Search results
Search for "sub-micrometer" in Full Text gives 56 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Current status of using adsorbent nanomaterials for removing microplastics from water supply systems: a mini review
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 1837–1850, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.127

- pollution. Standardized testing protocols, comprehensive LCAs, and advanced recovery strategies are urgently needed to ensure safe and sustainable deployment. Moreover, detecting and removing sub-micrometer plastics (<1 μm), which pose significant health risks due to their ability to penetrate tissues
Enhancing the therapeutical potential of metalloantibiotics using nano-based delivery systems
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 1350–1366, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.98

- by phagocytic cells, which is particularly beneficial for treating infections with biofilm-forming bacteria [67][68][69]. Solid lipid nanoparticles: SLNs are sub-micrometer colloidal carriers, typically ranging from 50 to 1000 nm, composed of lipids that remain solid at room and body temperatures
Shape, membrane morphology, and morphodynamic response of metabolically active human mitochondria revealed by scanning ion conductance microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 951–967, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.73

- nanopipette with a sub-micrometer aperture, which is brought near the sample surface via piezo actuators in an electrolyte bath. A voltage applied between two Ag/AgCl electrodes, one in the pipette and the other in the bath, generates an ion current. If the pipette approaches the sample, the ionic current
Insights into the electronic and atomic structures of cerium oxide-based ultrathin films and nanostructures using high-brilliance light sources
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 860–871, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.65

- in selected areas with sub-micrometer spatial resolution [55]. In addition, the morphology of zirconia–ceria mixed oxides supported on Rh(111) and the oxidation states of the two oxides, individually and in the mixed phase, were determined [39]. Studies at ambient pressure The identification of
Nanoscale capacitance spectroscopy based on multifrequency electrostatic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2025, 16, 637–651, doi:10.3762/bjnano.16.49

- difference (CPD) [18]. Its exceptional spatial resolution, ranging from sub-micrometer [24][26] to atomic scales [27][28], makes AFM a powerful tool for nanoscale analysis. Scanning probe-based capacitance mapping methods can be divided into two categories: Methods measuring the tip–sample capacitance
Atomistic insights into the morphological dynamics of gold and platinum nanoparticles: MD simulations in vacuum and aqueous media
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 995–1009, doi:10.3762/bjnano.15.81

- scattering [23], and optical microscopy [24], have provided accurate estimates of nucleation rates and critical nucleation sizes, but little data have been produced for the sub-micrometer size regime regarding crystal facet formation and the mechanism of crystal growth. Moreover, a fundamental prerequisite
Beyond biomimicry – next generation applications of bioinspired adhesives from microfluidics to composites
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 965–976, doi:10.3762/bjnano.15.79

- to sub-micrometer size [8][9]. It has been an active area of academic research for well over 30 years. Microfluidics technology has eventually enabled a variety of new innovations, including COVID-19 rapid tests [10], microfluidic displays [11], and low-cost diagnostics [12]. Soft robotics is a newer
Hierarchically patterned polyurethane microgrooves featuring nanopillars or nanoholes for neurite elongation and alignment
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 1157–1168, doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.96

- uncrosslinked PDMS monomers (Supporting Information File 1, Figure S3C). Atomic force microscopy (AFM) scans of the samples (Figure 1F–H) show that the nanopillars and nanoholes have sub-micrometer feature sizes and a periodicity of around 1.2 µm. Due to AFM measurement artifacts, especially for lateral
Gap-directed chemical lift-off lithographic nanoarchitectonics for arbitrary sub-micrometer patterning
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 34–44, doi:10.3762/bjnano.14.4

- -off lithography; gap; self-assembled monolayer; sub-micrometer; surface patterning; Introduction The development of lithographic techniques is crucial to the advancement of the electronics and semiconductor industry, the backbones of modern technology. Advances in photolithography have pushed the
Direct measurement of surface photovoltage by AC bias Kelvin probe force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 712–720, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.63

- shown in Figure 3c. The AC-KPFM successfully resolved the inhomogeneous SPV distribution with fluctuations on scales of 10–50 nm and a few millivolts, whereas classical KPFM observed a homogeneous SPV distribution over the TiO2 surface with sub-micrometer resolution [12][51] because of the influence of
Micro- and nanotechnology in biomedical engineering for cartilage tissue regeneration in osteoarthritis
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 363–389, doi:10.3762/bjnano.13.31

Progress and innovation of nanostructured sulfur cathodes and metal-free anodes for room-temperature Na–S batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 995–1020, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.75

- and can be distinguished in aqueous and organic solvent routes [57]. The so-called Weimarn sols are produced by dissolution of sulfur powder in ethanol or acetone-based solutions and the subsequent precipitation of sub-micrometer-size particles in water [57]. The so-called Raffo sols are obtained by a
- sub-micrometer-sized sulfur NPs within milliseconds [62]. The resulting sulfur–PVP composite cathode had a capacity of 808 mAh·g−1 after 50 cycles at 0.1C. Sodium metal-free anodes The reason for the widespread use of metal Na anodes in Na–S batteries is the very high capacity of 1165 mAh·g−1 of
Determination of elastic moduli of elastic–plastic microspherical materials using nanoindentation simulation without mechanical polishing
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 213–221, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.17

- –displacement data alone. This avoids the need to measure the area of indentation by imaging and facilitates the measurement of properties at the sub-micrometer scale. During nanoindentation, a diamond indenter with a geometry known to high precision is pressed into the surface of the specimen with increasing
Bulk chemical composition contrast from attractive forces in AFM force spectroscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2021, 12, 58–71, doi:10.3762/bjnano.12.5

- of atomic force microscopy (AFM) is the measurement of physical properties at sub-micrometer resolution. Methods such as force–distance curves (FDCs) or dynamic variants (such as intermodulation AFM (ImAFM)) are able to measure mechanical properties (such as the local stiffness, kr) of nanoscopic
Fabrication of nano/microstructures for SERS substrates using an electrochemical method
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1568–1576, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.139

- , all PEO-treated Mg specimens demonstrate the typical surface morphology, which comprises of micrometer and sub-micrometer-sized quasi-circular pores and cracks. This porous and uneven surface is a result of the consecutive dielectric breakdown of the passivation layer and the heat generated during
High permittivity, breakdown strength, and energy storage density of polythiophene-encapsulated BaTiO3 nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 1190–1197, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.103

- exhibit irregular surface profile, which confirms the occurrence of sub-micrometer clusters and nanoscale particles on the surface. The permittivity or dielectric constant (ε′), loss tangent (tan δ), dielectric loss (ε″), and ac conductivity (σac) of the synthesized materials are measured as a function of
- the SEM image shown in Figure 4a. PTh, on the other hand, exhibits an inhomogeneous surface morphology with large flakes of polymer randomly distributed on the surface. In case of core–shell BTO-PTh nanoparticles (Figure 5b), the surface topography is very consistent with uniformly distributed sub
- -micrometer particles or agglomerate on the surface. The same is observed in the surface profile of core–shell BTO-PTh nanoparticles, which is monotonous on the height scale. Pristine PTh shows a variable surface profile because of the inconsistent presence of large polymer flakes. BTO nanoparticles also
Atomic force acoustic microscopy reveals the influence of substrate stiffness and topography on cell behavior
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2329–2337, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.223

- stripes patterns of sub-micrometer size. Figure 4 shows that the cells on the developed substrate cannot spread freely and become elongated in the stripe direction. The alignment and elongation of the L929 cells are attributed to the topographical pattern. Similar responses to the patterned topography
Microfluidics as tool to prepare size-tunable PLGA nanoparticles with high curcumin encapsulation for efficient mucus penetration
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2280–2293, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.220

- sub-micrometer particles, because it is a simple and straightforward technique, without the involvement of any chemical additives, and also does not require harsh formulation parameters, such as high energy input or mechanical shear stress (e.g., by sonification) [30][31]. Nonetheless, the preparation
- of sub-micrometer NPs in a conventional “bench-top” nanoprecipitation method still faces several critical challenges, such as the lack of reproducibility, which restricts it from being widely adopted in the pharmaceutical industry [32][33]. This issue is mainly attributed to the poor control of the
Nitrogen-vacancy centers in diamond for nanoscale magnetic resonance imaging applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2128–2151, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.207

- NV centers and employed to image thin ferromagnetic films. The accuracy obtained is sub-micrometer over surfaces as wide as 100 × 100 µm2 and the imaging speed is fast enough to obtain a real-time video of the evolution of stray magnetic patterns. It is not necessary to supply a microwave signal to
- allows imaging of metal spins via the Hall effect [55]. NV center wide-field microscopy was applied in [11] to characterize and image magnetic samples; sample thin ferromagnetic films were used to map and image their sub-micrometer stray magnetic field patterns by using an array of NV center spins. Using
- ODMR, wide-field magnetic imaging over an area of 100 × 100 μm2 with sub-micrometer spatial resolution (440 nm) and a temporal resolution of 20 ms and 1.5 μT·Hz−1/2 sensitivity could be achieved at room temperature. Without using an applied microwave field, all-optical spin relaxation contrast imaging
Optimization and performance of nitrogen-doped carbon dots as a color conversion layer for white-LED applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2004–2013, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.197

- per hour as the operating conditions of the electrospinning process. Owing to the potential difference between the syringe tip and the collector aluminum foil, the N-CDots were confined into sub-micrometer fibers by electrospinning. Results and Discussion Structural characterization of the N-CDots
Green fabrication of lanthanide-doped hydroxide-based phosphors: Y(OH)3:Eu3+ nanoparticles for white light generation
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1200–1210, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.119

- properties, a desired amount of the red Y(OH)3:Eu3+ sub-micrometer phosphor in mass was introduced into the PDMS/YAG:Ce3+. The resulting mixture was stirred until all phosphors mixed homogenously. Then, this mixture was dropped into a mold having a fixed thickness of 0.2 cm and a diameter of 2.0 cm and the
- -scale size distribution (Figure 2a). After 15 min of reaction, the crystals grow larger and started to show a rod-like structure with sub-micrometer sizes (Figure 2b). As the reaction time is extended to 60 min, the crystals transform into a rice-like structure (Figure 2c). For more detailed information
- conversion layer Red-emitting Y(OH)3:Eu3+ sub-micrometer phosphors were integrated into a YAG-based white LED configuration, and the resulting optical features were investigated. Among the varying doping ratios, Y(OH)3:20% Eu3+ fabricated at 60 min was selected as a model material since the results from
Pull-off and friction forces of micropatterned elastomers on soft substrates: the effects of pattern length scale and stiffness
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 79–94, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.8

- micropatterns with microscale dimples that are about one order of magnitude larger than the (sub-)micrometer-sized dimples reported in [28][30][33][34], with stiffness values down to 280 kPa, which is lower than the typical stiffness in the megapascal-range achieved by soft molding [35]. This fabrication method
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
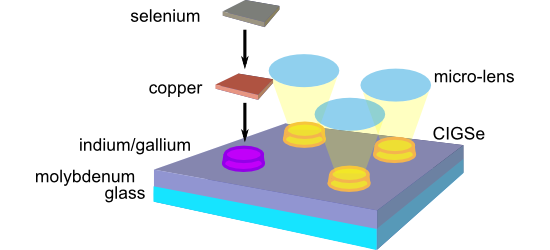
- -induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS [19]) and round melting features form on the glass surface (Figure 5b). The LIPSS with periods in the sub-micrometer range are generated via intra-pulse scattering and interference of the fs-laser radiation at the roughened glass surface, leading to the spatially
Electrostatic force microscopy for the accurate characterization of interphases in nanocomposites
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2999–3012, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.279

- ]. In fact, as our samples were highly rough owing to the sub-micrometer PS spheres, spin-coating could not produce uniformly thin films [37]. However, this did not affect our study because the EFM results were compared at the center of the particles. Concerning the EFM signals, the average values
- dielectric materials, each with a specific dielectric permittivity, were assembled in the form of sub-micrometer particles covered by two thin shells that represent the interphase and the matrix in the “real” systems. The study of the signals above the central region of the particles at constant tip–sample
High-temperature magnetism and microstructure of a semiconducting ferromagnetic (GaSb)1−x(MnSb)x alloy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2457–2465, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.230

- ) demonstrates the presence of sub-micrometer ferromagnetic inclusions with aligned magnetic poles. Combining these results with SEM and TEM data suggests that MnSb inclusions are ferromagnetic and located mostly close to the film surface, rather than being evenly distributed within the sample volume. This








































































































































































































