Search results
Search for "microenvironment" in Full Text gives 31 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Configuration–packing synergy enabling integrated crystalline-state RTP and amorphous-state TADF
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2026, 22, 224–236, doi:10.3762/bjoc.22.16
- reasonably inferred that, in the amorphous state, intermolecular π–π stacking interactions are significantly suppressed. This suppression of π–π interactions, along with a more disordered molecular conformation and microenvironment, makes it difficult to establish effective rigid constraints necessary for
Chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of helically chiral, planarly chiral and inherently chiral molecules
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1864–1889, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.145

- effects of the CPAs, which establish a chiral microenvironment within the chiral scaffold that governs the stereoselectivity of asymmetric reactions. Chiral molecules, characterized as three-dimensional structures that are nonsuperimposable with their mirror image, have significant applications in
Research progress on calixarene/pillararene-based controlled drug release systems
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1757–1785, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.139

- encapsulate DOX. This structure integrates multiple non-covalent interactions, such as hydrophobic interactions and π–π stacking, endowing the micelles with both structural stability and pH responsiveness. When targeted to the tumor microenvironment (acidic pH), the core of the micelles dissociates to achieve
- 2023, Zhang and colleagues [109] constructed a tumor microenvironment (TME)-activated supramolecular nanoplatform (Figure 8) which was consisted of a pillar[5]arene-based amphiphilic polymer (POPD), a phototherapeutic agent (Cy7-CN), an antimalarial drug with respiratory function (atovaquone, ATO), and
- Gram-negative bacteria. 2.3 Enzyme-responsive controlled release Elevated enzyme levels often mark the microenvironment of many pathological tissues, as well as intracellular and cellular compartments. These enzymes can serve as effective triggers for drug release in stimulus-responsive systems. Owing
Recent advances in controllable/divergent synthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 890–914, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.73

- activation induces selective migration of the less sterically hindered secondary carbon center with concomitant dinitrogen elimination, yielding 3-aza-BCHepe as the final product. Solvent control The solvent microenvironment emerged as a critical determinant in governing stereochemical outcomes, exerting
Advances in the use of metal-free tetrapyrrolic macrocycles as catalysts
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 3085–3112, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.257

- -defined binding pockets, offer a preorganized arrangement of functional groups as a suitable microenvironment for organocatalysis. In 2008, Kohnke, Soriente and co-workers first reported [37] the H-bonding organocatalytic activity of calix[4]pyrrole derivatives 3 and 4 and acyclic dipyrromethane 5 for the
The Groebke–Blackburn–Bienaymé reaction in its maturity: innovation and improvements since its 21st birthday (2019–2023)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1839–1879, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.162

Comparison of glycosyl donors: a supramer approach
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 181–192, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.18
- the presentation [39] (i.e., microenvironment) of glycosyl donor molecules, which are incorporated in supramers, hence their chemical properties [35], thus making possible a shift of a fragile and not well-understood borderline between different reaction pathways at the SN1–SN2 interface [22][24][25
pH-Responsive fluorescent supramolecular nanoparticles based on tetraphenylethylene-labelled chitosan and a six-fold carboxylated tribenzotriquinacene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 635–645, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.45

- stimuli, pH response is of particular interest in the construction of supramolecular systems for intelligent drug delivery because of the presence of pH gradients in the microenvironment of organs, tissues, and cell organelles [5]. In the past years, pH-responsive and other stimuli-responsive
Insight into oral amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles for colorectal cancer: comprehensive mathematical model of drug release kinetic studies and antitumoral efficacy in 3D spheroid colon tumors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 139–157, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.14

- primarily responsible for the anticancer action [8][14][16][17][18]. To avoid CPT inactivation at alkaline medium, the concept that the lactone form can be kept stable by being encapsulated in an acidic microenvironment is also fascinating. Custom synthesized polycationic cyclodextrin amphiphiles have shown
Shift of the reaction equilibrium at high pressure in the continuous synthesis of neuraminic acid
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 567–579, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.59

- methacrylate and aldolase: amino methacrylate). The microenvironment and material surrounding the enzyme have a significant influence on the enzyme activity [30]. For reusability studies, the three most appropriate carriers were selected and analyzed with respect to the activity of the immobilized enzymes
Site-selective reactions mediated by molecular containers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 309–324, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.35
- ; microenvironment; molecular containers; noncovalent protective group; site-selectivity; Introduction To run reactions with discriminate control over product selectivity represents one of the huge challenges in organic synthetic chemistry [1], among which, site-selectivity is always crucial to a reaction when
- more reactive alkynes and allylic alcohols. Both the microenvironment of the supramolecular catalyst and the steric profile of the substrate were responsible for the site-selectivity of hydrogenation. This beautiful work of a supramolecular-mediated catalytic site-selective reaction exhibited the
- containers, which have drawn much attention in the past years and shown broad prospects in the future. The supramolecular cavity and its constrained microenvironment resemble the active site of natural enzymes, where the guest substrate is encapsulated and positioned with a specific fixed orientation and
Constrained thermoresponsive polymers – new insights into fundamentals and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2123–2163, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.138

Biochemistry of fluoroprolines: the prospect of making fluorine a bioelement
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 439–460, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.40

- crystallization. Finally, the study revealed a few polar interactions of the fluoropyrrolidine ring within the protein microenvironment. In a study on thioredoxin, four out of five proline residues were mutated to alanine, and the only remaining proline residue was the one adopting a cis-amide-bond conformation
- ) reoccurs in the protein structures, given that a statistically significant number of residues is analyzed. Nonetheless, in some individual cases, the native preference of a fluoroproline residue can be overridden due to the residue microenvironment and the overall packing of the protein structure. 7 The
Selected peptide-based fluorescent probes for biological applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2971–2982, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.247

- >> ADP > UDP. Nucleobases undergo differential interactions with the tryptophan residues and naphthimide which varies the hydrophobic microenvironment around the fluorophore and results in dissimilar fluorescence enhancement. The addition of monophosphorylated species such as HPO42−, c-AMP, AMP, CMP, GMP
- emission increases due to the increased hydrophobic microenvironment around the pyrenes and the restriction of their intramolecular rotation under bound conditions. The structurally similar two proteins trypsin and chymotrypsin as well as bovine serum albumin does not exhibit any significant changes in
Vicinal difluorination as a C=C surrogate: an analog of piperine with enhanced solubility, photostability, and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2663–2670, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.216

- microenvironment of a protein binding site could also change the relative energies of the various F–C–C–F and F–C–C=O rotamers, offering the possibility that analog 2 might be an effective conformational mimic of 1 in some environments but not in others. Herein, we describe the optimisation of a synthetic route to
Synergy between supported ionic liquid-like phases and immobilized palladium N-heterocyclic carbene–phosphine complexes for the Negishi reaction under flow conditions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1924–1935, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.159
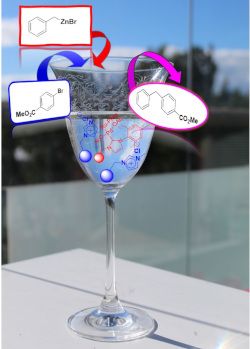
- -like phases (SILLPs) [33][34][35][36][37][38]. In these systems, the microenvironment provided by the ionic liquid-like units can have a remarkable influence on the overall process, particularly on the catalytic activity and recyclability of the supported species. Indeed, the appropriate design of the
The interaction between cucurbit[8]uril and baicalein and the effect on baicalein properties
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 71–77, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.9
- benzene ring. In spectrum (d), the peaks at 704, 778 and 898 cm−1 for the guest disappeared due to the inclusion of Q[8] and the molecular microenvironment of BALE being changed. From DTA (Figure 6), we can also see that BALE and Q[8] interacted with each other. Q[8] (Figure 6b) has a broad endothermic
Synthesis of a water-soluble 2,2′-biphen[4]arene and its efficient complexation and sensitive fluorescence enhancement towards palmatine and berberine
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2236–2241, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.198

- , compounds P and B alone only displayed fairly feeble fluorescence emission. Upon addition of 2,2’-CBP4, the fluorescence intensity was remarkably improved more than 600 times (Figure 2 and Supporting Information File 1, Figure S10). This was due to the effect of lowering polar microenvironment when P or B
- was included by 2,2’-CBP4; the guest emits stronger fluorescence in a more hydrophobic microenvironment [48]. Combined with NMR results, we can unambiguously conclude the alkaloid molecules must insert into the hydrophobic cavity of 2,2’-CBP4 to form inclusion complexes. Interestingly, the emission
Natural and redesigned wasp venom peptides with selective antitumoral activity
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 1693–1703, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.144

- cancer cells versus normal cells is likely due to the acidic microenvironment that accompanies cancer cells, and the increased net negative charge of cancer cells versus normal cells, which display a net neutral charge [12][20]. The mechanism of peptide-mediated cell death was further analyzed using flow
On the design principles of peptide–drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery to the malignant tumor site
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 930–954, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.80

- tumor microenvironment In order to selectively deliver cytotoxic drugs to malignant tumor sites, scientists can take advantage and map first the differential microenvironment between cancer and normal cells. The first one to report a fundamental difference between malignant and normal cells was Otto
- ]. Overwhelming production of stimulus agents and enzymes [21]. For instance, many types of cancer show enhanced levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) which are reactive molecules and play a crucial role in cell proliferation [22]. The slightly acidic pH of the tumor microenvironment [23] (Warburg effect
- vehicles and formulates like nanoparticles [24] and calixarenes or cyclodextrins [25][26], where the cytotoxic drug is loaded and can be released at the malignant tumor site; b) installation of labile chemical groups to the tumor microenvironment (i.e., low pH) able to mask the cytotoxic drug and form a
Regulation of integrin and growth factor signaling in biomaterials for osteodifferentiation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 773–783, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.87

- Intelligent Systems, Stuttgart, Germany Department of Internal Medicine V, Oncology, Hematology, and Rheumatology, Heidelberg University Hospital, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany 10.3762/bjoc.11.87 Abstract Stem cells respond to the microenvironment (niche) they are located in. Under natural conditions, the
- , chondrocytes, adipocytes, and reticular cells (Figure 1) [3]. Osteogenic differentiation is especially valuable in regenerative medicine approaches [4]. It has been proven that stem cell fate can be regulated from the specific microenvironment known as stem cell niche. The extracellular matrix (ECM), which
- -bound cells and their cytoskeleton. Second, the signals resulting from these interactions enable cells to sense the chemical and mechanical properties of the microenvironment (niche) and to respond by activating signaling systems for regulating the cell fate [19]. Conversely, the contraction of the
Multivalent polyglycerol supported imidazolidin-4-one organocatalysts for enantioselective Friedel–Crafts alkylations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 730–738, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.83

- supported catalyst has proven beneficial with regard to rate acceleration and increased selectivity due to formation of an aqueous microenvironment favored by the swelling properties of polymeric materials [43]. Particularly, in the case of dendritic proline derivatives [44][45][46] and N-alkylimidazole
Synthesis of a hexasaccharide partial sequence of hyaluronan for click chemistry and more
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 604–607, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.67
- the cells, nowadays it is well known that the ECM composes the ideal microenvironment for cells in order to interact with each other and also for supporting signaling between ECM macromolecules and intracellular components [2]. Besides water, the ECM consists of electrolytes, amino acids
Natural phenolic metabolites with anti-angiogenic properties – a review from the chemical point of view
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 249–264, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.28

- secretion of pro-angiogenic factors either by the tumor cells themselves or by cells of the tumor microenvironment. After the tumor reaches a diameter of 1–2 mm, the tumor cells located far away from blood vessels undergo apoptosis or necrosis resulting from the lack of oxygen and nutrients. At that point
TEMPO-derived spin labels linked to the nucleobases adenine and cytosine for probing local structural perturbations in DNA by EPR spectroscopy
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 219–227, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.24
- three labels, in particular TA, can report minor changes in their microenvironment, such as protonation, when placed in structured regions of nucleic acids. Base pairing of TC with G (A), TA with T (B), UC with G (C) and UA with T (D). EPR spectra of 14-mer DNA duplexes 5′-d(GACCTCGTAATCGTG)•5′-d
























































































































































































































































































































































































