Search results
Search for "nematic" in Full Text gives 41 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Efficient synthesis of fluorinated triphenylenes with enhanced arene–perfluoroarene interactions in columnar mesophases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 3263–3273, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.270
- ] in combination with tunable absorption and emission of visible light. Polar nematic phase [23] and chiral columnar phase materials [24] based on polar fluorobenzene rings have also recently emerged as interesting new classes of fluorous materials, revealing their enormous potential in the high-tech
4,6-Diaryl-5,5-difluoro-1,3-dioxanes as chiral dopants for liquid crystal compositions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2940–2945, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.246
- chemistry [1][2][3]. In particular, cholesteric, i.e., chiral nematic, liquid crystals (LCs) are attractive for many display applications due to their chiroptical characteristics as well as the selective reflection of light giving rise to Bragg interference colors [4]. Cholesteric LCs can be obtained either
- from neat chiral mesogens, or through the addition of a chiral dopant to an achiral nematic liquid crystal [5][6]. The ability of the dopant to induce chirality in the nematic phase is defined as the helical twisting power [HTP; β = (pc)−1; with p the helical pitch and c the molar concentration]. The
- most common type of liquid crystal displays (LCD) is based on the so-called twisted nematic (TN) mode and requires only a quite small HTP (typically around 10–15 µm−1) with a low dopant concentration (around 0.1%) [1][2][7]. However, there are other display modes, such as super-twisted nematic (STN
Switchable molecular tweezers: design and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 504–539, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.45

- conversion to the Z open form is achieved, in which the cholesteryl units are oriented in an anti-fashion. This conformational change results in a significant increase in the solvent-accessible surface area. Tweezers 5 were utilized as a dopant for the achiral liquid crystalline material nematic phase 5 (NP5
- ) to produce a chiral nematic phase, whose reflected color can change from green to purple under cross-polarized view upon protonation. This system serves as an elegant example of a macroscopic effect induced by a conformational change at the molecular level. In a different approach where the stimuli
Perspectives on push–pull chromophores derived from click-type [2 + 2] cycloaddition–retroelectrocyclization reactions of electron-rich alkynes and electron-deficient alkenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 125–154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.13

- resulted from optically active constituents. Compound 53, due to its elongated rigid structure, holds potential for use as a chiral dopant in nematic liquid crystals (LCs); however, the helical twisting powers of 53 within nematic LCs are limited. Recently, Alonso-Gómez et al. reported the synthesis and
Preparing a liquid crystalline dispersion of carbon nanotubes with high aspect ratio
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 52–58, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.7

- transition concentrations from isotropic phase to biphasic state, and from biphasic state to nematic phase are lowered, which is consistent with the predictions of the Onsager theory. An aligned DWCNT film was prepared from the DWCNT dispersion by a simple bar-coating method. Regardless of the higher aspect
- ) method [22][23]. The transition concentrations from the isotropic phase to the biphasic state, and from the biphasic state to the nematic phase were inversely proportional to the aspect ratio (L/D) of the SWCNT, following the same trend as the Onsager theory [7][9][11][15][20][23][24]. By using
- dispersions with a higher L/D were successfully prepared utilizing highly crystalline DWCNTs. Indeed, the transition concentrations from the isotropic phase to the biphasic coexisting state and from the biphasic coexisting state to the nematic phase were found to be lower than those in the previous study. In
Tuning the solid-state emission of liquid crystalline nitro-cyanostilbene by halogen bonding
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 124–131, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.13

- with 4-alkoxystilbazoles [10]. Recently, Li and co-workers reported on a series of halogen-bonded assemblies to induce chirality in nematic liquid crystalline hosts and studied the light-induced manipulation of the photonic properties of these materials [11] In 2019, our group investigated the role of
- and S15). In our initial set of assemblies, we combined F4St with NO2-Cn with varying alkoxy-chain lengths (n = 8, 9, 10 and 11). The halogen-bonded assemblies exhibited mesogenic behaviour starting with an alkoxy chain length of n = 8. POM investigations revealed nematic mesophases for all complexes
- supramolecular entities in the solid state. This effect was also confirmed by the fluorescence behaviour (see paragraph on photophysical properties) and affects mainly the transition from the nematic to crystalline phase. In addition, it was observed that only assemblies with an odd number of carbon atoms in the
Synthesis of organic liquid crystals containing selectively fluorinated cyclopropanes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 674–680, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.65
- the requirements for different LCD technologies. For the traditional twisted nematic (TN) LCD technology, devices require liquid crystals with display positive dielectric anisotropy by which the molecular dipole moment is oriented parallel to the long axis of the molecule, while for the current
The use of isoxazoline and isoxazole scaffolding in the design of novel thiourea and amide liquid-crystalline compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 175–184, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.20
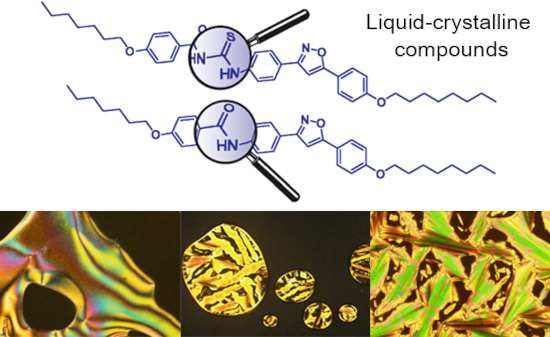
- . Thiourea and amide derivatives were predominantly SmA mesophase inductors. A nematic mesophase was observed only for thioureas and amides containing an isoxazole ring. Additionaly, the liquid crystal behavior was also dependent on the relative position of nitrogen and oxygen atoms on the 5-membered
- , mainly due to their structural and electronic features. Isoxazoline and isoxazole cores show strong dipole moments, polarizabilities, anisotropic interactions and geometrical aspects that favor the formation of stable smectic A and nematic mesophases, respectively [19][20]. This work aimed at
- behavior. A smectic A mesophase (SmA) was preponderant in this study. However, a nematic mesophase (N) appeared for thioureas 18a and 18c and amide 20. Thioureas 17b, 18b and 18c and amides 19, 20, 22 and 24 displayed an enantiotropic SmA mesophase, except thiourea 17a which showed a monotropic SmA
High performance p-type molecular electron donors for OPV applications via alkylthiophene catenation chromophore extension
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2298–2314, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.223

- devices with PTB7-Th resulting in high-performance OPV devices with up to 10.7% PCE. Keywords: molecular materials; nematic liquid crystal; organic solar cells; organic synthesis; p-type organic semiconductors; small molecule; Introduction Bulk heterojunction (BHJ) organic solar cells (OSC), a blend of
- and cooling with the formation of a high-temperature nematic liquid crystalline (NLC) phase change at 186 °C, with a change to the isotropic phase at 196 °C [14]. BQR can then be compared to BTR where, surprisingly, a single phase change is seen on heating, while three phase changes are observed on
Determination of the absolute stereostructure of a cyclic azobenzene from the crystal structure of the precursor containing a heavy element
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2211–2215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.212
- . Results and Discussion Figure 1 shows the schematic representation of experiments involved in the separation and reductive debromination of the enantiomer (E)-1B. The enantiomers of molecules (E)-1 and (E)-2 are previously reported as photocontrolled chiroptical switches for various nematic liquid
- crystalline hosts for tuning the reflection colors through the entire visible region [45][46]. The molecule (E)-1 has been also used to demonstrate the completely photocontrolled rotation of the micro glass rods on the chiral nematic liquid crystalline films induced by the rotational reorganization of the
Novel biphenyl-substituted 1,2,4-oxadiazole ferroelectric liquid crystals: synthesis and characterization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 233–241, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.26

- -oxadiazoles with different configurations have been reported [11][20][21][22] which exhibited the thermotropic liquid crystalline nematic (N), smectic and polar smectic (bent or banana) phase structures. Due to the presence of three heteroatoms in the ring structure of the oxadiazole, it possesses a high
The influence of intraannular templates on the liquid crystallinity of shape-persistent macrocycles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 910–920, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.89

- °C (33 kJ/mol) into a nematic phase (N1) followed by a transition into another nematic phase (N2) at 70 °C (4.3 kJ/mol). The X-ray data of both phases are alike (see below). Upon cooling, no crystallization can be observed, either for 1a or 1d. However, for 1d an exotherm followed by an endotherm is
- kind of a nematic phase, in agreement with the optical textures. Obviously, similar clusters as in the isotropic phase are observed in the nematic phase. No changes of the X-ray pattern indicating a phase transition could be detected on heating above or on cooling below 70 °C (see Figure S1 in
- Supporting Information File 1) in contrast to those found for the nematic discotic (ND)–nematic columnar (NC) transition in liquid crystalline polymers [56] and for the ND–nematic lateral (NL) transition in liquid crystalline charge transfer complexes [57]. Neither magnetic nor surface alignment of the
Triphenylene discotic liquid crystal trimers synthesized by Co2(CO)8-catalyzed terminal alkyne [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 2852–2861, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.321
- mesomorphism. Keywords: Co2(CO)8 catalyzed cycloaddition; columnar mesophase; discotic liquid crystal; triphenylene; oligomer; Introduction Discotic liquid crystals (DLCs) with nematic phase have been commercially utilized in the liquid crystal display industry as optical compensating films for widening the
Thermotropic and lyotropic behaviour of new liquid-crystalline materials with different hydrophilic groups: synthesis and mesomorphic properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 425–436, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.45

- . Four of these nonchiral and chiral materials exhibit nematic and chiral nematic phases, respectively. For some molecular structures, smectic phases have also been detected. A contact sample of one of the prepared compounds with diethylene glycol clearly shows the lyotropic behaviour; namely a lamellar
- systems composed of amphiphilic molecules can exhibit smectic phases with layered structure [2] or nematic (eventually cholesteric) phases. Lyotropic systems usually form a lamellar liquid-crystalline mesophase, i.e., a lyotropic analogue of the thermotropic orthogonal smectic A (SmA) phase [3], and more
- rarely nematic, columnar and cubic mesophases [4][5]. Combination of thermotropic and lyotropic properties for materials with definite molecular structure has been intensively studied so far [6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16] and is of high importance in particular for developing new types of
A new family of four-ring bent-core nematic liquid crystals with highly polar transverse and end groups
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 26–35, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.4

- characterization is consistent with data from elemental and spectroscopic analysis. The materials thermal behaviour and phase characterization have been investigated by differential scanning calorimetry and polarizing microscopy. All the compounds exhibit a wide-ranging monotropic nematic phase. Keywords: bent
- -core mesogens; cyanobiphenyl; dipole moment; liquid crystals; nematic phase; polarity; Introduction Following the discovery of chiral and polar properties of mesomorphic bent-core compounds [1][2][3][4][5][6] the area of design, synthesis and properties of banana or bent-shaped liquid crystals (LC
- -ring systems and exhibit the so-called banana phases. However, there are relatively few examples reported in the literature based on bent-core compounds exhibiting a nematic phase [6][19][20][21][22][23][24] and in particular with possible ferroelectric switching [25][26] and a biaxial nematic phase
The chemistry of bisallenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1936–1998, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.225
- determined by electron diffraction in the vapor phase [94]. The results obtained by both of these physical methods are consistent with C2h-symmetry of the molecule, i.e. the transoid conformation is the most stable one. From its 1H NMR spectrum [95], measured in a nematic solvent at room temperature, it has
Restructuring polymers via nanoconfinement and subsequent release
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1318–1332, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.151
- “nematic-like” regions, i.e., without a preferred orientation of their directors. For a discussion of Vectra, a liquid-crystalline ester/arylate copolymer, which exhibits a macroscopically anisotropic melt, much like that suggested above locally for coalesced polymers and with similar rheological behavior
Formation of smectic phases in binary liquid crystal mixtures with a huge length ratio
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 1118–1125, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.124

- revealed a destabilization of the nematic phase, which is present in the pure short compound, while the smectic state was stabilized. The short compound forms smectic A and smectic C phases, whereas the longer compound forms a broad smectic C phase and a narrow higher-ordered smectic phase. Nevertheless
- these studies, chemically similar mesogens with length ratios ranging from 1 to 1.8 were investigated. In the systems with a large difference in length, strong changes in the phase diagram were observed. The nematic phase was destabilized while the smectic state was stabilized. The temperature range of
- and a narrow higher-ordered smectic phase. Its molecular length was determined by molecular modelling as 50.6 Å. The component with short molecular length is the asymmetric compound 2-(4-butoxyphenyl)-5-octyloxypyrimidine (2PhP) [4]. It exhibits the typical liquid-crystalline phase sequence of nematic
Synthesis of 2,6-disubstituted tetrahydroazulene derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 693–698, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.77
- . In contrast to the core system presently used in most nematic LC materials, our new core based on perhydroazulenes showed [13], e.g., improved properties regarding phase-transition temperatures. Therefore, due to its potential use as a subsystem of many natural products, as well as as the core moiety
Liquid-crystalline heterodimesogens and ABA-heterotrimesogens comprising a bent 3,5-diphenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole central unit
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 472–485, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.54
- studied by optical polarizing microscopy (PM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). All dimesogens exhibit broad ranges of cybotactic nematic phases (NcybA and NcybC), in some cases accompanied by additional mesophases (CybA or SmC) at lower temperature. The combination of
- the 3,5-diphenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole unit with one cyanobiphenyl core leads to the removal of tilted smectic and cybotactic nematic phases (SmC, NcybC), which are replaced by the nontilted CybA phases and nematic phases composed of SmA-type clusters (NcybA). The orthogonal cybotactic nematic phases of
- bent-core mesogens are of special interest for achieving biaxial nematic phases of the orthorhombic type. The orthogonal (NcybA) and skewed (NcybC) cybotactic nematic phases were distinguished by XRD and optical observations. Keywords: bent-core mesogens; cybotactic nematic phases; dimesogen; liquid
Perhydroazulene-based liquid-crystalline materials with smectic phases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 403–410, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.44
- . The mesomorphic properties of the new LC compounds were investigated by differential scanning colorimetry, polarizing optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction. We report here on the LC properties of nonchiral materials, which predominantly exhibit smectic phases and display nematic phases only within
- ; nematic phases; smectic phases; Introduction Liquid crystals for display applications have to fulfill a complex, interdependent set of properties [1]. First of all, they must display a broad nematic phase, typically ranging from −30 °C to +80 °C. The absolute value for the dielectric anisotropy Δε should
- formulation of various components, including about 15–20 individual LC molecules. The nematic (N) liquid crystal phase, with its orientational order only, is the most important mesophase; it is used in almost all commercially available LC displays. On the other hand, the smectic (Sm) LC phases, with their
Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of calamitic malonates and cyanoacetates tethered to 4-cyanobiphenyls
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 371–378, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.40
- with methyl 3-chloro-3-oxopropionate or cyanoacetic acid, giving liquid-crystalline linear malonates and cyanoacetates. These compounds formed monotropic nematic phases at 62 °C down to ambient temperature upon cooling from the isotropic liquid. The mesomorphic properties were investigated by
- differential scanning calorimetry, polarizing optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction (WAXS). Keywords: cyanoacetates; 4-cyanobiphenyls; liquid crystals; malonates; nematic; Introduction Nematic liquid crystals display mesophases in which the molecules are oriented along one vector defined by the director
- axis, but with the molecular arrangement in random positional order [1]. Nematic phases typically display low viscosity [2][3][4]. Due to the long-range orientational order they reveal anisotropic properties. These features make nematic liquid crystals very attractive materials for electronics [5][6][7
Liquid-crystalline nanoparticles: Hybrid design and mesophase structures
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 349–370, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.39

- , based on the shape and chemical characteristics of the mesogen under investigation. The simplest is the nematic phase, whereby the mesogenic moieties exhibit an average alignment along a common direction (or director), whereas the smectic phases also display a degree of positional ordering (i.e., the
- , 90 and 100 °C indicated the existence of periodic particle interactions at an interval of 33.2 nm, which corresponded to the width of the NPs plus the surrounding organic sheath, and the authors concluded that the mesophase possessed a quasi-nematic 1-D order in the direction of the long axis of the
- respectively, which corresponded to the width of the NPs with a layer of ligand molecules on the surface. As was observed for TiO2@1, these results indicated that the hybrids of α-Fe2O3@3 exhibited a quasi-nematic one dimensional order in the direction of the long axis of the spindlelike NPs, which was lost
The interplay of configuration and conformation in helical perylenequinones: Insights from chirality induction in liquid crystals and calculations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 155–163, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.16
- introduced as dopants in nematic solvents. We evaluated the role of the different conformations of the chiral hydroxyalkyl side chains in determining the helical twisting power: They were found to affect the strength of the chirality transfer, although the handedness of the induced cholesteric phase is
- essentially determined by the axial chirality (helicity) of the core of the perylenequinones. Keywords: chirality; conformational analysis; DFT calculations; helical twisting power; nematic liquid crystals; Introduction The phenomenon of chiral induction in nematic mesophases has been known for a long time
- [1]. By addition of a chiral nonracemic compound, a nematic liquid crystal is transformed into a chiral nematic (or cholesteric) phase. Here the director, i.e., the local alignment direction, rotates in space in helical way, along a perpendicular axis [2][3]. The handedness of this helix reflects the
Laterally substituted symmetric and nonsymmetric salicylideneimine-based bent-core mesogens
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 129–154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.15

- exhibiting liquid crystal (LC) phases have to be rodlike, so-called calamitic LCs. As is well known, such compounds exhibit nematic and smectic phases, which are commonly referred to as “calamitic phases”. However, the inherent fallacy of this notion was pointed out in the middle of the seventies when
- columnar (Col) phases were discovered in disklike (discotic) mesogens; such mesogens also exhibit nematic behaviour like that of calamitics. In fact, a survey of the literature shows clearly that molecules with a bent (banana) shape prepared earlier than discotics by Vorlaender (in 1929) possess the
- spacer these dimers exhibit a bent shape and form nematic, columnar nematic, smectic and columnar phases. Columnar phases were not found for the dimers having even-numbered spacers, because these molecules are more linear [23][24][25][26][27]. Interestingly, for a nonsymmetric chiral dimer the reentrant

































































































































































































































































































































































![[Graphic 3]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-151-i3.png?max-width=637&scale=1.063638) conformations of PET [76].
conformations of PET [76].




































































![[Graphic 5]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i5.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the
phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the ![[Graphic 6]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i6.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) pla...
pla...





![[Graphic 8]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i8.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...
symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...













































