Search results
Search for "surface science" in Full Text gives 69 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Electron interactions with the heteronuclear carbonyl precursor H2FeRu3(CO)13 and comparison with HFeCo3(CO)12: from fundamental gas phase and surface science studies to focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 555–579, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.53

- ratio. Low temperature (≈213 K) surface science studies on thin films of H2FeRu3(CO)13 demonstrate that electron stimulated decomposition leads to significant CO desorption (average of 8–9 CO groups per molecule) to form partially decarbonylated intermediates. However, once formed these intermediates
- could desorb at room temperature under high vacuum conditions, which may explain the slight increase in the Ru/Fe ratio of deposits in FEBID. With the combination of gas phase experiments, surface science studies and actual FEBID experiments, we can offer new insights into the low energy electron
- ; focused electron beam induced deposition; heteronuclear FEBID precursors; surface science; Introduction Direct-write technologies using electron beams for nanostructure deposition can surpass the limitations of standard lithography techniques, such as the growth of three-dimensional nanostructures with
Review: Electrostatically actuated nanobeam-based nanoelectromechanical switches – materials solutions and operational conditions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 271–300, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.29

- interface interactions govern materials properties and behaviour [4]. Thus, NEM switches provide an exciting opportunity for gaining fundamental insight in such fields as surface science and electrical and mechanical processes in nanocontacts. The NEM switch components can be produced from a wide range of
Electron-driven and thermal chemistry during water-assisted purification of platinum nanomaterials generated by electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 77–90, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.10

- an electron-driven process but also proceeds via additional thermal chemistry. Such thermal chemistry that assists the removal of ligands from the precursor has been described before. In particular, previous surface science studies on the FEBID precursor Pt(PF3)4 have shown that the initial electron
- nitrogen temperature. These thermal processes must be taken into account when comparing the results of a surface science model study to an actual FEBID process. Based on the present results in connection with previous experiments we can safely confirm that CH4 and not CH3 is released from the condensed
Response under low-energy electron irradiation of a thin film of a potential copper precursor for focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 57–65, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.8

- ligands that are solid and stable under ambient conditions. They are directly deposited on the surface for studying the fragmentation with surface science tools. Results: Infrared spectroscopy and high-resolution electron energy loss spectroscopy (HREELS) are combined to show that the precursor is able to
- same range [41]. Conclusion The present study is our first attempt to use surface science tools, usually dedicated to the study of low-energy electron induced processes, to gain insights on dissociation processes induced on potential precursors for FEBID. The HREEL spectroscopy allowed us to show that
- compound has been measured from evolution of the signal directly linked to the rarefaction of the precursor in the irradiation area. Experimental The precursor in gel form can be directly deposited on a surface or can be diluted in solvent for a dip-coating deposition, which both allow the study by surface
Localized growth of carbon nanotubes via lithographic fabrication of metallic deposits
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2592–2605, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.260

- CNT yield [21]. The existence of the corresponding carbon contamination was traced back to deposits from the residual gas in the high-vacuum (HV) environment and the dissociation of the carbon-containing precursor ligands [19]. With our “surface science approach” to FEBIP, that is, working in an ultra
Direct writing of gold nanostructures with an electron beam: On the way to pure nanostructures by combining optimized deposition with oxygen-plasma treatment
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2530–2543, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.253

- the deposition parameters, making use of conventional equipment and a standard precursor. The ultrahigh vacuum/surface science approach to studying the effect of electron beam irradiation on nanometer thin films of a common Me2-Au-acac precursor from Wnuk et al. [69][70] represents a valuable starting
Adsorption of iron tetraphenylporphyrin on (111) surfaces of coinage metals: a density functional theory study
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2484–2491, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.248

- spin switches. Keywords: activation barrier; density functional theory; iron tetraphenylporphyrin; spin switch; spin states; Introduction Porphyrins, phthalocyanines and their transition-metal (TM) complexes are largely investigated in surface science as reported in detail by Gottfried [1]. The
Towards molecular spintronics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2464–2466, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.245

- molecules; (magneto-)optical spectroscopy; molecular spintronics; photoelectron spectroscopy; surface science; thin films; The discovery of tunneling and giant magnetoresistance in inorganic spin valves has led to a revolution in the field of magnetic memory and the significant increase in the storage
Comparing postdeposition reactions of electrons and radicals with Pt nanostructures created by focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2410–2424, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.240

- etch substrates or equipment. The use of electrons was motivated in part by previous ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) surface science studies which showed that for 1–2 monolayer (ML) thin films of organometallic precursors with halide ligands, the halogens can be removed [29][31]. The importance of halogen
- % to ≈87%). This is qualitatively consistent with our previous low-temperature UHV surface science studies on the effect of electron irradiation on 1–2 mL cis-Pt(CO)2Cl2 films [29]. Based on earlier studies [29][31] it is reasonable to assume that the purification process (PtCl2 + 2e− → Pt(s) + 2 Cl−(g
Electron beam induced deposition of silacyclohexane and dichlorosilacyclohexane: the role of dissociative ionization and dissociative electron attachment in the deposition process
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2376–2388, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.237

- into applicable design criteria for superior FEBID precursors. In this context a considerable number of gas-phase studies have been conducted, mainly on DEA and DI of different organometallic FEBID precursors. Complementary surface science studies have been carried out to better relate the gas-phase
- current experiments are thus largely confined to DEA and DI of FEBID precursors. Despite this, significant insight has been provided by the gas-phase and surface-science studies and in individual cases a distinction between the role of DEA and DI in the deposition process has been achieved
Suppression of low-energy dissociative electron attachment in Fe(CO)5 upon clustering
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2200–2207, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.219

- Equations 4–7. The argon support influences this energy range only very little. The present findings are well in line with several surface science studies. Hauchard and Rowntree [21] studied electron-induced decarbonylation of Fe(CO)5 films on Au(111)/mica using IR spectroscopy. They concluded that massive
Stable Au–C bonds to the substrate for fullerene-based nanostructures
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1073–1079, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.109

- in 1985 [5], fullerenes have played an important role in molecular surface science, organic photovoltaics and single-molecule electronics. Fullerenes can be deposited on a series of metallic and semiconducting substrates [6][7][8]. In molecular transport, they have been used both as target molecules
Biological and biomimetic materials and surfaces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 403–407, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.42

- leaves [4]. This first publication was largely ignored outside of the botanical community and the importance of this observation was, at that time, not realized by any surface science physicists or chemists. It took about 15 years before in the 1990s Wilhelm Barthlott, now serving as chair for Botany at
Innovations from the “ivory tower”: Wilhelm Barthlott and the paradigm shift in surface science
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 394–402, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.41

Noise in NC-AFM measurements with significant tip–sample interaction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1885–1904, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.181
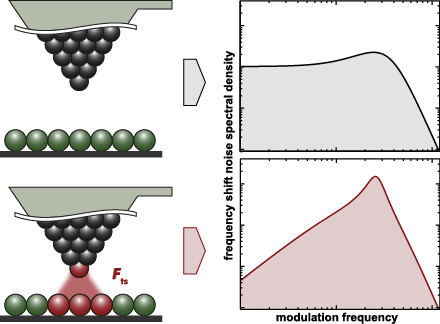
- : amplitude noise; cantilever stiffness; closed loop; detection system noise; frequency shift noise; non-contact atomic force microscopy (NC-AFM); Q-factor; spectral analysis; thermal noise; tip–sample interaction; Introduction Non-contact atomic force microscopy (NC-AFM) [1][2] is an unmatched surface
- science tool, especially when it comes to studying non-conducting surfaces [3][4], to map sub-molecular structures [5] or to measure forces [6] and force fields [7] with highest resolution. The primary imaging signal in NC-AFM is the frequency shift Δf of a probe resonator carrying a tip interacting with
Surface roughness rather than surface chemistry essentially affects insect adhesion
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1471–1479, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.139

- relatively little attention from researchers working on surface science and engineering [24][25]. Another possible reason might be that the properties of unwettable biological surfaces, other than surface wetting/de-wetting, have not been tested. The question of whether surface chemistry or surface roughness
Advanced atomic force microscopy techniques III
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1052–1054, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.98

- measurements in between atoms of single molecules or molecular assemblies at positions where chemical bonds are expected [4][5][6]. However, the origin of this contrast is under intense discussion [7][8]. The extension of the technique towards other physical properties in surface science is pushed continuously
- ultrahigh-vacuum (UHV) and low-temperature conditions. Therefore, the traditional field in surface science based on diffraction and scattering of charged particles, mostly electrons, which are used as probes in a variety of experimental methods is extended by a powerful local and real space imaging and
Synthesis and applications of carbon nanomaterials for energy generation and storage
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 149–196, doi:10.3762/bjnano.7.17

Distribution of Pd clusters on ultrathin, epitaxial TiOx films on Pt3Ti(111)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 2007–2014, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.204

- ) standard surface science techniques can be applied due to the high conductivity of these films compared to the respective bulk oxides, (b) the films can be prepared with a very high degree of structural preciseness, and (c) the influence of bulk effects such as subsurface oxygen vacancies is excluded. In
The role of low-energy electrons in focused electron beam induced deposition: four case studies of representative precursors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1904–1926, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.194

- studies on adsorbed precursor molecules can provide information on surface speciation and identify species desorbing from a substrate during electron irradiation under conditions more representative of FEBID. Comparing gas phase and surface science studies allows for insight into the primary deposition
- FEBID), in contrast to the well-defined incident energies that characterize the gas phase studies. The energy dependence of the observed processes is therefore not known directly. Consequently, a comparison of the products formed in gas phase and surface science studies combined with the energy
Transformations of PTCDA structures on rutile TiO2 induced by thermal annealing and intermolecular forces
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1498–1507, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.155

- challenging and encouraging directions in the surface science of oxide materials [14][15][16][17][18]. Studying prototypical systems gives us a chance to recognize the basic elements of the investigated phenomena and to identify underlying interactions. The necessity of understanding model systems becomes
Boosting the local anodic oxidation of silicon through carbon nanofiber atomic force microscopy probes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 215–222, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.20

- scale. Interest of developing SPL-based nanofabrication methods relies on its extraordinary performance in terms of resolution and flexibility, as well as its potential for applications, e.g., in materials/surface science, quantum devices and nanoelectronics [1]. Moreover, SPL has the additional
Formation of stable Si–O–C submonolayers on hydrogen-terminated silicon(111) under low-temperature conditions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 19–26, doi:10.3762/bjnano.6.3

- essential towards directing the nature of surface linkage. Keywords: hydrogen abstraction; thermal hydrosilylation; UV-initated hydrosilylation; X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy; Introduction Forming covalently-attached organic submonolayers on silicon remains one of the challenges in surface science. In
Advanced atomic force microscopy techniques II
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 2326–2327, doi:10.3762/bjnano.5.241

- Technology (KIT), 76021 Karlsruhe, Germany 10.3762/bjnano.5.241 Keywords: AFM; Surface science and nanotechnology are inherently coupled because of the increased surface-to-volume ratio at the nanometer scale. Most of the exciting and astonishing properties of nanoscale materials are related to certain
Localized surface plasmon resonances in nanostructures to enhance nonlinear vibrational spectroscopies: towards an astonishing molecular sensitivity
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 2275–2292, doi:10.3762/bjnano.5.237

- . Therefore, to make vibrational techniques more efficient for surface science purposes, many efforts have been made to increase the surface sensitivity of IR and Raman spectroscopies. For instance, from IR spectroscopy is born polarization-modulation IR reflection–absorption spectroscopy (PM-IRRAS) [1], and




























































































































![[Graphic 32]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i73.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...

![[Graphic 34]](/bjnano/content/inline/2190-4286-7-181-i75.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) wit...
wit...






































































































































