Search results
Search for "bacteria" in Full Text gives 330 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Confirmation of the stereochemistry of spiroviolene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 852–858, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.77
- cyclization process of fungi-derived deoxyconidiogenol and bacteria-derived spiroviolene by sharing the common C6-cation intermediate IM-3 with cyclopiane skeleton (Scheme 1A). Conclusion We have unambiguously confirmed the structural revision of spiroviolene with cis-oriented 19- and 20-methyl groups by
Activity assays of NnlA homologs suggest the natural product N-nitroglycine is degraded by diverse bacteria
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 830–840, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.75

- antibiotic activity towards Gram-negative bacteria. An NNG degrading heme enzyme, called NnlA, has recently been discovered in the genome of Variovorax sp. strain JS1663 (Vs NnlA). Evidence is presented that NnlA and therefore, NNG degradation activity is widespread. To achieve this objective, we
- characterized and tested the NNG degradation activity of five Vs NnlA homologs originating from bacteria spanning several classes and isolated from geographically distinct locations. E. coli transformants containing all five homologs converted NNG to nitrite. Four of these five homologs were isolated and
- NnlA cannot degrade the NNG analog 2-nitroaminoethanol. The combined data strongly suggest that NnlA enzymes specifically degrade NNG and are found in diverse bacteria and environments. These results imply that NNG is also produced in diverse environments and NnlA may act as a detoxification enzyme to
Discovery and biosynthesis of bacterial drimane-type sesquiterpenoids from Streptomyces clavuligerus
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 815–822, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.73
- University, Nanjing 211198, China 10.3762/bjoc.20.73 Abstract Drimane-type sesquiterpenoids (DMTs) are characterized by a distinctive 6/6 bicyclic skeleton comprising the A and B rings. While DMTs are commonly found in fungi and plants, their presence in bacteria has not been reported. Moreover, the
- analogs. This discovery not only broadens the known chemical diversity of DMTs from bacteria, but also provides new insights into DMT biosynthesis in bacteria. Keywords: bacterial terpenoid; cytochrome P450s; drimane-type sesquiterpenoid; Streptomyces clavuligerus; terpenoid biosynthesis; Introduction
- associated with DMT biosynthesis have been identified in bacteria, the corresponding natural DMTs have not been discovered [17]. In this study, we isolated and characterized three drimenol congeners (2–4) from Streptomyces clavuligerus (Figure 2a). In the genome of S. clavuligerus, we identified a cav
Methodology for awakening the potential secondary metabolic capacity in actinomycetes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 753–766, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.69

- Zeeck and co-workers in the early 2000s, is a method in which the target bacteria are cultured under various conditions (medium composition, temperature, pH, oxygen supply, light quality and quantity, addition of precursors and enzyme inhibitors, etc.) and all metabolites obtained from them are analyzed
- in the genetically programmed death of the producing organism. In addition, Nishiyama et al. suggested that actinorhodin (8) produced by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) functions as an organocatalyst to kill bacteria by catalyzing the production of toxic levels of H2O2 [99]. They also suggested that
- Streptomyces and mycolic acid-containing bacteria (MACB) activates secondary metabolism [111]. In their method, direct attachment by live MACB cells is thought to alter secondary metabolism in the Streptomyces cells [112]. Using this method, Onaka et al. identified a variety of new compounds, such as
Research progress on the pharmacological activity, biosynthetic pathways, and biosynthesis of crocins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 741–752, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.68
- efficacious in preventing macular degeneration, cataracts, and cardiovascular diseases [83]. Many microorganisms, such as bacteria, cyanobacteria, and microalgae, can also produce 7 [84]. The biosynthesis of 7 in bacteria is analogous to that in plants. The difference is that in bacteria, 7 is formed through
Substrate specificity of a ketosynthase domain involved in bacillaene biosynthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 734–740, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.67
- organism shares the same habitat with the predator Myxococcus xanthus that feeds on other bacteria including B. subtilis, and bacillaene is the primary factor conferring B. subtilis cells resistance to predation by M. xanthus [8]. The identification of its biosynthetic gene cluster (bae) revealed that the
Genome mining of labdane-related diterpenoids: Discovery of the two-enzyme pathway leading to (−)-sandaracopimaradiene in the fungus Arthrinium sacchari
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 714–720, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.65
- catalyzes these reactions is also known [7]. Bacteria also use two enzyme systems for the biosynthesis of LRDs, but the domain organization of the corresponding TCs is different from those of plant enzymes. In bacteria, the class II enzymes with βγ domains and the class I enzyme with a single α domain are
New variochelins from soil-isolated Variovorax sp. H002
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 692–700, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.63
- fatty acyl groups. Furthermore, the variochelin biosynthetic gene cluster was identified through draft genome sequencing and gene knockout experiments. Compounds 1–5 exhibited antimicrobial activities against Gram-negative bacteria, including several soil-isolated plant pathogens. Keywords
- development across several conditions, such as increased levels of auxin plant hormone (IAA) [6] and reduced ethylene levels [7]. They also play a crucial ecological role in the degradation of environmentally harmful pollutants [8][9][10]. Moreover, these bacteria produce unique photoreactive siderophores
- draft genome sequence of the H002 strain identified the variochelin biosynthetic gene cluster (var), which encodes PKS (polyketide synthase) and NRPS (non-ribosomal peptide synthetase) genes. Finally, the siderophores isolated in this study exhibited antibacterial activity against several bacteria
Chemical and biosynthetic potential of Penicillium shentong XL-F41
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 597–606, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.52
- −1; for 1H NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) and 13C NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) spectral data, see Table 1; LC–MS (m/z): [M − H]− calcd for 283.2; found, 283.2. Antimicrobial activity evaluation All isolated compounds were dissolved in 1% DMSO and introduced to pathogenic bacteria or fungi in LB or PDB media. The 96
Synthesis and biological profile of 2,3-dihydro[1,3]thiazolo[4,5-b]pyridines, a novel class of acyl-ACP thioesterase inhibitors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 540–551, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.46
- A protein was expressed in E. coli BL21Star(DE3) cells. 5 mL of an overnight culture of E. coli cells grown in LB medium with 100 µg/mL carbenicillin were used to inoculate 0.5 L of autoinduction medium containing 100 µg/mL carbenicillin [28]. The bacteria were grown at 37 °C and 120 rpm for about
- 4.5 h to reach OD600 = 0.6 and then further cultivated at 21 °C overnight. The bacteria were harvested by centrifugation (20 min, 6,000g) and stored frozen at −80 °C. LpFAT A protein was purified using the Ni-NTA Fast Start Kit (Qiagen GmbH, Germany) according to the instructions of the manufacturer
A new analog of dihydroxybenzoic acid from Saccharopolyspora sp. KR21-0001
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 497–503, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.44
- the presence of a new compound designated KR21-0001A (1). The structure was elucidated by NMR, and the absolute stereochemistry was determined by advanced Marfey’s method. The results indicated that 1 is a new analog of dihydroxybenzoic acid. 1 has no antimicrobial activity against bacteria and fungi
- but showed potent antioxidant activity. Keywords: antioxidant activity; dihydroxybenzoic acid analog; rare actinomycetes; Introduction Actinomycetes are Gram-positive bacteria with high GC content in their genome. They are well-known as the main producers of bioactive compounds such as antibiotic
- ). Antioxidant activity of 1 was measured via the DPPH radical. 1 showed potent DPPH radical scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 5.0 μg·mL−1, which is lower than that of trolox (IC50; 7.5 μg·mL−1) (Table 2). In contrast, 1 did not show antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria
Pseudallenes A and B, new sulfur-containing ovalicin sesquiterpenoid derivatives with antimicrobial activity from the deep-sea cold seep sediment-derived fungus Pseudallescheria boydii CS-793
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 470–478, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.42

- –3 were tested against seven human- and marine-derived aquatic pathogenetic bacteria (Edwardsiella tarda, Escherichia coli, Micrococcus luteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Vibrio anguillarum, Vibrio harveyi, and Vibrio vulnificus), and six plant pathogenic fungi (Alternaria brassicae, Colletotrichum
- pathogenic bacteria (Escherichia coli QDIO-1 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa QDIO-4) and aquatic pathogens (Edwardsiella tarda QDIO-2, Micrococcus luteus QDIO-3, V. anguillarum QDIO-6, Vibrio harveyi QDIO-7, and V. vulnificus QDIO-10), as well as plant pathogenic fungi (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides QDAU-2
- , the bacteria were cultivated in the LB broth medium at 37 °C for the human pathogenic bacteria, while the temperature was 28 °C for the aquatic pathogens, and they were prepared at a concentration of 1.5 × 108 CFU/mL. Tested compounds and positive control (chloramphenicol) were dissolved in DMSO to
Development of a chemical scaffold for inhibiting nonribosomal peptide synthetases in live bacterial cells
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 445–451, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.39
- ]. Moreover, the intracellular concentrations of a series of AMS derivatives in Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Mycobacterium smegmatis have been investigated by Tan et al., demonstrating non-obvious correlations between the chemical structure and permeability among various bacteria, owing to the
Green and sustainable approaches for the Friedel–Crafts reaction between aldehydes and indoles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 379–426, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.36
- clinical trials as neuroprotective agents, presenting an attractive alternative to traditional anti-inflammatory and anti-Parkinson’s disease drugs [7]. With the increased drug resistance of bacteria to modern medicine, BIMs have emerged as an interesting alternative, due to their antibacterial and
- antiviral properties. BIMs function as selective antibacterial agents against several virulent Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains, which can cause many gut and urinary tract infections. They act by damaging DNA molecules and inhibiting their replication in bacteria, while also targeting the proteins that
Elucidating the glycan-binding specificity and structure of Cucumis melo agglutinin, a new R-type lectin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 306–320, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.31

- in bacteria as well as the oxidative environment of the secretory pathway, as CMA1 exhibits predicted disulfide bridges. A single step of His-tag affinity chromatography was sufficient to yield protein of adequate purity and good yield (≈15 mg of eluted protein from 800 mL of cell culture, Figure 1c
- from the expression of CMA1 protein in CHO-S cells. Note the smeared band indicating the presence of glycosylation. (d) Recombinant expression of CMA1 in bacteria. SDS-PAGE gels of the His-tag affinity chromatography and cation exchange chromatography from the expression of CMA1 protein in E. coli BL21
- measure its ability to agglutinate erythrocytes, compared to other lectins, such as AAL, ConA, RCA1, and SNA-I, as well as a PBS negative control. (b, c) Thermal shift assay. After comparing the melting curves of CMA1 produced in mammalian cells (CHO-S) and bacteria (E. coli), we incubated the bacterially
Photochromic derivatives of indigo: historical overview of development, challenges and applications
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 228–242, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.23

- (Figure 14). Indirubin (26) is a purple colored dye that can be found in Isatis tinctoria and Indigofera tinctoria plants along with indigo and its derivatives or can be obtained as a metabolism product of some bacteria [68]. Given to the wide range of biological activities, including anticancer and anti
Optimizations of lipid II synthesis: an essential glycolipid precursor in bacterial cell wall synthesis and a validated antibiotic target
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 220–227, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.22
- bacteria. Accessing this valuable cell wall precursor is important both for studying cell wall synthesis and for studying/identifying novel antimicrobial compounds. Herein, we describe optimizations to the modular chemical synthesis of lipid II and unnatural analogues. In particular, the glycosylation step
- study the mechanism of action of antimicrobial peptides that kill bacteria through binding to these polyprenyls [21][28][29][30][31][32][33][34]. Lipid II has been of particular interest, and during our synthesis of multiple different lipid II analogues, we have developed several optimizations, which we
Synthetic approach to 2-alkyl-4-quinolones and 2-alkyl-4-quinolone-3-carboxamides based on common β-keto amide precursors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1804–1810, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.132
- most prominent examples in this regard are the fluoroquinolone antimicrobials [3] – a remarkably successful drug class, used to treat bacterial infections caused by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [4]. Other notable 4-quinolones of synthetic origin are ivacaftor [5] and elvitegravir [6
- great research interest, with many reviews published in the recent years [20][21][22]. Some of the compounds are known to act as antibiotics [23][24][25][26], while others function as quorum-sensing signal molecules which regulate the production and release of virulence factors in bacteria, thus helping
Synthesis and biological evaluation of Argemone mexicana-inspired antimicrobials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1511–1524, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.108
- (five Gram-positive and four Gram-negative bacteria, and three fungi). Additionally, the crystal structures of two berberine variants are described. Several berberine variants show enhanced antibacterial activity compared to the unaltered plant-derived molecule. We also report promising preliminary
- concern, antimicrobial-resistant microbes are also a threat to the health of the individuals on the international space station (ISS). According to recent studies, a diverse population of bacteria and fungi, including several opportunistic pathogens, have colonized the ISS [5], and many of these strains
- explored screening methanol and hexane extracts of various parts of the A. mexicana plant (seeds, leaves, inner vs outer roots) for biological activity with the outer root methanol extract showing the highest activity against Gram-positive bacteria as well as inhibitory effects against human colon cancer
Functional characterisation of twelve terpene synthases from actinobacteria
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1386–1398, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.100
- structures were elucidated by NMR spectroscopy, resulting in the discovery of the first terpene synthases for (+)-δ-cadinol and (+)-α-cadinene, besides the first two bacterial (−)-amorpha-4,11-diene synthases. For other terpene synthases with functions reported from bacteria before the products were
- bacterial terpene synthases have been identified [11], including enzymes for the non-canonical compounds geosmin (7) [12] and 2-methylisoborneol (8) [13]. Recent developments also revealed the presence of sesterterpene synthases in bacteria exemplified by the enzymes for sesterviridene (9) in Kitasatospora
- recently identified in which sesquiterpenes from bacteria showed an enantiomeric relationship to plant compounds [36]. The enzyme from K. kofuensis represents the first terpene synthase for the biosynthesis of 10 and was thus identified as Kutzneria kofuensis (+)-δ-Cadinol Synthase (KkdCS). A few closely
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- correspond, for instance, to biosynthesized intermediates (e.g., 1-O-alkyl-glycerol-3-phosphate [4], lyso-PAF [5]) or neutral ether lipids (e.g., diacyl ether glycerol [6]). Ether glycerolipids are present in mammalian but also in anaerobic bacteria [7], archea (with an inverted stereochemistry at the sn-2
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
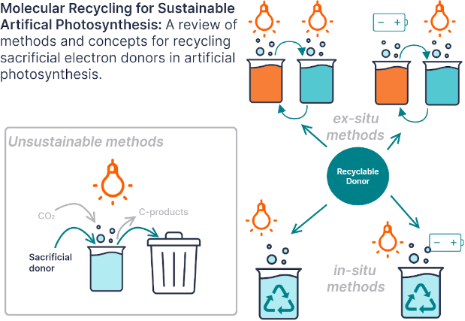
- body of work using simple alcohols as a proton and electron source in electrochemical hydrogenations [43]. This could also evolve into an extension of artificial photosynthesis if the alcohols used as donors are generated by artificial or natural photosynthesis (i.e., photosynthetic bacteria). NADH and
Two new lanostanoid glycosides isolated from a Kenyan polypore Fomitopsis carnea
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1161–1169, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.84
- , compound 2 was identified as 2α-hydroxy,3α-[(3′S)-4′-carboxyl-3′-hydroxy-3′-methylbutanoyloxy]lanosta-8,24(31)-dien-21-oic acid 21-O-β-ᴅ-glucopyranoside that was named as forpinioside C. Biological activities Compounds 1–4 were tested for their antimicrobial effects against fungi and bacteria; where
- compound 1 was moderately active against the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus at MIC values of 8.3 µg/mL and 16.6 µg/mL, respectively. The antagonism of 1 against B. subtilis and S. aureus was compared to the positive controls oxytetracycline and gentamycin, with MICs
- 128: HRESIMS profiles and NMR spectroscopic data of 1, 2 and 4 in CD3OD, and of 3 in (CD3)2S=O; half inhibitory concentrations (IC50) for various mammalian cell lines as well as minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of 1–4 for bacteria, yeasts and filamentous fungi. Acknowledgements The technical
Intermediates and shunt products of massiliachelin biosynthesis in Massilia sp. NR 4-1
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 909–917, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.69
- biosynthetic intermediates or shunt products of massiliachelin. Their bioactivity was tested against one Gram-positive and three Gram-negative bacteria. Keywords: Massilia; massiliachelin; siderophore; structure elucidation; Introduction Iron is crucial for many important biological processes, such as
- +) [1]. To maintain iron homeostasis, all living organisms need to regulate the intake of this essential element from the environment. In bacteria, this is typically achieved through the use of siderophores [2], which are small molecules that are secreted under iron-limiting conditions to solubilize and
- Burkholderia gladioli, which possesses an unprecedented citrate-derived fatty acid moiety [11]. Furthermore, lipopeptide siderophores with photocleavable moieties, like taiwachelin, were reported from bacteria of the genera Cupriavidus and Variovorax [12][13][14]. The β-proteobacterial genus Massilia was
Cyclodextrins as building blocks for new materials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 889–891, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.66

- infection (Ad26.COV2.S) was also a milestone for CD research and has served as a large-scale safety test for 2-(hydroxypropyl)-β-CD (HP-β-CD). CDs have also been used to functionalize face mask textiles to block and inactivate bacteria and viruses [7]. Apart from the COVID-19 pandemic, CDs are well































































































































































































































































































































