Search results
Search for "viologen" in Full Text gives 19 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Research progress on calixarene/pillararene-based controlled drug release systems
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1757–1785, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.139

- in organic solvents, [77] which is not feasible for crown ethers, CAs, and resorcinarenes. In addition, PAs can form supramolecular systems in the following ways: (1) the electron-rich cavity interacts electrostatically with cationic guests, such as methyl viologen derivatives, pyridinium salts, and
Mechanistic investigations of polyaza[7]helicene in photoredox and energy transfer catalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1236–1245, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.106

- extinction coefficient, Δε455(Rubpy*) = −10100 M−1 cm−1 [37][79], following excitation (Figure 4B). 0.3 mM methyl viologen (MV2+) were added to Aza-H to quantitatively quench the triplet-excited photocatalyst in an electron transfer reaction yielding Aza-H•+ and MV•+, which are clearly observed in the TA
- the reliability of our procedure. Taking the literature-known extinction coefficient of the methyl viologen radical cation Δε395(MV•+) ≈ 39000 M−1 cm−1 [82] to calculate its concentration and the initial Aza-H excited-state concentration obtained through Rubpy* actinometry allows us to determine the
Switchable molecular tweezers: design and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 504–539, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.45

Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
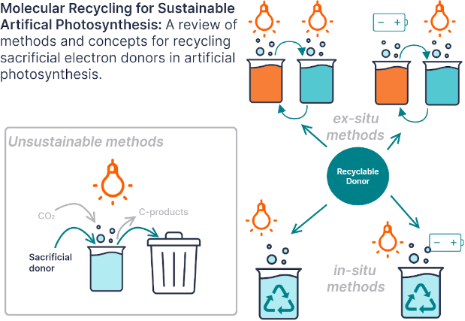
- photosynthesis using liposomes was thoroughly reviewed with special attention paid to donors and redox mediators [38]. Species such as methyl viologen were employed as redox mediators in some of the systems reviewed, however, the regeneration still required consumption of species other than water, such as EDTA
- species was so stable that it could be stored in the dark for hours and then be used to reduce methyl viologen. If DMT can be replaced with a more sustainable electron source, this could be part of a decoupled cycle either regenerating an oxidized sacrificial donor or using the reduced Cu(I) 4H
- recyclable amine species for comparison [32]. The ferrocene, TEMPO, and viologen derivatives shown in Figure 4 are used in aqueous organic redox flow batteries [59][63]. The batteries store charge in concentrated aqueous solutions of small organic redox mediators that can be oxidized and re-reduced (or
Synthesis of a new water-soluble hexacarboxylated tribenzotriquinacene derivative and its competitive host–guest interaction for drug delivery
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 539–548, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.56
- water-soluble hexacarboxylated tribenzotriquinacene derivative (TBTQ-CB6) was synthesized and used as a supramolecular drug carrier to load the model anticancer drugs dimethyl viologen (MV) and doxorubicin (DOX) via host–guest interactions. The drugs could be effectively released by spermine (SM), a
- larger cavity as compared to TBTQ-C6 due to the introduction of triazole rings. Two anticancer drug molecules, dimethyl viologen (MV) with a smaller size and DOX with a larger size, were selected as model anticancer agents for encapsulation by TBTQ-CB6 to form the host–guest complexes of TBTQ-CB6MV and
- synthesized compounds were fully characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry (see Supporting Information File 1) and the data were found to be consistent with the proposed structures. Host–guest complexation of TBTQ-CB6 with dimethyl viologen (MV). The host–guest complexation between
Diametric calix[6]arene-based phosphine gold(I) cavitands
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 190–196, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.21
- devised a new family of triphosphine calix[6]arene gold(I) complexes (Figure 1c) [30]. These cavitands are able to form (pseudo)rotaxane species, by threading viologen-based guests, with a conformational control operated by the sulfonamido hydrogen-bonding donor domain [31][32]. Furthermore, their
A review of asymmetric synthetic organic electrochemistry and electrocatalysis: concepts, applications, recent developments and future directions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2710–2746, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.264

- asymmetric reduction of 135 using enolate reductase that afforded the corresponding chiral acid 136 in 95% yield and 95% ee. It has been shown that the cofactor NADH is oxidized during this process and can be regenerated using methyl viologen 137 as a reductive mediator (Scheme 43) [78]. In 1997, Yoneyama
Host–guest interactions in nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril: novel guest-dependent molecular recognition and stereoisomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1705–1711, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.166
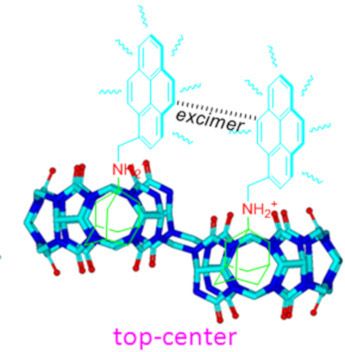
- ], a new member of the extended Q[n] family that contains two identical cavities. Different from the Q[8] host, NS-CB[10] can not only accommodate two aromatic guest molecules such as 4,4-bipyridinium (viologen), but also has the ability to accommodate two other guest molecules such as
Synthesis, enantioseparation and photophysical properties of planar-chiral pillar[5]arene derivatives bearing fluorophore fragments
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1601–1611, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.164

- separation of these conformational isomers is impossible. Inhibiting the rotation of the phenolic units is prerequisite to isolate the isomers. A complexation with a suitable guest molecule, such as a viologen derivative, can significantly slow down the rotation of the phenolic rings, and a conformational
Mild and selective reduction of aldehydes utilising sodium dithionite under flow conditions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1529–1536, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.129
- piperidines [17], benzil groups [19], nitroarenes and nitroalkanes in the presence of dialkyl viologen electron transfer catalysts [20][21] and immobilized nitroarene’s under phase transfer conditions [22][23]. In this publication we report the efficient reduction of aldehydes under flow conditions utilising
A versatile route to polythiophenes with functional pendant groups using alkyne chemistry
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2682–2688, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.265
- quinone moieties are vulnerable in nucleophilic and acidic environments. Furthermore, the viologen moiety, available from 4,4’-bipyridine (BP) has potential for energy storage and electrochromic applications [35][36], but it has previously been anchored to a polymer backbone only by oxidative coupling via
- carbon of the pendant group precursors, with yields of 61% (9), 82% (10) and 65% (12), respectively. Methylation of bipyridyl intermediate 10 by methyl iodide produced viologen derivative 11 after exchanging the iodide for the PF6− anion. For the methylation step drying of both the reactants 10 and
- methyl iodide and the solvent was essential, since its omission resulted in polymerization of the viologen-pyEDOT, as indicated by 1H NMR (see Supporting Information File 1, Figure S11). We suspect that the polymerization was triggered by the acid generated from methyl iodide reacting with water
Biocatalysis for the application of CO2 as a chemical feedstock
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2370–2387, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.259

- the visible spectrum (>1.35 eV) and coupled to FDH activity through a mediator to drive CO2 reduction. Two W-dependent FDHs, isolated from the syntrophic bacterium Syntrophobacter fumaroxidans, showed high catalytic activity for CO2 reduction, using reduced methyl viologen as the electron donor. Later
Supramolecular chemistry: from aromatic foldamers to solution-phase supramolecular organic frameworks
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2057–2071, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.222

- successive intramolecular C–H····F or C–H····Cl hydrogen bonds [70]. Conjugated radical cation dimerization-driven pleated foldamers. The stacking of the radical cations of viologen or TTF were observed in 1964 and 1979 [71][72]. This stacking is typically weak. Several approaches have been developed to
- ) precursors by forming dynamic hydrazone bonds [79] (Scheme 16). This dynamic covalent chemistry approach allowed for quick synthesis of viologen/TTF-alternating polymers. Driven by the intramolecular donor–acceptor interaction between the TTF and viologen units, the polymers folded into pleated conformations
- in acetonitrile. Upon oxidation of the TTF units to radical cation TTF·+, the polymers adopted flexible conformations. When the viologen units were reduced to radical cations, the radical cations stacked intramolecularly to induce the backbone to form another kind of pleated secondary structure
Single-molecule conductance of a chemically modified, π-extended tetrathiafulvalene and its charge-transfer complex with F4TCNQ
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 1068–1078, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.120

- viologen [5][6], aniline [7][8], thiophene [9], anthraquinone [10] and ferrocene [11] have been previously studied. However, a particularly suitable redox-active molecule for molecular electronics is the well-known electron donor tetrathiafulvalene (TTF) molecule. Pristine TTF, as well as the
Molecular ordering at electrified interfaces: Template and potential effects
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 2243–2254, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.233

- effects, in the structure formation process of DBV cations on these modified Cu electrode surfaces. Keywords: cyclic voltammogram; scanning tunneling microscopy; self-assembly; template effect; viologen; Introduction The precise control of the self-organization of molecular layers on either conducting
- deposition and structure formation of the molecular layers. In this paper we will present results on the self-organization of 1,1’-dibenzyl-4,4’-bipyridinium, in short dibenzyl-viologen (DBV), cations on a chloride precovered Cu(111) electrode surface. A comparison of these findings with those described
- different symmetry. The motivation for the choice of viologen molecules is twofold. On the one hand molecular viologen-based self-assemblies have attracted a great deal of attention in recent years due to their widespread applications in electronic devices [8][9], and light-harvesting operators [10]. On the
Synthesis of guanidinium–sulfonimide ion pairs: towards novel ionic liquid crystals
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1093–1101, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.121
- -crystalline phases were found for viologen salts [23][24][25][26][27][28], imidazolium ILCs [29][30][31], pyrrolidinium ILCs [32][33] and ionic polymers [34][35][36][37]. Sulfonimides, which are directly bound to a mesogenic group, have not been described until now. We have recently described the concept of
Supramolecular hydrogels formed from poly(viologen) cross-linked with cyclodextrin dimers and their physical properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1594–1600, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.182
- employs cyclodextrin (CD) as a host molecule, because CD effectively forms polyrotaxanes with polymers. Herein we report the formation of supramolecular hydrogels with an α-CD dimer (α,α-CD dimer) as a topological linker molecule, and a viologen polymer (VP) as the polymer chain. The supramolecular
- VP does not form a supramolecular hydrogel, indicating that complexation between the C10 unit of VP and the α-CD unit of the α,α-CD dimer plays an important role in the formation of supramolecular hydrogels. Keywords: cyclodextrins; poly(viologen); supramolecular hydrogel; Introduction Development
- formation of supramolecular hydrogels with the α,α-CD dimer, we chose the viologen polymer (VP), which possesses multiple cations, as the axis molecules. Decamethylene units function as recognition sites of α-CD, and bipyridyls work as electric barriers. Results and Discussion Preparation of CD dimers and
Formation of carbohydrate-functionalised polystyrene and glass slides and their analysis by MALDI-TOF MS
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 753–762, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.86
- in the mass-to-charge ratio [14]. Previous attempts to get around this issue have involved coating polymer or glass surfaces with a thin membrane of conductive material, such as gold, carbon or indium-tin oxide [15][16][17], or the addition of electron-accepting additives, such as methyl viologen
Aromatic and heterocyclic perfluoroalkyl sulfides. Methods of preparation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, 880–921, doi:10.3762/bjoc.6.88
- likely. Homogeneous catalysis by the methyl viologen (MV) [186] supports this. This catalyst can oxidize the radical anion [ArSRF]−• via its dication (MV2+) [200][202], accelerating the last step (Scheme 52). 4.2. Radical perfluoroalkylation Synthetic methods for aryl perfluoroalkyl sulfides via RF























































































































































































































![[Graphic 1]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-11-222-i19.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) 16 and dynamic [2]catenane formed by compounds 17–19.
16 and dynamic [2]catenane formed by compounds 17–19.











































































































































