Search results
Search for "liquids" in Full Text gives 230 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology. Showing first 200.
Spin-chemistry concepts for spintronics scientists
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1427–1445, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.143

- radical pair is termed a spin-correlated radical pair (SCRP). In liquids, where radicals can diffuse, radical pairs are usually classified as geminate pairs (G-pairs), that is, pairs of radicals born in the same chemical event, or radical pairs formed upon encounters of free radicals in the solvent bulk
- interactions of spins with the external field B0 (hereafter, the static field directed parallel to the z-axis), HFC and electronic exchange interaction. For simplicity, we consider only the case of isotropic liquids. In this situation the Hamiltonian takes the form (here written in the angular frequency units
- spectrum, one should add the corresponding terms to the Hamiltonian. Such terms are generally time-dependent but typically vanish in the MW-rotating frame of reference. The nuclear Zeeman interaction is omitted in the expression for the Hamiltonian because in liquids it is usually irrelevant. The reason is
A top-down approach for fabricating three-dimensional closed hollow nanostructures with permeable thin metal walls
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1231–1237, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.124

- indicates that the resonance must be sensitive to refractive index changes of the superstrate. This was corroborated by immersing the nanostructure array in different liquids. Figure 5a shows the measured spectral reflectance of a hollow nanopillar array in different top cladding media: air, methanol
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of cell lysates mixed with silver nanoparticles for tumor classification
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1183–1190, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.120

- overcome by signal-enhancement approaches including surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS), resonance Raman scattering, coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering and stimulated Raman scattering [3]. For the analysis of liquids, SERS is the most frequently applied approach and has been used for analyte
Measuring adhesion on rough surfaces using atomic force microscopy with a liquid probe
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 813–825, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.84

- instrument and a procedure to measure forces between a liquid drop and flat surfaces when the adhesion is too large to be measured with an AFM [10]. Indeed, in general, adhesion between liquids and solids can be high. However, interactions between a liquid probe and supersolvophobic or highly patterned
- location distribution. The topological differences between the two surfaces are reflected in the force of adhesion results we obtain, suggesting it is possible to implement this method as a tool to characterize the interaction between liquids and rough surfaces. This article is organized as follows: In the
- experiments of cylindrical nanofibers dipped in liquids of different γ, where γ is the liquid–vapor surface tension [36]. For contact angles above 50–60°, the spring constants are almost insensible to the contact angle, and although these authors did not explore angles corresponding to hydrophobic surfaces
First examples of organosilica-based ionogels: synthesis and electrochemical behavior
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 736–751, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.77

- : ionic liquids; ionogels; organosilica; proton conductivity; Introduction Ionic liquids (ILs), that is, substances solely composed of ionic species have been studied for virtually every application from organic synthesis to lubrication and battery technology [1][2][3][4]. A particularly promising field
Liquid permeation and chemical stability of anodic alumina membranes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 561–570, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.60

- during degradation of the membranes. Several pathways for improving the AAO stability and performance are suggested. Results and Discussions The permeation of liquids through freshly prepared AAO membranes agrees well with Darcy’s law: liquid flux linearly depends on transmembrane pressure (Figure 1a
- transducers and the mass of accumulated permeate. The time step of the measurement was 5 min. Before the experiment, all tested liquids and solutions were prefiltered through Chromafil Xtra 0.2 μm filters. The chemical stability and buffer solution permeation experiments were performed using water solutions
Formation and shape-control of hierarchical cobalt nanostructures using quaternary ammonium salts in aqueous media
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 494–505, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.53

- extended to obtain other anisotropic shapes formed by using various quaternary ammonium compounds. The quaternary ammonium salts used here are also commonly used, in their pure form as ionic liquids, as solvents [28]. In this form they exhibit structures of high directionality and were recently used as
The longstanding challenge of the nanocrystallization of 1,3,5-trinitroperhydro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 452–466, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.49

- extraction system (ASES), sorted among the supercritical processes for a better understanding. Melting and milling processes for producing sub-micrometer energetic materials require one or more additional liquids, therefore these techniques are classified as wet methods. Wet production methods
- simple acoustic measurement can be used to monitor the atomization of superheated liquids. The current application of flashing liquid jet is the improvement of MSF desalination processes of sea water [105][106], where a much higher evaporation rate is obtained in contrast to static flash evaporation
Multimodal cantilevers with novel piezoelectric layer topology for sensitivity enhancement
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 358–371, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.38

- impossible in liquids [23][24] and can alter the cantilever response rendering the identification and subsequent analysis of higher modes exceedingly difficult. For this reason, numerous integrated actuation methods such as magnetic [25], photothermal [26], resistive thermal [27], ultrasonic [28] or via a
Influence of hydrofluoric acid treatment on electroless deposition of Au clusters
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 183–189, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.19

- papers dealing with dynamic coalescence of metal nanoparticles in liquids [34][35][36]. In a previous work, we found that silver nanoparticles are subjected to Smoluchowski [37] ripening in DHF solutions by increasing their size and decreasing their surface density. For the case of gold nanoparticles on
Structural and tribometric characterization of biomimetically inspired synthetic "insect adhesives"
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 45–63, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.6

- surfaces [35][36], the molecular biomimetics of the adhesive liquids (adhesives) involved in biological adhesive systems remains in its infancy [37][38]. Emulsion-based glues are widely spread in technology and are deployed not only in casein glues, but also in releasable contact adhesives such as tapes
- detachment process. In our experiments, in order to ensure that the shear stress of the bulk emulsions was assessed in a hydrostatic or hydrodynamic sliding regime (preventing solid–solid contact between the sliding surfaces or solidification processes that might occur in confined liquids), the load employed
- expected for insect tarsi during locomotion. Several mechanisms might influence the flow behaviour of liquids in confined spaces (e.g., [56][57]). In our nanotribometry experiments, at least the larger droplets of the emulsions are in the size range of the measurement gap applied, so that they might have
A dioxaborine cyanine dye as a photoluminescence probe for sensing carbon nanotubes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1991–1999, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.190

- background of their surroundings (εbg). Dielectric-screening effects become particularly evident when the SWNTs dispersed in liquids are compared to the nanotubes in air [23], so an increase of εbg results in a redshift of the Eii transition energies [23][24][25]. On one hand, in our work, the maximum and
Noise in NC-AFM measurements with significant tip–sample interaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1885–1904, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.181
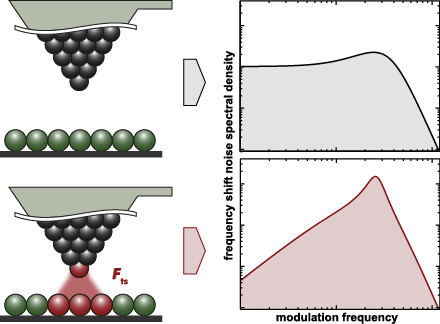
- the intrinsic value Q0 [14][15]. Our analysis can, however, be applied to any NC-AFM detection scheme and sample environment, specifically also to measurements in liquids where signal-to-noise-ratio considerations play a paramount role [16][17][18]. From our findings, we derive a general strategy for
Low temperature co-fired ceramic packaging of CMOS capacitive sensor chip towards cell viability monitoring
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1871–1877, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.179

- world of biology meets the dry world of electronics, the technical challenge arises to build a package for the LoCMOS device that is able to withstand the hostile biological environment, which may include high temperature, humidity, and corrosive liquids (mammalian cells typically require 37 °C, >95
Surface roughness rather than surface chemistry essentially affects insect adhesion
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1471–1479, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.139

- reference surfaces, i.e., smooth, hydrophilic silicon wafers (Si) and glass surfaces. Our sample surfaces displayed a wide range of surface chemical and topographical properties, and while both of these had a significant effect on the magnitude of CAs for probe liquids, the attachment abilities of the
Three-gradient regular solution model for simple liquids wetting complex surface topologies
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1377–1396, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.129

Influence of ambient humidity on the attachment ability of ladybird beetles (Coccinella septempunctata)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1322–1329, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.123

- about where tarsal liquids are actually secreted and delivered in hairy attachment pads of beetles. Moreover, assuming capillarity to be responsible for the generated traction forces, it is not clear how the proposed increase in the viscoelastic bulk energy dissipation with increasing humidity should
Functional diversity of resilin in Arthropoda
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1241–1259, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.115

- transparent or sometimes, when the sclerotisation is very pronounced, not transparent at all. When immersed in aqueous media and in many anhydrous hydrophilic liquids, resilin exhibits an isotropic swelling, which is reversible and depends on the pH. (It is least pronounced at pH values of about 4.) In its
- soft bases have a low adhesion and a pronounced clusterisation (Figure 2F). Only setae with short soft tips and rigid bases feature optimal adhesion properties and simultaneously a minimum of clusterisation (Figure 2D), which confirms the hypothesis. Tarsal liquids produced by beetles are assumed to
- contribution of the large resilin proportions in the setal tips to the attachment performance of the adhesive pads on a high level, the hydration of the resilin must be maintained. It is imaginable that this is achieved by slowly evaporating tarsal liquids covering the setae and thereby keeping the resilin in
Mesoporous hollow carbon spheres for lithium–sulfur batteries: distribution of sulfur and electrochemical performance
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1229–1240, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.114

- pores are blocked by sulfur and thus, are no longer accessible for nitrogen gas during the measurements. We believe that the strong capillary forces on liquids/melts in the mesopores are responsible for the pore blocking effect. Once sulfur has filled the mesopores there is no further driving force for
Reasons and remedies for the agglomeration of multilayered graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1174–1196, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.109

- viscosity of the polymer using a suitable organic solvent as dispersion medium. A homogeneous composite may be obtained after solvent evaporation. Sonication is applicable for liquids with low viscosity. However, the polymers are either highly viscous or solid. So, they first need to be dissolved in a
Multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrids as MRI contrast agents
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1086–1103, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.102

- T2 are sensitive to the mobility of water molecules and are specific to certain tissues and liquids in the organism. Since the recording mode of the MRI tomograph could be tuned to the duration of these times (the so-called T1- and T2-weighted images), the organs are well visible in the images
Advanced atomic force microscopy techniques III
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1052–1054, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.98

- presented by Andrzej J. Kulik and co-workers [30]. High-resolution measurements of the adhesion effect of a water film on CaF2 [31], electric and transport phenomena determined by liquid KPFM in ionically-active and -inactive liquids [32], the spray deposition of single molecules to insulating and ionic
Reorientation of single-wall carbon nanotubes in negative anisotropy liquid crystals by an electric field
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 825–833, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.74

- spontaneously while filling or relaxing in a homogeneously aligned cell, due to the intrinsic anisotropy of both components. In positive LC cells [15][16], the SWCNTs and the LC both switch and relax together. On the other hand, SWCNTs dispersed in liquids also align according to the electric field [17]. This
Molecular machines operating on the nanoscale: from classical to quantum
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 328–350, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.31

Time-dependent growth of crystalline Au0-nanoparticles in cyanobacteria as self-reproducing bioreactors: 2. Anabaena cylindrica
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 312–327, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.30

- element specific characteristic peaks as listed in databases [55]. A quantitative elemental analysis using LIBS spectra is only known for bulk materials and liquids for trace element analysis [52][56][57], but up to now unknown for diluted nanoparticles in a matrix. The herein presented semi quantitative

















































































































![[Graphic 32]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i73.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...

![[Graphic 34]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i75.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...


























![[Graphic 10]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-129-i31.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) and standard deviation as a function of the cavity diameter d (in...
and standard deviation as a function of the cavity diameter d (in...

![[Graphic 20]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-129-i41.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) and the corresponding fluctuations (measured along the x-direction) indica...
and the corresponding fluctuations (measured along the x-direction) indica...

![[Graphic 28]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-129-i49.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) and the corresponding standard deviation as measure of variation in the ...
and the corresponding standard deviation as measure of variation in the ...

![[Graphic 39]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-129-i60.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) and standard deviation as function of cut-off fraction c for fixed ...
and standard deviation as function of cut-off fraction c for fixed ...

























































![[Graphic 40]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-31-i86.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) with depth ε. Bias Δμ < 0 per one rotation tur...
with depth ε. Bias Δμ < 0 per one rotation tur...

![[Graphic 48]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-31-i94.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) , for the most asymmetric sawtooth mod...
, for the most asymmetric sawtooth mod...
















