Search results
Search for "electrochemical impedance spectroscopy" in Full Text gives 72 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Rational design of block copolymer self-assemblies in photodynamic therapy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 180–212, doi:10.3762/bjnano.11.15

Polyvinylpyrrolidone as additive for perovskite solar cells with water and isopropanol as solvents
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2374–2382, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.228

- simulator (Newport Oriel Sol3A Class AAA, 64023A Simulator), which was calibrated using a NREL standard Si solar cell. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were conducted by using an electrochemical workstation (CHI660d) (1 MHz to 100 Hz) and for fitting the Zview software was used. The
Design and facile synthesis of defect-rich C-MoS2/rGO nanosheets for enhanced lithium–sulfur battery performance
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2251–2260, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.217

- overlap, indicating the superior electrochemical reversibility of the C-MoS2/rGO-6-S cathode. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results of MoS2-S, C-MoS2/rGO-S, C-MoS2/rGO-6-S electrodes are shown in Figure 6b. Obviously, the C-MoS2/rGO-S and C-MoS2/rGO-6-S electrodes have the minor semicircles
- impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were achieved at the open-circuit potential between 0.01 Hz and 100 kHz. All the tests were carried out at room temperature. Results and Discussion The preparation of the C-MoS2/rGO composite is shown in Figure 1. The C-MoS2/rGO composite is synthesized by the
- voltammetry tests were carried out on a LAND battery cycler (CT2001A) in a voltage range of 1.7 to 2.9 V (vs Li/Li+). The specific capacity was calculated based on the mass of sulfur. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) tests were carried out between 1.6 and 2.9 V at a scan rate of 0.1 mV·s−1. The electrochemical
A novel all-fiber-based LiFePO4/Li4Ti5O12 battery with self-standing nanofiber membrane electrodes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2229–2237, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.215

- assembled in an Ar-filled glovebox by using lithium foil as anode and 1 M LiPF6 electrolyte (ethylene carbonate/dimethyl carbonate/ethyl methyl carbonate = 1:1:1). A Celgard 2400 polypropylene membrane was used as separator. The cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements were
Ultrathin Ni1−xCoxS2 nanoflakes as high energy density electrode materials for asymmetric supercapacitors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2207–2216, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.213

- ) at room temperature of 24 °C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) of the electrode material was carried out in the frequency range from 100 kHz to 0.01 Hz at AC voltage under open-circuit conditions. The cycling stability was tested by using a LAND system (Wuhan LAND electronics). The
Facile synthesis of carbon nanotube-supported NiO//Fe2O3 for all-solid-state supercapacitors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1923–1932, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.188

- the CC-CNT@Fe2O3 electrode. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was carried out to explore the resistance of the electrode (Figure 4d). The measured curve can be well fitted by equivalent circuits, and the insert is an enlarged view in the high-frequency area. All fitted values are shown in
- counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) as the reference electrode, and the CC-CNT@Fe2O3 or CC-CNT@NiO as the binder-free working electrode. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) curves were measured in frequencies from 100 kHz to 0.01 Hz at open-circuit voltage with an AC voltage
TiO2/GO-coated functional separator to suppress polysulfide migration in lithium–sulfur batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1726–1736, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.168

- electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) analysis to analyze the charge transfer kinetics in Li/S batteries with pristine and TiO2/GO-coated separators. Figure 8 presents the Nyquist plots of Li/S batteries with pristine and TiO2/GO-coated separators before and after cycling. As shown in Figure 8a, the charge
Hierarchically structured 3D carbon nanotube electrodes for electrocatalytic applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1475–1487, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.146

- transfer resistance with respect to the primary CNTs as determined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Thus, we speculate that the improvement in Pt dispersion is due to a better conductivity within the 3D network and a facilitated electron transfer, which may facilitate Pt nucleation at the CNT
BiOCl/TiO2/diatomite composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity for the degradation of rhodamine B
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1412–1422, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.139

- efficiency of the samples, photoluminescence spectroscopy, photocurrent and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy were tested. The recombination rate of photogenerated carriers (electrons and holes) in photocatalysts was characterized by photoluminescence spectra. Generally, the lower the spectral intensity
- internal structure of the material to its surface [48]. BTD shows the most prominent photocurrent density, proving that the carrier recombination rate is low and the lifetime is long, which contributes to the enhancement of photocatalytic activity. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is one of the
Construction of a 0D/1D composite based on Au nanoparticles/CuBi2O4 microrods for efficient visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1360–1367, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.134

- photocatalytic activity after three cycles. This decrease of photocatalytic performance is mainly due to the mass of catalysts being inevitably lost in the recycling process [39]. Photocurrent response and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were carried out to obtain some insights into the
Porous N- and S-doped carbon–carbon composite electrodes by soft-templating for redox flow batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1131–1139, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.113

- (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The N- and S-doped carbon electrodes show promising activity for the positive side reaction and could be seen as a significant advance in the design of carbon felt electrodes for use in redox flow batteries. Keywords: N- and S-doped carbon
- readily on the composite electrodes than on the undoped reference materials. Additional electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was performed to study the charge transfer of the VO2+/VO2+ redox reaction. The corresponding Nyquist plots are displayed in Figure 7. In the described circuit Ru stands for the
Glucose-derived carbon materials with tailored properties as electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1089–1102, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.109

- basic electrolyte at 1600 rpm and the Nyquist plot obtained from electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements are shown in Figure 2a and 2b, respectively. To evaluate the performance of the prepared electrocatalysts, cyclic voltammetry (CV) and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) were performed. LSV
- microporosity, which can be related to the more developed porous structure. These two effects can be confirmed by the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements (Figure 2b). The Nyquist plot shows that a higher degree of activation results in a lower cell resistance and a smaller semicircle at high
- the current obtained from the electrolyte saturated with N2 from the current measured in the O2-saturated electrolyte. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was also applied to the fully discharged cell at 0 V in the frequency region of 10 kHz to 10 mHz with an AC amplitude of 10 mV. EIS was
In situ AFM visualization of Li–O2 battery discharge products during redox cycling in an atmospherically controlled sample cell
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 930–940, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.94

- design permitted acquisition of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, contributing information about electrical double layers under the system’s controlled environment. This characterization method can be applied to a wide range of reactive surfaces undergoing transformations under carefully controlled
- rather than for the highest capacity. The main aim was to obtain electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), discharge/recharge voltages and capacities time-domain-correlated with AFM images of topography, all in a completely atmospherically isolated and controlled setting. In our recent study [30
- every 10th scan thus allowing correlation of time-domain information with cell voltage and capacity. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) EIS [34] was employed to measure the impedance of the AFM electrochemical system over the range of frequencies between 1 MHz and 100 mHz. This frequency
An efficient electrode material for high performance solid-state hybrid supercapacitors based on a Cu/CuO/porous carbon nanofiber/TiO2 hybrid composite
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 781–793, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.78

- pseudo-capacitance behavior. Electrochemical measurements were performed by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge–discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The highest specific capacitance value of 530 F g−1 at a current density of 1.5 A g−1 was obtained for the Cu/CuO/PCNF/TiO2 composite
- The electrochemical studies of developed electrode materials for supercapacitors were executed by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge–discharge, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in a 1 M H2SO4 aqueous electrolyte in a three-electrode configuration. Figure 10a shows the CV curves of TiO2
- densities. (a) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) spectrum of the SSHSC and (b) rate capability plot of the SSHSC at different current densities. Capacitance retention and coulombic efficiency of the SSHSC at a current density of 5 A g−1. Ragone plot for the SSHSC and comparison with previous
A porous 3D-RGO@MWCNT hybrid material as Li–S battery cathode
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 514–521, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.52

- the conductivity during cycling a Li–S battery equipped with the S-3D-RGO@MWCNT cathode, were investigated using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Figure 8 presents the Nyquist plots for the Li–S cell assessed before cycling, and after the 1st and the 4th cycle. In the high-frequency
- impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was carried out in the frequency range from 10−2 to 105 Hz. Synthesis of S-3D-RGO@MWCNT. SEM images of (a) RGO@MWCNT@SiO2, (b, c) 3D-RGO@MWCNT at different magnifications and (d) S-3D-RGO@MWCNT, and corresponding elemental maps of (e) sulfur and (f) carbon. TEM images of (a) 3D
- cycling performances of the Li–S battery was investigated using a battery testing station (Neware, Shenzhen) in potential range of 1.5–3.0 V. The electrochemical workstation (Princeton, VersaSTAT 4) was used to evaluate cyclic voltammetry (CV) also in a potential range of 1.5–3.0 V. Electrochemical
A Ni(OH)2 nanopetals network for high-performance supercapacitors synthesized by immersing Ni nanofoam in water
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 281–293, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.27

- employed as the working electrodes, the counter electrode and the reference electrode, respectively. Cyclic voltammograms (CV), galvanostatic charge/discharge curves (GCD) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements were carried out using an electrochemical workstation (Chenhua CHI660D
Amorphous NixCoyP-supported TiO2 nanotube arrays as an efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in acidic solution
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 62–70, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.6

- by cyclic voltammetry, linear sweep voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. We show that after incorporating Co into Ni–P, the resulting NixCoyP/TNAs present enhanced electrocatalytic activity due to the improved electron transfer and increased electrochemically active surface area
- electrochemical workstation (Chenhua, Shanghai) including linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), cyclic voltammetry (CV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and Tafel analysis at 25 °C. The three electrode system was constituted of the sample working electrode, a platinum counter electrode, a Ag/AgCl
Electrolyte tuning in dye-sensitized solar cells with N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) iron(II) sensitizers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3069–3078, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.285

- achieved giving η in the range of 0.47 to 0.57% which represents 7.8 to 9.3% relative to an N719 reference DSC set at 100%. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy has been used to understand the role of the MBI additive in the electrolytes. Keywords: dye-sensitized solar cell; electrolyte; nanoparticles
- mV (no TBP) to 541 mV (0.5 M TBP). However, this gain is not sufficient to enhance the global efficiency which drops from 0.51% to 0.26% (Table 4). The trends are reproduced for duplicate DSCs (Table S2, Supporting Information File 1). Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) Electrochemical
- impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is an important technique for the investigation of interfaces in DSCs [49][50]. Fitting of the Nyquist and Bode plots, which are used to describe the EIS results, leads to parameters including the recombination resistance (Rrec), electron/hole transport resistance (Rtr), charge
Impact of the anodization time on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotubes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2628–2643, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.244

- hypothesis of a doping effect originating from an extended anodization time (Figure S3a, Supporting Information File 1). As it was stated in previous sections, a relation between the capacitive processes seems to be associated with the length of the TNTs. Consequently, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy
Correlative electrochemical strain and scanning electron microscopy for local characterization of the solid state electrolyte Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1564–1572, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.148

- improvement of solid state electrolytes such as LATP is a better understanding of interfacial and ion transport properties on relevant length scales in the nanometer to micrometer range. Using common techniques, such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, only global information can be obtained. In this
- grain boundaries with an overall conductivity of 0.2 mS cm−1 [11] and has therefore attracted much research within the last decade [12][13][14][15]. In classical electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), the ionic conductivity is measured through the entire sample and over the full electrode contact
Ag2WO4 nanorods decorated with AgI nanoparticles: Novel and efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for the degradation of water pollutants
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1308–1316, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.123

- RhB in the presence of 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. (a) The cycled photocatalytic degradation of RhB over 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4; (b) XRD patterns of the fresh and used 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. Active-species trapping tests over 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) Nyquist plots of AgI and 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4
- impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurement was applied to study the charge transport and separation [49]. A smaller arc radius commonly signifies a higher charge transport rate. As displayed in Figure 10, the arc radius of 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4 is smaller than that of AgI, suggesting that 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4 holds a higher
- −) scavenger) or ammonium oxalate (a hole radical (h+) scavenger) was introduced, the degradation rate of RhB was severely depressed. That is, •O2−, •OH, and h+ were generated in the 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4 mediated degradation system, but •O2− and h+ played a more crucial role in RhB degradation. Electrochemical
Cyclodextrin inhibits zinc corrosion by destabilizing point defect formation in the oxide layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 936–944, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.86
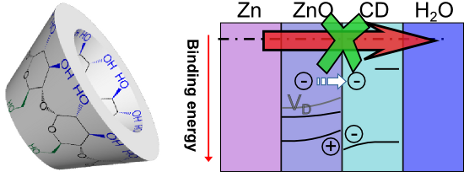
- . This work uses electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to show the cyclic oligosaccharide β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) to inhibit corrosion of zinc in 0.1M chloride with an inhibition efficiency of up to 85%. Only a monomolecular adsorption layer of β-CD is present on the surface of the oxide covered metal
- inhibitors [8][12][13]. Metallic zinc is industrially used for cathodic protection of steel [15]. In this work, the inhibition of zinc corrosion by β-CD was investigated electrochemically. Inhibition efficiencies were determined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). After exposure to chloride
Synthesis and characterization of electrospun molybdenum dioxide–carbon nanofibers as sulfur matrix additives for rechargeable lithium–sulfur battery applications
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 262–270, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.28

- electrodes were evaluated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge–discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). The electrochemical characteristics of the cells with S/MoO2–CNF cathodes and pure sulfur cathodes were examined by CV in the voltage range of 1.7–3.0 V at the scanning rate
- effect of the MoO2–CNF matrix material calcined at different temperatures on the electrochemical performance of the sulfur cathode. Compared to the CV technique, the diffusion coefficients under equilibrium conditions can be expressed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Additionally, the
- temperatures with S/composite cathodes and pure sulfur cathode at 0.25 mA cm−2. (a) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of MoO2–CNFs calcined at different temperatures with sulfur cathodes and a pure sulfur cathode. (b) The dependence of Z’ (Zre) on the reciprocal square root of the frequency ω−1/2 in the
Facile synthesis of silver/silver thiocyanate (Ag@AgSCN) plasmonic nanostructures with enhanced photocatalytic performance
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2781–2789, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.277

- source. N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms were determined by using a Quadrasorb SI apparatus to obtain the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was recorded on a CHI660A electrochemical workstation (CH Instrument Company, Shanghai, China
One-step chemical vapor deposition synthesis and supercapacitor performance of nitrogen-doped porous carbon–carbon nanotube hybrids
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2669–2679, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.267

- concentration of incorporated nitrogen. The hybrid materials were tested as electrodes in a 1M H2SO4 electrolyte and the best performance was found for a nitrogen-enriched material produced using the Fe/Mo catalyst. From the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy data, it was concluded that the nitrogen doping
- reduces the resistance at the carbon surface/electrolyte interface and the nanotubes permeating the porous carbon provide fast charge transport in the cell. Keywords: bimetallic catalyst; electrochemical impedance spectroscopy; N-doped carbon; porous carbon–carbon nanotube hybrid; supercapacitor
- composition of the obtained CNx hybrids were correlated with the data of cyclic voltammetry (CV) and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements in 1 M H2SO4 electrolyte. Experimental Synthesis Catalysts were prepared using polyoxomolybdate clusters of the ε-Keggin-type structure Mo12O28(μ2-OH
































































































































































































































