Search results
Search for "microcavities" in Full Text gives 14 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Nanostructured materials characterized by scanning photoelectron spectromicroscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 700–710, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.54

- can be occasionally necessary in order to avoid overlapping of Ni 2p signal with other XPS contributions in doped NiO or Ni-based compounds. Taeño et al. [46] recently reported the study of NiO microcrystals with self-organized microcavities synthesized by a vapor–solid process at temperatures ranging
Various CVD-grown ZnO nanostructures for nanodevices and interdisciplinary applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 1390–1399, doi:10.3762/bjnano.15.112

- microcavities [9]. Additionally, it is a transparent semiconductor with significant piezoelectricity [10]. These noble characteristics suggest ZnO to be a potential material in the fabrication of UV/blue/green LEDs, solid-state random lasers, UV-absorption devices, and nanogenerators [9][11][12][13]. Magnetic
Analytical and numerical design of a hybrid Fabry–Perot plano-concave microcavity for hexagonal boron nitride
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 1030–1037, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.90

- -defined spatio-temporal mode along with an accessible numerical aperture (NA) to increase the light extraction efficiency that is required for effective coupling into optical waveguides. Based on a previously developed experimental approach to fabricate hybrid Fabry–Perot microcavities (Ortiz-Huerta et al
- a SPE (i.e., in-plane dipole) hosted by a 2D hBN layer inside the hybrid plano-concave microcavity. Keywords: Fabry–Perot; hBN; microcavities; plano-concave; polymers; Introduction Pure and indistinguishable SPEs are key components needed for their application in upcoming quantum technologies [1
- microcavities [8], microdisk resonators [9], and photonic crystals [10][11] have been designed and built around color centers in hBN to increase its spontaneous emission by means of Purcell effect. An alternative and low-cost approach to build photonic structures uses polymers to embed different types of SPEs
Fabrication and testing of polymer microneedles for transdermal drug delivery
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 629–640, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.55

- fabrication of MN array master and replica The 9 × 9 MN arrays were successfully fabricated by TPP, and Zeonor 1060R replicas were made (>20 cycles) using hot embossing on PDMS mold. During the cycles, no damage was observed to the PMDS mold or its microcavities. Three 9 × 9 MN patch replicas were selected
Rational design of block copolymer self-assemblies in photodynamic therapy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 180–212, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.15

Label-free highly sensitive probe detection with novel hierarchical SERS substrates fabricated by nanoindentation and chemical reaction methods
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2483–2496, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.239

- . Therefore, arrayed microcavities could be machined by a tip-based indention method previously described by us [31]. This prior work [31] is mainly concerned with the fabrication of arrayed inverted pyramid cavities as SERS substrates using an indentation method that studied the effect of the Raman intensity
Correlation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) with the surface density of gold nanoparticles: evaluation of the critical number of SERS tags for a detectable signal
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1016–1023, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.102

- plasmonic nanoparticles dispersed on a substrate [38], inside microcavities [39], or even while monitoring electrochemical reactions [40]. This work reports on the study of SERS tags obtained by laser ablation synthesis in liquid solution (LASiS) of gold (Au) nanoparticles, their coating with three
Electromagnetic analysis of the lasing thresholds of hybrid plasmon modes of a silver tube nanolaser with active core and active shell
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 294–304, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.28

- microcavities [18]. To date, the LEP approach has been successfully applied to a variety of 2D microlasers, which appear as reasonable approximations of 3D configurations shaped as thin flat “disks” or “patches”: single fully active microcavities in the form of a circle [19], kite [20], and square [21], active
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
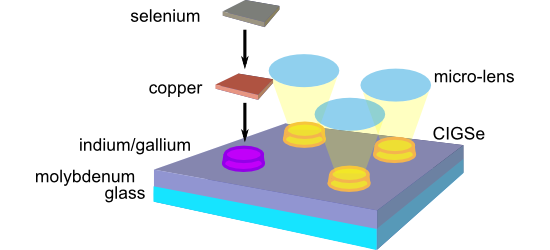
- compensated, since the spin-coated photoresist insulates any potentially occurring irregularities such as microcavities. The microcells were connected in a parallel manner and exhibited efficiencies between 0.15% and 2.9% under 1 sun illumination. Under concentrated illumination, significant efficiency
Temperature-tunable lasing from dye-doped chiral microdroplets encapsulated in a thin polymeric film
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 379–383, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.37

- 87036, Italy 10.3762/bjnano.9.37 Abstract In the last decade, much interest has grown around the possibility to use liquid-crystal droplets as optical microcavities and lasers. In particular, 3D laser emission from dye-doped cholesteric liquid crystals confined inside microdroplets paves the way for
Design of photonic microcavities in hexagonal boron nitride
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 102–108, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.12

Fabrication of gold-coated PDMS surfaces with arrayed triangular micro/nanopyramids for use as SERS substrates
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2271–2282, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.227

- of the force signal in the vertical direction and the machining velocity of the precision stage in the horizontal direction simultaneously, arrayed micro/nanocavities were formed by the overlap of the pile-ups with high efficiency. In the present study, arrays of triangular microcavities on a Cu(110
Constant-distance mode SECM as a tool to visualize local electrocatalytic activity of oxygen reduction catalysts
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 141–151, doi:10.3762/bjnano.5.14

- microscopy (4D SF/CD-SECM) was utilized for the investigation of the activity distribution of oxygen reduction catalysts. Carbon-supported Pt model catalyst powders have been immobilized in recessed microelectrodes and compared to a spot preparation technique. Microcavities serve as platform for the binder
- ). Furthermore, recessed microelectrodes fabricated by etching inlayed Au disk microelectrodes are demonstrated as a flexible platform for immobilization of catalyst powders for cd-mode SECM experiments. The microcavities (also referred to as micropores) have already demonstrated their applicability for integral
- overcome these drawbacks, an alternative sample preparation protocol based on the utilization of recessed microelectrodes as flexible platform for catalyst immobilization was applied for cd-mode SECM imaging. Microcavities as flexible platform for sample preparation in constant-distance mode SECM The
Diamond nanophotonics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2012, 3, 895–908, doi:10.3762/bjnano.3.100

- observed, which is even slightly better than the result obtained with the macroscopic SIL. The device is therefore a highly promising microstructure that provides a universal performance boost for diamond quantum applications. 4 Dielectric pillar microcavities with embedded diamond nanocrystals An
- structure with one-dimensional confinement of light. In order to achieve a three-dimensional light confinement, pillar microcavities are milled out of the planar structure by focused ion beam. As a consequence, the light field is concentrated vertically between the two dielectric Bragg mirrors and laterally
- resonator geometries, with a shortening of the excited state lifetime six times. By using dielectric diamond hemispheres, the photon collection efficiency was increased by a factor of up to six. Dielectric pillar microcavities with embedded diamond nanocrystals containing single NV centers have been



































































































































