Search results
Search for "signal-to-noise ratio" in Full Text gives 155 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Synthesis of graphene–transition metal oxide hybrid nanoparticles and their application in various fields
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 688–714, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.74

- extremely high carrier mobility, high carrier density, and low intrinsic noise for better detection by virtue of the high signal-to-noise ratio. In the anchored structure, electroactive NPs are anchored on the GS (Figure 1c) [76], and in the mixed structure, the graphene and NPs are synthesised separately
Copper atomic-scale transistors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 530–538, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.57

- operation current leads to a low signal-to-noise ratio. The interface-coupling problem between the functional block and the electrodes does not exist in the copper atomic-scale transistor, because the material of the electrodes and the building blocks is the same. The “switching on” current of a copper
Thin SnOx films for surface plasmon resonance enhanced ellipsometric gas sensing (SPREE)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 522–529, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.56

- chosen because only the change of the ellipsometric quantities is relevant for the gas measurement. We decided to focus on the evaluation of the ΔΔ values instead of analyzing the ΔΨ values because the signal to noise ratio is much better for the ΔΔ measurement. The calculated values of the standard
- deviation σ for the gas measurement of CO on a Fe:SnOx overlayer, as shown in Figure 5, are 0.04° for ΔΨ and 0.016° for ΔΔ, respectively. This lower σ value leads to a better signal to noise ratio and, consequently, a higher sensitivity in the gas measurement. The measurement of three different gases is
- resolved with ΔΔ = 1.6°. The better resolution in comparison to the undoped sample is a result of the much better signal to noise ratio achieved with the Fe:SnOx add-on layer. This effect is probably due to a changed thickness (5 nm for Fe:SnOx and 7 nm for SnOx) of the layer which also effects the
Flexible photonic crystal membranes with nanoparticle high refractive index layers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 203–209, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.22

- steps of 2 wt %. 14 wt % was also tested but the resonance quality regarding to signal to noise ratio of our sample was too low for meaningful statements. Therefore, all experiments were conducted only with the concentrations below 14 wt %. Furthermore 0.5 wt % of fluorosurfactant (PFT) (NOVEC FC-4430
Studying friction while playing the violin: exploring the stick–slip phenomenon
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 159–166, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.16

- . It is therefore desirable to minimize these possible sources of systematic errors or complications by reducing the contact region of the rubbing pieces without decreasing the signal-to-noise ratio of the relevant parameter, and by limiting the analysis to interfaces that can endure many friction
Nanocrystalline TiO2/SnO2 heterostructures for gas sensing
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 108–122, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.12

- composition (Figure 5a). As one discusses 10 mol % SnO2/90 mol % TiO2 it appears that at 1 ppm H2 the signal-to-noise ratio becomes much worse. However, the sensor signal is still discernible. Within the studied temperature range SnO2-rich nanomaterials exhibit better gas-sensing performance (Figure 5c,d
Sub-nanosecond light-pulse generation with waveguide-coupled carbon nanotube transducers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 38–44, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.5

- signal to noise ratio. The acquired histogram was averaged over many cycles. The count rate under RF pulses was typically 1 kHz to 1 MHz. Figure 4b shows the time-resolved optical emission versus the electrical signal amplitude applied with the pulse generator. The optical signal of the WG-CNT
Ferromagnetic behaviour of ZnO: the role of grain boundaries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1936–1947, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.185

- (10 to 75 nm). No dependence on temperature or penetration depth was observed. Therefore, the µSR spectra were obtained by averaging the data obtained at different temperatures and different sample penetration depths in order to improve the signal to noise ratio. Three different samples were
Noise in NC-AFM measurements with significant tip–sample interaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1885–1904, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.181
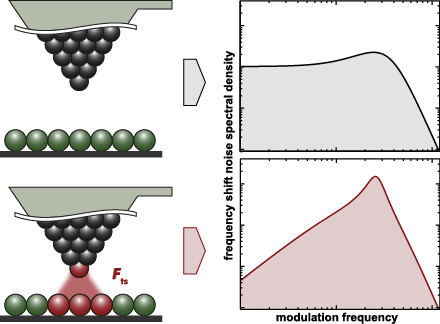
- the intrinsic value Q0 [14][15]. Our analysis can, however, be applied to any NC-AFM detection scheme and sample environment, specifically also to measurements in liquids where signal-to-noise-ratio considerations play a paramount role [16][17][18]. From our findings, we derive a general strategy for
- optimum in stability, accuracy and signal-to-noise ratio can be done by a rational, systematic approach following the findings described in this paper, provided the measurement system is well characterised and offers sufficient choice and flexibility in system parameter settings. The starting point is
Monolayer graphene/SiC Schottky barrier diodes with improved barrier height uniformity as a sensing platform for the detection of heavy metals
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1800–1814, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.173

- is graphene [14]. Due to its large surface area (2600 m2/g) [15], high chemical activity [16] and exceptionally high signal-to-noise ratio [17], graphene provides a rich platform for surface chemistry and the desirable conditions for detection of heavy metals because of the strong sensitivity of its
Dynamic of cold-atom tips in anharmonic potentials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1543–1555, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.148

- good signal-to-noise ratio, all data have thus been averaged over 50 experimental cycles. At higher outcoupling rates, tip oscillations can be detected in a single run. Figure 8 shows an example of the measured ion signal as averaged over 50 experimental runs with the outcoupling position tuned to y0
- single particle events rather than the binned detector signal to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. Figure 9 shows an example of the binned detector signal alongside the Fourier transform and the autocorrelation function as extracted from the measurement at y0 = 32.6 μm (Δ = 2π × 2.03 MHz). The
- the correlation analysis. Signal-to-noise ratio As described earlier, the detection signal strongly depends on the outcoupling position. For an application-orientated assignment of a cold-atom tip, the signal-to-noise ratio should thus be optimized. Therefore, we take a series of oscillation
Generalized Hertz model for bimodal nanomechanical mapping
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 970–982, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.89
- . In AM-AM and AM-PM, the second eigenmode drive frequency is held fixed. In that case, when the second eigenmode resonance frequency shifts by more than its bandwidth (fc/2Qc), the signal-to-noise ratio degrades because the signal drops relative to the noise floor. Furthermore, in AM-AM operation, A2
- decreases upon interaction with the surface – further aggravating the drop in signal-to-noise ratio. It is therefore often advisable to operate the second eigenmode in FM mode in practical situations. On the other hand, the first eigenmode typically undergoes more modest changes in resonance frequency upon
- interaction with the surface. Also, these changes are controllable by the AFM user by the setting of an amplitude setpoint. For this reason, AM operation on the first eigenmode does not cause the same decrease in signal-to-noise ratio often observed on the second eigenmode. More importantly, dynamic AFM
Investigating organic multilayers by spectroscopic ellipsometry: specific and non-specific interactions of polyhistidine with NTA self-assembled monolayers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 544–553, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.48

- Experimental section. δΔ2,1 and δΨ2,1 difference spectra shown in Figure 4a,b are representative of the observed behavior. Despite the reduced refractive index mismatch between the film and the ambient and the use of cell windows tending to lower the signal-to-noise ratio, the emerging picture appears rather
Active multi-point microrheology of cytoskeletal networks
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 484–491, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.42

- ability of the network to transmit mechanical forces. We also take a closer look at the influence of noise on lock-in measurements and state some simple rules for improving the signal-to-noise ratio. Keywords: cytoskeleton; intermediate filaments; lock-in technique; microrheology; optical tweezers
- closer look at the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is also necessary in order to to ensure applicability of the method over the whole range of experimentally accessible parameters. With this technique we characterized keratin networks with crosslinks of different strength. The concept of the lock-in
Length-extension resonator as a force sensor for high-resolution frequency-modulation atomic force microscopy in air
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 432–438, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.38

- comparable to the value measured by Giessibl et al. for signal-to-noise ratio calculations of the LER [9]. Compensation of environment-induced frequency shift The frequency shift signal Δf is a measure of the force gradient kts according to Δf = f0kts/2k, where f0 is the free resonance frequency. The high
Functional fusion of living systems with synthetic electrode interfaces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 296–301, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.27

- -noise ratio is likely due to an increased electrical coupling coefficient based on the “close” contact between the sharp, monocrystalline electrode tips and the plasma membrane in combination with the PC isolation layer increasing the seal resistance. Comparable improvements of the signal-to-noise ratio
- were achieved with several nano- or microstructured electrode surfaces, such as chemically functionalized micrometer-sized mushroom-shaped gold protrusions [13][14], highlighting the general advantages of such surfaces over planar electrodes. The signal-to-noise ratio of intracellular NEI measurements
- potential changes frequently became detectable (Figure 3, green). These are well understood for Physarum p. and closely related to its oscillating cytoplasmic shuttle streaming that develops over a similar time frame [2]. When compared to PGE/PGE recordings, the significant enhancement of the signal-to
High-bandwidth multimode self-sensing in bimodal atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 284–295, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.26
- strain sensitivity on the fifth eigenmode leading to a remarkable signal-to-noise ratio. Experimental results using bimodal AFM imaging on a two component polymer sample validate that the self-sensing scheme can therefore be used to provide both the feedback signal, for topography imaging on the
- values obtained during AFM imaging. To qualify the resolution of the overall AFM system, a noise image with the actively driven cantilever in contact with the sample surface should be acquired [35] which takes into account all contributing noise processes. Additionally, the signal-to-noise-ratio (SNR) is
Single-molecule mechanics of protein-labelled DNA handles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 138–148, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.16

- lengths, one can choose a certain trap separation during experiments that minimizes contributions due to crosstalk. DH lengths of 1000, 3034 and 4056 bp were chosen for the PDHs in this study. Short handles with greater stiffness could be produced quite easily and increase the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR
- increasing the distance between the two optically trapped beads. For nanomechanical experiments short molecular handles are preferred due to their increased mechanical stiffness, resulting in a favourable signal-to-noise ratio [14]. In order to achieve optimal positional and force resolution a balance had to
- the signal-to-noise ratio. The upper PDHs length limit is defined by the range of the steerable piezo-mirror (ca. 8 µm in the device used here). For tweezers systems utilizing a pipette and an optical trap (see Figure 1a–d) PDH molecules as short as 30 nm up to 30 µm can be investigated. Using these
Chemical bath deposition of textured and compact zinc oxide thin films on vinyl-terminated polystyrene brushes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 102–110, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.12

- signal-to-noise ratio, PS brushes grafted to a Si-wafer coated with 10 nm SiO2, 100 nm Au and 5 nm Ti as adhesive layer between Au and Si were prepared [46]. For the sample measurement between 900 and 1300 scans have been cumulated, the spectra were recorded until no water bands could be observed in the
Probing the local environment of a single OPE3 molecule using inelastic tunneling electron spectroscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2477–2484, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.257

- extract a reliable IETS signal. In our approach, we record a large number of IVs, from which we calculate the first and the second derivative. We then divide point by point the second derivative by the first derivative to obtain the IETS signal. To increase the signal-to-noise ratio and reduce the effect
Blue and white light emission from zinc oxide nanoforests
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2463–2469, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.255

- PIN diode to the sample was adjusted to achieve adequate signal-to-noise ratio without saturating the diode during the experiments. The voltage output of the built-in amplifier was significantly larger than any noise or perturbations coupled into the signal lines caused by the fast pulses. Hence, this
Au nanoparticle-based sensor for apomorphine detection in plasma
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2224–2232, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.228

- experiences in the biological matrix as compared to the aqueous solution. To reach a comparable SERS intensity with respect to 100 µg/mL APO in water, an acquisition time of 10 s was applied, while 60 s was the acquisition time required for a reasonable signal-to-noise ratio of the SERS spectrum of 20 µg/mL
- by the selection of two SERS peaks. Minimal sample preparation and the capability to operate in an aqueous environment make the detection of APO by means of this technique rapid, with good signal-to-noise ratio, and characterized by adequate spatial reproducibility. The method is promising for
- dynamic range of the sensor To be considered a useful SERS-based method for drug detection, the procedure, based on the use of gold substrates pulsed laser deposition, should be rapid and quantitative. An acquisition time of 5 s, which corresponds to a fast measurement with an adequate signal-to-noise
Kelvin probe force microscopy for local characterisation of active nanoelectronic devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2193–2206, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.225

- transitions and observations, respectively. As the noise at the output, , increases for a fixed , the bandwidth is reduced (Figure 7a). The ratio resembles a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), which increases for large K and small filter bandwidths BW. The closed-loop bandwidth is a function of this SNR. Therefore
Electrochemical coating of dental implants with anodic porous titania for enhanced osteointegration
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2183–2192, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.224

- measurements, given the limited thickness of APT, we had to use collecting conditions of low magnification (objective of 10×), high laser power (≈100 mW) and long accumulation time (1 min) to obtain spectra with reasonable signal to noise ratio. A representative Raman spectrum is presented in Figure 5
Imaging of carbon nanomembranes with helium ion microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1712–1720, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.175

- particle microscopy techniques such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM) or helium ion microscopy (HIM). As illustrated in Supporting Information File 1, Figure S1, SEM shows a low signal-to-noise-ratio for freestanding CNMs, especially at higher magnifications, due to charging issues [4][16]. This tends
- to be destructive for freestanding membranes. For example, an attempt at imaging perforated CNMs with SEM failed due to charging-induced rupture during the imaging process [9]. On the other hand, HIM is very well-suited to image CNMs with high signal-to-noise-ratio at high magnification. In this
- , the high surface sensitivity of the HIM is well suited to obtain CNM images with high signal-to-noise-ratio. It is also important to note that the helium beam easily penetrates the CNM and also strikes objects below the freestanding membrane, for example, the sample holder. Figure 1 shows an example











































































![[Graphic 32]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i73.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...

![[Graphic 34]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i75.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...































![[Graphic 4]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-89-i40.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) approximation applied to Equation 6 i...
approximation applied to Equation 6 i...










































































![[Graphic 33]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-6-225-i48.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) for different modulation amplitu...
for different modulation amplitu...























