects for targeted
- amphiphiles has significantly expanded, bringing revolutionary breakthroughs to drug delivery systems. These structures, which possess both hydrophobic and hydrophilic characteristics, can self-assemble through non-covalent interactions to form well-defined aggregates such as micelles, vesicles, and
- nanoparticles [62]. Their morphologies mainly depend on molecular structure, concentration, and environmental properties. The cylindrical geometry of vesicles [63] promotes the arrangement of amphiphilic molecules with their hydrophobic tails pointing inward and hydrophilic heads pointing outward, forming a
Beyond symmetric self-assembly and effective molarity: unlocking functional enzyme mimics with robust organic cages
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 421–443, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.30
- enzyme dynamics. The wider history of supramolecular and cavity catalysis [3][13][15][16][17][18][19][21][48][49], and catalysis using confined transition-metal catalysts [50][51][52], dendrimers [53] or synzymes [54], micelles [55] or vesicles [56], catalytic antibodies [57][58][59] or molecularly
Hot shape transformation: the role of PSar dehydration in stomatocyte morphogenesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 47–54, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.5
- across various applications. In this study, we present a comprehensive methodology for synthesizing, self-assembling, and transforming polysarcosine-poly(benzyl glutamate) block copolymers, resulting in the formation of bowl-shaped vesicles, disks, and stomatocytes. Under ambient conditions, the shape
- transformation is restricted to bowl-shaped vesicles due to the membrane's flexibility and permeability. However, dehydration of the polysarcosine broadens the possibilities for shape transformation. These novel structures exhibit asymmetry and possess the capability to encapsulate smaller structures, thereby
- glutamate); polysarcosine; shape transformation; stomatocyte; supramolecular chemistry; Introduction Polymeric vesicles represent a promising candidate for usage in drug delivery systems due to their facile assembly and ability to provide a stable soft interface. Among these materials, polyethylene glycol
Understanding X-ray-induced isomerisation in photoswitchable surfactant assemblies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2005–2015, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.176

- on their own and in mixed micelles with lipids, on irradiation with either UV or blue light [21][22]. In addition, Ober et al. showed that in-situ UV irradiation stimulates a steady decrease in bilayer thickness for vesicles formed using Azo-modified phosphatidylcholine lipids, due to the shorter
New variochelins from soil-isolated Variovorax sp. H002
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 692–700, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.63
- ) resembles those of other amphiphilic marine siderophores such as marinobactins and aquachelins exhibiting the membrane affinity [21] as well as the self-assembling ability to form iron-containing vesicles [22]. This study presents another suite of amphiphilic peptidic siderophores originating in the
Switchable molecular tweezers: design and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 504–539, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.45

- arms, can encapsulate planar aromatic molecules, making this system promising for drug delivery. The advancement of pH-switchable molecular tweezers laid the groundwork for the development of switchable lipids [20]. When such lipids are incorporated in lipid vesicles, they provide means for controlled
- their open conformation. This causes fluctuations and local defects in the packing of a bilayer (Figure 3), leading to membrane disruption and release of active components from within the vesicles [22]. Such concept makes these tweezers good candidates for controlled drug delivery. The group of F. Wang
Photochromic derivatives of indigo: historical overview of development, challenges and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 228–242, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.23

- assemblies as well as precise switching of the biological activity of the photoswitchable derivative. Along these lines, in 2023, Leung and co-workers prepared amphiphilic indigo-based photoswitches and incorporated them into vesicles [88]. Irradiation of the vesicles with red light resulted in the E–Z
- isomerization of the indigo derivatives that led to the disassembly of well-shaped vesicles and formation of irregular aggregates. The thermal Z–E relaxation of the indigo scaffold provided the restoration of the vesicle structure. The system contributed to the development of red-light-controllable biomedical
Perspectives on push–pull chromophores derived from click-type [2 + 2] cycloaddition–retroelectrocyclization reactions of electron-rich alkynes and electron-deficient alkenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 125–154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.13

- solution as well as contradictory propensity to form luminescent nanostructure suspensions in hexane (Figure 5) [137]. It was posited that 65 features hollow vesicles, with vesicle fusion releasing curvature energy, leading to a thermodynamically more stable tubular structure. Such aggregation-induced
Cyclodextrins permeabilize DPPC liposome membranes: a focus on cholesterol content, cyclodextrin type, and concentration
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1570–1579, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.115

- dose-dependent manner [15]. Additionally, the CHOL content was demonstrated to reduce and sometimes to inhibit the permeability of DPPC vesicles induced by bioactive agents [16][17]. Given the condensing and ordering effect that CHOL exerts on the membrane, the presence of CHOL in the lipid bilayer
- obtained by subtracting the SRB release from vesicles in the presence of CDs from that obtained in their absence as explained earlier. Results are presented in Figures 3, 4, and 5. The obtained data are also reported in Tables S1–S4 (Supporting Information File 1) in which the vertical reading points out
- 1 h of incubation whereas those from membranes containing higher CHOL contents did not exceed 5% after the same time. After 4 h of incubation, the SRB release reached 16.41% for 10% CHOL liposomal membranes and less than 10% for vesicles composed of higher CHOL content. After 48 h of incubation, 63
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- ) KO mouse which is a mouse model that stop the biosynthesis of ELs [22]. In that case, a reduction of the levels of various neurotransmitters were evidenced likely due to an alteration of the transport efficacy assumed by the synaptic vesicles. The phenotype of these KO mouse shows impaired social
- mesenchymal transition of breast epithelium cell lines [33], the fusion of membranes with extracellular or intracellular vesicles [34] including neurotransmission vesicles [35]. ELs could also be used as a probe to evaluate climate change [36]. All the articles and reviews reporting the description of natural
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
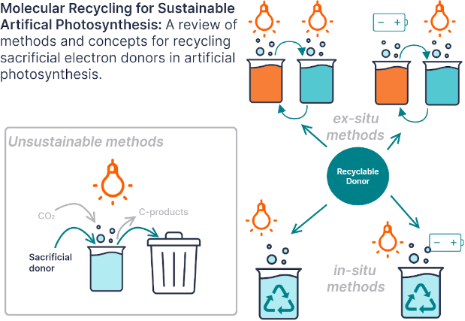
- microscopy [36][37]. In nature, chemical gradients and phase separation are maintained by compartmentalization in liposomes, micelles, and vesicles rather than at interfaces such as ITIES. Artificial photosynthesis systems are being designed to mimic this behavior and recently the field of artificial
pH-Responsive fluorescent supramolecular nanoparticles based on tetraphenylethylene-labelled chitosan and a six-fold carboxylated tribenzotriquinacene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 635–645, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.45

- construct pH-responsive supramolecular vesicles and molecule-scale drug carriers, respectively. Both of them exhibited pH-responsive properties, with the host–guest binding disintegrating when the pH of the solution is adjusted to 5.5 and the binding regenerated when the pH is restored to 7.4. These
- stimulus-responsive supramolecular vesicles and molecule-scale drug carriers are considered to have potential for cancer drug delivery. However, such supramolecular systems are not suitable for oral administration, which is a convenient and patient-preferred method of drug delivery, especially for patients
- in the range of 200 to 800 nm at 25 °C. Fluorescence spectroscopy. The solid-state fluorescence intensities of three CS-TPE bioconjugates and their fluorescence intensities at different pH values, as well as those of the three TBTQ-C6/CS-TPE supramolecular vesicles at different pH values were
Synthesis of a new water-soluble hexacarboxylated tribenzotriquinacene derivative and its competitive host–guest interaction for drug delivery
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 539–548, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.56
- -containing amphiphile (trans-AZO) to produce the TBTQ-C6-trans-AZO supra-amphiphile by host–guest interactions in water. The supra-amphiphile was further self-assembled into photo and pH dual-responsive supramolecular vesicles that have a potential to serve as drug nanocarriers to enable controlled drug
Tetraphenylethylene-embedded pillar[5]arene-based orthogonal self-assembly for efficient photocatalysis in water
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 429–437, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.45

- tunable self-assembly, such as vesicles [14][15][16], micelles [17][18][19], nanocrystals [20], coordination-driven assemblies [9][21][22], host–guest interactions [15][23][24][25], etc. In the above systems, catalysts are encapsulated by supramolecular assemblies and thus provide a suitable environment
- acceptors. The obtained vesicles could be utilized as a nanoreactor for photocatalyzed dehalogenation reactions in water. However, the above reported supramolecular nanosystem requires a long time to produce the dehalogenated product with high yield. Therefore, the development of a potential nanoreactor for
Cationic oligonucleotide derivatives and conjugates: A favorable approach for enhanced DNA and RNA targeting oligonucleotides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1828–1848, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.125
- , ASOs carrying the novel guanidinium modification were mainly localized in the cytoplasm, indicating that the ASOs are taken up by endocytosis but are retained in part in the endocytic vesicles [112]. Utilizing the phosphorus atom as an attachment point for cationic aminoalkyl groups has been employed
DNA with zwitterionic and negatively charged phosphate modifications: Formation of DNA triplexes, duplexes and cell uptake studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 749–761, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.65
- transfection reagent, whereas, N+ONs remain concentrated in vesicles within the cytoplasm. These results indicate that both N+ and Ts-modified ONs are promising for various in vivo applications. Keywords: cell uptake; charge neutral modification; DNA; modified phosphates; Staudinger reaction; Introduction
- microscopy. Figure 3 shows that FAM-labelled Ts and N+-modified DNAs are concentrated in vesicles (punctate foci in the oligo/FAM panel) that accumulate around the edge of the nucleus. Interestingly, the Ts-modified oligo is also present in the nucleus as indicated by the colocalisation of the ON (Figure 3E
- ) with the nuclear DNA (Figure 3D). The diffuse nuclear pattern of the Ts-modified ON suggests they can escape the endocytic vesicles and enter the nucleus via the nuclear pores. This is in contrast to the lack of colocalisation of the FAM signal with the nuclear DNA in the negative control (no oligo
19F NMR as a tool in chemical biology
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 293–318, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.28

- nuclei such as 1H or 15N PREs. 19F NMR has also been applied to study the conformational heterogeneity and dynamics of a broad range of proteins and peptides upon their interaction with model lipid vesicles [59], micelles [60] and bicelles [61]. It has enabled the quantification and mechanistic
Supramolecular polymerization of sulfated dendritic peptide amphiphiles into multivalent L-selectin binders
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 97–104, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.10

- to its functionalization with negatively charged sulfate groups. The binding behavior of dPGS to L-selectin has been thoroughly probed as dendrimer [26][27], conjugated to a polymer [28] or as amphiphilic adamantyl conjugates that are able to self-assemble on cyclodextrin vesicles [29]. Our group
Nonenzymatic synthesis of anomerically pure, mannosyl-based molecular probes for scramblase identification studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1732–1739, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.145
- of MPD across the ER. Although the activity of MPD scramblase has been described in microsomal vesicles and reconstituted systems [1][2][9], the molecular identity of this protein remains unknown. To circumvent the need for traditional purification strategies to identify the scramblase, we considered
Plasma membrane imaging with a fluorescent benzothiadiazole derivative
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2644–2654, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.257

- its selectivity seems to be smaller than the one observed for the new green emitter. Although the plasma membrane separates the interior of the cell from the extracellular environment, there is a massive material transfer between both sides [59]. These materials typically are transported by vesicles
Probing of local polarity in poly(methyl methacrylate) with the charge transfer transition in Nile red
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2552–2562, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.248

- -controlled drug delivery systems [4][6][7][8][9][10], as well as dynamics of polymers at interfaces [11]. To be able to understand local properties of polymers, in particular in nanoenvironments of polymeric vesicles (polymersomes), comprising a hydrophilic corona and a hydrophobic wall [1][12], or in
Sugar-derived oxazolone pseudotetrapeptide as γ-turn inducer and anion-selective transporter
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2419–2427, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.234

- [17][18], we investigated the ion transport activity of 1 and 2a across lipid bilayer membranes. In this study, the collapse of the pH gradient (pHout = 7.8 and pHin = 7.0), created across egg yolk ʟ-α-phosphatidylcholine (EYPC) vesicles with entrapped 8-hydroxypyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid trisodium
- 2b. The influx of Cl‒ ion by these transporters were monitored using EYPC-LUVslucigenin. Additionally, compound 9, which has a free amino group and a free carboxylic acid group, was also subjected to the Cl‒ transport study. The Cl– sensitive dye lucigenin, was entrapped within the lipid vesicles and
An overview of the cycloaddition chemistry of fulvenes and emerging applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2113–2132, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.209
- phospholipid unilamellar vesicles at low concentrations (5 µg/mL), and in a dose and molecular weight dependent fashion, indicating their potential antimicrobial properties. Further studies revealed that co-polymerisation of norbornene imide monomers with different alkyl groups provided optimal antimicrobial




















































































































































































































































































































































































































