Search results
Search for "mesophases" in Full Text gives 33 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Efficient synthesis of fluorinated triphenylenes with enhanced arene–perfluoroarene interactions in columnar mesophases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 3263–3273, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.270
- -67034 Strasbourg, France 10.3762/bjoc.20.270 Abstract The high potential of non-covalent arene–fluoroarene intermolecular interactions in the design of liquid crystals lies in their ability to strongly promote self-assembly, improve the order and stability of the supramolecular mesophases, and enable
- chains and derived from the classical triphenylene core self-assembling in columnar mesophases based on this paradigm. These mesogenic compounds were simply obtained in good yields by the nucleophilic substitution (SNFAr) of various types of commercially available fluoroarenes with the electrophilic
- chain distribution had a net impact on both stability and nature of the mesophases. The versatility of this synthetic approach allows us to synthesize another set of mesomorphic compounds, based on a triphenylene core, 1,2,4-trifluoro-6,7,10,11-tetra(alkyloxy)-3-phenyltriphenylenes (PHn, and extended to
Understanding X-ray-induced isomerisation in photoswitchable surfactant assemblies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2005–2015, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.176

- increasing the concentration of PS to form higher-concentration LLC mesophases, the X-ray-induced reversal was less pronounced, likely due to the lower water content available for radiolysis. The X-ray irradiation time required to obtain a good signal-to-noise ratio differs depending on the specific
Charge carrier transport in perylene-based and pyrene-based columnar liquid crystals
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1755–1765, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.128

- understanding charge transport in columnar mesophases [9][10][11][12][13][14]. High charge carrier mobilities of 1.1 cm2 V−1 s−1 for p-type and up to 6.0 cm2 V−1 s−1 for n-type liquid-crystalline semiconductors have already been reported [15]. Among the various discotic liquid crystal materials, perylene
- observed mesophases. Compound 1 presents a wide range columnar hexagonal phase (Colhex) preserved at room temperature by cooling from the isotropic. Compound 2 shows an additional columnar rectangular phase (Colrect) below the Colhex and crystallizes under 166 °C. The HOMO and LUMO energy levels are also
- 1758 cm−1 (C=O). X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements of 1 and 2 are shown in Figure 2. The Miller indices indicate the Colhex and Colrect character of the mesophases [31]. Despite crystallization of 2, the Colrect order is partially preserved at room temperature. The Colhex lattice parameter (a
Tuning the solid-state emission of liquid crystalline nitro-cyanostilbene by halogen bonding
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 124–131, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.13

- exhibit mesomorphic behaviour. In contrast, mesophases were observed for components employing NO2-Cn with longer alkyl chains. NO2-C10 showed focal-conic textures at 94 °C during cooling (see Figure 2a) and NO2-C11 showed an enantiotropic smectic behaviour (see Supporting Information File 1, Figures S11
- and S15). In our initial set of assemblies, we combined F4St with NO2-Cn with varying alkoxy-chain lengths (n = 8, 9, 10 and 11). The halogen-bonded assemblies exhibited mesogenic behaviour starting with an alkoxy chain length of n = 8. POM investigations revealed nematic mesophases for all complexes
- induces the formation of nematic mesophases with broad temperature ranges, the temperature range of the mesophase of the azobenzene-based assemblies is significant narrower. Theoretical calculations and the modular use of halogen bond donors with changing fluorination degree reveal that at least three
The use of isoxazoline and isoxazole scaffolding in the design of novel thiourea and amide liquid-crystalline compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 175–184, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.20
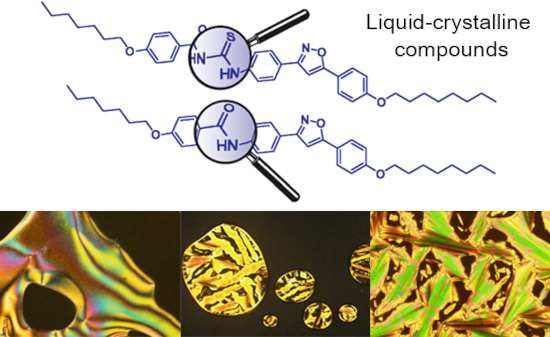
- , mainly due to their structural and electronic features. Isoxazoline and isoxazole cores show strong dipole moments, polarizabilities, anisotropic interactions and geometrical aspects that favor the formation of stable smectic A and nematic mesophases, respectively [19][20]. This work aimed at
- behavior [25][26] by segregation effects. Interestingly, isoxazoline 17a presented a monotropic SmA mesophase, while its regioisomer 17c did not show a mesophase. Corresponding isoxazoles formed stable mesophases as expected (N for 18a; SmA and N for 18c) [20]. Figure 1 shows the selected textures of the
- analogous compounds such as thiourea 18a,b, containing an isoxazole ring, displayed enantiotropic SmA and N mesophases, confirming that the isoxazole ring favors the formation of a stable mesophase. It is interesting to notice that the nematic mesophase appeared only in compounds with the isoxazole ring
Synthesis, liquid crystalline behaviour and structure–property relationships of 1,3-bis(5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 149–158, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.17

- core, the obtained compounds do not exhibit mesomorphism, only crystal–isotropic transitions were observed [26]. The absence of mesophases is mainly due to the strong bend (134°) between the aromatic rings, which disturbs the linear shape of the whole molecule [27]. Herein we describe the synthesis and
- compounds 2 and 4 is constituted by a rigid core (three aromatic rings) to which are attached the terminal chains. Based on this structure, some liquid crystalline mesophases were expected. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarized optical microscopy (POM) and X-ray diffraction pattern analysis
- , compared to two-chain and shorter-chain homologues. Taking into account these observations, the inability of 2d to exhibit mesophases becomes axiomatic, since this compound is devoid of any terminal alkyl chain. X-ray patterns analysis In order to correlate the obtained results from POM and DSC, we have
Aggregation behaviour of amphiphilic cyclodextrins: the nucleation stage by atomistic molecular dynamics simulations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2459–2473, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.267

- concentration and on the solvent) and by their shape, which may preferentially determine stable mesophases, ranging from micelles to membranes, or even liquid crystals. It is well-known that the shape and the interactions among native or modified cyclodextrins can drive specific packing in the solid state, but
The influence of intraannular templates on the liquid crystallinity of shape-persistent macrocycles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 910–920, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.89

- immediately to an isotropic melt, but thermotropic mesophases are observed when the macrocycles have an appropriately substituted rim [29][30][31][32][33][34][35]. If the macrocycles pack on top of each other, hexagonal columnar or rectangular columnar phases can be observed in which the (empty) interior is
- able to accommodate small guest molecules [36][37][38][39]. In some cases, however, macrocycles with a filled interior seem to exhibit more stable mesophases compared to the compounds alike but with an empty interior [40]. Moreover, it has also been observed that even macrocycles with a flexible
- interior only, lacking the flexible rim, can form stable mesophases (macrocycles with an inverse structure) [41][42][43]. Recently, we presented a series of gel forming macrocycles that have an identical periphery but bear different intraannular substituents [11]. We were able to show that these
Unusual polymorphism in new bent-shaped liquid crystals based on biphenyl as a central molecular core
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 794–807, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.75
- formation of mesophases, and the introduction of a chiral lactate terminal chain destabilizes mesophases for the first type of mutual orientation of ester groups, attached to the central core. On the contrary, for the opposite orientation of esters, the terminal chain has no effect on the mesomorphic
- crystalline (LC) compounds have attracted broad interest in the past years due to their ability to form polar mesophases [1]. From the extensive studies, molecular structure–mesomorphic property correlation have been generalized and summarized in several reviews [2][3][4][5][6][7]. The structure of bent
- cyano end-capped bent-shaped materials it was documented [29][30][31] that reversing the position of hydroxylic and carboxylic groups exerts a profound effect on the mesophase properties. The bent-shaped molecules can create polar mesophases in spite of lack of molecular chirality. The most frequently
Triphenylene discotic liquid crystal trimers synthesized by Co2(CO)8-catalyzed terminal alkyne [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 2852–2861, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.321
- view angles [1][2]. More interestingly, DLCs can self-organize into columnar mesophases with a high degree of order, and show fast unidirectional charge migration properties, and have been studied as soft organic semiconductors [3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12]. Solution-processed and ink-jet printing
- (Colro) and hexagonal columnar mesophases (Colho). Furthermore, the structure-mesomorphic property relationship is discussed. The synthetic route is shown in Scheme 1 and Scheme 2. Results and Discussion Synthesis and characterization We synthesized the key intermediate 1, 2-hydroxy-3,6,7,10,11-pentakis
- alkyne [2 + 2 + 2] cycloaddition reaction in moderate yields. Three of the four 1,2,4-trisubstituted benzene-cored discotic trimers have shown stable Colho and Colro mesophases and wide mesophase ranges including room temperature. The connecting linker group to the triphenylene and the spacer length to
Self-assembly of 2,3-dihydroxycholestane steroids into supramolecular organogels as a soft template for the in-situ generation of silicate nanomaterials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1826–1836, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.213

- organogelators [22]. The steroidal LMOGs usually have substituents attached to the 3β-OH of the cholestane A ring and synthetic variations at the steroidal skeleton are scarce. Cholesterol-based LMOGs build mesophases in which steroid–steroid stacking is controlled by van der Waals forces. These interactions
Synthesis of guanidinium–sulfonimide ion pairs: towards novel ionic liquid crystals
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1093–1101, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.121
- sulfonimide anion directly attached to the mesogenic unit. Keywords: anion exchange; ionic liquid crystals; ion pairs; mesophases; sulfonimides; Introduction While ionic liquids, i.e., molten salts composed of either organic cation or anion (or both) with melting points far below 100 °C, are extensively
- ). These patterns are typical for smectic mesophases and further confirm the assignment of a SmA phase based on POM observations. The exact layer spacing at each temperature was determined by fitting the first-order peak with a Gaussian distribution (Figure 3 and Supporting Information File 1, Table S1
Thermotropic and lyotropic behaviour of new liquid-crystalline materials with different hydrophilic groups: synthesis and mesomorphic properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 425–436, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.45

- rarely nematic, columnar and cubic mesophases [4][5]. Combination of thermotropic and lyotropic properties for materials with definite molecular structure has been intensively studied so far [6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16] and is of high importance in particular for developing new types of
- functional LC materials [15][17][18]. Series of alkyl glucosides and related materials usually possess thermotropic mesophases [16] as well as lyotropic columnar phases in water solution [3]. The thermotropic SmA phase and hexatic/cubic/lamellar lyotropic phases have been detected for a series of 4
- , many open questions still remain. The objective of this work is to contribute to a better understanding of the chemical-structure–physical-property relationship for materials forming both, thermotropic and lyotropic mesophases. This understanding is of high potential interest for challenging issues
A new family of four-ring bent-core nematic liquid crystals with highly polar transverse and end groups
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 26–35, doi:10.3762/bjoc.9.4

- ) has attracted considerable attention from different research groups in the past two decades. Bent-core compounds that exhibit mesomorphic properties were first reported by Vorlander [7][8] and later by Matsunaga et al. [9][10][11]. Later the mesophases were confirmed to be banana-type phases [12][13
Liquid-crystalline heterodimesogens and ABA-heterotrimesogens comprising a bent 3,5-diphenyl-1,2,4-oxadiazole central unit
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 472–485, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.54
- studied by optical polarizing microscopy (PM), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). All dimesogens exhibit broad ranges of cybotactic nematic phases (NcybA and NcybC), in some cases accompanied by additional mesophases (CybA or SmC) at lower temperature. The combination of
- -1,3,4-thiadiazole unit is incorporated (Scheme 3). All compounds form nematic phases over wide temperature ranges, in some cases accompanied by additional nontilted (CybA) or tilted (SmC) mesophases at lower temperatures. Results and Discussion Synthesis and characterization The dimesogens and
- differential scanning calorimetry (DSC, DSC-7, Perkin-Elmer). The assignment of the mesophases is based on the combined results of optical textures and X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies. XRD investigations on aligned samples were performed by using a 2D wire detector (HI-Star, Siemens AG). Alignment was achieved
Perhydroazulene-based liquid-crystalline materials with smectic phases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 403–410, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.44
- introduce terminal chains, they can provide flexibility to stabilize the molecular alignment within the mesophase. Such terminal chains can either be nonpolar straight alkyl chains or carry a polar substituent. Such molecules may form both nematic and smectic mesophases depending upon the type of
Synthesis and mesomorphic properties of calamitic malonates and cyanoacetates tethered to 4-cyanobiphenyls
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 371–378, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.40
- differential scanning calorimetry, polarizing optical microscopy and X-ray diffraction (WAXS). Keywords: cyanoacetates; 4-cyanobiphenyls; liquid crystals; malonates; nematic; Introduction Nematic liquid crystals display mesophases in which the molecules are oriented along one vector defined by the director
- investigate the phase behaviour of metal β-diketonate complexes such as 1 [15] (Scheme 1). Although they were not able to detect any mesophases, their study motivated others to examine the mesomorphic properties of β-diketonates in more detail [16]. Among the first examples of a nematic β-diketonate is the Cu
- tautomers of ferrocenophanes have been previously studied by Galyametdinov [39]. In the first cooling runs the appearance of nematic mesophases was observed for both series 11a,b and 13a,b. All compounds displayed small transition enthalpies in a range between −0.3 and −0.7 kJ/mol (Table 1) for the
Liquid-crystalline nanoparticles: Hybrid design and mesophase structures
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 349–370, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.39

- mesogens with essentially calamitic structures are arranged into layers). Columnar phases arise from the stacking of disclike mesogenic moieties into columns, which are in turn often arranged in a parallel manner into 2-D ordered lattices. Other mesophases include those possessing 3-D symmetry (cubic or
- particles to develop anisotropic shapes, which is crucial for their arrangement into liquid-crystalline phases (except cubic structures). Despite their apparently ideal shape characteristics, publications reporting on the thermotropic mesophases of suitably functionalised anisotropic NPs are relatively
- acicular particles. The mesophase behaviour was lost for hybrids prepared with 1 and NPs with lower aspect ratios and a deliberately prepared polydisperse sample, and furthermore, none of the hybrids prepared with the cyanobiphenyl based amine 2 exhibited any mesophases. In an extension of this work
The interplay of configuration and conformation in helical perylenequinones: Insights from chirality induction in liquid crystals and calculations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 155–163, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.16
- essentially determined by the axial chirality (helicity) of the core of the perylenequinones. Keywords: chirality; conformational analysis; DFT calculations; helical twisting power; nematic liquid crystals; Introduction The phenomenon of chiral induction in nematic mesophases has been known for a long time
Laterally substituted symmetric and nonsymmetric salicylideneimine-based bent-core mesogens
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 129–154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.15

- , Jalahalli, Bangalore 560 013, India 10.3762/bjoc.8.15 Abstract Bent-core mesogens have gained considerable importance due to their ability to form new mesophases with unusual properties. Relationships between the chemical structure of bent-core molecules and the type and physical properties of the formed
- mesophases are relatively unknown in detail and differ strongly from those known for calamitic liquid crystals. In this paper symmetric and nonsymmetric five-ring salicylideneaniline-based bent-core mesogens are presented, and the effect of lateral substituents attached at the outer phenyl rings (F, Cl, Br
- ) or the central phenyl ring (CH3) on the liquid-crystalline behaviour and on the physical properties is studied. Corresponding benzylideneaniline-based compounds were additionally prepared in order to study the influence of the intramolecular hydrogen bond. The occurring mesophases were investigated
Improved syntheses of high hole mobility phthalocyanines: A case of steric assistance in the cyclo-oligomerisation of phthalonitriles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2012, 8, 120–128, doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.14
- low-angle X-ray diffraction. The DSC data is summarised in Table 2, the phase behaviour of the isoalkyl series is compared graphically with that for the n-alkyl series in Figure 1 and typical polarizing micrographs are shown in Figure 2. Compounds 7b and 7c exhibit Colh columnar mesophases. For
A surprising new route to 4-nitro-3-phenylisoxazole
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2010, 6, No. 68, doi:10.3762/bjoc.6.68
- and smetic mesophases associated with their rod-like core structure [9]. The pioneering work on furoxans as nitric oxide donors by Gasco et al. has stimulated a large number of further studies. One of these reports deals with a synthetic route and structural characterization of two isomeric
Ring-alkyl connecting group effect on mesogenic properties of p-carborane derivatives and their hydrocarbon analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5, No. 83, doi:10.3762/bjoc.5.83
- the SmF phase in the latter. A DSC trace for 16D[6] is shown in Figure 3, and representative textures of its mesophases are presented in Figure 4. The tilted phases in both terphenyl compounds were identified by the appearance and subsequent characteristic changes of the Schlieren textures in the
Low temperature enantiotropic nematic phases from V-shaped, shape-persistent molecules
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5, No. 73, doi:10.3762/bjoc.5.73
- connected via alkyloxy spacers, was efficiently prepared by a two-step procedure. Phase engineering results in an optimum of the mesophase range and low melting temperature when the nematogens are desymmetrised with a butoxy and a heptyloxy spacer. The mesophases are enantiotropic and over the whole
- engineering; thiadiazoles; V-shaped mesogens; Introduction Most molecules forming nematic liquid crystals, the nematogens, are based on rod-shaped (calamitic), anisometric cores with peripheral flexible chains along the molecular long axis [1]. Nematic phases are the simplest liquid crystalline mesophases
- supercooled without crystallisation. Some materials can be stored for more than 1 h at 25 °C without visible formation of crystal grains. Microscopy studies were performed to examine the nature of the mesophases. POM revealed for all samples Schlieren textures with two and four brushed disclinations (Figure 5
Influence of spacer chain lengths and polar terminal groups on the mesomorphic properties of tethered 5-phenylpyrimidines
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2009, 5, No. 63, doi:10.3762/bjoc.5.63

- nucleophilic substitution. The mesomorphic behaviour of these compounds was investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), polarizing optical microscopy (POM) and X-ray diffraction (WAXS and SAXS) and revealed smectic A mesophases for bromides, chlorides and azides 3, 4 and 6. For these compounds a
- crystallization peak at 24 °C. The SmA to crystalline transition tends to strong supercooling in the order of 10–30 K (Table 1, Figure 1). POM observation of 3a–e revealed fan-shaped textures typical of SmA phases. An illustrative example is depicted in Figure 2. The assignment of the SmA mesophases was further
- derivative 6c is shown in Figure 5. POM revealed fan-shaped and focal conic texture, see for example Figure 6. Figure 7 and Figure 8 reveal that due to substantial supercooling for all spacer chain lengths and terminal groups the mesophases are smaller during the heating cycle as compared to the cooling





















































































































































































![[Graphic 5]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i5.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the
phase of Au@C12/13 recorded with the beam (a) parallel to the ![[Graphic 6]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i6.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) pla...
pla...





![[Graphic 8]](/bjoc/content/inline/1860-5397-8-39-i8.png?max-width=637&scale=1.18182) symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...
symmetry composed of truncated octahedrons. Top right:...


























































































