Search results
Search for "N-terminal" in Full Text gives 107 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Fluorinated phenylalanines: synthesis and pharmaceutical applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1022–1050, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.91

- 148 in variable yields with partial racemization. Phthalimido and trifluoroacetyl N-terminal protecting groups (R1 = Phth or TFA) and unprotected C-terminal derivatives (R2 = H) provided the most efficient outcomes (80 and 67% yield, respectively). An N-acetyl group was also suitable as protecting
- group for the reaction providing the desired product with 57% yield. Also, methyl and ethyl esters as C-terminal protecting groups in combination with phthalimino as the N-terminal protecting group, were both successfully explored. However, when the trifluoroacetyl amide was used as a substrate the
Photocontrolled DNA minor groove interactions of imidazole/pyrrole polyamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 60–70, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.8
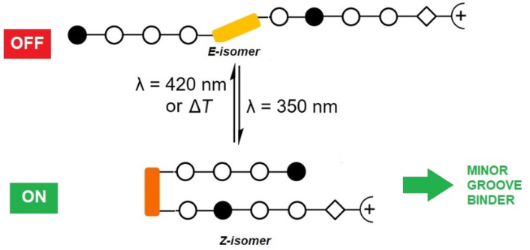
- required because this allowed for an alignment between hydrogen-bonding groups in long polyamides and in the minor groove of DNA [41]. The Fmoc-protected heterocyclic amino acids 2 were obtained from N-methylpyrrole and N-methylimidazole, respectively (Scheme 2A). The N-terminal N-methylpyrrole and N
- -methylimidazole units were introduced by employing diamino derivatives 3 (Scheme 2A) [40]. Moreover, it turned out that coupling the subsequent building block to an N-terminal Im building block was problematic because the amino group of the imidazole derivative 2b is a weak nucleophile, and therefore the Fmoc–Py
Chemical synthesis of tripeptide thioesters for the biotechnological incorporation into the myxobacterial secondary metabolite argyrin via mutasynthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2922–2929, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.286
- , acid-mediated deprotection of the Boc group and final coupling to Boc-ᴅ-alanine. Fully protected tripeptides were transformed by base hydrolysis into the free carboxylic acids, followed by activation of the unprotected C-terminus as a SNAc thioester. Subsequent cleavage of the N-terminal Boc protecting
Synthesis of novel sulfide-based cyclic peptidomimetic analogues to solonamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2544–2551, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.247
- have been synthesized via solid-phase peptide synthesis and SN2’ reaction on a Morita–Baylis–Hillman (MBH) residue introduced at the N-terminal of a tetrapeptide. This last step takes advantage of the electrophilic feature of the MBH residue and represents a new cyclization strategy occurring. The
- repetitive Fmoc-amino acid couplings yielding the linear resin-bound tetrapeptides 5 (Scheme 3) [37][38]. The MBH acids 3 were coupled to the free amine at the N-terminal of 5 to afford the resin-bound linear peptidomimetics 6, which subsequently had the hydroxy group of the MBH residue acylated with acetic
Sugar-derived oxazolone pseudotetrapeptide as γ-turn inducer and anion-selective transporter
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2419–2427, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.234

- (TSFAA)-derived homologated linear pentapeptide which showed a well defined intramolecular hydrogen-bonding-stabilized helical array [9][10][11]. Our group has reported a trans-vicinal ᴅ-glucofuranoroic-3,4-diacid with a TAA framework and incorporated it into the N-terminal tetrapeptide sequence (H-Phe
Current understanding and biotechnological application of the bacterial diterpene synthase CotB2
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2355–2368, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.228

- of CotB2. [36][37][38]. Overall structure of CotB2wt in the open, inactive conformation The structure of CotB2wt (PDB-ID 4OMG [38] and PDB-ID 5GUC [36]) is complete, except for the 15 N-terminal and 12 C-terminal residues. CotB2 consists of ten core α-helices (A to J) that are connected by short loop
Synthesis and conformational preferences of short analogues of antifreeze glycopeptides (AFGP)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1581–1591, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.162

- azidochlorination [25]. Glycosylated building blocks, containing ʟ- or ᴅ-Thr were synthesized (Figure 1) over three steps [26]. The glycosylated building blocks were used in SPPS of model tri- and pentapeptides. The N-terminal end of the products was acetylated and the carboxy terminus was in a form of N
- ] 1.11 (d, J = 6.3 Hz, 3H, Hγ Thr2), 1.19 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 3H, Hβ Ala3), 1.24 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 1H, Hβ Ala1), 1.85 (s, 3H, Ac N-terminal), 1.89 (s, 3H, CH3Ac Gal), 2.55 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 3H, Me C-terminal), 3.46 (dd, J = 10.8, 5,7 Hz, 1H, CH2C6(1) Gal), 3.52 (dd, J = 10.7, 6,6 Hz, 1H, CH2C6(2) Gal), 3.61 (dd
- Thr2), 8.00 (d, J = 7.1 Hz, 1H, HN Ala3), 8.18 (d, J = 7.4 Hz, 1H, HN Ala1); 13C NMR (150 MHz, DMSO-d6) δ [ppm] 18.2 (Cβ Ala1), 18.6 (Cβ Ala3), 19.0 (Cγ Thr2), 22.8 (CAc N-terminal), 23.3 (CAc Gal), 25.9 (Me C-terminal), 48.4 (Cα Ala1), 48.5 (Cα Ala3), 49.9 (C2 Gal), 56.4 (Cα Thr2), 61.1 (C6 Gal), 68.8
Phylogenomic analyses and distribution of terpene synthases among Streptomyces
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1181–1193, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.115

- of type I terpene synthases, including the aspartate-rich motif, the NSE triad, the pyrophosphate sensor and the RY pair [19][20][21]. Both domains have a catalytic activity, the N-terminal domain for the conversion of FPP into the intermediate sesquiterpene alcohol (1(10)E,5E)-germacradien-11-ol (12
- -dependent methyl transferases were found forming a cluster together with the 2-MIB synthase in several Streptomyces species [26][27]. Besides the C-terminal domain typical of class I terpene synthases, these enzymes contain an additional proline-rich N-terminal domain that appears to be disordered in the
Stereo- and regioselective hydroboration of 1-exo-methylene pyranoses: discovery of aryltriazolylmethyl C-galactopyranosides as selective galectin-1 inhibitors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1046–1060, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.102
- using a highly diastereoselective hydroboration of C1-exo-methylene pyranosides giving inhibitors with fourfold or better selectivity for galectin-1 over galectin-3, -4C (C-terminal CRD), -4N (N-terminal CRD), -7, -8C, -8N, -9C, and -9N and dissociation constants down to 170 µM. Keywords: C-galactoside
- substituents other than fluorine could be prepared, as they were dehalogenated during the final debenzylation. Galectin binding Galectin-1, -3, -4C (C-terminal CRD), -4N (N-terminal CRD), -7, -8C, -8N, -9C, and -9N affinities for (aryltriazolyl)methyl galactopyranosyls 1a–n were determined in a competitive
- sequence of larger glycans [1][2][3]. Some galectins contain one CRD and occur as monomers or dimers, including galectins -1, -2, -7, -10 and -13 in humans. Others contain 2 different CRDs within the same peptide sequence and include galectins -4, -8, -9 and -12. Galectin-3 contains one CRD and a long N
Non-native autoinducer analogs capable of modulating the SdiA quorum sensing receptor in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2651–2664, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.243

- proteins consist of two domains: a larger N-terminal ligand-binding domain (LBD) connected to a smaller C-terminal DNA-binding domain (DBD). In 2006, the structure of the EHEC SdiA LBD was solved by NMR in the presence and absence of AHL and demonstrated increased folding and structure upon ligand binding
Targeting the Pseudomonas quinolone signal quorum sensing system for the discovery of novel anti-infective pathoblockers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2627–2645, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.241

- could prevent activation of the carbonyl group as a CoA-ester. In 2017, Witzgall et al. were able to co-crystallize 6-FABA-AMP within the N-terminal domain of PqsA (Figure 4) [46]. Key interactions involve a water-mediated hydrogen bond between the amino function of the compound and Q162, as in
Comparative cell biological study of in vitro antitumor and antimetastatic activity on melanoma cells of GnRH-III-containing conjugates modified with short-chain fatty acids
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2495–2509, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.226

- 4Lys could negatively affect the fitting of the conjugates to the N-terminal part of the GnRH-R. On the basis of these findings [4Lys(Bu)]-GnRH-III(Dau=Aoa), was chosen for the further studies (e.g., in vivo experiments [22]) to evaluate the suitability of this conjugate for targeted chemotherapy
Recyclable hypervalent-iodine-mediated solid-phase peptide synthesis and cyclic peptide synthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1112–1119, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.97
- coupling reagent, which was developed by Ye’s group in order to reduce racemization and side reactions [50]. The precursor 2 was obtained via successive deprotection of the C-terminal and the N-terminal protecting group of 14. The overall yield of this route is 28%. With the precursor 2 in hand, we then
An overview of recent advances in duplex DNA recognition by small molecules
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1051–1086, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.93

- hydrophobic interactions (Figure 2). Figure 2a shows that the arginine side chain of the MATα2 N-terminal arm facilitates interaction between portions of the heterodimer MATα1–MATα2 with the minor groove of the DNA substrate by forming alternate H-bond interactions [25]. The main characteristic feature of
- lipophilicity [53]. These structural analogs comprise of branched N-alkyl- and N-cycloalkylpyrroles to test the conformational flexibility towards DNA binding. Hydrophobic N-terminal amides and substituted thiazole replacing pyrrole were installed in order to impart more lipophilicity. All these compounds were
- shown to bind A·T-rich regions preferentially. The compounds containing branched N-alkylpyrrole, hydrophobic N-terminal amide, and especially C-isopropylthiazole (thiazotropsin A as shown in the Figure 4) showed significant antimicrobial activity against MRSA and Candida albicans strains. Thiazotropsin
On the design principles of peptide–drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery to the malignant tumor site
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 930–954, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.80

- on its building block 2-pyrrolino-DOX and tried to construct new PDCs using other peptides. Therefore, they synthesized a new analog, designated AN-238, consisting of the octapeptide RC-121 linked through the α-amino group of its N-terminal D-Phe moiety and a glutaric acid spacer to the 14-OH group
Development of novel cyclic NGR peptide–daunomycin conjugates with dual targeting property
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 911–918, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.78
- homing devices may provide dual targeted delivery of anticancer drugs. According to literature data, one of the most stable and tumor-selective cyclic NGR-peptides is c[KNGRE]-NH2, in which the α-amino group of the N-terminal Lys is coupled to the γ-carboxyl group of the glutamic acid residue (head-to
Volatiles from three genome sequenced fungi from the genus Aspergillus
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 900–910, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.77

- ). A phylogenetic analysis of 878 fungal terpene synthase homologs (Figure S1 in Supporting Information File 1) demonstrates that this enzyme is closely related to the bifunctional ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase/ent-kaurene synthase from Fusarium fujikuroi [33]. The N-terminal domain shows the DXDD
Carbohydrate inhibitors of cholera toxin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 484–498, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.34

- a non-binding mutant of the target CTB protein [66], oxidised the N-terminal threonine residue of each subunit to an aldehyde and then chemically attached GM1os ligands by oxime ligation (Figure 15). This neoglycoprotein was able to display the five copies of the carbohydrate ligand with appropriate
Stimuli-responsive oligonucleotides in prodrug-based approaches for gene silencing
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 436–469, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.32
- nucleic acids (PNAs), a lipophilic triphenylphosphonium (TPP) cation was attached to the N-terminal extremity of a PNA through a biodegradable carbamate linker containing a disulfide bridge (Scheme 4B) [20]. It was shown that such PNA conjugates entered cells rapidly and efficiently. Furthermore, a 16-mer
Position-dependent impact of hexafluoroleucine and trifluoroisoleucine on protease digestion
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2869–2882, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.279
- this study when positioned N-terminal to the cleavage site. These results provide valuable information for the application of fluorinated amino acids in the design of proteolytically stable peptide-based pharmaceuticals. Keywords: fluorinated amino acids; hexafluoroleucine; peptide drugs; protease
- enzymes in humans. It exhibits specificity for hydrophobic, especially aromatic residues like Phe, Trp, and Tyr at the P1 and P1’ positions [50][51][52][53][54]. It has an extended active site that can bind at least seven residues [66][67], and peptide bond cleavage occurs N-terminal to the residue at
- ). Only P2’-HfLeuFA is not hydrolyzed at the designed cleavage site, instead cleavage occurs exclusively N-terminal to the HfLeu residue, thus demonstrating that HfLeu occupies the P1’ position. In the case of P2’-TfIle we found two further peptide bonds that are cleaved by pepsin, namely N-terminal
Synthetic mRNA capping
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2819–2832, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.274

- ]. Peyrane et al. demonstrated that using the N-terminal fragment bearing the primase activity resulted in comparable preparation yield for the RNA while expression and solubility of the fragment were improved [53]. mRNA cap analogues Preparation of cap analogues The co-transcriptional capping described
- pioneering work of the Rosenberg group [35]. To date, the capping enzymes from the Vaccinia virus are commercially available and most widely used for post-transcriptional in vitro capping. They consist of two viral proteins D1 and D12. The triphosphatase and guanylyltransferase activity are located in the N
- -terminal half and the methyltransferase in the C-terminal half of the large D1 protein, whereas the small D12 protein has no catalytic activity but activates D1 [36][37][38]. Originally, the RNA capping with the Vaccinia capping apparatus was reported to be inefficient [35][37][39][40]. To date, the enzyme
Development of a fluorogenic small substrate for dipeptidyl peptidase-4
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2690–2697, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.267
- fluorescence push–pull system would be destroyed. To confirm this, we modified 1 to provide a peptidic substrate for an enzyme. The serine protease DPP-4 was used as the test enzyme because its substrate specificity is clear: it hydrolyses the C-terminal of proline or alanine second to the N-terminal of the
Recent progress in the racemic and enantioselective synthesis of monofluoroalkene-based dipeptide isosteres
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2637–2658, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.262

- methyl ester using trimethylsilyldiazomethane, followed by its reduction to the corresponding alcohol and a Mitsunobu reaction, permitted the incorporation of the N-terminal moiety. Then, removal of the Ns group of 28 and deprotection of the primary alcohol was performed to obtain 29 which underwent a
- ). The resulting ester 33 was then reduced to the corresponding aldehyde, followed by the formation of the terminal imine and its subsequent reduction to access the N-terminal moiety of 34. The alcohol and the amine deprotections were then achieved, followed by reprotection of the amine with a
- synthesized by a HWE olefination of the chiral cyclopentanone 101 (Scheme 20) [54]. The resulting ester was converted into the aldehyde and β-fluoroenimine 104 was obtained using Ellman’s conditions. At this stage, the lateral chain of the N-terminal residue was added by an alkylation reaction using a
What contributes to an effective mannose recognition domain?
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2584–2595, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.255

- enables uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) to adhere to urothelial host cells [33][34], which represents the first and most critical step in UTI, triggering a cascade of pathogenic processes ultimately leading to infection. The ligand on urothelial cells binding to the N-terminal lectin domain of FimH
Mechanochemical synthesis of small organic molecules
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1907–1931, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.186
- NaHCO3 (base); 2) esterification of N-protected amino acid using different dialkyl dicarbonate or alkyl chloroformate in the presence of DMAP as catalyst and followed by acidic workup. For N-terminal protection, different precursors like Fmoc-Cl, benzoyl chloride and Boc2O were used successfully to get




















































































































































































































































































































































































































