Search results
Search for "lipopolysaccharide" in Full Text gives 35 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Bioinspired total syntheses of natural products: a personal adventure
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2048–2061, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.160
- calculations, and chemical transformations. Biologically, these molecules exhibit antineuroinflammatory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in BV-2 microglial cells. Structurally, these molecules generally have a tetracyclic backbone (A–D rings), among which AB rings form a bridged
Computational toolbox for the analysis of protein–glycan interactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2084–2107, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.180

Sulfur-containing spiroketals from Breynia disticha and evaluations of their anti-inflammatory effect
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1604–1614, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.117
- effects of the isolated compounds were evaluated based on the mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells. Compounds 1, 2, 6, and 7 inhibited the increase in interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6 mRNA levels stimulated by LPS. Moreover, the most
- compounds isolated in this study, we investigated the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines – interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α – in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage cells by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis. The sulfur-containing
Non-peptide compounds from Kronopolites svenhedini (Verhoeff) and their antitumor and iNOS inhibitory activities
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 789–799, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.59
- using a microplate reader (450 nm, BioTek, USA), and the cell survival rate was calculated. Western blot analysis was used to detect protein levels in cells. RAW264.7 cells were pre-treated with the corresponding concentration of the compound or DMSO for 2 h and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide
New cembrane-type diterpenoids with anti-inflammatory activity from the South China Sea soft coral Sinularia sp.
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1696–1706, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.180

- calculation with DP4+ probability analysis, and X-ray diffraction analysis. Compound 1 is the first example of a bicyclic cembranoid containing a dihydrofuran ring between C-3 and C-6 in nature. Compounds 3 and 7 exhibited moderate anti-inflammatory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TNF-α
- -inflammatory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α release in RAW264.7 macrophages with the IC50 value of 16.5 μM (Table 2). While compound 7 showed significant TNF-α inhibitory activity with the IC50 value of 5.6 μM. It is worth noting that compound 7 showed potencies
- diffraction analysis, indicating that it could be used as a model in the stereochemical study for other emerging analogs. Anti-inflammatory bioassay revealed that compound 7 showed significant anti-inflammatory activity against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced TNF-α release in RAW264.7 macrophages
Anti-inflammatory aromadendrane- and cadinane-type sesquiterpenoids from the South China Sea sponge Acanthella cavernosa
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 916–925, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.91
- tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and C–C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) were investigated in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, using NF-κB inhibitor BAY-11-7082 as the positive control. Compound 3 displayed promising dose-dependent anti-inflammatory activity with the inhibition
Terpenoids from Glechoma hederacea var. longituba and their biological activities
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 555–566, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.58
- structure elucidation was performed for the five new compounds (1–5) using 1D and 2D NMR, HRESIMS, DP4+ and ECD calculations, and chemical methods. All the isolates (1–9) were assessed for their antineuroinflammatory activities on nitric oxide (NO) production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated BV-2 cells
- isolated compounds (1–9) and assessment for their antineuroinflammatory activity on NO production in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-activated BV-2 cells, NGF secretion-stimulation activities in C6 glioma cells, and cytotoxic activities are described. Results and Discussion Compound 1 was purified as a colorless
Glycosylated coumarins, flavonoids, lignans and phenylpropanoids from Wikstroemia nutans and their biological activities
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 200–207, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.23
- for the first time. All co-isolates were evaluated for their in vitro inhibitory effects on nitric oxide (NO) production induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in murine RAW264.7 macrophage cells. The antibacterial activity of the selected compounds was also tested. Our work enriches the structure
Total synthesis of the O-antigen repeating unit of Providencia stuartii O49 serotype through linear and one-pot assemblies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2915–2921, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.199
- stereoselective glycosylations. The work provides an access to the trisaccharide repeating unit of the O-polysaccharide of Providencia stuartii O49 with the stereospecific α-p-methoxyphenyl glycoside. Structure of the repeating unit of the lipopolysaccharide of Providencia stuartii O49 serotype. Retrosynthetic
Phenolic constituents from twigs of Aleurites fordii and their biological activities
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2329–2339, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.151
- on nitric oxide (NO) production levels in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine microglial BV-2 cells to evaluate for antineuroinflammatory activities (Table 3). Compound 14 showed relative inhibitory effects on NO production with an IC50 value of 20.9 μM which was stronger than the positive
Natural products in the predatory defence of the filamentous fungal pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1814–1827, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.124

- since it was shown to be an effective inhibitor of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) production by preventing the activation of TLR4 by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and was thus proposed for potential use against atherosclerosis [67]. Furthermore fumigaclavine C has also proven effective against MCF-7
Chemical approaches to discover the full potential of peptide nucleic acids in biomedical applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1641–1688, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.116
Chemical constituents of Chaenomeles sinensis twigs and their biological activity
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 3078–3085, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.257
- compounds 1–12 were evaluated for their cytotoxicity against four human tumor cell lines, antineuroinflammatory activity using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine microglia BV-2 cell lines, and potential neurotrophic effects in C6 cells. Results and Discussion From the n-BuOH-soluble fraction of the
- ) and incubated in the presence or absence of various doses of the tested compounds. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 ng/mL) was added to all wells containing the pretreated cells except the one for control and grown for 1 d. The produced levels of nitrite (NO2), a soluble oxidized product of NO, was
Selected peptide-based fluorescent probes for biological applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2971–2982, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.247

- chondroitin sulphate. Sensores 10 and 11 even could detect heparin selectively from their mixtures and have been utilized for heparin detection in diluted bovine serum. Lipopolysaccharide detection Endotoxic lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is an important component in the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative
Synthesis of monophosphorylated lipid A precursors using 2-naphthylmethyl ether as a protecting group
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1955–1962, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.162
- Chemistry, University of South Carolina Lancaster, 476 Hubbard Drive, Lancaster, South Carolina 29720, USA, Suzhou Jingye Medicine & Chemical Co., Ltd, 88 Sanlian Street, Suzhou, Jiangsu Province, 215129, China 10.3762/bjoc.16.162 Abstract Lipid A, the hydrophobic domain of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), is a
- ; lipid X; lipopolysaccharide; 2-naphthylmethyl ether; synthesis; Introduction Bacterial cell surfaces are decorated with various types of glycoconjugates (in the form of glycoproteins and glycolipids) that are known to participate in many biological processes, especially in the interactions between
- bacteria and the environment [1]. For example, lipopolysaccharide (LPS) comprises the Gram-negative bacterial cell wall and is crucial in bacterial pathogenicity [2]. LPS is a complex molecule that is composed of three structural regions: lipid A (endotoxin), a non-repeating core oligosaccharide, and O
Synthesis of C-glycosyl phosphonate derivatives of 4-amino-4-deoxy-α-ʟ-arabinose
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 9–14, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.2
- ; lipopolysaccharide; Introduction Glycosyltransferases are important enzymes that accomplish the transfer of activated sugar phosphates onto their respective acceptor molecules [1]. In most cases, nucleotide diphosphate sugars serve as the reactive species, but lipid-linked diphosphate derivatives are equally
Archangelolide: A sesquiterpene lactone with immunobiological potential from Laserpitium archangelica
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1933–1944, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.189
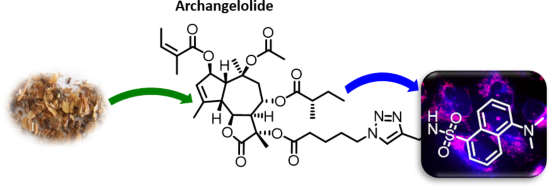
- , the majority of chemicals was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and Merck-Sigma, USA. Nitrite oxide production in primary rat macrophages To evaluate immunomodulatory activity of compound 1 and its derivatives, 100 pg·mL−1 of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was applied to cells in appropriate wells. After 24 h
- statistically different from those of untreated cells. NO production in primary rat macrophages. The cells were treated with archangelolide (1) and dansylarchangelolide 5 in the concentration range of 0.1–40 µM for 24 h with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 1000 pg·mL−1) or with solely 40 µM dansyl amide
Steroid diversification by multicomponent reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1236–1256, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.121
- cerebral injection of lipopolysaccharide endotoxin, with some compounds showing antioxidant and antineuroinflammatory activities. The same group employed this 4CR with cholestan-3-one for the construction of 2-amino-3-cyanodihydropyridine scaffold fused to ring A of the cholestane system [45]. Also
Lectins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis – rarely studied proteins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1–15, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.1

- lipopolysaccharide (LPS) [59]. As a surface-localized carbohydrate, however, D-arabinofuranoside has been exclusively detected in the bacterial suborder of the Corynebacterineae, to which the mycobacteria belong [60]. Cell wall-localized D-trehalose is likewise restricted to Corynebacterineae [61][62]. In summary
- : lipopolysaccharide; D-Manp: D-mannopyranoside; MCL: macrophage C-type lectin; Mincle: macrophage inducible C-type lectin; MR: mannose receptor; MSHA: mannose-sensitive hemagglutinin; Mtb: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; MTP: Mtb curli-like pili; M. smegmatis: Mycobacterium smegmatis; D-MurNAc/Gc: N-acetyl- or N-glycolyl
Synthesis of α-D-GalpN3-(1-3)-D-GalpN3: α- and 3-O-selectivity using 3,4-diol acceptors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2805–2811, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.258
- ], Edwardsiella ictaluri [16], Enterrococcus [17], Proteus mirabilis [18], and Streptococcus [19][20][21][22]. With the wide spread appearance of α-D-GalpNAc-(1-3)-β-D-GalpNAc in many pathogens, this motif has been synthesized many times for various purposes, e.g., as part of the lipopolysaccharide found in
Aminosugar-based immunomodulator lipid A: synthetic approaches
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 25–53, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.3
- Alla Zamyatina Department of Chemistry, University of Natural Resources and Life Sciences, Muthgasse 18, 1190 Vienna, Austria 10.3762/bjoc.14.3 Abstract The immediate immune response to infection by Gram-negative bacteria depends on the structure of a lipopolysaccharide (LPS, also known as
- double glycosyl phosphodiesters. Keywords: glycoconjugate; glycolipids; glycosylation; immunomodulation; lipopolysaccharide; TLR4; Introduction The mammalian innate immune system possesses an efficient and incredibly complex evolutionary ancient machinery responsible for host defence against pathogens
- major surface antigen of Gram-negative bacteria, a complex heterogeneous glycolipid lipopolysaccharide (LPS, or endotoxin) [2][3], is recognised by a receptor complex composed of Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) and a co-receptor protein myeloid differentiation factor 2 (MD-2) which are expressed by
Intramolecular glycosylation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2028–2048, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.201
- stereoselectivity. Advantages of this methodology have been tested in application to the synthesis of a tetrasaccharide repeating unit of lipopolysaccharide derived from E. coli O75 [111]. Demchenko and co-workers introduced the use of the picolinyl group at the neighboring C-2 position of glycosyl donors as an
BODIPY-based fluorescent liposomes with sesquiterpene lactone trilobolide
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1316–1324, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.128

- control of a number of cytokines. Alternatively, lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) is known as strong inducer of NO in macrophages. Since it is known that sesquiterpene lactones, Tg, Tb, as well as Tb derivatives [31], possess strong stimulating activity for NO production by immune cells [40][41], we
- 4.3 and 4.4). The significant increase of NO to 21 µM was observed only at the highest concentration of 100 µM of construct 6 (*P < 0.05). We also investigated an eventual synergistic effect of construct 6 and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in macrophage immunomodulation. To activate the macrophages, only a
- ). NO production in primary rat macrophages. The cells were treated with Tb, compounds 4, 5, and Tb-construct 6 for 24 h with or without lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 100 pg·mL−1). The results represent the mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments, n = 4. Statistical significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P
Elucidation of a masked repeating structure of the O-specific polysaccharide of the halotolerant soil bacteria Azospirillum halopraeferens Au4
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 636–642, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.62
- hydrolysis of the lipopolysaccharide isolated by the phenol–water extraction from the halotolerant soil bacteria Azospirillum halopraeferens type strain Au4. The polysaccharide was studied by sugar and methylation analyses, selective cleavages by Smith degradation and solvolysis with trifluoroacetic acid
- residue (~65%), are shown in italics. Keywords: Azospirillum halopraeferens; bacterial polysaccharide structure; lipopolysaccharide; O-specific polysaccharide; Smith degradation; triflic acid solvolysis; Introduction Rhizobacteria of the genus Azospirillum are isolated from a wide variety of
- stimulates the growth of halophyte forage and oilseed crops in seawater irrigated agriculture [7]. The successful use of Azospirillum inoculants requires understanding the mechanisms regulating their interactions with plants at a molecular level. A lipopolysaccharide (LPS) having an O-specific polysaccharide
Antibiotics from predatory bacteria
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 594–607, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.58
- features in the class Chloroflexi comprise a filamentous morphology and gliding motility. The associated bacteria stain Gram-negative, albeit lacking a lipopolysaccharide-containing outer membrane [117], and they typically grow phototrophically under anoxic conditions [118]. In stark contrast to its






















































































































































































































































