Search results
Search for "RNA" in Full Text gives 170 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Beyond ribose and phosphate: Selected nucleic acid modifications for structure–function investigations and therapeutic applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 908–931, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.76

- oligonucleotides that have been explored for gene silencing. Keywords: antisense; chemically modified oligonucleotides; crystallography; siRNA; structure; Introduction The natural nucleic acids sugar-phosphate backbone comes in two flavors, 2'-deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA. However, this relative
- simplicity combined with the five natural bases, adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U, in RNA) belies the fact that both DNA and RNA are decorated with chemical modifications. For a catalogue of natural modifications in DNA, see https://dnamod.hoffmanlab.org/ [1], and in RNA, see
- phosphorothioate Rp-stereoisomer (Rp-PS, i.e., phosphate with one of the non-bridging oxygens replaced by sulfur) in bacterial genomes, where it may serve a protective role against nucleases [4] and its loss results in genomic instability [5]. There are over a hundred known base modifications in RNA and the Rp-PS
Enhanced target cell specificity and uptake of lipid nanoparticles using RNA aptamers and peptides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 891–907, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.75

- LNPs that can cross the BBB, we developed and assessed two approaches. The first was centered on the BBB-penetrating trans-activator of transcription (Tat) peptide or the peptide T7, and the other on RNA aptamers targeted to glycoprotein gp160 from human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) or C-C chemokine
- receptor type 5 (CCR5), a HIV-1 coreceptor. We report herein a CCR5-selective RNA aptamer that acts to facilitate entry through a simplified BBB model and that drives the uptake of LNPs into CCR5-expressing cells, while the gp160 aptamer did not. We further observed that the addition of cell-penetrating
- ) represent an effective platform for delivering small molecules, RNA, or DNA into target cells [1]. LNPs have been successfully deployed via different administration routes in vivo to distribute cargo into target tissues [2][3][4][5][6][7][8]. By changing lipid composition [6] and/or including short peptides
DNA with zwitterionic and negatively charged phosphate modifications: Formation of DNA triplexes, duplexes and cell uptake studies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 749–761, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.65
- incorporated into the oligodeoxynucleotides (ONs). For both N+ and Ts-modified ONs, the antiparallel duplexes formed with complementary RNA were more stable than those formed with complementary DNA (except for ONs with modification in the middle of the sequence). Additionally, the incorporation of N
- The ability to detect and modify the genome of living organisms is important for the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of many diseases [1]. The site-specific targeting and manipulation of genomic DNA or RNA using chemically modified short oligodeoxynucleotides (ONs) is considered to be a viable
- parallel triple-helix structure, a polypyrimidine TFO binds to dsDNA through Hoogsteen base-pairing [17], in which the cytosine bases in the TFO are protonated at the N3 atom (Figure 1B). In antisense strategies, antisense ONs (AOs) interact with RNA molecules to interfere with protein expression [18][19
Synthesis and properties of oligonucleotides modified with an N-methylguanidine-bridged nucleic acid (GuNA[Me]) bearing adenine, guanine, or 5-methylcytosine nucleobases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 622–629, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.54
- . For applications in antisense technology, chemical modifications aimed at enhancing the duplex-forming ability toward a target RNA (i.e., a complementary single-stranded RNA) and improving the stability against enzymatic degradations are commonly utilized. For instance, antisense oligonucleotides
- 1). In our previous studies, DNA/RNA (A-form) duplexes containing a multiple GuNA[H] modification displayed similar spectral patterns to the natural and the 2',4'-BNA/LNA-modified counterparts [19]. Since GuNA[Me] showed similar results to GuNA[H] in terms of the duplex-forming ability [25], a
19F NMR as a tool in chemical biology
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 293–318, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.28

- their functional architecture. Such an approach typically includes the use of a variety of high-resolution proteomic tools, cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography to achieve full molecular characterization at the atomic level. However, macromolecules such as DNA/RNA and proteins are not
- -structural protein 1 (NS1A) homodimer (Figure 9) [64]. Protein NS1A is a highly conserved virulence factor from influenza virus (H3N2) comprised of an N-terminal double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding domain (RBD) and a multifunctional C-terminal effector domain (ED), each of which can independently form
- distance restraints for ion channels and other protein complexes that would be difficult to be defined by using other analytical tools. DNA and RNA secondary and tertiary structure 19F NMR spectroscopy also represents a useful analytical approach to study the structure, function and molecular dynamics of
Molecular basis for protein–protein interactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1–10, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.1

- (or any other organic molecule [19]) structure. A resolution of up to 0.6 Å (RNA-binding protein FUS, residues 37–42, EMD-0699, PDB: 6KJ4 [20]) were obtained when using this method. Nannenga and Gonen gave a detailed account on MicroED [21]. As another category, mass spectrometry methods are used to
- more complicated systems, such as in cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV), the viral capsid is made up of different assembly units. In vivo, viral nucleic acids may serve as biological scaffold to attract free assembly units [84] and organise on the surface [85]. Assembly with viral RNA present can be
- cooperativity, whereas as a value greater than 1000 represents a high cooperativity, with the assembly occurring in two steps. CCMV shows a low cooperativity, and thus assembles gradually [87]. In contrast, HBV binds to RNA with a high cooperativity, resulting in a quantified assembly [88]. These results show
Incorporation of a metal-mediated base pair into an ATP aptamer – using silver(I) ions to modulate aptamer function
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2870–2879, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.236

- phosphoramidite-protected imidazole nucleoside as required for automated DNA solid-phase synthesis was synthesized as previously reported [30]. The oligonucleotides were synthesized on a DNA/RNA synthesizer H-8 (K&A Laborgeräte) using standard protocols for automated solid-phase synthesis (coupling time: 1000 s
Changed reactivity of secondary hydroxy groups in C8-modified adenosine – lessons learned from silylation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2854–2861, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.234

- oligonucleotides has become a major tool for RNA structure and function studies. Reporter groups or specific functional entities are required to be attached at a pre-defined site of the oligomer. An attractive strategy is the incorporation of suitably functionalized building blocks that allow post-synthetic
- being preferentially formed. Optimization of the protection scheme lead to a new and economic route to the desired C8-alkynylated building block and its incorporation in RNA. Keywords: nucleoside chemistry; protecting groups; RNA synthesis; Sonogashira reaction; Introduction Oligoribonucleotides
- . Accordingly, the field has developed to a stage that allows custom-design of RNA probes and tools for specific application. For example, investigations of RNA structures by NMR, EPR, or fluorescence spectroscopy require labeling of the RNA molecules with specific reporter groups [2][4][7][8][9][10]. Likewise
NMR Spectroscopy of supramolecular chemistry on protein surfaces
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2505–2522, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.203

- multimeric proteins like the hexameric AAA+ ATPase p97 [124]. Furthermore, methyl-TROSY-HMQC has been employed to investigate the allosteric mode of action of the synthetic inhibitor filibuvir to the selectively Ileδ1 methyl-labeled hepatitis C virus RNA polymerase NS5B [125]. This study also includes a good
Tools for generating and analyzing glycan microarray data
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2260–2271, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.187

- structural informatics tools. Keywords: data analysis; glycan binding; glycan microarray; glycomics; informatics; Introduction Glycans represent a major type of biomolecule in all living things, along with DNA, RNA, lipids and proteins [1]. In mammals, glycans commonly occur as post-translational
Naphthalene diimide bis-guanidinio-carbonyl-pyrrole as a pH-switchable threading DNA intercalator
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2201–2211, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.185

- -DNAs only at pH 5, while at neutral conditions (pH 7) NDI-GCP2 switched to the DNA minor groove binding. Intriguingly, NDI-GCP2 was at both pH values studied bound to the ds-RNA major groove, still showing a higher affinity and thermal denaturation effect at pH 5 due to GCP protonation. At excess over
- the DNA/RNA conjugate NDI-GCP2 showed also aggregation along the ds-polynucleotide and AFM and DLS demonstrated that NDI-GCP2 has pronounced ds-DNA condensation ability. Keywords: AFM; circular dichroism; DNA/RNA recognition; fluorescence; guanidinio-carbonyl-pyrrole; naphthalene diimide
- ; Introduction The small molecules non-covalently binding to DNA or RNA are essential for life as we know it, and therefore it was not surprising that a huge number of synthetic small molecules has been prepared and studied for broad biochemical and biomedical applications [1][2]. Among the most studied small
Naphthalene diimide–amino acid conjugates as novel fluorimetric and CD probes for differentiation between ds-DNA and ds-RNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2032–2045, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.170
- interacted with ds-DNA/RNA by threading intercalation. Different from a reference NDI dye with identical visible range absorbance (520–540 nm) and Stokes shifts in emission (+60 nm, quantum yield > 0.2), only these amino acid–NDI conjugates showed selective fluorimetric response for GC-DNA in respect to AT(U
- )-polynucleotides. The DNA/RNA binding-induced circular dichroism (ICD) response of NDI at 450–550 nm strongly depended on the length and rigidity of the linker to the amino acid unit, which controls the orientation of the NDI unit inside within the intercalative binding site. The ICD selectivity also depends on
- the type of polynucleotide, thus the studied NDI dyes act as dual fluorimetric/ICD probes for sensing the difference between here used GC-DNA, AT-DNA and AU-RNA. Keywords: amino acid–fluorophore conjugate; circular dichroism; DNA/RNA recognition; fluorescence; intercalation; naphthalene diimide
Synthesis of new dihydroberberine and tetrahydroberberine analogues and evaluation of their antiproliferative activity on NCI-H1975 cells
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1606–1616, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.133
- activity [13][14][15][16][17][18][19], and an increased DNA and RNA binding efficacy [4][6][9], due to its aromatic interactions with the biological macromolecules [20]. Another interesting and promising derivative is dihydroberberine (DHBER), the reduced form of BER. The enaminic function of this alkaloid
Photocatalyzed syntheses of phenanthrenes and their aza-analogues. A review
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1476–1488, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.123
- topoisomerase 1 inhibitor [14] and DNA intercalator), bicolorine (5-methyl-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-j]phenanthridin-5-ium ion, a trypanocidal) [15], and the antimalarian nitidine, as well as ethidium bromide (EB), that has been employed as a DNA- and RNA-fluorescent marker for a long time (some examples are collected
Anthelmintic drug discovery: target identification, screening methods and the role of open science
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1203–1224, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.105
- . elegans. A rich diversity of mutants is available via the Caenorhabditis Genetics Centre [91]. The discovery of RNA interference delivered via feeding worms double-stranded DNA [92] has opened the door to genome-scale gene knockdown in the search for new drug targets. These approaches can expedite the
- /pharmacological proof-of-concept for target validation. Whilst RNA interference and CRISPR methodologies are now being applied to parasites themselves [110][111][112], inevitably, large-scale functional genomic resources are mainly found in C. elegans. The C. elegans Gene Knockout Consortium has obtained putative
A smart deoxyribozyme-based fluorescent sensor for in vitro detection of androgen receptor mRNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1135–1141, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.100

- receptor mRNA was developed. It consists of several functional modules including two deoxyribozymes 10–23, an RNA-dependent split malachite green aptamer, and an oligonucleotide platform. Deoxyribozymes specifically release a 27-nucleotide RNA fragment that is readily available for the interaction with the
- aptamer module. This solves a problem of secondary structure in hybridization with the target sequence of full-length mRNA. It was shown that within 24 hours the proposed sensor specifically recognized both a synthetic 60-nucleotide RNA fragment (LOD is 1.4 nM of RNA fragment at 37 °C) and a full-sized
- mRNA molecule of the androgen receptor. The constructed sensor is easy to use, has high efficiency and selectivity for the RNA target, and can be reconstructed for the detection of various nucleic acid sequences due to its modular structure. Thus, similar biosensors may be useful for the differential
Microwave-assisted efficient and facile synthesis of tetramic acid derivatives via a one-pot post-Ugi cascade reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 663–669, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.63
- exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including antibiotic [8], antiviral [9], antifungal [10], phytotoxic [11], cytotoxic [12][13], and enzyme inhibitory activities against bacterial DNA-directed RNA polymerase [14]. The wide range of biological activity and structural variation of this class of
Recent developments in photoredox-catalyzed remote ortho and para C–H bond functionalizations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 248–280, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.26

- previously reported methods required high temperatures [118][119][120]. A library of compounds was reported by that group using this approach, and a plausible mechanism is shown in Figure 13. Arylation of purines: Purine bases and purine nucleosides, which are common structural motifs in DNA and RNA, have an
Photocontrolled DNA minor groove interactions of imidazole/pyrrole polyamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 60–70, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.8
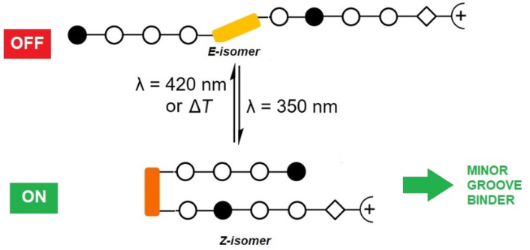
- suitable as bi-stable switches. Azobenzene and other small photoreactive molecules have been employed as ligands to control DNA or RNA assembly by light [14][15][16][17][18][19][20]. Mascareñas et al. reported the first photoisomerizable transcription factor (Tf) that recognized its target sequences by
Emission and biosynthesis of volatile terpenoids from the plasmodial slime mold Physarum polycephalum
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2872–2880, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.281
- manufacturer’s manual (https://www.qiagen.com). Total RNA was isolated using Plant RNA Purification Reagent (https://www.thermofisher.com). cDNA was prepared using 1st strand cDNA synthesis kit (https://www.gelifesciences.com). Full length cDNAs of individual PpolyTPS genes were amplified using gene specific
Design, synthesis and investigation of water-soluble hemi-indigo photoswitches for bioapplications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2822–2829, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.275

- that allowed to obtain an RNA-binding hemi-indigo derivative with photoswitchable fluorescent properties. Keywords: hemi-indigo; molecular switches; photochromism; photoswitching; visible light; water solubility; Introduction The application of organic photochromes in biological systems is fraught
- provided. Additionally, synthetic peculiarities of the introduction of an RNA-affine alkylamino substituent to the hemi-indigo scaffold are discussed. Results and Discussion Synthesis of hemi-indigo derivatives Z-1a–c The synthesis of hemi-indigo derivatives Z-1a–c with different substitution patterns of
- File 1). Introduction of an alkylamino substituent to the hemi-indigo scaffold Based on the data on photoswitching in water (vide supra), the dimethoxy-substituted hemi-indigo Z-1c was selected as a core structure for the design of RNA binders with photoswitchable properties [12]. To increase the
In search of visible-light photoresponsive peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) for reversible control of DNA hybridization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2500–2508, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.243

- targets without causing a permanent knockout. During the last years, the pioneering structural studies of reversible photoregulation of DNA/RNA duplex stability of Asanuma and Komiyama [16][17] have become functional ones, affecting DNA/RNA cleavage [18][19][20], transcription [21][22][23], and
- been employed. In vivo application demands the development of a new generation of artificial agents to target DNA/RNA-associated processes. These compounds must be able to maintain their specificity and effectivity while still being nuclease resistant, nontoxic and susceptible to light of tissue
- -penetrating wavelengths. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) [31] are synthetic nucleic acid analogues, in which nucleobases are linked to a repeating N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine polyamide backbone. The lack of phosphate groups provides them with both higher binding affinities to complementary DNA or RNA sequences and
Identification of optimal fluorescent probes for G-quadruplex nucleic acids through systematic exploration of mono- and distyryl dye libraries
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1872–1889, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.183

- cationic dyes was synthesized and investigated with respect to their optical properties, propensity to aggregation in aqueous medium, and capacity to serve as fluorescence “light-up” probes for G-quadruplex (G4) DNA and RNA structures. Among the 61 compounds, 57 dyes showed preferential enhancement of
- fluorescence intensity in the presence of one or another G4-DNA or RNA structure, while no dye displayed preferential response to double-stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA analytes employed at equivalent nucleotide concentration. Thus, preferential fluorimetric response towards G4 structures appears to be a
- ] or its 4-isomer, as optimal fluorescent light-up probes characterized by high fluorimetric response (I/I0 of up to 550-fold), excellent selectivity with respect to double-stranded DNA or single-stranded RNA controls, high quantum yield in the presence of G4 analytes (up to 0.32), large Stokes shift
Electrophilic oligodeoxynucleotide synthesis using dM-Dmoc for amino protection
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1116–1128, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.108
- MerMade 6 DNA/RNA synthesizer. The dT-Dmoc-CPG (4) was used as the solid support. Detritylation was carried out under standard conditions suggested by the synthesizer manufacturer for 1 µmol synthesis. The 0.1 M acetonitrile solutions of phosphoramidite monomers 3a–c and the commercially available 5'-DMTr
New terpenoids from the fermentation broth of the edible mushroom Cyclocybe aegerita
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1000–1007, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.98
- . The biomass and suspended substrates was separated by centrifugation. RNA extraction, cDNA synthesis and qPCR During fermentation, mycelial samples were taken at day 2, 4, 7, 9, 11 and 14 and stored in RNAlater (Qiagen, Venlo, Netherlands) until further use. Fungal mycelium was freeze-dried and ground
- with liquid nitrogen. RNA was extracted from ground mycelium using Ambion TRIzol™ Reagent (life Technologies, Carlsberg, California, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions with minor changes according to the method of Chomczynski and Sacchi [21]. RNA concentration was determined
- photometrically by a NanoPhotometer® Pearl (Implen, Munich, Germany). Reverse transcription was performed with the Invitrogen M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. 10 µL of extracted RNA and 1 µL of 10 µM oligo-(dT)30











































































































































































































































































