Search results
Search for "tension" in Full Text gives 202 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology. Showing first 200.
Four self-made free surface electrospinning devices for high-throughput preparation of high-quality nanofibers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2261–2274, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.218

- of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (SDBS) could significantly reduce the surface tension of the spinning solution facilitating the spinning process [24]. The mass production of silk fibroin nanofibers was successfully accomplished by this method [23]. A schematic of the MBE device is illustrated in
- its surface tension. The effects of the MBE, MFSE, OSFSE and SSFSE device design on the morphology and the yield of the produced nanofibers were experimentally investigated. The differences between them were explained based on simulations of the electric field distribution using the Maxwell 3D
- . Figure 4 and Figure 5 illustrate the working principle of the free surface electrospinning method: the surface tension of the spinning solution is overcome by the applied electric field to form jets at the solution surface that finally touch the collector being stretched into nanofibers. Figure 6 shows
Microbubbles decorated with dendronized magnetic nanoparticles for biomedical imaging: effective stabilization via fluorous interactions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2103–2115, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.205

- interfacial tension. This suggests that fluorous interactions are at play between the supernatant fluorocarbon gas and the fluorinated end groups of the dendrons. Furthermore, small perfluorohexane-stabilized microbubbles (MBs) with a dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) shell that incorporates IONP@CnX2n
- rapidly onto the interface, as indicated by the instant reduction of the interfacial tension σ by ≈4 mN m−1 (from 72 to 68 ± 0.5 mN m−1, Supporting Information File 1, Figure S3). The concentration of Fe in the IONP dispersions was varied from 10−4 to 10−1 mol L−1. The variations of the interfacial
- tension σ over time are collected in Figure 3 and Table 1. The results show that, not surprisingly, σ decreases with increasing Fe concentration in all cases. The lowest σ values were obtained for the IONPs grafted with the fluorinated dendrons, reflecting their higher hydrophobicity. We also observed
The importance of design in nanoarchitectonics: multifractality in MACE silicon nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2094–2102, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.204

- , while other metals are partly dissolved in many instances. Because the fabrication step occurs in liquid ambient a final drying step is inherently involved. Under certain conditions of 1) high NW density and 2) high aspect-ratio of NWs, the surface tension between the residual fluid film and the NWs
- surface tension of the fluid. Elastocapillary self-assembly of NWs is an extensively investigated versatile and scalable method to design complex and robust surface nanoarchitectures [18]. For tuning and selectivity of the design of NW assemblies other approaches should be considered [19]. In hierarchical
- force FC between two cylindrical pillars when partially immersed in a liquid is [29] where γliq is the liquid surface tension, θ is the contact angle between the liquid and the surface of the pillar, r is the radius of the pillar and 2x is the interdistance between the axes of the two pillars (see
Nanostructured and oriented metal–organic framework films enabling extreme surface wetting properties
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1994–2003, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.196

- diiodomethane as a nonpolar organic liquid, which exhibits a relatively high surface tension, and water as a polar liquid (see Figure 1). CA measurements on M-CAT-1 pellets reveal shallow angles of about 12° for diiodomethane and WCA values of about 46°. This illustrates that in air the M-CAT-1 materials
- a solid is related to the sum of a polar and dispersive components of the liquid’s surface tension [68]. Utilizing the measured CAs of diiodomethane exhibiting solely a dispersive component and water, having a dispersive and polar components, enabled the calculation of the overall surface energy for
First principles modeling of pure black phosphorus devices under pressure
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1943–1951, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.190

- the use as field-effect transistor [1][25][26][27][28]. Different from the planar 2D materials, such as graphene and silicene, the puckered configuration of BP makes structural deformation much easier by tension or compression along any direction. Meanwhile, large-scale bandgap modulation accompanied
Novel hollow titanium dioxide nanospheres with antimicrobial activity against resistant bacteria
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1716–1725, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.167

- nanostructures, such as fibers and spherical particles, through the application of a high voltage that breaks the surface tension of the droplet of a polymeric solution located at the tip of a needle [16][17]. The morphology of the resulting nanostructures is influenced by the properties of the polymeric
Materials nanoarchitectonics at two-dimensional liquid interfaces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1559–1587, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.153

Development of a new hybrid approach combining AFM and SEM for the nanoparticle dimensional metrology
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1523–1536, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.150

- equipped with a GEMINI optical column with an in-lens detector. All SEM measurements have been performed using the same adjustment parameters. The extra-high tension (EHT, accelerating voltage) corresponding to the incident electron energy at the time of interaction with sample is set at 3 kV. The working
Tailoring the stability/aggregation of one-dimensional TiO2(B)/titanate nanowires using surfactants
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1024–1037, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.103

- tension with increase of surfactant concentration up to almost constant σ values, indicating the formation of micelles. As expected, 12-2-12 exhibited considerably lower σ values as well as a lower critical micelle concentration (cmc) than DTAB (Table S1 in Supporting Information) indicating its greater
- adsorption efficiency and stronger aggregating ability. The obtained results are in good agreement with literature data [32][33]. Based on the surface tension measurements, the surfactant concentrations reflecting different aggregation states (monomers and micelles) were chosen. Characterization of TNWs The
- critical micelle concentration (micelles) were selected based on surface tension measurements (Figure S1, Table S1, Supporting Information File 1). It should be noted that in micellar surfactant solutions, monomers and micelles coexist in dynamic equilibrium [26]. In Table 3 the compositions of TNW
Capillary force-induced superlattice variation atop a nanometer-wide graphene flake and its moiré origin studied by STM
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 804–810, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.80

- scanning of STM tip. The capillary force between two objects of spherical and planar geometry can be approximated as F = 4πγR where R is the radius of the sphere (not the meniscus), and γ is the surface tension of the liquid [32][50], which is 39.1 mN/m for 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene. This is the maximum force
- capillary force is equal to the work done [51] when the surface tension lifts a liquid upward in a tube over a distance h. Here, unlike the rise of liquid in a capillary tube, most of the energy is utilized for rotation of the flake. So, we estimate the force required for the rotation and hence the spread
Features and advantages of flexible silicon nanowires for SERS applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 725–734, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.72

- ), and observed a significant increase of SERS intensity after immersion into the liquid. The surface tension of the liquid influences position and shape of the SiNWs. The SiNWs are displaced and pulled together in bundles. As a result, flexible hot spots with significantly increased SERS intensity occur
- . During the synthesis of flexible SiNWs the fabrication parameters are of a crucial importance. The small-diameter SiNWs synthesized and described in this paper are sensitive not only to the surface tension of the liquid. Their flexibility also depends on the metal plating [22]. The paper compares Ag
- water has a stronger impact than ethanol on the surface morphology. This can be explained by the higher average number of hydrogen bonds in water (ca. 3.8) than in ethanol (ca. 2) and the, consequently, stronger surface tension, 72.86 and 22.39 mN·m−1 at 20 °C, respectively [38][39]. SiNWs are captured
Deposition of metal particles onto semiconductor nanorods using an ionic liquid
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 718–724, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.71

- ][15][16][17]. The low surface tension of ionic liquids causes high nucleation rates and allows for the synthesis of small nanoparticles with minimal Ostwald ripening [17]. Further, many ionic liquids consist of a large anion with diffuse negative charge; this lack of strongly binding anionic ligands
Mechanical and thermodynamic properties of Aβ42, Aβ40, and α-synuclein fibrils: a coarse-grained method to complement experimental studies
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 500–513, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.51

- achieve this by applying different types of deformation (e.g., tension, shearing and indentation) and analysing the intermolecular contacts between amino acids. Our simulations reveal significant differences in the mechanical behaviour between Aβ40 and Aβ42 and α-syn fibrils. Moreover, we find that the α
Pull-off and friction forces of micropatterned elastomers on soft substrates: the effects of pattern length scale and stiffness
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 79–94, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.8

- are present is referred to as the elastocapillary length l, which is defined as l = γ/μ, where γ is the surface tension of the substrate and μ is the elastic shear modulus of the substrate [26]. If the length scale of the microscale features is in the order of the elastocapillary length, indentation
- is dominated by surface-tension effects, whereas for larger features, surface-tension effects are balanced by elasticity [25]. Summarizing, whereas for rigid substrates, adhesive micropatterns have been designed to gain a low Eeff, it remains to be investigated whether this design approach should
- PVA-18, respectively. The elastocapillary length of PVA (defined as l = γPVA/μPVA [26], with surface tension γPVA ≈ 50 kPa [32] and elastic shear modulus μPVA ≈ 12 kPa for PVA-12) is in the order of 400 nm. Similarly, the elastocapillary length of PVA-18 is in the order of 300 nm. Pull-off forces of
A new bioinspired method for pressure and flow sensing based on the underwater air-retaining surface of the backswimmer Notonecta
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3039–3047, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.282

- Figure 7. Since water can be considered as incompressible, a pressure wave that impinges on an air layer compresses the air. If so, the air–water interface is deformed and the club-setae, i.e., the setae that hold the air layer, are deflected due to surface tension. The mechanosensitive cells at the base
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
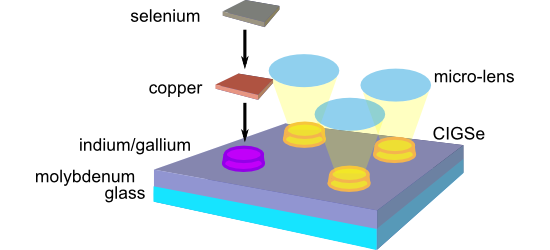
- islands and the associated contact angle were significantly influenced by the temperature during PVD. At higher temperatures the islands became flatter, probably due to the decrease in surface tension of the liquid indium. The deposition rate of indium, however, had little influence on the contact angle
Hydrogen-induced plasticity in nanoporous palladium
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3013–3024, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.280

- on plasticity in nanoporous gold have pointed towards the surface tension (in units of energy per area) being the relevant capillary parameter for plastic deformation, rather than surface stress, which is only responsible for elastic contributions [47][48]. This is reflected in an asymmetric
- deformation behaviour in compression and tension as shown by Lührs et al. [48], where expansion under a tensile load is inhibited and a contraction under compressive force is promoted. Mameka et al. reported that surface-tension-driven deformation leads to changes in the total surface area, as supported by
- palladium. As pointed out in the discussion the actual driving force for plastic deformation is surface tension. From surface tension, which is a scalar quantity, it is not possible to determine a corresponding surface stress, which is a tensor quantity, without additional information. The surface stress
Layered calcium phenylphosphonate: a hybrid material for a new generation of nanofillers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2906–2915, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.269

- profile of the particles was measured by AFM with a Dimension ICON instrument, Bruker, Germany, in peak force mode with a ScanAsyst tip. The dynamic mechanical properties were measured with a Discovery hybrid rheometer, DHR2, TA Instruments. The experiment was performed in tension mode with a deformation
The effect of flexible joint-like elements on the adhesive performance of nature-inspired bent mushroom-like fibers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2893–2905, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.268

- than vertically aligned [10]. This tilt, in addition to enhanced performance [11], equips the gecko with directional adhesion properties as shown by Autumn et al. [12]. When they tested setae using a load–drag–pull (LDP) experiment, they found that setae exhibit very high interfacial shear and tension
Biomimetic surface structures in steel fabricated with femtosecond laser pulses: influence of laser rescanning on morphology and wettability
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2802–2812, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.262

- , also termed Wenzel and Cassie-Baxter regimes, respectively, wetting can in principle be described by taking into account the interfacial tension between substrate, liquid, and vapor and the surface geometry. Yet, the sole presence of one or another regime is a matter of debate [45]. While this
Low cost tips for tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy fabricated by two-step electrochemical etching of 125 µm diameter gold wires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2718–2729, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.254

- Euler’s constant, g = 981 cm/s2 is the gravitational constant and is the capillary constant, where γ ≈ 30 dyn/cm and ρ = 0.98 g/cm3 are the surface tension and the density of the HCl/ethanol solution, respectively. In Figure 4b we plot the predicted values of the meniscus extension h as a function of the
Effect of electrospinning process variables on the size of polymer fibers and bead-on-string structures established with a 23 factorial design
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2466–2478, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.231

- ][8][9][10]. Not only do they concern the values but also the change of process parameters such as: polymer solution properties (type of polymer, type of solvent, solution viscosity [11], surface tension, conductivity [11][12], etc.) and process variables (electrical voltage delivered to the nozzle
- was also concluded that the properties of the polymer solution (concentration, viscosity and surface tension) had the biggest influence on the size of fibers obtained in the electrospinning process. In terms of solution concentration, the proportional relationship between the polymer concentration and
Evidence of friction reduction in laterally graded materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2443–2456, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.229

- in Figure 5, but in the opposite direction. Thus, the material portion of the sliding plate is in tension for Δ > 0 and in compression for Δ < 0. Qualitatively speaking, a positive gradient in the Young’s modulus is equivalent to a negative gradient in the local coefficients of friction. Again, FEM
Adhesive contact of rough brushes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2405–2412, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.225

- heights (see the side of the contact) one can see the “negative spikes” which stem from the not-yet-destroyed adhesive contacts of individual pillars loaded in tension. The scheme of indenting and pull-off stages of an adhesive contact of exponentially distributed pillars. An example of a pillar structure
Surface energy of nanoparticles – influence of particle size and structure
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2265–2276, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.211

- Gibbs using the term “surface tension” [1][2]. In the meantime, it has become clear that in case of solids one has to distinguish between “surface energy” and “surface stress”. Both quantities are related by the Shuttleworth equation [3]. Since the surface stress, σ, exerts a pressure, p, on a curved
- tension”). The analysis of the surface energy data of nanoparticles and the dependence of the surface energy on particle size and temperature is of essential importance because the phase (crystalline or liquid) depends on the particle size. Additionally, it is possible that the particles form a stable
- this, the basic ideas of both approaches are explained in this paper. Approach based on classical thermodynamics and continuum considerations When Gibbs [1][2] introduced surface energy using the term surface tension he predicted a decrease of the surface energy with decreasing droplet size. As an



























































































































































































































































