Search results
Search for "surface modification" in Full Text gives 187 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Label-free highly sensitive probe detection with novel hierarchical SERS substrates fabricated by nanoindentation and chemical reaction methods
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2483–2496, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.239

- ) surface, and surface cleaning was carried out further using deionized water to remove any residual AgNO3 reagent and copper nitrate production. A stream of nitrogen was then used to dry the hierarchical substrate as shown in Figure 13. Hydrogen ions play an important role in the surface modification
pH-Controlled fluorescence switching in water-dispersed polymer brushes grafted to modified boron nitride nanotubes for cellular imaging
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2428–2439, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.233

- (DU145) and are suitable for further evaluation in cellular imaging applications. Keywords: boron nitride nanotubes; cellular imaging; fluorescence; pH switching; polymer brushes; surface modification; Introduction In recent years, considerable effort has been devoted to the development of hybrid
- fluorescent probes for a number of bio-responsive applications, ranging from drug delivery to genomics [29][30][31]. Similar to other nanotubes, the pristine BNNTs were not fluorescent, and a fluorophore (e.g., organic molecule or quantum dot) is added via surface modification to make them fluorescent [29][30
- ][31][32][33][34]. In [35], the fluorescent CdSe quantum dots were attached to BNNT surfaces, and in [36] the halloysite nanotubes were modified with carbon dots and used for cellular imaging. Another approach is surface modification with grafted polymers bearing organic fluorophores. One of the most
Synthesis of highly active ETS-10-based titanosilicate for heterogeneously catalyzed transesterification of triglycerides
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 2039–2061, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.200

- OH groups on the surface of the created mesopores originating from the partial removal of TiO6 octahedra and SiO4 tetrahedra from the framework and subsequent protonation of the oxygen radicals. The quantitative information of the surface modification was obtained from the 29Si MAS NMR experiments
Gold-coated plant virus as computed tomography imaging contrast agent
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1983–1993, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.195

- 28 nm and a surface charge of ca. 13 mV [38]. Surface functionalization and UV–visible studies One of the objectives of the present work was the development of a smart cell-specific contrast agent based on the surface modification of Au-CPMV with specific antibodies to target desired cells
- functionalization of Au-CPMV. The localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) spectrum shifted by almost 4 nm (Figure 3A). This shift of the extinction maximum from 534 nm to 538 nm is a result of an increase in the local refractive index at the Au-CPMV surface as reported in the literature following surface
- modification with proteins [40] and indicates that the surface of the Au-CPMV particles is “smooth”. The shift would be greater if the surface had an uneven shape. In addition, the 4 nm red-shift of the LSPR peak suggests that the modification of the Au-CPMV surface with antibodies has been successful. This
Engineered superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for dual-modality imaging of intracranial glioblastoma via EGFRvIII targeting
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1860–1872, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.181

- studied with regard to their long blood half-life [11], easy surface modification and excellent biocompatibility [12]. In the past years, several multifunctional vehicles for glioblastoma imaging have been developed, such as gold nanoparticles [13][14], which were integrated for diagnosis and treatment
Toxicity and safety study of silver and gold nanoparticles functionalized with cysteine and glutathione
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1802–1817, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.175

- +). The comparison with data published on polymer-coated nanoparticles evidenced that surface modification with biothiols made them safer for the biological environment. In vitro evaluation on human cells demonstrated that the toxicity of AgNPs and AuNPs prepared in the presence of cysteine was similar to
- vivo assessment of NP toxicity on aquatic organisms evidenced that surface modification of metallic NPs with biothiols made them safer for the environment, while in vitro experiments on mammalian cells demonstrated that AgNPs and AuNPs functionalized with glutathione had a significant biological impact
- , the need emerges for the development of safe, surface-modified nanosystems. For the first time, safety profiling of AgNPs and AuNPs prepared by using cysteine and glutathione as stabilizing agents was performed. A careful and comprehensive evaluation of physico-chemical properties and surface
Scavenging of reactive oxygen species by phenolic compound-modified maghemite nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 1073–1088, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.108

- ), to yield γ-Fe2O3@Hep-CS-G, γ-Fe2O3@Hep-CS-H, and γ-Fe2O3@Hep-CS-P particles, respectively. Surface modification of the particles was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric
- method chosen to attach phenolic compounds on the chitosan rather than by the phenolic compounds themselves. Moreover, the chitosans with low molecular weight were highly soluble in 2 wt % acetic acid; they could also be dissolved in water, which is important for surface modification of the magnetic
- , such as pigs and cattle [28]. Unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparins are used in medicine as indirect anticoagulants for thrombosis prevention and treatment [29]. The presence of sulfate and carboxyl groups in heparin was critical for surface modification of the positively charged γ-Fe2O3
Ultrathin hydrophobic films based on the metal organic framework UiO-66-COOH(Zr)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 654–665, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.65

- . Keywords: hydrophobic coating; Langmuir–Blodgett (LB) films; metal organic framework (MOF); surface modification; UiO-66-COOH(Zr); Introduction Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) are well-known, crystalline, porous materials formed by metal ions (or metallic clusters) and organic ligands coordinated in a pre
Hydrophilicity and carbon chain length effects on the gas sensing properties of chemoresistive, self-assembled monolayer carbon nanotube sensors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 565–577, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.58

- length of these carbon nanotubes is 1.5 µm and the average diameter is 9.5 nm. The surface of the carbon nanotubes was modified with –COOH groups, with a value of mass greater than 8%. This surface modification was performed by Nanocyl S.A. via an oxygen-plasma treatment. An attempt to decorate pristine
Direct observation of the CVD growth of monolayer MoS2 using in situ optical spectroscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 557–564, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.57

- reflectance spectroscopy (DRS), which measures the normalized difference between the reflectance of the bare surface and the surface covered by thin films, possesses an enhanced sensitivity to the surface modification and ultrathin film growth [25][26]. This technique has been successfully applied to reveal
One-step nonhydrolytic sol–gel synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 phosphonate hybrid materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 356–362, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.35
- hybrids are obtained in two steps, by surface modification of a porous metal oxide support [17][18][19]. Nonhydrolytic (or nonaqueous) sol–gel (NHSG) chemistry has provided simple and powerful routes to synthesize oxides or mixed oxides with different morphologies (e.g., nanoparticles) or textures (e.g
- the 10 to 35 ppm range. Similar broad resonances have been reported for TiO2–phenylphosphonate hybrid materials prepared in a two-step sol–gel process from Ti(OiPr)4 and PhPO3H2 [15], whereas the hybrid materials obtained by surface modification of anatase supports usually show narrower resonances [36
Wet chemistry route for the decoration of carbon nanotubes with iron oxide nanoparticles for gas sensing
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 105–118, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.10

- with iron oxide nanoparticles substantially ameliorated the response towards nitrogen dioxide. Keywords: benzene detection; doping; gas sensor; metal nanoparticle decoration; multiwalled carbon nanotubes; NO2 detection; room temperature gas sensing; surface modification; Introduction Carbon nanotubes
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
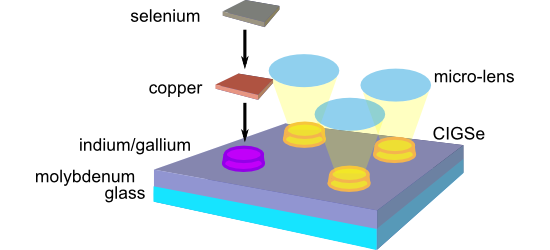
- array. The series of spots at the surface illustrates, that a stronger surface modification or even the formation of a crater can be achieved by increasing the number of laser pulses per spot as well as by increasing the laser fluence (energy density). Selected scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images
Colloidal chemistry with patchy silica nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2989–2998, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.278

- nanoparticles and the chemical composition of the spherical satellites, we demonstrate that a vast collection of CMs are accessible through assemblies that are analogous to chemical reactions (Figure 1). Results and Discussion Synthesis and surface modification of the precursors The first type of precursors
- . Butyl chloromethyl ether was synthesized according to a recipe already published [27]. Synthesis and surface modification of the spherical satellites Synthesis of the “pre-seeds” In a similar manner as described in [28], 100 mL of L-arginine aqueous solution (6 mM) were added into a 150 mL vial
- by the citrate-reduction method reported by Turkevich [29]. SiO2 coating was carried out after surface functionalization of the gold nanoparticles by using a PEG-SH (Mw = 5000) aqueous solution in a similar manner as described in [23]. The surface modification allowed for the replacement of the
Co-intercalated layered double hydroxides as thermal and photo-oxidation stabilizers for polypropylene
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2980–2988, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.277

- further washed twice with acetone with surface modification and then was used for the preparation of H1M1-Ca2Al/PP composites. To obtain the H1M1-Ca2Al powder, part of the slurry was dried in an oven at 80 °C for 24 h. Co-intercalated HnMn′-Ca2Al with different molar ratios and MP-Ca2Al were obtained
Layered calcium phenylphosphonate: a hybrid material for a new generation of nanofillers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2906–2915, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.269

- structure or by a surface modification [3][4] by grafting organophilic functional groups onto the clay surface, leading to the synthesis of hybrid organic–inorganic materials [5]. Layered metal organophosphonates are a class of materials which exhibit a hybrid character by their nature. They are generally
Controlling surface morphology and sensitivity of granular and porous silver films for surface-enhanced Raman scattering, SERS
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2813–2831, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.263

- ][60]. Recently, other methods emerged with the aim of producing SERS substrates at low cost, enabling their large-scale production. These methods include inkjet-printing and pen-on-paper approaches [61][62]. Plasma treatment has been widely used for the last decades for microelectronics and surface
- modification in industry [63][64]. A large variety of plasmas exist depending on the excitation source, the operating pressure and the device geometry [63][65]. Advantages of the use of a radio frequency (rf) plasma for chemical modification is that no hazardous chemicals and solvents are involved. Moreover
Biomimetic surface structures in steel fabricated with femtosecond laser pulses: influence of laser rescanning on morphology and wettability
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2802–2812, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.262

- influences the surface energy and thus the wetting behavior [5][6][7][8][9][10]. A particular kind of controllable surface modification induced by pulsed lasers was discovered in 1965 by Milton Birnbaum [11] – upon irradiation of a germanium wafer with multiple laser pulses, self-organized periodic surface
Cytotoxicity of doxorubicin-conjugated poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide]-modified γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles towards human tumor cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2533–2545, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.236

- relatively high values of Dh. The ζ-potential of the particles amounted to −35 mV (pH 7.3), which is sufficient for short-term colloidal stability of the particles. Coating of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles with poly[N-(2-hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide] (PHPMA) Surface modification of nanoparticles is a general
Preparation of micro/nanopatterned gelatins crosslinked with genipin for biocompatible dental implants
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1735–1754, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.165

- surfaces using genipin crosslinking, with the aim of understanding the use of patterning in surface modification of dental implants. Results: Grooves, holes, and pillars, with widths or diameters of 2 µm, 1 µm, or 500 nm were fabricated using a combination of molding and genipin crosslinking of gelatin
- . Following this, cell attachment and proliferation on the resulting gelatin surface patterns were assessed using human osteoblastic Saos-2 cells, with the aim of understanding the use of these gelatin patterned surfaces in surface modification of dental implants. Cell attachment increased as a result of
Cr(VI) remediation from aqueous environment through modified-TiO2-mediated photocatalytic reduction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1448–1470, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.137

Surface characterization of nanoparticles using near-field light scattering
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1228–1238, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.114

- nanoparticles have a shorter biological half-life and are cleared by the reticuloendothelial system [32]. For biomedical purposes, SPIOs must be biocompatible, colloidally stable, and well-dispersed in physiological buffers, which is often accomplished by surface modification of the magnetic nanoparticles with
- capable of initiating a strong electrostatic repulsion between the nanoparticles and the negatively charged waveguide. However, unlike PEG-SPIOs, uncoated SPIOs likely stuck to the waveguide owning to the absence of surface modification. Without a surface coating, which acts like a lubricant or spring
Noble metal-modified titania with visible-light activity for the decomposition of microorganisms
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 829–841, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.77

- , by morphology design [22][23][24][25][26], surface modification [27][28][29][30][31][32], doping [33][34][35][36], or the formation of heterojunctions with other semiconductors [37][38][39][40]. Modification with noble metals seems the most promising as it is well known that under UV irradiation
Surface-plasmon-enhanced ultraviolet emission of Au-decorated ZnO structures for gas sensing and photocatalytic devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 771–779, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.70

- factors, including absorbed oxygen species (O2−, O−, and O2−), charge carrier concentration, and the defects and vacancies on the ZnO surfaces. The gas response performance can be improved by a charge transfer process through surface modification [3][5][6] and doping of catalytic materials [7][8][9]. The
Heavy-metal detectors based on modified ferrite nanoparticles
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 762–770, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.69

- composition and surface modification. The aim of the study is to examine the efficiency of adsorption of heavy metals in artificial solutions on doped magnetite nanoparticles (Ca, Co, Mn, Ni) surface-modified with PA, SA, AA, 3-PPA or 16-PHDA linkers. Experimental Reagents and solutions Chemicals used in this
- surface modification. The obtained images for each kind of fabricated ferrites are presented in Figure 2. The TEM images show that regardless of doping (Ca2+, Co2+, Mn2+ or Ni2+), the studied nanoparticles exhibit a similar round shape and average size. In Table 1, diameters of every type of synthesized
- [15]. Therefore, the origin of these signals is most probable due to heavy ion adsorption. However, due to a lack of reference information, it is the only speculation on the origin of appearing new signals. Raman spectroscopy After every step (synthesis, surface modification, and heavy metal












































































































































































































































