Search results
Search for "microporous" in Full Text gives 34 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Systematic pore lipophilization to enhance the efficiency of an amine-based MOF catalyst in the solvent-free Knoevenagel reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1854–1863, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.144

- ], and metal-organic-frameworks (MOFs), among others [18][19][20]. Within this group of porous materials, MOFs boast the advantages of their crystallinity, the uniformity of their pores that are typically in the microporous range (5–20 Å), and the ability to fine-tune their pore chemical environment [21
Recent advances in synthetic approaches for bioactive cinnamic acid derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1031–1086, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.85

- )-coordinated to microporous N-doped carbon (Zn/NC-950). the reaction proceeds through homolytic β-scission involving intermediates 183 and 184 (Scheme 58) [101]. 2.3 Alkenyl/alkynyl carboxylation 2.3.1 Alkenyl carboxylation: Li and co-workers (2021) investigated a photoinduced oxidative alkoxycarbonylation of
Green and sustainable approaches for the Friedel–Crafts reaction between aldehydes and indoles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 379–426, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.36
Perspectives on push–pull chromophores derived from click-type [2 + 2] cycloaddition–retroelectrocyclization reactions of electron-rich alkynes and electron-deficient alkenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 125–154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.13

Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
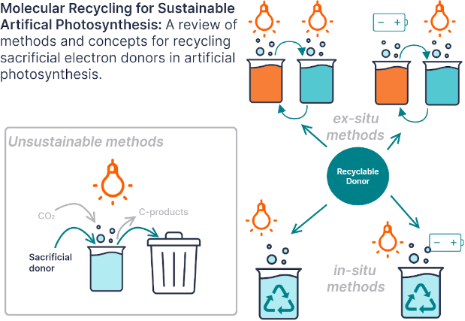
- of artificial photosynthesis research investigating the compartmentalization of different reactions using liposomes and membranes [38]. Another alternative could be to use redox-active polymers as recyclable donors which would allow microporous membrane separation. Redox-active polymers are a very
- active area of research for aqueous and non-aqueous RFBs [59][60]. This is because often the most expensive component of an RFB is the ion-exchange membrane used to prevent the mixing of charged species and recombination. Microporous membranes are much less expensive, and the particulate size of redox
Preparation of β-cyclodextrin/polysaccharide foams using saponin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 78–88, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.7

- 15 mg/g of matrix. Similar results are found for the liquid path in the absence of saponin. The favourable influence of saponin to produce a more efficient matrix is confirmed. The freeze drying of solutions permits to produce microporous materials, as seen in the SEM images of Figure 2, where the
Recent advances in the asymmetric phosphoric acid-catalyzed synthesis of axially chiral compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2729–2764, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.185
- -catalyzed enantioselective transformations [9][14][22][23]. Axial chirality is also found in chiral stationary phases for enantioselective separation, dopants in liquid-crystalline materials, chiroptical molecular switches, microporous soluble polymers, and interlocked nanotubes (Figure 3) [24]. In addition
Activation of pentafluoropropane isomers at a nanoscopic aluminum chlorofluoride: hydrodefluorination versus dehydrofluorination
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2623–2635, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.213
- investigated [16][28][32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39]. Especially microporous aluminum chlorofluoride (ACF, AlClxF3−x; x = 0.05–0.3), which has a large surface area (>200 m2g−1) and was patented by Dupont in 1992, has been extensively studied [40][41][42][43][44][45][46]. It is an amorphous aluminum fluoride
One-pot synthesis of isosorbide from cellulose or lignocellulosic biomass: a challenge?
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1713–1721, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.143

- (5.0 wt % Ru, Ru nanoparticles (NPs): 0.9 nm) in 30 mL H2O after 1 h of reaction at 220 °C under 60 bar of H2. Trace amounts or even no isosorbide was obtained over microporous HZSM-5, NaY, and γ-Al2O3-supported Ru catalysts. A bifunctional Ru catalyst supported on mesoporous niobium phosphate with a
Heterogeneous photocatalysis in flow chemical reactors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1495–1549, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.125

Activated carbon as catalyst support: precursors, preparation, modification and characterization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1188–1202, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.104

- ) activation methods for the modification of the porosity of anthracite-based activated carbons. The final pore size distribution (mainly microporous or mainly mesoporous) depends on the choice of the activation agent, the treatment time and temperature and the initial textural properties of anthracite as
- ruptured surface obtained [46]. SEM micrographs also allow the determination of different types of pores. The group of Okman showed SEM investigations on activated carbons prepared from grape seeds by activation with KOH. The sponge-like surface of the activated carbon indicates a microporous structure [56
- approaches the limiting value p/p0 → 1. This type is formed by microporous solids with a relatively small external surface, for example, activated carbons or molecular sieve zeolites [117]. Numerous methods are available for calculating surface area, pore size, pore distribution and pore volume by fitting to
A systematic review on silica-, carbon-, and magnetic materials-supported copper species as efficient heterogeneous nanocatalysts in “click” reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 551–586, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.52
- . This solid material was washed with MeOH and dried. The resulting GO/intrinsically microporous polymer (Pim) material and CuSO4 were added into water and heated at 50 °C overnight to afford the material GO/Pim/Cu (100, Scheme 22). The powder was collected by filtration and washed by water/methanol. The
Carbazole-functionalized hyper-cross-linked polymers for CO2 uptake based on Friedel–Crafts polymerization on 9-phenylcarbazole
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2856–2863, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.279
- ; hyper-cross-linked polymers; microporous; Introduction HCPs get more attention in recent years due to their high BET specific surface area [1], made under mild reaction conditions [2], used nonprecious materials as catalyst [3] and wide applications [4][5][6][7][8][9], etc. The synthesis methods of
- microporous HCPs and came to the conclusion that 2D and 3D-conjugated architectures with nonplanar rigid conformation and dendritic building blocks were favorable for getting a high BET specific surface area [6][19][20][21][23][24][25]. Qiao synthesized five microporous materials using carbazole with
- the temperature raised up to 800 °C (Supporting Information File 1, Table S1), demonstrated the splendid thermal stability of P1–P11 as reported for microporous polymers [34]. Morphology analysis The morphology of P1–P11 was investigated by SEM images (Figure 4), which showed that HCPs were composed
Mechanochemical synthesis of hyper-crosslinked polymers: influences on their pore structure and adsorption behaviour for organic vapors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1154–1161, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.112
- sorption experiments with benzene and cyclohexane. Keywords: hyper-crosslinked polymers; mechanochemistry; microporous; solvent-free; vapor sorption; Introduction The widespread use of microporous materials in areas like gas storage, gas separation, and catalysis has led to the development of a wide
- the physical and thermal properties of the polymer, the textural properties of the NG-HCP were evaluated utilizing nitrogen physisorption. While the first tries directly yielded a microporous polymer (SSABET = 850 m2g−1, Vp = 0.60 cm−3g−1, Figure 2B in Supporting Information File 1), the SSA (specific
MoO3 on zeolites MCM-22, MCM-56 and 2D-MFI as catalysts for 1-octene metathesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2931–2939, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.272

- ]. The positive effect of these supports on the catalyst activity was ascribed to their high surface areas enhancing the spreading of MoO3 molecules on the surface and large pores increasing the substrates/products transport rate. Microporous zeolites like HZSM-5 impregnated by ammonium heptamolybdate
An overview on recent advances in the synthesis of sulfonated organic materials, sulfonated silica materials, and sulfonated carbon materials and their catalytic applications in chemical processes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2745–2770, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.253
- temperature. The esterification of long chain-free fatty acids with methanol was performed well for 10–12 h (Scheme 20). To check the effect of acid groups, HMP-1 (113) was also used as a catalyst for the reaction and low yields of corresponding products were obtained [68]. In another study, a new microporous
Novel approach to hydroxy-group-containing porous organic polymers from bisphenol A
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2131–2137, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.211

- ). There is a weight loss of about 5% up to 150 °C, which is attributed to the evaporation of trapped solvent, carbon dioxide, or adsorbed water that could not be easily removed from the microporous structure of the polymers during the after-synthesis treatment and drying process. There is not any obvious
- high gas uptake at relative pressure (P/P0) less than 0.02, indicating that the materials are microporous. Meanwhile, a nitrogen condensation step could be found for all the polymers at P/P0 above 0.90, which is an indication of characteristic macroporosity that might correspond to interparticular
- voids associated with the pack of small particles of about 4 μm adhered to the external surface of spherical particles (Supporting Information File 1, Figure S5). The BET specific surface area values are calculated in the relative pressure range P/P0 = 0.01–0.10 for the microporous materials [31] for
Encaging palladium(0) in layered double hydroxide: A sustainable catalyst for solvent-free and ligand-free Heck reaction in a ball mill
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1661–1668, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.160

- . Thus, Pd catalysts anchored on heterogeneous solid support materials such as MCM-41 [29], alumina [30], silica [31], carbon nanotubes [32], microporous polymers [33], SBA-15 [34], or some dendrimers [35] were preferred to develop a ligandless and recyclable catalyst system. However, to the best of our
Mechanochemistry-assisted synthesis of hierarchical porous carbons applied as supercapacitors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1332–1341, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.130

- . Keywords: electrochemical energy storage; mesoporous; microporous; solvent-free; supercapacitor; templated carbon; Introduction Porous carbons are key components in many energy and environmentally-relevant applications, such as catalysis [1], gas storage and separation [2][3], and electrochemical energy
- influence of the pore size and the pore structure on (electro)sorption in energy storage devices [15][16][17]. Moreover, purely microporous carbons suffer from diffusion limitations resulting in low electrochemical performances at high charge/discharge rates [4][18][19]. Larger pores, like mesopores, or
Sugar-based micro/mesoporous hypercross-linked polymers with in situ embedded silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 1212–1221, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.120
- to tune the porosity. These obtained polymers exhibit microporous and mesoporous features. The highest Brunauer–Emmett–Teller specific surface area for the resulting polymers was found to be 1220 m2 g−1, and the related carbon dioxide storage capacity was found to be 14.4 wt % at 1.0 bar and 273 K
- microporous organic materials with a high specific surface area (SSA) [1][2]. The preparation of HCPs mainly includes three different synthesis strategies, namely postcross-linking of polymeric precursors containing functional groups [3], the “knitting” of rigid aromatic building blocks by external cross
- microporous HCPs based on carbohydrates for carbon dioxide capture and storage by hydrogen bonding and dipole–quadrupole interactions [17]. The reported pore-size distribution (PSD) and related porosity tuning are in the range of micropore size. Considering that the polyhydroxylated and chiral structure
Fast and efficient synthesis of microporous polymer nanomembranes via light-induced click reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 558–563, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.54
- microporous polymers (CMPs) are materials of low density and high intrinsic porosity. This is due to the use of rigid building blocks consisting only of lightweight elements. These materials are usually stable up to temperatures of 400 °C and are chemically inert, since the networks are highly crosslinked via
- induced thiol–yne click reaction. Using this reaction, we could greatly enhance the CMP nanomembrane synthesis and further broaden the variability of the LbL approach. Keywords: click chemistry; conjugated microporous polymers (CMPs); microporous materials; nanomembranes; thin films; thiol–yne coupling
- reaction (TYC); Introduction The synthesis of microporous organic and inorganic materials such as zeolites [1], mesoporous silica [2] as well as metal-organic frameworks (MOF) [3][4] and covalent organic frameworks (COF) [5][6][7] attracted large attention because of their high potential in catalysis, gas
Synthesis of three-dimensional porous hyper-crosslinked polymers via thiol–yne reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2570–2576, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.252
- HCPs 3 and 5. The low-pressure hysteresis is most probable due to swelling effects or ill-connected pores. The pore-size distributions of HCPs 3 and 5 both show a broad distribution in the microporous scale as well as in the mesoporous scale. These findings also point out that both HCPs have amorphous
Robust C–C bonded porous networks with chemically designed functionalities for improved CO2 capture from flue gas
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2274–2279, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.220

- COP-156-amine showed fast and increased CO2 uptake under simulated moist flue gas conditions compared to the starting network and usual industrial CO2 solvents, reaching up to 7.8 wt % uptake at 40 °C. Keywords: C–C bond; CO2 capture; microporous materials; porous polymers; postmodification
- microporous polymers (CMPs) [5]. Most of these networks have the advantage of high porosity, but they are all made through precious metal-catalyzed reactions, which elevates the synthesis cost and limits their mass production. Another type of C–C bonded porous networks are hypercrosslinked polymers (HCPs) [6
Diels–Alder reactions in confined spaces: the influence of catalyst structure and the nature of active sites for the retro-Diels–Alder reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2181–2188, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.208
- selectivity and atom economy. Moreover, Diels–Alder cycloadditions in combination with heterogeneous catalysts (i.e. doped-microporous materials) represent an interesting approach for the conversion of biomass feedstock into stable chemicals such as furfural derivatives, platform molecules which can be
- and selectivity is the special confinement of the reactants and the presence of catalytic active sites, [15][16] by use of microporous materials doped with metals. While pore dimensions and topology of the microporous materials can affect the selectivity of the reaction, their activity can be strongly
- limited by a slow diffusion of reactants and products, unless microporous molecular sieves with the appropriated pore dimensions are used as catalyst. Thus, microporous molecular sieves with optimized pore diameters and topologies can be of interest to catalyze DAR [17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25][26
Hydroxy-functionalized hyper-cross-linked ultra-microporous organic polymers for selective CO2 capture at room temperature
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 1981–1986, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.185

- 10.3762/bjoc.12.185 Abstract Two hydroxy-functionalized hyper-cross-linked ultra-microporous compounds have been synthesized by Friedel–Crafts alkylation reaction and characterised with different spectroscopic techniques. Both compounds exhibit an efficient carbon dioxide uptake over other gases like N2
- , H2 and O2 at room temperature. A high isosteric heat of adsorption (Qst) has been obtained for both materials because of strong interactions between polar –OH groups and CO2 molecules. Keywords: carbon dioxide capture; hyper-cross-linked polymer; metal-organic framework; microporous organic polymer
- surface area and feasible interaction with carbon dioxide like MOFs and with high chemical stability have become one of top priority for researchers. Microporous organic polymers (MOP) are a relatively new class of porous materials, constructed from light elements like H, C, B, N, O etc. having a large













































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































