Search results
Search for "ultrahigh vacuum" in Full Text gives 174 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Hydrophilicity and carbon chain length effects on the gas sensing properties of chemoresistive, self-assembled monolayer carbon nanotube sensors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 565–577, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.58

- suggests the absence (or a non-detectable amount) of unbound thiol molecules (S 2p1/2 BE ≈ 165 eV), which confirms the correct formation of SAMs. The small amount of unbound thiol molecules detected by Raman spectroscopy were possibly removed under the ultrahigh vacuum needed to perform XPS, which would
Widening of the electroactivity potential range by composite formation – capacitive properties of TiO2/BiVO4/PEDOT:PSS electrodes in contact with an aqueous electrolyte
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 483–493, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.49

- and 300 W. XPS measurements were performed at room temperature under ultrahigh-vacuum conditions, with pressures below 1.1 × 10−8 mbar. Data analysis was performed with the CASA XPS software package using Shirley background subtraction and a least-squares Gaussian–Lorentzian curve fitting algorithm
Apparent tunneling barrier height and local work function of atomic arrays
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3048–3052, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.283

- of a barrier height increase with decreased lateral size of the tunneling-current path is expected to be reliable. These results predict a kinetic energy contribution of the order of 1 eV for tunneling between two atomically sharp structures. Experiments were performed in an ultrahigh vacuum STM
Femtosecond laser-assisted fabrication of chalcopyrite micro-concentrator photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3025–3038, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.281
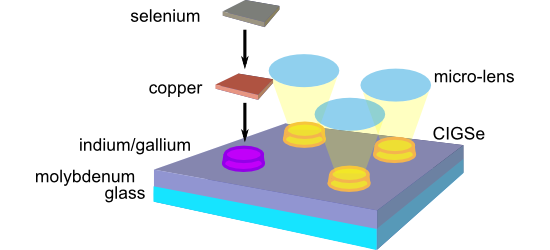
- pressure for CISe samples from the nucleation approach and all samples from the LIFT approach, or in an ultrahigh-vacuum chamber with a directed selenium beam for CIGSe samples from the nucleation approach. In both cases, the temperature protocol comprised an annealing step at around 200–250 °C followed by
Investigation of CVD graphene as-grown on Cu foil using simultaneous scanning tunneling/atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2953–2959, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.274

- ]. Experimental Our setup is a commercial STM/AFM operated in ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) that was modified and improved by the implementation of a Fabry–Pérot fiber interferometer in order to achieve high sensitivity in detecting lever deflection and measuring the oscillation amplitude, which in turn allows us to
In situ characterization of nanoscale contaminations adsorbed in air using atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2925–2935, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.271

- involving surfaces a well-defined surface condition is essential. Preparing such surfaces has thus been a field of intense research over many decades. One approach is to work under ultrahigh-vacuum (UHV) conditions, which has opened fascinating experimental possibilities [5]. More importantly, well-defined
Low cost tips for tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy fabricated by two-step electrochemical etching of 125 µm diameter gold wires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2718–2729, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.254

- ] and shear-force microscopy (ShFM) [15] allow for chemical imaging of nanostructured materials, surfaces and (bio)molecular layers with a spatial resolution of 4–10 nm in ambient conditions [15][16], and can even reach atomic-level sensitivity in ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) [17][18][19]. Excellent reviews
Silicene, germanene and other group IV 2D materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2665–2667, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.248

- concepts exploiting their topological properties. In recent years this search has lead to the discovery of other members of this family of 2D materials based on other group IV elements. In 2012 silicene was first synthesized under ultrahigh vacuum conditions on a silver(111) single crystal by Si molecular
- beam epitaxy (MBE) [1][2] and at around the same time on zirconium diboride thin films grown on Si(111) substrates by Si segregation through the film [3]. The synthesis of silicene further launched an intensive search for other 2D elemental materials synthesized under ultrahigh vacuum by MBE-like
Intrinsic ultrasmall nanoscale silicon turns n-/p-type with SiO2/Si3N4-coating
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2255–2264, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.210

- swiftly loaded into the ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) annealing chamber. All NWell samples were contacted via a lateral metal contact frame on the front surface which was processed by photolithographical structuring, wet-chemical mesa etching and thermal evaporation of Al. The reference Si-wafer was contacted
Localized photodeposition of catalysts using nanophotonic resonances in silicon photocathodes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2097–2105, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.198

- electrolyte. X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) X-ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS) was performed in a custom-built ultrahigh-vacuum chamber, operating at a base pressure below 5 × 10−9 mbar. A XM1200 monochromatic X-ray source (Al Kα line, Scienta Omicron) was used for X-ray excitation of the sample
Recent highlights in nanoscale and mesoscale friction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1995–2014, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.190

- important prerequisite of these experiments is to operate the instrument under ultrahigh-vacuum conditions, where contaminants can be avoided. In the case of Kawai et al. [58], the GNRs were grown by on-surface chemistry through evaporating a precursor of 10,10’-dibromo-9,9’-bianthryl monomers. By suitable
Quantitative comparison of wideband low-latency phase-locked loop circuit designs for high-speed frequency modulation atomic force microscopy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1844–1855, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.176

- [1]. It has been used under ultrahigh vacuum conditions for high-resolution imaging of various materials, including metals, semiconductors, metal oxides, and organic molecules [2][3][4][5]. Furthermore, recent advances in FM-AFM have enabled atom manipulation and identification at room temperature [6
Know your full potential: Quantitative Kelvin probe force microscopy on nanoscale electrical devices
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1809–1819, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.172

- capacitance. Thus, FM detection is more sensitive to the electrostatic interaction of the tip apex with the sample surface [20]. Originally, the peroiodic oscillations in Δf were directly detected by means of a phased-locked loop in non-contact AFM under ultrahigh vacuum conditions. An elegant way of
Multimodal noncontact atomic force microscopy and Kelvin probe force microscopy investigations of organolead tribromide perovskite single crystals
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1695–1704, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.161

- inverse temperature solubility. The single crystal investigated under ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) was fixed on a stainless steel sample UVH holder with a compatible electrically conductive silver epoxy paste (EPO-TEK E4110), which was cured at room temperature (RT) over 24 hours. The sample was subsequently
- cleaved with a scalpel just before being introduced in the load-lock of the VT-AFM (after cleavage, the sample thickness was estimated to be on the order of 1 mm). Noncontact AFM and Kelvin probe force microscopy The nc-AFM experiments were carried out with an Omicron VT-AFM setup in ultrahigh vacuum (UHV
Friction force microscopy of tribochemistry and interfacial ageing for the SiOx/Si/Au system
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1647–1658, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.157

- ultrahigh vacuum. We measured very low friction forces compared to adhesion forces and found a modulation of lateral forces reflecting the atomic structure of the surfaces. Holding the force-microscopy tip stationary for some time did not lead to an increase in static friction, i.e., no contact ageing was
- minutes) [5], while contact ageing between chemically reactive surfaces may occur very fast (nanoseconds to milliseconds) [14]. Here, we report FFM experiments in ultrahigh vacuum that address contact ageing and atomic-scale friction for contacts formed by Si, SiOx, and Au. We found that no contact ageing
- layers, in particular oxide films, from surface and tip. The control of surface oxidation required the implementation of all experiments in ultrahigh vacuum. We report on tribochemical processes between Si, SiOx, and Au, which were initiated by removal of the passivating layers. Experimental Tip and
Atomistic modeling of tribological properties of Pd and Al nanoparticles on a graphene surface
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1239–1246, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.115

- ][14]. There are many studies concerning the tribological properties of nanoobjects. For example, alumina nanoparticles were studied in [9] and self-organized monolayers in [4]. In [5] the authors studied the interaction in ultrahigh vacuum between a nanoasperity and an alkali-metal halide surface at
- surfaces in ultrahigh vacuum [5]. The temperature dependence of the friction shown in Figure 8 can be understood as follows [20][21][22][23]: At high temperatures the friction decreases with increasing temperature due to thermal fluctuations, which help to move the particles over the energy barriers they
- , which is similar to that of hexadecanethiol self-assembled monolayers on Au substrates [4] and NaCl crystal surfaces in ultrahigh vacuum [5]. We found that the friction force, i.e., the force acting on the particles from the substrate, depends nearly linearly on the contact area consistent with [13][14
Field-controlled ultrafast magnetization dynamics in two-dimensional nanoscale ferromagnetic antidot arrays
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1123–1134, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.104

- -thick protective layer of Al2O3 was deposited on top of the Py film in an ultrahigh vacuum chamber at a base pressure of 2 × 10−8 Torr. The Al2O3 capping layer was deposited on the Py film to protect the samples from external contamination of the environment, degradation with time, and also from direct
Electron interactions with the heteronuclear carbonyl precursor H2FeRu3(CO)13 and comparison with HFeCo3(CO)12: from fundamental gas phase and surface science studies to focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 555–579, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.53

- carbonyl complex H2FeRu3(CO)13 covering its low energy electron induced fragmentation in the gas phase through dissociative electron attachment (DEA) and dissociative ionization (DI), its decomposition when adsorbed on a surface under controlled ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) conditions and exposed to irradiation
Dopant-stimulated growth of GaN nanotube-like nanostructures on Si(111) by molecular beam epitaxy
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 146–154, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.17

- Discussion Growth technique In our experiments, we used p-type Si(111) substrates that were treated with the Shiraki cleaning procedure prior to loading into the MBE chamber, where each substrate was annealed in ultrahigh vacuum. The annealing temperature varied from sample to sample in the range of 850 to
Electron-driven and thermal chemistry during water-assisted purification of platinum nanomaterials generated by electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 77–90, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.10

- (methylcyclopentadienyl)platinum(IV) (MeCpPtMe3). The experiments performed under ultrahigh vacuum conditions apply a combination of different desorption experiments coupled with mass spectrometry to analyse reaction products. Electron-stimulated desorption monitors species that leave the surface during electron exposure
- FEBID from MeCpPtMe3. Experimental All experiments were performed in an ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) chamber [39] with a base pressure of about 10−10 mbar. In all experiments, multilayer films of MeCpPtMe3 were condensed on a polycrystalline Ta sheet held between 105 K and 110 K by liquid N2 cooling. The
Patterning of supported gold monolayers via chemical lift-off lithography
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2648–2661, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.265

- ., Chestnut Ridge, NY, USA) under ultrahigh vacuum conditions (10−9 torr) using a monochromatic Al Kα X-ray source (20 mA, 14 kV) with a 200 μm diameter circular spot size. The pass energy was 80 mV for the survey spectra and 20 mV for high-resolution spectra of the C 1s, S 2p, O 1s, and Au 4f regions. All
Direct writing of gold nanostructures with an electron beam: On the way to pure nanostructures by combining optimized deposition with oxygen-plasma treatment
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2530–2543, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.253

- the deposition parameters, making use of conventional equipment and a standard precursor. The ultrahigh vacuum/surface science approach to studying the effect of electron beam irradiation on nanometer thin films of a common Me2-Au-acac precursor from Wnuk et al. [69][70] represents a valuable starting
Au nanostructure fabrication by pulsed laser deposition in open air: Influence of the deposition geometry
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2438–2445, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.242

- geometry [17][18]. Despite the attractive properties and practical advantages of PLD, there still exist some drawbacks and limitations in using this method. The PLD process is typically performed in a vacuum chamber at ultrahigh vacuum or in the presence of a background gas, such as oxygen, nitrogen or
Comparing postdeposition reactions of electrons and radicals with Pt nanostructures created by focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2410–2424, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.240

- etch substrates or equipment. The use of electrons was motivated in part by previous ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) surface science studies which showed that for 1–2 monolayer (ML) thin films of organometallic precursors with halide ligands, the halogens can be removed [29][31]. The importance of halogen
Identifying the nature of surface chemical modification for directed self-assembly of block copolymers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 1972–1981, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.198

- an ultrahigh vacuum chamber with a base pressure in the high 10−9 mbar range. To prevent beam damage, measurements were taken at different locations on the sample. In addition, the radiation was stopped (beam shutter closed) when spectra were not acquired (e.g. in case of monochromator setting change
























































































































































































