Search results
Search for "electrodeposition" in Full Text gives 65 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
A Ni(OH)2 nanopetals network for high-performance supercapacitors synthesized by immersing Ni nanofoam in water
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 281–293, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.27

- . demonstrated a nickel hydroxide@nanoporous gold/Ni foam electrode, which was synthesized by electrodeposition of a Sn–Au alloy on nickel foam with subsequent dealloying of Sn and electrodepostion of Ni(OH)2 on the nanoporous gold/Ni foam [25]. Liu et al. created Ni(OH)2/Cu2O nanosheets on nanoporous NiCu alloy
Site-specific growth of oriented ZnO nanocrystal arrays
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 274–280, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.26

- electrodeposition technique. Further, vertically aligned periodic nanocrystal (NC) growth is engineered at predefined positions on polymer-coated ITO substrates patterned with ordered pores. The vertical alignment of ZnO NCs along the c-axis is achieved via ion-by-ion nucleation-controlled growth for patterned
- correlated to the pore size. As ordered NC arrays have the potential to generate new collective properties different from single NCs, our first demonstration of a cost effective and facile fabrication process opens up new possibilities for devices with versatile functionalities. Keywords: electrodeposition
- patterned substrates and a cost-effective growth technique. In particular, we demonstrate the growth of hexagonal faceted self-assembled twin ZnO NCs on bare indium tin oxide (ITO) substrate via a facile low temperature electrodeposition technique that has the potential of yielding good crystal quality with
Amorphous NixCoyP-supported TiO2 nanotube arrays as an efficient hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in acidic solution
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 62–70, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.6

- attention due to their synergistic effect for improving the hydrogen evolution reaction as compared to monometallic phosphides. In this work, NiCoP modified hybrid electrodes were fabricated by a one-step electrodeposition process with TiO2 nanotube arrays (TNAs) as a carrier. X-ray diffraction
- , which is an improvment of 79% over that of 1.07 V at 10 mA cm−2. Keywords: electrocatalysis; electrodeposition; HER; NiCoP bimetallic phosphides; Introduction Significant research efforts have been invested in the electrochemical splitting of water using renewable energy to attempt to overcome the
- components [25][26]. Accordingly, in this study, the TNAs work as the support material in the preparation of NixCoyP/TNA hybrid electrodes by a one-step electrodeposition process. The physiochemical and electrochemical properties of as-prepared NixCoyP/TNAs electrodes were investigated in detail. In acidic
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
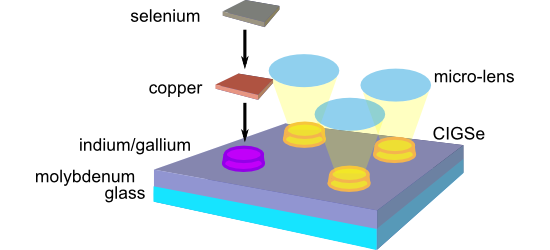
- efficiency potential of the micro-concentrator concept for CIGSe solar cells, the aspect of material saving was not considered in the chosen top-down approaches. Recently, bottom-up approaches were developed to locally deposit metallic precursors for CIGSe microabsorbers. By means of electrodeposition, the
Magnetism and magnetoresistance of single Ni–Cu alloy nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2345–2355, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.219

- magnetic hysteresis loops derived from magnetoresistance measurements and the associated micromagnetic modeling. Results and Discussion SEM micrographs of arrays of Ni–Cu alloy nanowires show that the nanowires obtained at all four different electrodeposition potentials have a regular cylindrical shape
- Information File 1). The compositions of the four types of nanowires, corresponding to the four different electrodeposition potentials, as more precisely obtained by the EDX analysis performed on bunches of nanowires, are 20, 54, 75 and 92 atom % of Ni. Also, the saturation magnetization of the corresponding
- different Ni content were grown using electrodeposition in polycarbonate nanoporous membranes. Contacting single Ni–Cu alloy nanowires by means of EBL allowed magnetoresistance measurements to be made on individual single Ni–Cu alloy nanowires with diameters of 100 nm. Magnetoresitive effects of the order
Localized photodeposition of catalysts using nanophotonic resonances in silicon photocathodes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2097–2105, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.198

- deposition of the platinum catalyst on the nanostructures. The sample served as the working electrode (WE) with a platinum wire counter electrode (CE) and Ag/AgCl reference electrode (RE) (Figure 1). During a typical photo-electrodeposition experiment, the sample was mounted in direct contact with a Pt
- silicon, so TiO2 acts as an electron blocking layer here [5][43][44]. Therefore, the presence of TiO2 offers a control over the potential we could apply to selectively promote photodeposition while avoiding electrodeposition. In the absence of a TiO2 layer the recorded dark current is much higher than the
- Si nanostructures and on the substrate, when the samples were illuminated without the TiO2 layer but still under biased conditions. The final potential value (−0.8 V) for photo-electrodeposition of platinum nanoparticles in the presence of a TiO2 layer was chosen because it yields a high current
Synthesis of rare-earth metal and rare-earth metal-fluoride nanoparticles in ionic liquids and propylene carbonate
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1881–1894, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.180
- electrodeposition process of Al3+, stemming from the Al collector, indicating that the used potential cannot be lower than 0.2 V. The open-circuit potential (OCP) of the cell is around 2.7 V vs Li+/Li. The standard electrode potential values of the involved redox couples are: Li+ + e− → Li (−3.04 V vs SHE), Er3
Nanoscale electrochemical response of lithium-ion cathodes: a combined study using C-AFM and SIMS
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1623–1628, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.154

- conductive atomic force microscopy (C-AFM) and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS). As model systems, we focus on LiMn2O4 (LMO) as cathode material [7] deposited by wet electrodeposition (thickness 260 nm) and RF-sputtered (thickness 100 nm) and compare their properties on a local (sub-100 nm) scale. In
Electrodeposition of reduced graphene oxide with chitosan based on the coordination deposition method
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1200–1210, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.111

- Mingyang Liu Yanjun Chen Chaoran Qin Zheng Zhang Shuai Ma Xiuru Cai Xueqian Li Yifeng Wang School of Materials Science and Engineering, Wuhan University of Technology, 122 Luoshi Road, Wuhan 430070, China 10.3762/bjnano.9.111 Abstract The electrodeposition of graphene has drawn considerable
- attention due to its appealing applications for sensors, supercapacitors and lithium-ion batteries. However, there are still some limitations in the current electrodeposition methods for graphene. Here, we present a novel electrodeposition method for the direct deposition of reduced graphene oxide (rGO
- deposited on an electrode through codeposition with chitosan, based on the coordination deposition method. After electrodeposition, the homogeneous, deposited rGO/chitosan films can be generated on copper or silver electrodes or substrates. The electrodeposition method allows for the convenient and
Semi-automatic spray pyrolysis deposition of thin, transparent, titania films as blocking layers for dye-sensitized and perovskite solar cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1135–1145, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.105

- prepared by electrodeposition or ALD for example [3][8]. Therefore the central motivation for this work was SPD fabrication of blocking TiO2 films using conventional [6] and novel [13] spray protocols using a semi-automatic spray device, enabling reproducible and uniform thin transparent titania films to
Review on nanoparticles and nanostructured materials: history, sources, toxicity and regulations
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1050–1074, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.98

- allows them to float on water without sinking [194][195]. Based on these reports, many artificial superhydrophobic materials with self-cleaning ability have been manufactured [196] through electrodeposition, photolithography and colloidal systems [197][198][199] with unique morphology and roughness [200
Single-crystalline FeCo nanoparticle-filled carbon nanotubes: synthesis, structural characterization and magnetic properties
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1024–1034, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.95

- devices. Different techniques have been applied for the synthesis of these magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), such as mechanical alloying [23], electrodeposition [24], radio frequency (rf)-plasma torch [25], sol–gel methods [26][27], reverse micelle systems [28] and thermal decomposition of bimetallic alloys
Synthesis and catalytic application of magnetic Co–Cu nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1769–1773, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.178

- mainly electrodeposition by different templates, as found in the previous literature. For example, many papers have reported Co–Cu nanowires electrodeposited into a porous anodic aluminum oxide template [1][2][3][4]. Additionally, L. Gravier et al. [8] prepared Co–Cu multilayered nanowires by
- electrodeposition in a polymer matrix. However, the electrodeposition method using templates increases the cost of production and the complexity of the synthetic process. Thus, it is necessary to devote attention to the development of a facile method for the preparation of Co–Cu nanowires. In the present paper
Oxidative chemical vapor deposition of polyaniline thin films
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1266–1276, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.128

- over the deposition (such as film thickness, conformality, uniformity, morphology) than current solution-based techniques such as chemical bath deposition [18], electrodeposition [19], and casting from suspension [20]. As a result, oCVD has garnered significant attention in recent years as an
Gas sensing properties of MWCNT layers electrochemically decorated with Au and Pd nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 592–603, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.64

- of CNT-based sensors, due to an increase in the number of the adsorption sites for the targeted gases [18]. CNT sidewalls can be decorated with various noble metals such as Au, Pt, Pd, Rh, and Ag [19][20][21][22][23][24]. Different methods have been used to decorate CNTs, including electrodeposition
Formation and shape-control of hierarchical cobalt nanostructures using quaternary ammonium salts in aqueous media
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 494–505, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.53

- by using NH4OH during electrodeposition [26]. The growth of these unique cone nanostructures is initiated by screw dislocations. In this study, interesting spindles with peculiar conical edges are synthesized that can be, in principle, surface-functionalized for various applications. A magnified
A new approach to grain boundary engineering for nanocrystalline materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1829–1849, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.176

- high performance nanocrystalline materials, especially those produced by electrodeposition and sputtering, is discussed on the basis of some important findings from recently available results on GBE for nanocrystalline materials. In order to optimize their utility, the beneficial effects of grain
- enhanced strength and brittle fracture control in structural and functional nanocrystalline materials produced by electrodeposition and sputtering. This was first applied by Gleiter and coworkers during the very early stage development of nanocrystalline materials [1][2] and was later practically applied
- relationship between the Vickers hardness and the average grain size for pure nickel (Ni) and nickel–phosphorus (Ni–P) alloy specimens produced by electrodeposition and subsequent annealing. The data obtained from our recent investigation are shown together with those for pure Ni [62][64] and Ni–1.2 mass % P
Properties of Ni and Ni–Fe nanowires electrochemically deposited into a porous alumina template
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1709–1717, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.163

- template substantially define the result of metal electrodeposition. Therefore, in spite of the fact that this procedure became almost standard, the technology for the formation of the PA template is constantly improved by researchers. Generally, before the deposition of NWs, the thick alumina film is
- of the pores on a surface of 1 cm2 is equal to about 0.2 cm2. For example, a current density of 15 mA·cm−2 corresponds to an effective current density of about 3 mA·cm−2 for electrodeposition on a porous template. It has been found experimentally that, by applying a low current density of 3.0 mA·cm−2
- during galvanostatic dc deposition on a porous template, uniform, highly ordered, densely packed NWs of about 25 micrometers length are formed. Similar data have been described in [2] for the synthesis of Co NWs in an oxalic acid alumina template. The solution for Ni–Fe NWs electrodeposition was prepared
Functional fusion of living systems with synthetic electrode interfaces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 296–301, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.27

- homogenous, low defect and parallel-oriented crystal planes were produced by electrodeposition as previously described [1]. This process employed polycarbonate (PC), track-etched filter membranes with a pore density of 1 × 106 pores/cm2 and a pore size of 100 nm (Figure 1a, 1–4). Aluminium (Al) contacts were
- -coated with a gold layer and applied to titanium/gold coated coverslips (a, 2). During wet chemical electrodeposition, monocrystalline gold pillars grow within the filter pores (a, 3). After dissolving the filter membrane using dichloromethane (DCM), free-standing electrodes (a, 4) are covered with a
Self-assembly mechanism of Ni nanowires prepared with an external magnetic field
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2123–2128, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.217

- electrodeposition [7][8][9][10], block copolymer lithography [11], and wet chemical reduction [12]. Among these methods, template-based electrodeposition is the most widely used to prepare Ni nanowires as highly-ordered and size-controlled nanowires can be obtained with this method. However, additional steps such
Nanostructured superhydrophobic films synthesized by electrodeposition of fluorinated polyindoles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2078–2087, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.212

- 6-position of indole) were synthesized and electropolymerized (Scheme 1). We report the influence of the fluorocarbon chain length and the substituent position on the surface morphology and hydrophobicity. Results and Discussion Electrodeposition In order to develop structured polymeric films, the
- properties were reached due to the presence of spherical nanoparticles and the fluorinated compounds on the surface. This work opens new ways in the formation of superhydrophobic polyindoles films by electrodeposition for future applications. Experimental Monomer synthesis and characterization 4-(aminomethyl
- ), 27.56 (t, J = 4.0 Hz); MS (70 eV) m/z: M+ 420 (85), C9H9N2+• 145 (85), C9H8N+• 130 (100), C8H8N+ 118 (70). Electrodeposition parameters The polyindole films were electrodeposited by using a potentiostat (Autolab). For this, 2 cm2 gold plates were chosen as working electrode, a carbon rod as counter
Electrochemical behavior of polypyrrol/AuNP composites deposited by different electrochemical methods: sensing properties towards catechol
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2052–2061, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.209

- the electrooxidation of the pyrrole monomer in the presence of colloidal gold nanoparticles, referred to as trapping method (T), and the second one by electrodeposition of both components from one solution containing the monomer and a gold salt, referred to as cogeneration method (C). In both cases
- , electrodeposition was carried out through galvanostatic and potentiostatic methods and using platinum (Pt) or stainless steel (SS) as substrates. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) demonstrated that in all cases gold nanoparticles of similar size were uniformly dispersed in the Ppy matrix. The amount of AuNPs
- electrochemical conditions during film generation [17]. The electrodeposition of the composite can be achieved using different strategies [18], mainly through the electrooxidation of the monomer in the presence of colloidal gold nanoparticles and the corresponding doping agent [19] but also by electrodeposition
Optimized design of a nanostructured SPCE-based multipurpose biosensing platform formed by ferrocene-tethered electrochemically-deposited cauliflower-shaped gold nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1840–1852, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.187

- structured with cauliflower-shaped gold nanoparticles (cfAuNPs) and we show its applications in immunosensing and enzyme-based detection. The electrochemical reduction of Au(III) allows for the electrodeposition of highly dispersed cauliflower-shaped gold nanoparticles on the surface of screen-printed carbon
- SPCEs were cleaned using a 0.5 M H2SO4 acid solution to remove the impurities adsorbed on the surface. Five cycles, where the potential was swept from 0.0 to 1.5 V, seemed to be enough to get sufficiently clean surface for gold electrodeposition. This step is crucial in order to get reproducible results
- /growth mechanism [20]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case where the nanostructuration is systemically studied in order to optimize the electrodeposition procedure. The gold electrodeposition on SPCE allowed us to obtain a modified electrode with an active surface as large as that of a
Scalable, high performance, enzymatic cathodes based on nanoimprint lithography
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1377–1384, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.142

- performance biodevices based on MCOs and different nanomaterials [10][11][12][13][14]. Several techniques for reproducible fabrication of well-ordered porous electrodes have been already reported. The techniques are based on electrodeposition of metals using colloidal templates [15] or gas bubbling [16
Formation of substrate-based gold nanocage chains through dealloying with nitric acid
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1362–1368, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.140

- ), and potassium nitrate (KNO3) were obtained from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). The solutions were prepared using deionized water (>18 MΩ·cm). Silver template preparation The Ag NP templates on ITO glass strips were prepared by electrodeposition in a similar manner as described
































































































































































































