Search results
Search for "surface morphology" in Full Text gives 270 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology. Showing first 200.
Effect of electrospinning process variables on the size of polymer fibers and bead-on-string structures established with a 23 factorial design
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2466–2478, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.231

- in terms of the fiber surface morphology. It was also concluded that methanol and ethanol were best suited for electrospinning of PVP, in contrast to water and dimethylformamide (DMF), which prevented the polymer from spinning. What is more, the higher the water content of the solvent, the less
- conditions on the surface morphology of nanofibers is the one by Deitzel et al. [7]. This work focuses on the influence of two process variables: voltage and concentration of the polymer solution of polyethylene oxide (PEO) dissolved in water. In this study it was observed that the increase in electrical
Thickness-dependent photoelectrochemical properties of a semitransparent Co3O4 photocathode
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2432–2442, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.228

- oxidized the Co film into a Co3O4 film with controlled thickness and porosity, which is further validated below. Figure 1c,d shows the surface morphology of both the deposited Co and the RTP-grown Co3O4 film on the glass substrate, respectively. FESEM results confirm that the deposited film contains
- flat band to depletion condition); (c) 1.4 to 0.8 V vs RHE (covering the onset potential, which is close to the flat band potential as well as OER). Surface morphology of the 170 nm thick Co3O4 film on FTO/glass showing (a) the pores with diameters of 14–20 nm and (b) Co3O4 nanocrystals with diameters
ZnO-nanostructure-based electrochemical sensor: Effect of nanostructure morphology on the sensing of heavy metal ions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2421–2431, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.227

- to 7.6. In the time interval between the end of the growth process of nanostructures and the performance of electrochemical measurements, the electrodes were stored under ambient conditions. Characterization The surface morphology of the processed samples was investigated using a scanning electron
Electrospun one-dimensional nanostructures: a new horizon for gas sensing materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2128–2170, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.202

- , and CO. ZnO hollow NFs functionalized by rare earth metals, such as Ce, show enhanced acetone sensing [193]. The Ce ion occurs either as Ce4+ and Ce3+ which is effective for improving the performance of chemical sensors. The surface morphology of Ce-doped ZnO HNFs is concave–convex and porous with an
Direct AFM-based nanoscale mapping and tomography of open-circuit voltages for photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1802–1808, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.171

- employed [1][24], allowing scientists to focus on or ignore such regions depending on whether they are true local variations or experimental artifacts. In any case, in order to minimize the influence of such topography, our specimens are first partially planarized [8]. This provides a surface morphology
A visible-light-controlled platform for prolonged drug release based on Ag-doped TiO2 nanotubes with a hydrophobic layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1793–1801, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.170

- Morphology, phase composition and wettability The cross-section and surface morphology of the two-layer nanotubes with and without AgNP loading and the corresponding energy dispersive X-ray spectrum (EDS) spectrum of the Ag-loaded sample are shown in Figure 1. Figure 1a presents the cross-section morphology
- (LED) lamp without ultraviolet light (<450 nm), while the other half of tubes with NDM were kept in the dark. Materials characterization The surface morphology and microstructure of the fabricated samples were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM, Hitachi S4800, Japan) and X-ray
- titania nanotubes. (a,b) Cross-sectional morphology (the white circle in b shows the connection between the first and second layers where they are integrated) and (c) surface morphology without Ag nanoparticles and (d) with Ag nanoparticles. (e) Energy dispersive X-ray spectrum of titania nanotubes with
Uniform cobalt nanoparticles embedded in hexagonal mesoporous nanoplates as a magnetically separable, recyclable adsorbent
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1770–1781, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.168

- good distribution of Co nanoparticles formed by partially reducing the Co2+ with carbon after the heat treatment process. The pore characteristics and surface morphology of the hexagonal magnetic mesoporous NPLs can be tailored by adjusting the dopamine concentration and carbonization temperature. The
- (LDH). A uniform PDA coating initially covers the surface of LDH by dopamine self-polymerization under mild conditions. Well-dispersed Co nanoparticles are formed in the NPLs by the partial reduction of cobalt from Co2+ to Co0 with surface carbon during the heat treatment process. The surface
- morphology and specific surface area of the as-prepared NPLs can be tailored by adjusting the initial dopamine concentration and carbonization temperature. The mesoporous NPLs exhibit excellent sorption of rhodamine B (RhB) dye and fast magnetic separation in aqueous solution. Over 95% of RhB can be adsorbed
Preparation of micro/nanopatterned gelatins crosslinked with genipin for biocompatible dental implants
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1735–1754, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.165

Toward the use of CVD-grown MoS2 nanosheets as field-emission source
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1686–1694, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.160

- geometrical morphology of the emitter surface and thus it is important to control the surface morphology for producing better field emitters [9][30][31]. The emitter surface is rough for nanomaterials deposited as a planar cathode and, therefore, for a given emission site the applied electric field varies
Preparation and morphology-dependent wettability of porous alumina membranes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1423–1436, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.135

- ]. Recently membranes with special surface wettability have been investigated because of their potential application in microfluidics, self-cleaning and droplet-based technologies [19][29]. As shown in [30], by changing only the surface morphology of unmodified, bare PAMs, the wetting behavior could be
- solution of H3PO4, рН 5.5 at 35 ± 2 °C. From the given results, it can be concluded that the contact angle depends on the processing technique (back side of the membrane was processed in 4% H3PO4 and in argon plasma) and on the surface morphology. Therefore, differences in the measured contact angles and
- investigate only the effect of the native surface morphology on the ICA. It was shown that the contact angle depends not only on pore diameter, but also on PAM thickness. It was found that with the increase in etching time, the pore diameter and contact angle increased for both sides. It was shown that it is
Induced smectic phase in binary mixtures of twist-bend nematogens
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1297–1307, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.122

- features that can be related to a nanometer-scale pitch. Up to 40 mol % of BB large suppression of crystallization resulted in a wide temperature range of the NTB phase. This enabled direct comparison of the surface morphology and periodicity modulations between several mixtures of different concentration
- the mixture containing 18 mol % of BB. AFM imaging revealed very similar surface morphology for all three mixtures. The representative AFM images obtained on the mixture containing 27 mol % BB at 55 °C are shown in Figure 4. In the NTB phase, at 55 °C, a relatively smooth surface over 1 × 1 µm2
- phase at 120 °C, d) 2D XRD pattern in the NTB phase at 55 °C. a) AFM 2D-topographic image of the surface morphology of a binary mixture of 27 mol % BB; b) the inset shows a high-resolution AFM image of the marked region in a); c) 3D-topographic image; d) vertical section profile across the noted line; e
Heterostuctures of 4-(chloromethyl)phenyltrichlorosilane and 5,10,15,20-tetra(4-pyridyl)-21H,23H-porphine prepared on Si(111) using particle lithography: Nanoscale characterization of the main steps of nanopatterning
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1211–1219, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.112

- be subsequently characterized ex situ after each key step of the fabrication process. Results and Discussion An overview of the main steps for preparing nanostructures of H2TPyP within nanoholes of OTS is presented in Figure 1. The growth of nanopatterns and subsequent changes in surface morphology
- adsorption or reactions on areas between nanopatterns during successive chemical steps. Nanodots of CMPS were used as a linker for binding porphyrins to the surface. The changes in surface morphology were examined after each step using ex situ AFM studies. A model was proposed for attachment of H2TPyP to
Semi-automatic spray pyrolysis deposition of thin, transparent, titania films as blocking layers for dye-sensitized and perovskite solar cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1135–1145, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.105

- ) provides considerably better blocking properties of the corresponding titania films. To address this peculiarity, we investigated these substrates in more detail and the results are summarized below. Figure 5 shows the top surface morphology of both our FTO substrates. The grain size is between 100 and 200
- -calcination causes a strong deterioration of the blocking properties. The difference between as-deposited TiO2 films and those after post-calcination is a dampening with increasing number of SCs. For instance, at 70 SCs, the difference is almost negligible. Figure 7 shows the top surface morphology of our FTO
Cyclodextrin inhibits zinc corrosion by destabilizing point defect formation in the oxide layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 936–944, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.86
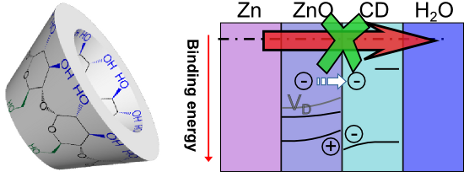
- . Increasing the β-CD concentration decreased Ecorr in the steady phase. Figure 1b (i) shows the state of the surface after exposure to 0.1 M KCl. In the presence of β-CD [Figure 1b (ii)], no precipitated corrosion products are visible. Comparison to the surface morphology before electrochemical experiments
Bioinspired self-healing materials: lessons from nature
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 907–935, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.85

Comparative study of antibacterial properties of polystyrene films with TiOx and Cu nanoparticles fabricated using cluster beam technique
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 861–869, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.80

- properties of composite films with Ti/TiOx NPs a simple setup has been constructed allowing for the illumination of the samples by UV light (λ = 320–380 nm) as shown in Figure 8. E.coli bacteria are used for the tests. Characterization techniques The surface morphology of the samples with supported NPs is
Surface-plasmon-enhanced ultraviolet emission of Au-decorated ZnO structures for gas sensing and photocatalytic devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 771–779, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.70

- microstructured oxides and that they exhibited an even higher effect than those of nanostructured oxides. Most recently, the microstructured oxide structures with particular surface morphology have been examined for their exciting characteristics [22][23]. Thus, plasmonic structures with micrometer-sized metal
- with rough surface morphology could provide an advantage for enhancing the plasmonic effect when incorporated with Au NPs, which showed great performance in gas sensing and photocatalytic decomposition of organic pollution substances [14][15][16][22][23][24][25]. Figure 3a shows the UV–vis absorption
Synthesis and characterization of two new TiO2-containing benzothiazole-based imine composites for organic device applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 721–739, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.67

- and their mixtures with TiO2 remained unchanged, which makes them an interesting material for organic devices, e.g., photovoltaic applications. In the AFM experiments the influence of the TiO2 and the chemical structure of the imines with the benzothiazole core on the surface morphology of the
- composites, the value of Rms decreases with increasing amount of titanium dioxide: 255.5 nm (3:1 w/w), 196.9 nm (3:2 w/w) and 149.7 nm (3:3 w/w). For pure titanium dioxide, the Rms was 45.26 nm. The most desired surface morphology would be a layer composed of TiO2 nanoparticles covered with SP1/SP2 molecules
Optimisation of purification techniques for the preparation of large-volume aqueous solar nanoparticle inks for organic photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 649–659, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.60

- concentration on the aqueous solar nanoparticle (ASNP) inks was investigated by monitoring the surface morphology/topography of the ASNP films using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and photovoltaic device performance as a function of ultrafiltration (decreasing SDS content
- ). The surface morphology/topography showed, as expected, a decreased number of SDS crystallites on the surface of the ASNP film with increased ultrafiltration steps. The device performance revealed distinct peaks in efficiency with ultrafiltration: centrifuge purified inks reached a maximum efficiency
- reached was 64 and 50 mN m−1 for the centrifugal and the crossflow purifications, respectively. Influence of free-SDS surfactant on the surface morphology/topography of ASNP films Optical microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM) were conducted for ASNP films with low, medium and high dilution factors
Fabrication and photoactivity of ionic liquid–TiO2 structures for efficient visible-light-induced photocatalytic decomposition of organic pollutants in aqueous phase
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 580–590, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.54

- lowest cell volume (Table 2). The surface morphology and microstructure of the IL–TiO2 composites were characterized by SEM. The morphology of four selected samples prepared with different IL concentrations (IL:TBOT molar ratio equal to 1:3 and 1:10) which revealed the highest and the lowest
Ultralight super-hydrophobic carbon aerogels based on cellulose nanofibers/poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide (CNFs/PVA/GO) for highly effective oil–water separation
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 508–519, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.49

- , USA) equipped with an energy disperse spectroscopy (EDS) device was used to investigate the surface morphology of the carbon aerogels. The FTIR profiles were obtained using a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy spectrometer (Nicolet iS10, Thermo Electron Corp., USA). The water contact angle (CA
Kinetics of solvent supported tubule formation of Lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) wax on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) investigated by atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 468–481, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.45

- characteristic final surface morphology is also independent of the concentration in solution. The first observation suggests that the growth process follows at least a two-step mechanism: where LWMsol denotes the concentration of dissolved "Lotus wax molecules" in chloroform, LWMsurf corresponds to the
Influence of the preparation method on the photocatalytic activity of Nd-modified TiO2
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 447–459, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.43

- of Ti–O–Nd bonds probably restricts direct contact between TiO2 crystallites and stabilizes the anatase phase and crystallite growth [25][35]. Morphology Surface morphology of the obtained photocatalysts was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Figure 2 shows a SEM image of pristine TiO2
Facile synthesis of ZnFe2O4 photocatalysts for decolourization of organic dyes under solar irradiation
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 436–446, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.42

- microscopy (FESEM) provides surface morphology and topography of the prepared materials. Figure 2 shows the surface topography of ZFO-500. The sample consists of agglomerated nanoparticles with smooth surface. The agglomeration of ZFO-500 is accompanied with the formation of small crystallites [28]. TEM The
Photocatalytic and adsorption properties of TiO2-pillared montmorillonite obtained by hydrothermally activated intercalation of titanium polyhydroxo complexes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 364–378, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.36

- surface morphology was performed using an IEK-2 scanning electron microscope (Zeiss SUPRA 50VP, Germany) by coating a conductive layer of iridium. Elemental analysis of the surface was carried out on a VEGA 3 SBH scanning electron microscope integrated with a Bruker energy-dispersive microanalyzer
































































































































































































































































