Search results
Search for "charging" in Full Text gives 199 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology.
Zn/F-doped tin oxide nanoparticles synthesized by laser pyrolysis: structural and optical properties
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2019, 10, 9–21, doi:10.3762/bjnano.10.2

- in order to compensate the surface charging effects. From Figure 2 it can observed that in the case of ZTOst sample, Sn exhibits only one oxidation state, while the Zn doping is accompanied by the formation of a secondary SnO phase, see Figure 2a. Also, the binding energy of Sn in the Zn-doped SnO2
Hydrogen-induced plasticity in nanoporous palladium
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 3013–3024, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.280

- counterparts considering the increasing importance of surface effects. The high surface-to-volume ratios in such materials allow for the control of bulk features by surface modifications. Electrostatic charging or electrochemical (surface) reactions are possible ways to influence metal surfaces in a well
- total, black curves) and, thus, hydrogen concentrations (compare Equation 1), while for desorption (red curves) the potential was held constant at −0.4 V similar to the potentiostatic experiment above (Figure 2). Monitoring the potential during the charging procedure revealed a transgression of the PdHβ
- reduction in double layer current of about 25% compared to the pristine, untreated npPd sample (black curve). The black curve shows a stronger contribution of pseudocapacitive surface charging, indicated by the larger deviation from the rectangular shape of ideal capacitors. A comparison of double-layer
Size limits of magnetic-domain engineering in continuous in-plane exchange-bias prototype films
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2968–2979, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.276

- resolution is limited by relatively thick polymer masks in combination with non-optimum edge steepness [36][37]. In addition, electrostatic charging of the mask [27] can lead to further beam broadening resulting in areas of gradually changing ion doses between bombarded and non-bombarded regions. Thus, at
Site-controlled formation of single Si nanocrystals in a buried SiO2 matrix using ion beam mixing
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2883–2892, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.267

- NC-based SET device is to obtain lateral control over the formation of few or even a single Si NC using the ion beam approach. To obtain an estimate for the charging energy of the Coulomb island we use the self capacitance of a sphere C = 4πεε0rNC. In order to have Ec larger than 5 kT at room
Impact of the anodization time on the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotubes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2628–2643, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.244

- fashion, where j corresponds to the charging of the electrode (i.e., capacitive current). This quasi-reversible behavior is indicative of a stable surface. In the potential range from 0.05 to 0.6 V/RHE, |j| increases for samples with higher ta and, since j is an extrinsic property, we attributed this to
- minimize the contribution of the charging current from the scan rate, linear-sweep voltammograms (LVS) were recorded at v = 5 mV/s in anodic direction from 0.05 to 1.0 V/RHE. A constant polarization at 0.05 V/RHE for 10 s was applied to the electrodes prior to running the LSV, as a pretreatment to minimize
- the initial charging spikes and to obtain a more accurate signal. The results are shown in Figure 5b and assessing those obtained from the CV measurements, provide support to the idea of j being a function of the nanotube length. The latter characteristic implies that the electrolyte is capable of
Pattern generation for direct-write three-dimensional nanoscale structures via focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2581–2598, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.240

- addition, the resolution may suffer due to charging issues caused by the electron beam. Conversely, short dwell times increase the time fraction of the total process time in which the electron beam is not placed at a writing position but moved in between two consecutive writing positions due to the limited
Hydrothermal-derived carbon as a stabilizing matrix for improved cycling performance of silicon-based anodes for lithium-ion full cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2381–2395, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.223

- requirements for automotive applications, e.g., extended driving range and fast charging ability. Such improvements can either be achieved by the optimized engineering of cell components or the development of new cell chemistries with advanced active materials [1][2][3][4][5][6]. In this context, it is
- -term cycling experiments were set as 0.01 V vs Li/Li+ and 1.50 V vs Li/Li+. During the rate performance experiments, cut-off potentials of 0.02 V vs Li/Li+ and 1.50 V vs Li/Li+ were chosen in order to avoid Li-metal plating at high charging rates. In the rate performance studies, specific charge
- at high charging rates. In order to verify if the incorporation of the Si into the carbon has a beneficial effect, a physical mixture of the pure carbon matrix and the pure Si-NPs was prepared in a ratio of 80:20, where the Si-NPs did not take part in the hydrothermal process. This mixture shows the
Lead-free hybrid perovskites for photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2209–2235, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.207

- stability [165]. Along with the chemical and photochemical stability, MABI retains perfect integrity during charging/discharging events. In particular, a MABI-based electrochemical capacitor retains around 85% of its initial maximal capacitance after more than ten thousand charge/discharge cycles [158]. A
Interaction-induced zero-energy pinning and quantum dot formation in Majorana nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2171–2180, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.203

- -length wire posses a finite charge, typically distributed uniformly along the wire [34], which can be susceptible to electrostatic interactions with the surrounding medium. We considered the case of a grounded parent superconductor, thus avoiding the effect of a charging energy associated to the Cooper
- , the Zeeman energy VZ and the induced potential energy . The magnetic field lowers the band bottom, charging the wire, whereas the induced potential energy, coming from electrostatic repulsion, tends to compensate that trend. In the finite-length wire, the evolution of the induced potential profile
Recent highlights in nanoscale and mesoscale friction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1995–2014, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.190

- and charging [120] concluded that friction increases when the applied surface potential changes from negative values to positive values, and that, for negative surface potential, friction depends on the alkyl-chain length of the cation of the RTIL. Assuming well-ordered anchored molecular layers, the
Synthesis of hafnium nanoparticles and hafnium nanoparticle films by gas condensation and energetic deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1868–1880, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.179

- combining X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). To our knowledge this is the first report about the fabrication and characterization of Hf NPs. The fabrication of nanoparticles with IGC leads to the charging of a significant fraction of the as formed NPs and, thus, their kinetic
- -called soft-landing regime [68][69][70]. In general, the particle beam produced contains neutral and charged (positive and negative) NPs. The charging of NPs occurs in the plasma region where the electron and ion densities are high [40]. In our system it seems that the vast majority of Hf NPs is charged
Robust topological phase in proximitized core–shell nanowires coupled to multiple superconductors
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1512–1526, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.142

- , = 3,5. We conclude that the presence of disorder induces low-energy localized states than can destroy the topological protection of the Majorana subspace. We note that within a topological quantum computation scheme based on qubits characterized by a finite charging energy [51][52], interaction-mediated
Electrostatically actuated encased cantilevers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1381–1389, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.130

- a slow change of the amplitude with a time constant of several minutes before settling to a new steady state. This phenomenon can be explained by charging or polarizing of the parylene film altering the strength of the electrostatic excitation. Fabricating a gold layer on the inside of the
- charging states in the encasement material, the electrical contact potential or any other static offsets. Not requiring any dc voltage greatly reduces the risk of electrolytic production of gas bubbles. Electrostatic actuation in encased cantilevers provides more gentle imaging and more reliable
Disorder-induced suppression of the zero-bias conductance peak splitting in topological superconducting nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1358–1369, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.128
- conductance peak spacings and reformation of the zero-bias peak, which we discuss below, is independent of Coulomb blockade physics. In the presence of a charging energy in the nanowire, it was shown that the zero-bias conductance values are considerably suppressed by the Coulomb energy [75]. The situation of
- interest to us is how intrinsic disorder in the nanowire affect the Majorana energy EM and the splitted zero-bias conductance peak induced by EM. In situations like this, the intrawire charging energy could modulate the actual conductance value, but the main physics induced by the disorder is captured even
- though the charging energy is not taken into account. The generic form of the Hamiltonian that models this Majorana hybrid structure reads as where the term Hnw, HL(R), and HT account for the superconducting nanowire, the left (right) normal metal lead, and the tunnel coupling between the leads and the
Cyclodextrin inhibits zinc corrosion by destabilizing point defect formation in the oxide layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 936–944, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.86
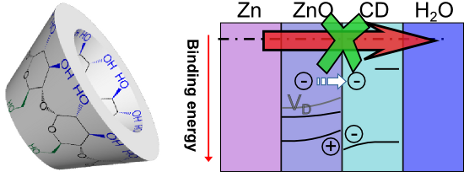
- electrostatic potential [34], the evident difference in the shift slope for the different examined signals (e.g., ZnO and β-CD related components of O 1s, Figure S4c, Supporting Information File 1) shows that charging effects can be ruled out. Charging can also be ruled out as it should cause the same energy
- desiccator in vacuum. ADXPS was carried out on a Physical Electronics PHI Quantera II spectrometer equipped with an Al Kα micro-focused source at 1486.74 eV. Samples for ADXPS were prepared in the same manner as for SEM. In ADXPS, to compensate X-ray source-induced charging effects, a dual-beam charge
Graphene composites with dental and biomedical applicability
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 801–808, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.73

- 0.47 eV). High resolution spectra for the core level C 1s and O 1s were recorded in 0.05 eV steps. An electron flood gun was used during the measurements to prevent sample charging. The FLG material was also characterized by TEM, HRTEM (Jeol ARM at 80 kV) and helium ion microscopy (HeIM, Zeiss Orion at
Combined pulsed laser deposition and non-contact atomic force microscopy system for studies of insulator metal oxide thin films
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 686–692, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.63

- potential difference (CPD) of the insulator surface synthesized with our PLD system is at most about 3 V. With our system, it is possible to measure without affecting the charging of the sample surface, which often occurs on insulator surfaces. Conclusion We have developed a combined system of NC-AFM and
Electron interactions with the heteronuclear carbonyl precursor H2FeRu3(CO)13 and comparison with HFeCo3(CO)12: from fundamental gas phase and surface science studies to focused electron beam induced deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 555–579, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.53

Single-step process to improve the mechanical properties of carbon nanotube yarn
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 545–554, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.52

- analyzer with a 128-channel detector. Survey data were collected at 200 eV pass energy and an energy resolution of 1 eV/step, while core level data were collected at 50 eV pass energy and 0.1 eV/step energy resolution. Sample charging was eliminated by using the dual-beam charge compensation source of the
Blister formation during graphite surface oxidation by Hummers’ method
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 407–414, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.40

- involves the intercalation of molecules and ions between the carbon layers, the sp2-lattice charging and oxidation [6]. The understanding of these processes is crucial for the reproducible synthesis of GO with desired structure and properties. The larger graphite flakes are used to produce GO, the more
Electron interaction with copper(II) carboxylate compounds
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 384–398, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.38

- both [Cu2(EtNH2)2(µ-O2CC2F5)4] (Table 2) and [Cu2(t-BuNH2)2(µ-O2CC2F5)4] (Table 3). However, the appearance energies were measured only for the fragments with highest intensity due to the charging effects of the monochromator electrodes relating to the measured sample. To avoid the total loss of the
Review: Electrostatically actuated nanobeam-based nanoelectromechanical switches – materials solutions and operational conditions
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 271–300, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.29

BN/Ag hybrid nanomaterials with petal-like surfaces as catalysts and antibacterial agents
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 250–261, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.27

- -ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) using an Axis Supra (Kratos Analytical) spectrometer. The powder samples were attached to the carbon tape covered with glue. The maximum lateral dimension of the analyzed area was 0.7 mm. To avoid differential charging of samples, the spectra were acquired with
Response under low-energy electron irradiation of a thin film of a potential copper precursor for focused electron beam induced deposition (FEBID)
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 57–65, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.8

- to avoid partial charging of the system that complicated the HREELS investigation in the present study. ESD measurements have shown that the loss of the amine ligands was not completely achieved under vacuum at room temperature and can then be reinforced by electron bombardment in the low-energy
Hyperthermic intracavitary nanoaerosol therapy (HINAT) as an improved approach for pressurised intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC): Technical description, experimental validation and first proof of concept
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 2729–2740, doi:10.3762/bjnano.8.272

- given in Figure 1. In contrast to PIPAC-MIP, the HINAT approach is based on extracavitary aerosol generation by means of a heatable liquid atomization unit (LAU). After generation, the aerosol passes a secondary heating unit and a charging unit before it is supplied into the abdominal cavity through an
- droplet flux to the peritoneum. Intracavitary aerosol conditioning (optional operation mode) To enable local, accelerated droplet deposition on the peritoneum, aerosol charging can also be performed intraperitoneal (cf. [8]) that requires an additional access into the abdominal cavity. Similar to the
- extracavitary charging, the supplied aerosol droplets are unipolar-charged by means of an approved brush electrode (IonwandTM, Alesi Surgical Ltd, Cardiff, UK). In contrast to extracavitary charging, particle deposition during intracavitary charging is supported by the formation of an electrical field between








































































































































































































































