Search results
Search for "nucleobases" in Full Text gives 83 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Synthesis of diaryl phosphates using phytic acid as a phosphorus source
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2026, 22, 213–223, doi:10.3762/bjoc.22.15
- phosphorus source [15]. There are three types of phosphate esters – monoesters, diesters, and triesters – which differ in their physical properties, reactivities, and practical applications (Figure 1). Phosphate monoesters and diesters are commonly found in biomolecules such as nucleobases and adenosine
Isoorotamide-based peptide nucleic acid nucleobases with extended linkers aimed at distal base recognition of adenosine in double helical RNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2513–2523, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.193

- bonding; modified nucleobases; peptide nucleic acids; PNA–RNA triplexes; RNA recognition; Introduction RNA is a key contributor in countless biological processes. Though coding RNA has a well-known role in the central dogma of biology, most RNA is non-coding (ncRNA) and plays a multitude of roles
- , and it is easily prepared using well established peptide synthesis protocols, allowing for accessible incorporation of synthetic nucleobases [17][18]. With these advantages in mind, Rozners’ lab first demonstrated in 2010 that PNA not only binds favorably and quickly to RNA, but that it binds more
- than 10 times stronger to RNA than to DNA [19]. Since the seminal report, much work has focused on exploring synthetic nucleobases in efforts to develop tools for sequence selective recognition of any RNA [13]. Figure 1 shows several of the most common monocyclic nucleobases used for each of the four
Synthesis of benzo[f]quinazoline-1,3(2H,4H)-diones
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 2708–2719, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.228
- was studied by UV–vis and fluorescence spectroscopy. Keywords: cross-coupling; cyclization; heterocycles; palladium; Introduction Nucleobases contain the coded information and give DNA and RNA their typical structure. As a nucleobase, uracil is involved in numerous vital processes and is therefore a
Synthesis of 1,4-azaphosphinine nucleosides and evaluation as inhibitors of human cytidine deaminase and APOBEC3A
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1088–1098, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.96
- ]. Scheme 1 shows the synthesis of the target nucleobases. N-Boc-vinylamine (3) was synthesised from commercially available N-vinylformamide (1) as a stable source of vinylamine by treatment of 1 with Boc2O in THF in the presence of a catalytic amount of DMAP, followed by cleavage of the formyl moiety under
- -protected phosphoramidite of nucleoside Va and the incorporation into DNA was more straightforward, but no inhibition of A3A was observed for these ODNs. These results suggest that negatively charged nucleobases cannot be accommodated in the active site of hCDA and A3A, and other options need to be
- considered for the development of new nucleobases mimicking transitions states and an intermediate of cytosine deamination to improve potency of DNA-based A3 inhibitors. A) Deamination of cytosine, dC and C as individual nucleosides or as part of a polynucleotide chain. B) Previously described CDA inhibitors
Synthesis and properties of 6-alkynyl-5-aryluracils
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 898–911, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.80
- -coupling; fluorescence; heterocycles; regioselectivity; Introduction Organic life is a complex interplay of many different building blocks. One of these building blocks is uracil. Discovered for the first time in 1901 by Alberto Ascoli, it is now known to be one of the four nucleobases of RNA [1]. It
Long oligodeoxynucleotides: chemical synthesis, isolation via catching-by-polymerization, verification via sequencing, and gene expression demonstration
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1957–1965, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.146

- methacrylamide group. Detritylation was not carried out in the last synthetic cycle, which would otherwise remove the polymerizable tag. A portion of the CPG was subsequently subjected to deprotection and cleavage. To prevent the potential Michael addition side reaction of acrylonitrile to nucleobases, the 2
- -cyanoethyl groups were removed by flushing the CPG with a solution of DBU in ACN. Under these conditions, the ODN remains on CPG and the nucleobases remain protected, both of which decrease the probability of the Michael addition side reaction. After washing off acrylonitrile, the CPG was subjected to
A new route for the synthesis of 1-deazaguanine and 1-deazahypoxanthine
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1617–1624, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.172
- chemistry. They can also be considered as deaza-modified purine nucleobases, and as such have attracted a lot of interest recently in the context of RNA atomic mutagenesis. In particular, for 1-deazaguanine (c1G base), a significant increase in demand is apparent. Synthetic access is challenging and the few
- nucleosides thereof [10][11][12], mostly associated with the inhibition of adenosine deaminase (ADA) [11] and as adenosine receptor antagonists [10]. Another important field of applications for deaza-modified nucleobases is their use in atom-specific mutagenesis experiments. For example, site specific 1-, 3
- -, and 7-deazapurine mutations of RNA have been fundamental to shed light on their structure, catalysis, and function [13][14][15]. However, difficulties in these fields arise from the lack of efficient synthetic protocols for various deaza-nucleosides and nucleobases. This is particularly true for the
Ferrocenoyl-adenines: substituent effects on regioselective acylation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1270–1277, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.133

- ], or structural motifs in xeno nucleic acids [18]. In continuation of our work on ferrocenoyl-substituted pyrimidine nucleobases [19], we report herewith a combined theoretical and experimental work on purine series. The novelty of these compounds is the carbonyl linker which connects the
Synthesis and bioactivity of pyrrole-conjugated phosphopeptides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 159–166, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.17
- shown nucleobases, as the heteroaromatic groups, are able to act as the N-capping group for EISA of phosphopeptides [67]. In this study, we chose to examine a different type of heteroaromatic group, pyrroles, because pyrrole is adaptable for solid-phase synthesis [68] so that it is feasible to conjugate
Chemical and chemoenzymatic routes to bridged homoarabinofuranosylpyrimidines: Bicyclic AZT analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 95–101, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.10
- chemotherapeutic agents used for the treatment of cancer were nucleoside analogues and nucleobases [10]. Azidothymidine (1, AZT) was the first approved drug for the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [11][12]. Subsequently, a large number of sugar modified nucleosides, such as ddC (zalcitabine) [13
Synthetic strategies toward 1,3-oxathiolane nucleoside analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2680–2715, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.182
- accompanied by coupling nucleobases via N-glycosylation. However, over the last three decades, efforts were made for the synthesis of 1,3-oxathiolane nucleosides by selective N-glycosylation of carbohydrate precursors at C-1, and this approach has emerged as a strong alternative that allows simple
- -oxathiolane ring with different nucleobases in a way that only one isomer is produced in a stereoselective manner via N-glycosylation. An emphasis has been placed on the C–N-glycosidic bond constructed during the formation of the nucleoside analogue. The third focus is on the separation of enantiomers of 1,3
- purine nucleobases via N-glycosylation. The anti-HIV activity of the nucleosides 83 was quantified by EC50 values of 94.7 µM and 11.6 µM when X = H or CH3 and Y = OH, respectively [33]. The α-anomers were also isolated by chromatographic separation methods. To study the structure–activity relationships
Cationic oligonucleotide derivatives and conjugates: A favorable approach for enhanced DNA and RNA targeting oligonucleotides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1828–1848, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.125
- discussed. Amino acids and cationic modifications that replace the core structure of the nucleobase, sugar, or the internucleotide linkage have been excluded. Cationic amine-functionalized group substitutions at nucleobases One strategy that has attracted a lot of interest is the attachment of cationic
- )-1-piperazine-ethanesulfonic acid) buffer (dimethylformamide/H2O 1:9) at 45 °C [118]. Initially, a 12-mer sequence containing the nucleobases guanine, thymine, and cytosine was tested by incorporating the earlier reported aminoethyl–PS linkage [118] (modification 82). However, cleavage products
Chemical approaches to discover the full potential of peptide nucleic acids in biomedical applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1641–1688, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.116
- a neutral and achiral pseudopeptide backbone (Figure 1) [1]. PNA retains the natural DNA nucleobases that are connected to the amide-linked backbone through additional amide linkages. PNA was originally designed as a DNA mimic to improve the properties of triplex-forming oligonucleotides [1][2]. Two
- , many research groups have worked on chemical modifications to the backbone and nucleobases of PNA, as well as conjugating PNA to other biomolecules (e.g., cell-penetrating peptides) [4]. The present review summarizes the most significant efforts and achievements in optimizing various aspects of PNA
- nucleobases of PNA was critical for effective nucleic acid binding as extension of either by additional methylene groups strongly decreased the binding affinity of PNA to either single- or double-stranded nucleic acids [46][47][48]. Furthermore, replacing amide linkages connecting the PNA’s backbone and the
Double-headed nucleosides: Synthesis and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1392–1439, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.98
- literature search regarding double-headed nucleosides disclosed that these modified nucleosides were constituted with any two naturally occurring nucleobases, i.e., adenine, guanine, thymine, uracil, and cytosine [9][10] or one naturally occurring nucleobase and one heterocyclic/carbocyclic moiety either
- attached directly to the sugar or via a linker. Further modifications were introduced by the substitution of some of the naturally occurring nucleobases by halogens or alkyl groups. On the other hand, a variety of heterocyclic/carbocyclic moieties were considered as the head of these modified nucleosides
- , the additional nucleobase/substituent or unsubstituted phenyl moiety/polyaromatic moiety/carbocyclic moiety/heterocyclic moiety is attached to the first nucleobase with/without a linker. Whereas, all the acyclic double-headed nucleosides had natural nucleobases or heterocyclic moieties attached at the
Beyond ribose and phosphate: Selected nucleic acid modifications for structure–function investigations and therapeutic applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 908–931, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.76

- suggested the addition of a polarizable group in the longer 2'-O-alkyl chains that could hydrogen bond with nucleobases in the minor groove of the duplex would be well tolerated [114]. This supported the hypothesis that the 2'-O-[2-(methoxy)ethyl] (MOE) modification (Figure 5B) wouldn’t lead to significant
Synthesis and properties of oligonucleotides modified with an N-methylguanidine-bridged nucleic acid (GuNA[Me]) bearing adenine, guanine, or 5-methylcytosine nucleobases
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 622–629, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.54
- technology. In this paper, we describe the synthesis of GuNA[Me] phosphoramidites bearing other typical nucleobases including adenine (A), guanine (G), and 5-methylcytosine (mC). The phosphoramidites were successfully incorporated into oligonucleotides following the method previously developed for the GuNA
- expected to provide further mechanistic insights into how small substituents affect the efficacy and safety of therapeutic oligonucleotides. Thus, the synthesis of GuNA[Me] phosphoramidites bearing other typical nucleobases, i.e., adenine (A), guanine (G), or 5-methylcytosine (mC), instead of the
- all four GuNA[H] phosphoramidites, where transglycosylations of the 2'-amino-LNA analog with the corresponding nucleobases were performed as the key reactions [24][25]. The transglycosylation is a powerful strategy that simplifies the preparation of phosphoramidites at the late stages of the syntheses
19F NMR as a tool in chemical biology
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 293–318, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.28

- advantage that can be easily incorporated either as internally fluorinated nucleobases or as external 19F-labelled terminal tags in longer oligonucleotides (Figure 14b). As a proof of concept, Bao et al. demonstrated the utility of these tags for the direct observation and quantitative thermodynamic
Selected peptide-based fluorescent probes for biological applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2971–2982, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.247

- peptidic arms equipped with lysine and an artificial strong anion binding site, the guanidinocarbonylpyrrole (GCP) moiety (Figure 2A). These arms also contain tryptophan for dissimilar aromatic interactions with different nucleobases. The fluorescence intensity of probe 1 increases by more than 4-fold at
- >> ADP > UDP. Nucleobases undergo differential interactions with the tryptophan residues and naphthimide which varies the hydrophobic microenvironment around the fluorophore and results in dissimilar fluorescence enhancement. The addition of monophosphorylated species such as HPO42−, c-AMP, AMP, CMP, GMP
Incorporation of a metal-mediated base pair into an ATP aptamer – using silver(I) ions to modulate aptamer function
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2870–2879, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.236

- to release a DNA-bound cargo (in the form of small organic molecules) [10]. Similarly, metal ions can trigger DNA folding into a catalytically active topology [11][12]. Metal-mediated base pairs are artificial base pairs in which hydrogen bonds between the complementary nucleobases are formally
- concluded that the nucleobases close to the binding pocket contribute to a large extent to the aptamer stability. All imidazole-containing aptamer derivatives (1bf, 1cf, 1df) show a significant increase in Tm upon the addition of the first equivalent of Ag(I) but only minor additional changes in the
- smaller increase in Tm. Moreover, the Tm of 1af increases more or less steadily with an increasing Ag(I) concentration, suggesting non-specific interactions between Ag(I) and the canonical nucleobases in 1af. To obtain further insight into the Ag(I)-binding behavior of the aptamer derivatives, CD spectra
Changed reactivity of secondary hydroxy groups in C8-modified adenosine – lessons learned from silylation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2854–2861, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.234

- conjugation of the desired moiety. A C8-alkynyl-modified adenosine derivative was synthesized, reviving an old synthetic pathway for iodination of purine nucleobases. Silylation of the C8-alkynyl-modified adenosine revealed unexpected selectivity of the two secondary sugar hydroxy groups, with the 3'-O-isomer
Selective recognition of ATP by multivalent nano-assemblies of bisimidazolium amphiphiles through “turn-on” fluorescence response
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2728–2738, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.223

- stacking interactions with the nucleobases which contributes to the stability of the complexes. In many cases, these stacking interactions provide binding selectivity among the nucleotides [53][54][55][56]. Most of the aforementioned receptors were predominantly “molecular” in nature with the binding of
Recent synthesis of thietanes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1357–1410, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.116
- to afford the corresponding thietanes 66. The subsequent introduction of nucleobases then gave the corresponding thietanose nucleosides 68 [45] (Scheme 15). The treatment of 2-(allylthio)benzimidazole 69 with iodine in CHCl3 followed by aq. KOH gave (iodomethyl)thiazolobenzimidazole 70 which was
Copper-based fluorinated reagents for the synthesis of CF2R-containing molecules (R ≠ F)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1051–1065, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.92

- ., glycals, nucleosides and nucleobases) [80]. In 2018, Hu and co-workers reported a complementary approach for the pentafluoroethylation of aryl iodides using TMSCF3 for the formation of CuCF2CF3 [81]. They suggested that in the presence of CuCl, KF and TMSCF3, the corresponding CuCF3 species will be formed
Photocontrolled DNA minor groove interactions of imidazole/pyrrole polyamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 60–70, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.8
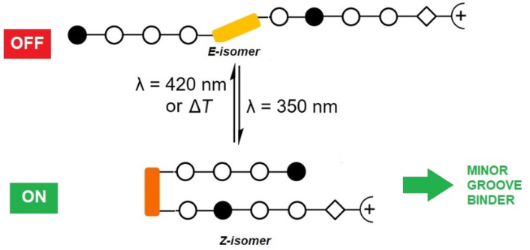
- wavelengths longer than 300 nm where dsDNA does not absorb. Therefore, the occurrence of ICD is a strong indication of the interaction between ligand and DNA [50][51]. This ICD signal originates from the coupling of the transition dipole moments of the nucleobases and the ligand and is usually positive for
In search of visible-light photoresponsive peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) for reversible control of DNA hybridization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2500–2508, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.243

- -penetrating wavelengths. Peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) [31] are synthetic nucleic acid analogues, in which nucleobases are linked to a repeating N-(2-aminoethyl)glycine polyamide backbone. The lack of phosphate groups provides them with both higher binding affinities to complementary DNA or RNA sequences and



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































