Search results
Search for "chlorinated solvents" in Full Text gives 37 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Thiazolidinones: novel insights from microwave synthesis, computational studies, and potentially bioactive hybrids
- Luan A. Martinho,
- Victor H. J. G. Praciano,
- Guilherme D. R. Matos,
- Claudia C. Gatto and
- Carlos Kleber Z. Andrade
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2618–2636, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.203
- greater charge separation in the excited state, which is more stabilized in polar solvents, typical of compounds that undergo an ICT upon excitation [86]. The use of EtOAc showed a hypochromic effect with a decrease in fluorescence emission. Similar results for chlorinated solvents (CH2Cl2, CHCl3) were
- solvents (MeOH, H2O) whereas lower values were recorded for chlorinated solvents (CH2Cl2, CHCl3). This trend matches with the Lippert–Mataga plots generated for these compounds to verify the relationship between the large values of Stokes shifts and the Reichardt polarity parameters. The graphs shown in

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Structure of thiazolidinone derivatives.

Figure 2: Selected examples of commercial drugs containing the thiazolidinone core.

Scheme 1: Multicomponent reaction of benzaldehyde, rhodanine, and piperidine in ethanol leading directly to a...

Scheme 2: Substrate scope of the EDA-catalyzed Knoevenagel condensation reactions using a range of aromatic/h...

Scheme 3: Limitations of the EDA-catalyzed Knoevenagel reactions for the synthesis of rhodanine or thiazolidi...

Scheme 4: Plausible reaction mechanism for the EDA-catalyzed Knoevenagel condensation reactions.

Scheme 5: Substrate scope of the HPW-catalyzed GBB reactions.

Scheme 6: Synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-thiazolidinone hybrids by EDA-catalyzed Knoevenagel condensatio...

Figure 3: Overlay of predicted (red) and experimental (black) NMR spectra for compound 3n: a) 1H NMR spectra ...

Figure 4: a) Molecular structure of 3n with crystallographic labeling (50% probability displacement). b) Pers...

Scheme 7: a) Tautomeric forms of thiazolidinones and b) resonance structures for compounds 3n and 4n.

Figure 5: Molecular energy as a function of the torsion angle obtained from a relaxed dihedral scan at the M0...

Figure 6: Identification of the carbon atoms used in the theoretical study of chemical shifts. In red, easily...

Figure 7: a) Visual impressions of the solvatochromic study in various solvents (10−5 M) after excitation wit...

Scheme 8: Proposed ICT-type mechanism for the fluorescence process, adapted from ref. [89].

Figure 8: Photophysical study in aqueous solution under different pH values for compound 3n (10−5 M) at room ...

Scheme 9: Two equilibria of compound 3n in aqueous solutions, adapted from ref. [92,93].

Figure 9: Molecular fragments associated with intramolecular charge transfer states.

Figure 10: Frontier molecular orbitals of compounds 3n and 4n in three different states: protonated, deprotona...
The high potential of methyl laurate as a recyclable competitor to conventional toxic solvents in [3 + 2] cycloaddition reactions
- Ayhan Yıldırım and
- Mustafa Göker
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2389–2415, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.184
- ) has led to limitations on the use of chlorinated solvents, toluene, DMF etc., with the implementation of particular prerequisites [89]. The double bond present in oleic acid and methyl oleate may be disadvantageous for these solvents in comparison to methyl laurate. The potential isomerization and

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Versatile compounds via cycloaddition reactions.

Scheme 1: Molecular structures of parent compounds 1a–f, 2a–d and cycloadducts 3a–u.

Figure 2: a) Radar view of the physical properties of methyl laurate. b) Oral toxicity values of methyl laura...

Figure 3: The oral toxicity values of all the solvents utilized in the present study obtained with ProTox 3.0....

Figure 4: Ecological, environmental risk assessments, pesticide similarity and biodegradability assessments o...

Figure 5: Ecological, environmental risk assessments, pesticide similarity and biodegradability assessments o...

Figure 6: Ecological, environmental risk assessments, pesticide similarity and biodegradability assessments o...

Figure 7: Various toxicity parameters of methyl laurate and a series of other solvents calculated by ADMETLab...

Figure 8: a) Visualization of the localization of conventional organic and bio-based solvents in the Hansen s...

Figure 9: Vapour pressures of the solvents used (values retrieved from the Chemeo molecular database).

Scheme 2: Endo and exo stereoisomeric approaches of nitrone 1a and maleimide 2a in [3 + 2] cycloaddition reac...

Figure 10: Signals of protons used in the calculation of the diastereomeric ratios (cis/trans) of cycloadditio...

Figure 11: Results of studies on the recovery of solvents used in the reaction.

Figure 12: Simplified scheme describing the reaction monitoring and solvent recovery.

Figure 13: a) The superimposed spectra of C,N-diphenylnitrone and N-phenylmaleimide. b) The spectrum of methyl...
Photochemical reduction of acylimidazolium salts
- Michael Jakob,
- Nick Bechler,
- Hassan Abdelwahab,
- Fabian Weber,
- Janos Wasternack,
- Leonardo Kleebauer,
- Jan P. Götze and
- Matthew N. Hopkinson
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1973–1983, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.153
- , switching from MeCN to the chlorinated solvents DCM, DCE and chlorobenzene led to a decline in the formation of the fully reduced product 2 with O-benzoylated species 3 being obtained as the major product (38% in DCM, 35% in DCE, 38% in PhCl cf. 6–8% of 2, Table 1, entries 10–12). Significant reduction of 1

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: (a) Combining N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalysis with photoredox catalysis for radical–ra...

Figure 2: Initial test reaction employing [Ir(dF(CF3)ppy)2(dtbpy)]PF6 as a photocatalyst in the presence of D...

Scheme 1: Plausible mechanism for the photocatalytic reduction of benzoylimidazolium salt 1 with DIPEA. [PC] ...

Scheme 2: Plausible mechanism for the photocatalyst-free reduction of benzoylimidazolium salt 1 into O-benzoy...

Figure 3: Reduction of 2-benzoylimidazolium triflate (1) under photocatalyst-free conditions monitored over 4...

Scheme 3: (a) Reduction of 2-benzoylimidazolium triflate (1) under photocatalyst-free conditions with DIPEA a...
Oxetanes: formation, reactivity and total syntheses of natural products
- Peter Gabko,
- Martin Kalník and
- Maroš Bella
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1324–1373, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.101
- chlorides (Scheme 11a) [44]. The authors found that the secondary alcohol precursors were less reactive and that best results were obtained at low temperature (≤−50 °C) and in chlorinated solvents. The synthesis of these cages was later revisited by Le Drian et al. in 2011 who studied a Lewis acid-catalysed

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Bond lengths and bond angles in oxetane at 140 K [2].

Figure 2: Analogy of 3-substituted oxetanes to carbonyl and gem-dimethyl groups [12].

Figure 3: Use of oxetanes in drug design – selected examples.

Figure 4: Examples of oxetane-containing natural products.

Scheme 1: Synthetic strategies towards construction of the oxetane ring.

Scheme 2: Overview of intramolecular Williamson etherification and competing Grob fragmentation.

Scheme 3: Synthesis of spiro-oxetanes via 1,4-C–H insertion and Williamson etherification.

Scheme 4: Use of phenyl vinyl selenone in the synthesis of spirooxindole oxetanes.

Scheme 5: Synthesis of bicyclic 3,5-anhydrofuranoses via double epoxide opening/etherification.

Scheme 6: Preparation of spirooxetanes by cycloisomerisation via MHAT/RPC.

Scheme 7: Oxetane synthesis via alcohol C–H functionalisation.

Scheme 8: Access to oxetanes 38 from α-acetyloxy iodides.

Scheme 9: The kilogram-scale synthesis of oxetane intermediate 41.

Scheme 10: Overview of the intramolecular opening of 3-membered rings.

Scheme 11: Synthesis of 4,7-dioxatricyclo[3.2.1.03,6]octane skeletons.

Scheme 12: Silicon-directed electrophilic cyclisation of homoallylic alcohols.

Scheme 13: Hydrosilylation–iodocyclisation of homopropargylic alcohols.

Scheme 14: Cu-catalysed intramolecular O-vinylation of γ-bromohomoallylic alcohols.

Scheme 15: Cu-catalysed intramolecular cross-coupling of hydroxyvinylstannanes.

Scheme 16: Isomerisation of oxiranyl ethers containing weakly carbanion-stabilising groups.

Scheme 17: Cyclisation of diethyl haloalkoxymalonates.

Scheme 18: Synthesis of oxetanes through a 1,5-HAT/radical recombination sequence.

Scheme 19: General approach to oxetanes via [2 + 2] cycloadditions.

Scheme 20: Synthesis of tricyclic 4:4:4 oxetanes through a photochemical triple cascade reaction.

Scheme 21: Iridium-catalysed Paternò–Büchi reaction between α-ketoesters and simple alkenes.

Scheme 22: Three-step synthesis of spirocyclic oxetanes 83 via Paternò–Büchi reaction, nucleophilic ring openi...

Scheme 23: Enantioselective Paternò–Büchi reaction catalysed by a chiral iridium photocatalyst.

Scheme 24: Synthesis of polysubstituted oxetanes 92 via Cu(II)-mediated formal [2 + 2] cycloadditions.

Scheme 25: Synthesis of alkylideneoxetanes via NHC- and DBU-mediated formal [2 + 2] cycloadditions.

Scheme 26: Use of sulphur-stabilised carbanions in ring expansions.

Scheme 27: Synthesis of α,α-difluoro(arylthio)methyl oxetanes.

Scheme 28: Ring expansion in an industrial synthesis of PF-06878031.

Scheme 29: Ring contraction of triflated 2-hydroxy-γ-lactones.

Scheme 30: Ring contraction in an industrial synthesis of PF-06878031.

Scheme 31: Photochemical ring contraction of 2,5-dihydrofurans by aryldiazoacetic acid esters.

Scheme 32: Synthesis of 3-oxetanones via O-H insertion of carbenes.

Scheme 33: Synthesis of phosphonate oxetanones via gold-mediated alkyne oxidation/O–H insertion.

Scheme 34: Syntheses and common derivatisations of 3-oxetanone.

Scheme 35: SN1 substitution of 3-aryloxetan-3-ols by thiols and alcohols.

Scheme 36: Fe–Ni dual-catalytic olefin hydroarylation towards 3-alkyl-3-(hetero)aryloxetanes.

Scheme 37: Synthesis of 3-aryloxetan-3-carboxylic acids.

Scheme 38: Decarboxylative alkylation of 3-aryloxetan-3-carboxylic acids.

Scheme 39: Synthesis of 3-amino-3-aryloxetanes via photoredox/nickel cross-coupling catalysis.

Scheme 40: Intermolecular cross-selective [2 + 2] photocycloaddition towards spirooxetanes.

Scheme 41: Synthesis of 3-aryl-3-aminooxetanes via defluorosulphonylative coupling.

Scheme 42: Two-step synthesis of amide bioisosteres via benzotriazolyl Mannich adducts 170.

Scheme 43: Functionalisation of oxetanyl trichloroacetimidates 172.

Scheme 44: Synthesis of oxetane-amino esters 176.

Scheme 45: Tandem Friedel–Crafts alkylation/intramolecular ring opening of 3-aryloxetan-3-ols.

Scheme 46: Synthesis of polysubstituted furans and pyrroles.

Scheme 47: Synthesis of oxazolines and bisoxazolines.

Scheme 48: Tandem, one-pot syntheses of various polycyclic heterocycles.

Scheme 49: Synthesis of 1,2-dihydroquinolines via skeletal reorganisation of oxetanes.

Scheme 50: Synthesis of benzoindolines and 2,3-dihydrobenzofurans and their derivatisations.

Scheme 51: Synthesis of polysubstituted 1,4-dioxanes.

Scheme 52: Preparation of various lactones via ring opening of oxetane-carboxylic acids 219.

Scheme 53: Tsuji-Trost allylation/ring opening of 3-aminooxetanes.

Scheme 54: Arylative skeletal rearrangement of 3-vinyloxetan-3-ols to 2,5-dihydrofurans.

Scheme 55: Reductive opening of oxetanes using catalytic Mg–H species.

Scheme 56: Opening of oxetanes by silyl ketene acetals.

Scheme 57: Rhodium-catalysed hydroacylation of oxetanes.

Scheme 58: Generation of radicals from oxetanes mediated by a vitamin B12-derived cobalt catalyst.

Scheme 59: Reductive opening of oxetanes by B–Si frustrated Lewis pairs.

Scheme 60: Zirconocene-mediated reductive opening of oxetanes.

Scheme 61: Enantioselective syntheses of small and medium-size rings using chiral phosphoric acids.

Scheme 62: Asymmetric synthesis of 2,3-dihydrobenzo[b]oxepines catalysed by a chiral scandium complex.

Scheme 63: Enantioselective synthesis of 1,3-bromohydrins under a chiral squaramide catalysis.

Scheme 64: Enantioselective opening of 2-aryl-2-ethynyloxetanes by anilines.

Scheme 65: Ru-catalysed insertion of diazocarbonyls into oxetanes.

Scheme 66: Ring expansion of oxetanes by stabilised carbenes generated under blue light irradiation.

Scheme 67: Expansion of oxetanes via nickel-catalysed insertion of alkynyltrifluoroborates.

Scheme 68: Nickel-catalysed expansion of oxetanes into ε-caprolactones.

Scheme 69: Expansion of oxetanes via cobalt-catalysed carbonyl insertion.

Scheme 70: Gold-catalysed intramolecular 1,1-carboalkoxylation of oxetane-ynamides.

Scheme 71: Expansion of oxetanes by stabilised sulphoxonium ylides.

Scheme 72: Cu-catalysed ring expansion of 2-vinyloxetanes by diazoesters.

Scheme 73: Total synthesis of (+)-oxetin.

Scheme 74: Total synthesis of racemic oxetanocin A.

Scheme 75: Total synthesis of (−)-merrilactone A.

Scheme 76: Total synthesis of (+)-dictyoxetane.

Scheme 77: Total synthesis of ent-dichrocephone B.

Scheme 78: Total synthesis of (−)-mitrephorone A.

Scheme 79: Total synthesis of (−)-taxol.
Recent advances in oxidative radical difunctionalization of N-arylacrylamides enabled by carbon radical reagents
- Jiangfei Chen,
- Yi-Lin Qu,
- Ming Yuan,
- Xiang-Mei Wu,
- Heng-Pei Jiang,
- Ying Fu and
- Shengrong Guo
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1207–1271, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.98
- chlorides exhibiting the highest reactivity (up to 90% yield). Furthermore, simple chlorinated solvents such as CCl4, CHCl3, CDCl3

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: DTBP-mediated oxidative alkylarylation of activated alkenes.

Scheme 2: Iron-catalyzed oxidative 1,2-alkylarylation.

Scheme 3: Possible mechanism for the iron-catalyzed oxidative 1,2-alkylation of activated alkenes.

Scheme 4: A metal-free strategy for synthesizing 3,3-disubstituted oxindoles.

Scheme 5: Iminoxyl radical-promoted cascade oxyalkylation/alkylarylation of alkenes.

Scheme 6: Proposed mechanism for the iminoxyl radical-promoted cascade oxyalkylation/alkylarylation of alkene...

Scheme 7: Bicyclization of 1,n-enynes with alkyl nitriles.

Scheme 8: Possible reaction mechanism for the bicyclization of 1,n-enynes with alkyl nitriles.

Scheme 9: Radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with isocyanides.

Scheme 10: Plausible mechanism for the radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with isocyanides.

Scheme 11: Electrochemical dehydrogenative cyclization of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds.

Scheme 12: Plausible mechanism for the dehydrogenative cyclization of 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds.

Scheme 13: Photocatalyzed cyclization of N-arylacrylamide and N,N-dimethylaniline.

Scheme 14: Proposed mechanism for the photocatalyzed cyclization of N-arylacrylamides and N,N-dimethylanilines....

Scheme 15: Electrochemical monofluoroalkylation cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with dimethyl 2-fluoromalonat...

Scheme 16: Proposed mechanism for the electrochemical radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with dimethyl 2...

Scheme 17: Photoelectrocatalytic carbocyclization of unactivated alkenes using simple malonates.

Scheme 18: Plausible mechanism for the photoelectrocatalytic carbocyclization of unactivated alkenes with simp...

Scheme 19: Bromide-catalyzed electrochemical trifluoromethylation/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides.

Scheme 20: Proposed mechanism for the electrochemical trifluoromethylation/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides.

Scheme 21: Visible light-mediated trifluoromethylarylation of N-arylacrylamides.

Scheme 22: Plausible reaction mechanism for the visible light-mediated trifluoromethylarylation of N-arylacryl...

Scheme 23: Electrochemical difluoroethylation cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with sodium difluoroethylsulfin...

Scheme 24: Electrochemical difluoroethylation cyclization of N-methyacryloyl-N-alkylbenzamides with sodium dif...

Scheme 25: Photoredox-catalyzed radical aryldifluoromethylation of N-arylacrylamides with S-(difluoromethyl)su...

Scheme 26: Proposed mechanism for the photoredox-catalyzed radical aryldifluoromethylation of N-arylacrylamide...

Scheme 27: Visible-light-induced domino difluoroalkylation/cyclization of N-cyanamide alkenes.

Scheme 28: Proposed mechanism of photoredox-catalyzed radical domino difluoroalkylation/cyclization of N-cyana...

Scheme 29: Palladium-catalyzed oxidative difunctionalization of alkenes.

Scheme 30: Two possible mechanisms of palladium-catalyzed oxidative difunctionalization.

Scheme 31: Silver-catalyzed oxidative 1,2-alkyletherification of unactivated alkenes with α-bromoalkylcarbonyl...

Scheme 32: Photochemical radical cascade cyclization of dienes.

Scheme 33: Proposed mechanism for the photochemical radical cascade 6-endo cyclization of dienes with α-carbon...

Scheme 34: Photocatalyzed radical coupling/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides and.

Scheme 35: Photocatalyzed radical-type couplings/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with sulfoxonium ylides.

Scheme 36: Possible mechanism of visible-light-induced radical-type couplings/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides...

Scheme 37: Visible-light-promoted difluoroalkylated oxindoles systhesis via EDA complexes.

Scheme 38: Possible mechanism for the visible-light-promoted radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with bro...

Scheme 39: A dicumyl peroxide-initiated radical cascade reaction of N-arylacrylamide with DCM.

Scheme 40: Possible mechanism of radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with DCM.

Scheme 41: An AIBN-mediated radical cascade reaction of N-arylacrylamides with perfluoroalkyl iodides.

Scheme 42: Possible mechanism for the reaction with perfluoroalkyl iodides.

Scheme 43: Photoinduced palladium-catalyzed radical annulation of N-arylacrylamides with alkyl halides.

Scheme 44: Radical alkylation/cyclization of N-Alkyl-N-methacryloylbenzamides with alkyl halides.

Scheme 45: Possible mechanism for the alkylation/cyclization with unactivated alkyl chlorides.

Scheme 46: Visible-light-driven palladium-catalyzed radical cascade cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with unac...

Scheme 47: NHC-catalyzed radical cascade cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with alkyl bromides.

Scheme 48: Possible mechanism of NHC-catalyzed radical cascade cyclization.

Scheme 49: Electrochemically mediated radical cyclization reaction of N-arylacrylamides with freon-type methan...

Scheme 50: Proposed mechanistic pathway of electrochemically induced radical cyclization reaction.

Scheme 51: Redox-neutral photoinduced radical cascade cylization of N-arylacrylamides with unactivated alkyl c...

Scheme 52: Proposed mechanistic hypothesis of redox-neutral radical cascade cyclization.

Scheme 53: Thiol-mediated photochemical radical cascade cylization of N-arylacrylamides with aryl halides.

Scheme 54: Proposed possible mechanism of thiol-mediated photochemical radical cascade cyclization.

Scheme 55: Visible-light-induced radical cascade bromocyclization of N-arylacrylamides with NBS.

Scheme 56: Possible mechanism of visible-light-induced radical cascade cyclization.

Scheme 57: Decarboxylation/radical C–H functionalization by visible-light photoredox catalysis.

Scheme 58: Plausible mechanism of visible-light photoredox-catalyzed radical cascade cyclization.

Scheme 59: Visible-light-promoted tandem radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with N-(acyloxy)phthalimides....

Scheme 60: Plausible mechanism for the tandem radical cyclization reaction.

Scheme 61: Visible-light-induced aerobic radical cascade alkylation/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with alde...

Scheme 62: Plausible mechanism for the aerobic radical alkylarylation of electron-deficient amides.

Scheme 63: Oxidative decarbonylative [3 + 2]/[5 + 2] annulation of N-arylacrylamide with vinyl acids.

Scheme 64: Plausible mechanism for the decarboxylative (3 + 2)/(5 + 2) annulation between N-arylacrylamides an...

Scheme 65: Rhenium-catalyzed alkylarylation of alkenes with PhI(O2CR)2.

Scheme 66: Plausible mechanism for the rhenium-catalyzed decarboxylative annulation of N-arylacrylamides with ...

Scheme 67: Visible-light-induced one-pot tandem reaction of N-arylacrylamides.

Scheme 68: Plausible mechanism for the visible-light-initiated tandem synthesis of difluoromethylated oxindole...

Scheme 69: Copper-catalyzed redox-neutral cyanoalkylarylation of activated alkenes with cyclobutanone oxime es...

Scheme 70: Plausible mechanism for the copper-catalyzed cyanoalkylarylation of activated alkenes.

Scheme 71: Photoinduced alkyl/aryl radical cascade for the synthesis of quaternary CF3-attached oxindoles.

Scheme 72: Plausible photoinduced electron-transfer (PET) mechanism.

Scheme 73: Photoinduced cerium-mediated decarboxylative alkylation cascade cyclization.

Scheme 74: Plausible reaction mechanism for the decarboxylative radical-cascade alkylation/cyclization.

Scheme 75: Metal-free oxidative tandem coupling of activated alkenes.

Scheme 76: Control experiments and possible mechanism for 1,2-carbonylarylation of alkenes with carbonyl C(sp2...

Scheme 77: Silver-catalyzed acyl-arylation of activated alkenes with α-oxocarboxylic acids.

Scheme 78: Proposed mechanism for the decarboxylative acylarylation of acrylamides.

Scheme 79: Visible-light-mediated tandem acylarylation of olefines with carboxylic acids.

Scheme 80: Proposed mechanism for the radical cascade cyclization with acyl radical via visible-light photored...

Scheme 81: Erythrosine B-catalyzed visible-light photoredox arylation-cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with ar...

Scheme 82: Electrochemical cobalt-catalyzed radical cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with arylhydrazines or po...

Scheme 83: Proposed mechanism of radical cascade cyclization via electrochemical cobalt catalysis.

Scheme 84: Copper-catalyzed oxidative tandem carbamoylation/cyclization of N-arylacrylamides with hydrazinecar...

Scheme 85: Proposed reaction mechanism for the radical cascade cyclization by copper catalysis.

Scheme 86: Visible-light-driven radical cascade cyclization reaction of N-arylacrylamides with α-keto acids.

Scheme 87: Proposed mechanism of visible-light-driven cascade cyclization reaction.

Scheme 88: Peroxide-induced radical carbonylation of N-(2-methylallyl)benzamides with methyl formate.

Scheme 89: Proposed cyclization mechanism of peroxide-induced radical carbonylation with N-(2-methylallyl)benz...

Scheme 90: Persulfate promoted carbamoylation of N-arylacrylamides and N-arylcinnamamides.

Scheme 91: Proposed mechanism for the persulfate promoted radical cascade cyclization reaction of N-arylacryla...

Scheme 92: Photocatalyzed carboacylation with N-arylpropiolamides/N-alkyl acrylamides.

Scheme 93: Plausible mechanism for the photoinduced carboacylation of N-arylpropiolamides/N-alkyl acrylamides.

Scheme 94: Electrochemical Fe-catalyzed radical cyclization with N-arylacrylamides.

Scheme 95: Plausible mechanism for the electrochemical Fe-catalysed radical cyclization of N-phenylacrylamide.

Scheme 96: Substrate scope of the selective functionalization of various α-ketoalkylsilyl peroxides with metha...

Scheme 97: Proposed reaction mechanism for the Fe-catalyzed reaction of alkylsilyl peroxides with methacrylami...

Scheme 98: EDA-complex mediated C(sp2)–C(sp3) cross-coupling of TTs and N-methyl-N-phenylmethacrylamides.

Scheme 99: Proposed mechanism for the synthesis of oxindoles via EDA complex.
SOMOphilic alkyne vs radical-polar crossover approaches: The full story of the azido-alkynylation of alkenes
- Julien Borrel and
- Jerome Waser
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 701–713, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.64
- minimized diazide formation. Next, a solvent screening was performed as it can vastly influence reaction proceeding via a carbocation intermediate. Alkynyltrifluoroborates have a low solubility in chlorinated solvents but are well soluble in acetonitrile. Although this solvent has been used in similar

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Overview of homopropargylic azides importance and strategies for azido-alkynylation.

Scheme 2: Screening of nucleophilic alkynes and investigation of the photocatalyst solubility. n.o = not obse...

Scheme 3: Selected scope entries of the azido-alkynylation. The data were already published in ref. [45].

Scheme 4: Unsuccessful examples. The conditions used are the same as in Scheme 3. The yields reported were determined...

Scheme 5: Proposed mechanism.
Application of N-heterocyclic carbene–Cu(I) complexes as catalysts in organic synthesis: a review
- Nosheen Beig,
- Varsha Goyal and
- Raj K. Bansal
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1408–1442, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.102
- ). The complexes were obtained in high yields (>95%). The copper complexes were air and moisture-stable as solids but decomposed in chlorinated solvents after several days. It may be mentioned that Cu(I) halide and pseudohalide complexes with NHCs Me2L, Et2L and AdL were prepared from direct reaction of

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: In situ generation of imidazolylidene carbene.

Scheme 2: Hg(II) complex of NHC.

Scheme 3: Isolable and bottlable carbene reported by Arduengo [3].

Scheme 4: First air-stable carbene synthesized by Arduengo in 1992 [5].

Figure 1: General structure of an NHC.

Figure 2: Stabilization of an NHC by donation of the lone pair electrons into the vacant p-orbital (LUMO) at ...

Figure 3: Abnormal NHC reported by Bertrand [8,9].

Figure 4: Cu(d) orbital to σ*C-N(NHC) interactions in NHC–CuX complexes computed at the B3LYP/def2-SVP level ...

Figure 5: Molecular orbital contributions to the NHC–metal bond.

Scheme 5: Synthesis of NHC–Cu(I) complexes by deprotonation of NHC precursors with a base.

Scheme 6: Synthesis of [NHC–CuX] complexes.

Scheme 7: Synthesis of [(ICy)CuX] and [(It-Bu)CuX] complexes.

Scheme 8: Synthesis of iodido-bridged copper–NHC complexes by deprotonation of benzimidazolium salts reported...

Scheme 9: Synthesis of copper complexes by deprotonation of triazolium salts.

Scheme 10: Synthesis of thiazolylidene–Cu(I) complex by deprotonation with KOt-Bu.

Scheme 11: Preparation of NHC–Cu(I) complexes.

Scheme 12: Synthesis of methylmalonic acid-derived anionic [(26a,b)CuCl]Li(THF)2 and zwitterionic (28) heterol...

Scheme 13: Synthesis of diaminocarbene and diamidocarbene (DAC)–Cu(I) complexes.

Scheme 14: Synthesis of the cationic (NHC)2Cu(I) complex 39 from benzimidazolium salts 38 with tetrakis(aceton...

Scheme 15: Synthesis of NHC and ADC (acyclic diamino carbenes) Cu(I) hexamethyldisilazide complexes reported b...

Scheme 16: Synthesis of NHC–copper(I) complexes using an acetylacetonate-functionalized imidazolium zwitterion...

Scheme 17: Synthesis of NHC–Cu(I) complexes through deprotonation of azolium salts with Cu2O.

Scheme 18: Synthesis of NHC–CuBr complex through deprotonation with Cu2O reported by Kolychev [31].

Scheme 19: Synthesis of chiral NHC–CuBr complexes from phenoxyimine-imidazolium salts reported by Douthwaite a...

Scheme 20: Preparation of linear neutral NHC–CuCl complexes through the use of Cu2O. For abbreviations, please...

Scheme 21: Synthesis of abnormal-NHC–copper(I) complexes by Bertrand, Cazin and co-workers [35].

Scheme 22: Microwave-assisted synthesis of thiazolylidene/benzothiazolylidene–CuBr complexes by Bansal and co-...

Scheme 23: Synthesis of NHC–CuX complexes through transmetallation.

Scheme 24: Preparation of six- or seven-membered NHC–Cu(I) complexes through transmetalation from Ag(I) comple...

Scheme 25: Synthesis of 1,2,3-triazolylidene–CuCl complexes through transmetallation of Ag(I) complexes genera...

Scheme 26: Synthesis of NHC–copper complexes having both Cu(I) and Cu(II) units through transmetalation report...

Scheme 27: Synthesis of new [(IPr(CH2)3Si(OiPr)3)CuX] complexes and anchoring on MCM-41.

Scheme 28: Synthesis of bis(trimethylsilyl)phosphide–Cu(I)–NHC complexes through ligand displacement.

Scheme 29: Synthesis of silyl- and stannyl [(NHC)Cu−ER3] complexes.

Scheme 30: Synthesis of amido-, phenolato-, thiophenolato–Cu(NHC) complexes.

Scheme 31: Synthesis of first isolable NHC–Cu–difluoromethyl complexes reported by Sanford et al. [44].

Scheme 32: Synthesis of NHC–Cu(I)–bifluoride complexes reported by Riant, Leyssens and co-workers [45].

Scheme 33: Conjugate addition of Et2Zn to enones catalyzed by an NHC–Cu(I) complex reported by Woodward in 200...

Scheme 34: Hydrosilylation of a carbonyl group.

Scheme 35: NHC–Cu(I)-catalyzed hydrosilylation of ketones reported by Nolan et al. [48,49].

Scheme 36: Application of chiral NHC–CuCl complex 104 for the enantioselective hydrosilylation of ketones.

Scheme 37: Hydrosilylation reactions catalyzed by NHC–Cu(Ot-Bu) complexes.

Scheme 38: NHC–CuCl catalyzed carbonylative silylation of alkyl halides.

Scheme 39: Nucleophilic conjugate addition to an activated C=C bond.

Figure 6: Molecular electrostatic potential maps (MESP) of two NHC–CuX complexes computed at the B3LYP/def2-S...

Scheme 40: Conjugate addition of Grignard reagents to 3-alkyl-substituted cyclohexenones catalyzed by a chiral...

Scheme 41: NHC–copper complex-catalyzed conjugate addition of Grignard reagent to 3-substituted hexenone repor...

Scheme 42: Conjugate addition or organoaluminum reagents to β-substituted cyclic enones.

Scheme 43: Conjugate addition of boronates to acyclic α,β-unsaturated carboxylic esters, ketones, and thioeste...

Scheme 44: NHC–Cu(I)-catalyzed hydroboration of an allene reported by Hoveyda [63].

Scheme 45: Conjugate addition of Et2Zn to cyclohexenone catalyzed by NHC–Cu(I) complex derived from benzimidaz...

Scheme 46: Asymmetric conjugate addition of diethylzinc to 3-nonen-2-one catalyzed by NHC–Cu complexes derived...

Scheme 47: General scheme of a [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction.

Scheme 48: [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of azides with alkynes catalyzed by NHC–Cu(I) complexes reported by Diez-Gonz...

Scheme 49: Application of NHC–CuCl/N-donor combination to catalyze the [3 + 2] cycloaddition of benzyl azide w...

Scheme 50: [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of azides with acetylenes catalyzed by bis(NHC)–Cu complex 131 and mixed NHC–...

Figure 7: NHC–CuCl complex 133 as catalyst for the [3 + 2] cycloaddition of alkynes with azides at room tempe...

Scheme 51: [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of a bulky azide with an alkynylpyridine using [(NHC)Cu(μ-I)2Cu(NHC)] copper ...

Scheme 52: [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of benzyl azide with phenylacetylene under homogeneous and heterogeneous cata...

Scheme 53: [3 + 2] Cycloaddition of benzyl azide with acetylenes catalyzed by bisthiazolylidene dicopper(I) co...

Figure 8: Copper (I)–NHC linear coordination polymer 137 and its conversion into tetranuclear (138) and dinuc...

Scheme 54: An A3 reaction.

Scheme 55: Synthesis of SiO2-immobilized NHC–Cu(I) catalyst 141 and its application in the A3-coupling reactio...

Scheme 56: Preparation of dual-purpose Ru@SiO2–[(NHC)CuCl] catalyst system 142 developed by Bordet, Leitner an...

Scheme 57: Application of the catalyst system Ru@SiO2–[Cu(NHC)] 142 to the one-pot tandem A3 reaction and hydr...

Scheme 58: A3 reaction of phenylacetylene with secondary amines and aldehydes catalyzed by benzothiazolylidene...

Figure 9: Kohn–Sham HOMOs of phenylacetylene and NHC–Cu(I)–phenylacetylene complex computed at the B3LYP/def2...

Figure 10: Energies of the FMOs of phenylacetylene, iminium ion, and NHC–Cu(I)–phenylacetylene complex compute...

Scheme 59: NHC–Cu(I) catalyzed diboration of ketones 147 by reacting with bis(pinacolato)diboron (148) reporte...

Scheme 60: Protoboration of terminal allenes catalyzed by NHC–Cu(I) complexes reported by Hoveyda and co-worke...

Scheme 61: NHC–CuCl-catalyzed borylation of α-alkoxyallenes to give 2-boryl-1,3-butadienes.

Scheme 62: Regioselective hydroborylation of propargylic alcohols and ethers catalyzed by NHC–CuCl complexes 1...

Scheme 63: NHC–CuOt-Bu-catalyzed semihydrogenation and hydroborylation of alkynes.

Scheme 64: Enantioselective NHC–Cu(I)-catalyzed hydroborations of 1,1-disubstituted aryl olefins reported by H...

Scheme 65: Enantioselective NHC–Cu(I)-catalyzed hydroboration of exocyclic 1,1-disubstituted alkenes reported ...

Scheme 66: Markovnikov-selective NHC–CuOH-catalyzed hydroboration of alkenes and alkynes reported by Jones et ...

Scheme 67: Dehydrogenative borylation and silylation of styrenes catalyzed by NHC–CuOt-Bu complexes developed ...

Scheme 68: N–H/C(sp2)–H carboxylation catalyzed by NHC–CuOH complexes.

Scheme 69: C–H Carboxylation of benzoxazole and benzothiazole derivatives with CO2 using a 1,2,3-triazol-5-yli...

Scheme 70: Use of Cu(I) complex derived from diethylene glycol-functionalized imidazo[1,5,a] pyridin-3-ylidene...

Scheme 71: Allylation and alkenylation of polyfluoroarenes and heteroarenes catalyzed by NHC–Cu(I) complexes r...

Scheme 72: Enantioselective C(sp2)–H allylation of (benz)oxazoles and benzothiazoles with γ,γ-disubstituted pr...

Scheme 73: C(sp2)–H arylation of arenes catalyzed by dual NHC–Cu/NHC–Pd catalytic system.

Scheme 74: C(sp2)–H Amidation of (hetero)arenes with N-chlorocarbamates/N-chloro-N-sodiocarbamates catalyzed b...

Scheme 75: NHC–CuI catalyzed thiolation of benzothiazoles and benzoxazoles.
Eschenmoser coupling reactions starting from primary thioamides. When do they work and when not?
- Lukáš Marek,
- Jiří Váňa,
- Jan Svoboda and
- Jiří Hanusek
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 808–819, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.61
- 5.44 in MeOH) [22] the formation of thiazole/thiazol-4-one (XI/XIII) is clearly preferred, whereas reactions in common chlorinated solvents (CH2Cl2, CHCl3) containing either an equivalent of strong base (methoxide) or excess of medium base in heterogeneous system (e.g., carbonate with pKa = 9.93 in
- ; entry 10 in Table 1) only decreased the combined yield of 8a and 8a-Me, but no ECR product 9a was detected. The change of polar aprotic to chlorinated solvents (DCM, CHCl3) as recommended by Eschenmoser [23] leads to ambiguous results. In amylene-stabilized CHCl3 at 55 °C and with 3 equivalents of solid

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Eschenmoser coupling reaction between 3-substituted oxindoles and thioamides.

Scheme 2: Possible reactions of α-haloketones, esters and amides with primary thioamides.

Figure 1: Studied α-bromoamides and α-bromolactams.

Scheme 3: Reaction of 4-bromo-1,1-dimethyl-1,4-dihydroisoquinolin-3(2H)-one (2b) with thiobenzamide and thioa...

Scheme 4: Reaction of 4-bromo-1,1-dimethyl-1,4-dihydroisoquinolin-3(2H)-one (2b) with 4’-substituted thiobenz...

Scheme 5: Reaction of 4-bromoisoquinoline-1,3(2H,4H)-dione (3) with thiobenzamide, thioacetamide, and thioben...

Scheme 6: Reaction of N-phenyl- and N-methyl-2-bromo(phenyl)acetamide (4a,b) with thiobenzamide in acetonitri...

Scheme 7: Transformation of salt 15 under kinetic and thermodynamic control conditions [1].

Figure 2: Comparison of energy profiles (relative Gibbs energies at 298 K in kJ·mol−1 for the ECR (right) and...
Introducing a new 7-ring fused diindenone-dithieno[3,2-b:2',3'-d]thiophene unit as a promising component for organic semiconductor materials
- Valentin H. K. Fell,
- Joseph Cameron,
- Alexander L. Kanibolotsky,
- Eman J. Hussien and
- Peter J. Skabara
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 944–955, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.94
- which oxalyl chloride was added at room temperature, and then reacted with aluminium trichloride at 0 °C. The resulting material was not soluble in cold dichloromethane/chloroform, but was found to be sufficiently soluble in hot chlorinated solvents. NMR spectroscopy in deuterated DMSO indicated that

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: EtH-T-DI-DTT (1).

Figure 2: Previously published, ‘bent’ diindenodithienothiophenes [16,24,25].

Figure 3: With crystalline films of 2,7-dioctyl[1]benzothieno[3,2-b][1]-benzothiophene (8), obtained by off-c...

Figure 4: ITIC, a system with fused thiophenes, in combination with donor polymer 11, also featuring a fused ...

Figure 5: The fluorinated derivative of ITIC, IT-4F, achieved, with donor polymer 13, PCEs in OPVs up to 17% [8]....

Figure 6: The non-fullerene acceptor Y6 (14) [30], in combination with donor polymer 15, both fused thiophene sys...

Figure 7: With a three component system of PBQx-TF, eC9-2Cl, and F-BTA3, a PCE of 19% was achieved [32].

Scheme 1: Synthetic route from thiophene to 2,6-bis(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)dithieno[3,2-b...

Scheme 2: Ring closure of key intermediate 27 to achieve 29: a) Methyl 5-bromo-2-iodobenzoate, Aliquat 336®, ...

Scheme 3: Synthesis of thiophene derivative 32: a) Magnesium, 2-ethylhexylbromide, spatula tip iodine, anhydr...

Scheme 4: Synthesis of the soluble target structure EtH-T-DI-DTT (1): a) 32, Pd(PPh3)4, K2CO3, THF, H2O, 70 °...

Figure 8: Normalised UV–vis spectra of EtH-T-DI-DTT in 10−5 M CH2Cl2 solution and in the solid state.

Figure 9: Cyclic voltammogram for EtH-T-DI-DTT (1), at a scan rate of 0.1 V s−1 using a Pt disk as the workin...

Figure 10: The structure of EtH-T-DI-DTT optimised on the B3LYP/6-311g(d,p) level of theory, viewed from the (...
Asymmetric organocatalytic Michael addition of cyclopentane-1,2-dione to alkylidene oxindole
- Estelle Silm,
- Ivar Järving and
- Tõnis Kanger
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 167–173, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.18
- ). To further optimise the reaction, we screened different solvents (apolar, polar aprotic, and chlorinated solvents) (Table 1, entries 5–7). According to the obtained results chloroform was clearly superior to other solvents. Previously the isolated yield of the product had been moderate and to

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Model of the catalyst action.

Figure 2: Catalysts screened.

Scheme 1: Screening of different N-protecting groups. Reaction conditions: 0.2 M solution of 1 (1 equiv), 2 (...

Scheme 2: Scope of the reaction (the relative configuration of the major diastereoisomer is depicted). Reacti...

Scheme 3: Comparison reactions of E- and Z-isomers (the relative configurations of the major diastereoisomers...
Iodine-catalyzed electrophilic substitution of indoles: Synthesis of (un)symmetrical diindolylmethanes with a quaternary carbon center
- Thanigaimalai Pillaiyar,
- Masoud Sedaghati,
- Andhika B. Mahardhika,
- Lukas L. Wendt and
- Christa E. Müller
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1464–1475, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.102
- employing indoles bearing bulky substituents at their 2-position (Ling et al.), or the need for chlorinated solvents (Sasaki et al.), as well as difficulty to scale up the reactions to a multigram scale, as well as a generally rather limited substrate scope. Therefore, finding a robust method with a broad
- to the synthesis of pentafluoroethylated and heptafluoropropylated-DIMs. It constitutes an important addition to the active field of DIM syntheses facilitating the preparation of unsymmetrical quaternary DIMs without the need for chlorinated solvents, high temperatures, or heavy-metal catalysts. A

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Diindolylmethanes and reported biological activities.

Figure 2: Synthetic strategies toward trifluoromethylated unsymmetrical quaternary DIMs.

Figure 3: Reactions performed to study the scope of the method.

Figure 4: Gram-scale synthesis of unsymmetrical DIMs 3a and 3ad.

Figure 5: Plausible reaction mechanism for the synthesis of fluoromethylated unsymmetrical DIMs, shown for co...
Valorisation of plastic waste via metal-catalysed depolymerisation
- Francesca Liguori,
- Carmen Moreno-Marrodán and
- Pierluigi Barbaro
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 589–621, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.53

- packaging, squeezable bottles, plastic bags and medical devices [140]. PEs (except cross-linked samples) are partially soluble in (hot) aromatic hydrocarbons or in chlorinated solvents [141]. Depolymerisation of PE by catalytic pyrolysis or cracking into liquid fuels was recently reviewed [67][142]. Most of
- alkali bases and chlorinated solvents [176][177], which makes them neither economically competitive nor environmentally friendly [178][179]. A survey of patents related to the chemical recycling of PET up to 2005 can be found in the literature [180]. Hydrogenolysis. In the recent years, hydrogenolysis

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Potential classification of plastic recycling processes. The area covered by the present review is ...

Figure 2: EG produced during glycolytic depolymerisation of PET using DEG + DPG as solvent and titanium(IV) n...

Scheme 1: Simplified representation of the conversion of 1,4-PBD to C16–C44 macrocycles using Ru metathesis c...

Figure 3: Main added-value monomers obtainable by catalytic depolymerisation of PET via chemolytic methods.

Scheme 2: Hydrogenolytic depolymerisation of PET by ruthenium complexes.

Scheme 3: Depolymerisation of PET via catalytic hydrosilylation by Ir(III) pincer complex.

Scheme 4: Catalytic hydrolysis (top) and methanolysis (bottom) reactions of PET.

Scheme 5: Depolymerisation of PET by glycolysis with ethylene glycol.

Figure 4: Glycolysis of PET: evolution of BHET yield over time, with and without zinc acetate catalyst (196 °...

Scheme 6: Potential activated complex for the glycolysis reaction of PET catalysed by metallated ILs and evol...

Scheme 7: One-pot, two-step process for PET repurposing via chemical recycling.

Scheme 8: Synthetic routes to PLA.

Scheme 9: Structures of the zinc molecular catalysts used for PLA-methanolysis in various works. a) See [265], b) ...

Scheme 10: Depolymerisation of PLLA by Zn–N-heterocyclic carbene complex.

Scheme 11: Salalen ligands.

Scheme 12: Catalytic hydrogenolysis of PLA.

Scheme 13: Catalytic hydrosilylation of PLA.

Scheme 14: Hydrogenative depolymerisation of PBT and PCL by molecular Ru catalysts.

Scheme 15: Glycolysis reaction of PCT by diethylene glycol.

Scheme 16: Polymerisation–depolymerisation cycle of 3,4-T6GBL.

Scheme 17: Polymerisation–depolymerisation cycle of 2,3-HDB.

Scheme 18: Hydrogenative depolymerisation of PBPAC by molecular Ru catalysts.

Scheme 19: Catalytic hydrolysis (top), alcoholysis (middle) and aminolysis (bottom) reactions of PBPAC.

Scheme 20: Hydrogenative depolymerisation of PPC (top) and PEC (bottom) by molecular Ru catalysts.

Scheme 21: Polymerisation-depolymerisation cycle of BEP.

Scheme 22: Hydrogenolysis of polyamides using soluble Ru catalysts.

Scheme 23: Catalytic depolymerisation of epoxy resin/carbon fibres composite.

Scheme 24: Depolymerisation of polyethers with metal salt catalysts and acyl chlorides.

Scheme 25: Proposed mechanism for the iron-catalysed depolymerisation reaction of polyethers. Adapted with per...
Using multiple self-sorting for switching functions in discrete multicomponent systems
- Amit Ghosh and
- Michael Schmittel
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2831–2853, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.233

- . Interestingly, the fullerene C60 was not taken up as a guest by the tetramer (6)4 in chlorinated solvents. For a more defined self-sorting, the authors switched the solvent from CDCl3 to [d8]-toluene. Now, a 2-fold completive self-sorting delivered the homoleptic inclusion complexes [(5)4(C60)] and [(6)4(C60

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Some selected self-sorting outcomes and their qualitative and quantitative assessment.

Figure 2: Illustration of an integrative vs a non-integrative self-sorting.

Figure 3: The pH-driven four-component 2-fold completive self-sorting based on host–guest chemistry.

Figure 4: (a) The monomers 5 and 6 and their H-bonding array. (b) The hydrogen-bonded octameric and tetrameri...

Figure 5: (a) Two new Zn4L6-type cages. (b) The encapsulation of C70 induced distinct reconstitutions within ...

Figure 6: The formation of octahedral cages (a) [Co6(10')4]12+ and (b) [Co6(11')4]12+. (c) The 2-fold complet...

Figure 7: Exchange of Ag+ for Au+ ions in poly-NHC ligand-based organometallic assemblies.

Figure 8: The reversible interconversion between the three-component rectangle [Cu4(16)2(17)2]4+ and the four...

Figure 9: a) Chemical structure of the monomer 20 with its quadruple hydrogen-bonding array and a metal-affin...

Figure 10: Communication between the nanoswitch 21 and the supramolecular assemblies [Cu4(22)2(24)2]4+ or [Cu6(...

Figure 11: (a) The chemical structures and cartoon representations of the switch 25, the decks 26 and 27, and ...

Figure 12: Double self-sorting leads to a catalytic machinery in SelfSORT-II, in which the 46 kHz-nanorotor ac...

Figure 13: ON/OFF control of a networked catalytic catch–release system.

Figure 14: A multicomponent information system for the reversible reconfiguration of switchable dual catalysis....

Figure 15: a) The chemically fueled cascaded ion translocation, monitored by distinct emission colors. b) Work...

Figure 16: Cyclic metallosupramolecular transformations.

Figure 17: Fully reversible multiple-state rearrangement of metallosupramolecular architectures depending upon...

Figure 18: The selective encapsulation and sequential release of guests in a self-sorted mixture of three tetr...

Figure 19: Two catalytic reactions are alternately controlled by a toggle nanoswitch.

Figure 20: A biped walking along a tetrahedral track and unfolding its catalytic action. Adapted with permissi...

Figure 21: A three state supramolecular AND logic gate.

Figure 22: Four-component nanorotor and its catalytic activity. Adapted with permission from (Biswas, P. K.; S...
Fluorohydration of alkynes via I(I)/I(III) catalysis
- Jessica Neufeld,
- Constantin G. Daniliuc and
- Ryan Gilmour
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1627–1635, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.135
- ). Having established that an amine/HF ratio of 1:7.5 provides the optimal Brønsted acidity for catalysis, a solvent screen was conducted to assess the effect of the reaction medium. Chlorinated solvents proved to be most effective, with reactions performed in CHCl3 slightly outperforming those in CH2Cl2

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: (A) Synthetic routes to α-fluoroketones from silyl enol ethers or acetophenone derivatives. (B) Sel...

Scheme 1: Substrate scope with standard reaction conditions: alkyne (0.2 mmol), p-TolI (20 mol %), Selectfluor...

Figure 2: X-ray molecular structure of compound 2. Conformation of the carbonyl group and the fluoride with a...

Figure 3: (A) Structure activity relationship of the core scaffold. (B) Exploring the effect of methyl benzoa...

Figure 4: (A) Hammett plot varying the para-substitution on the alkyne (ρ ≈ 0). (B) Hammett plot varying the ...

Figure 5: An overview of the I(I)/I(III)-catalysed fluorohydration of alkynes.
Recent developments in photoredox-catalyzed remote ortho and para C–H bond functionalizations
- Rafia Siddiqui and
- Rashid Ali
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 248–280, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.26

- of molecular oxygen as an oxidant. Although various photoredox catalysts and solvents were examined, the best results were obtained with photoredox catalyst 6 in chlorinated solvents. In the absence of a photoredox catalyst, the goup did not observe any product formation. A list of products assembled

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: List of photoredox catalysts used for C–H bond functionalizations.

Figure 2: List of metal-based photoredox catalysts used in this review article.

Figure 3: Jablonski diagram.

Figure 4: Photoredox catalysis via reductive or oxidative pathways. D = donor, A = acceptor, S = substrate, P...

Figure 5: Schematic representation of the combination of photoredox catalysis and transition metal catalysis.

Scheme 1: Weinreb amide C–H olefination.

Figure 6: Mechanism for the formation of 21 from 19 using photoredox catalyst 11.

Scheme 2: C–H olefination of phenolic ethers.

Scheme 3: Decarboxylative acylation of acetanilides.

Figure 7: Mechanism for the formation of 30 from acetanilide derivatives.

Scheme 4: Synthesis of fluorenone derivatives by intramolecular deoxygenative acylation of biaryl carboxylic ...

Figure 8: Mechanism for the photoredox-catalyzed synthesis of fluorenone derivatives.

Scheme 5: Synthesis of benzothiazoles via aerobic C–H thiolation.

Figure 9: Plausible mechanism for the construction of benzothiazoles from benzothioamides.

Scheme 6: Synthesis of benzothiazoles via oxidant-free C–H thiolation.

Figure 10: Mechanism involved in the synthesis of benzothiazoles via oxidant-free C–H thiolation.

Scheme 7: Synthesis of indoles via C–H cyclization of anilides with alkynes.

Scheme 8: Preparation of 3-trifluoromethylcoumarins via C–H cyclization of arylpropiolate esters.

Figure 11: Mechanistic pathway for the synthesis of coumarin derivatives via C–H cyclization.

Scheme 9: Monobenzoyloxylation without chelation assistance.

Figure 12: Plausible mechanism for the formation of 71 from 70.

Scheme 10: Aryl-substituted arenes prepared by inorganic photoredox catalysis using 12a.

Figure 13: Proposed mechanism for C–H arylations in the presence of 12a and a Pd catalyst.

Scheme 11: Arylation of purines via dual photoredox catalysis.

Scheme 12: Arylation of substituted arenes with an organic photoredox catalyst.

Scheme 13: C–H trifluoromethylation.

Figure 14: Proposed mechanism for the trifluoromethylation of 88.

Scheme 14: Synthesis of benzo-3,4-coumarin derivatives.

Figure 15: Plausible mechanism for the synthesis of substituted coumarins.

Scheme 15: Oxidant-free oxidative phosphonylation.

Figure 16: Mechanism proposed for the phosphonylation reaction of 100.

Scheme 16: Nitration of anilines.

Figure 17: Plausible mechanism for the nitration of aniline derivatives via photoredox catalysis.

Scheme 17: Synthesis of carbazoles via intramolecular amination.

Figure 18: Proposed mechanism for the formation of carbazoles from biaryl derivatives.

Scheme 18: Synthesis of substituted phenols using QuCN.

Figure 19: Mechanism for the synthesis of phenol derivatives with photoredox catalyst 8.

Scheme 19: Synthesis of substituted phenols with DDQ (5).

Figure 20: Possible mechanism for the generation of phenols with the aid of photoredox catalyst 5.

Scheme 20: Aerobic bromination of arenes using an acridinium-based photocatalyst.

Scheme 21: Aerobic bromination of arenes with anthraquinone.

Figure 21: Proposed mechanism for the synthesis of monobrominated compounds.

Scheme 22: Chlorination of benzene derivatives with Mes-Acr-MeClO4 (2).

Figure 22: Mechanism for the synthesis of 131 from 132.

Scheme 23: Chlorination of arenes with 4CzIPN (5a).

Figure 23: Plausible mechanism for the oxidative photocatalytic monochlorination using 5a.

Scheme 24: Monofluorination using QuCN-ClO4 (8).

Scheme 25: Fluorination with fluorine-18.

Scheme 26: Aerobic amination with acridinium catalyst 3a.

Figure 24: Plausible mechanism for the aerobic amination using acridinium catalyst 3a.

Scheme 27: Aerobic aminations with semiconductor photoredox catalyst 18.

Scheme 28: Perfluoroalkylation of arenes.

Scheme 29: Synthesis of benzonitriles in the presence of 3a.

Figure 25: Plausible mechanism for the synthesis of substituted benzonitrile derivatives in the presence of 3a....
Probing of local polarity in poly(methyl methacrylate) with the charge transfer transition in Nile red
- Aydan Yadigarli,
- Qimeng Song,
- Sergey I. Druzhinin and
- Holger Schönherr
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2552–2562, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.248

- and in chlorinated solvents lie also clearly below the straight line in Figure 3a. This is tentatively attributed to the different inductive solute–solvent interactions, which are neglected in Equation 1. Such additional red shift in the case of halogenated solvents has been explained before by the
- high stability also in the chlorinated solvents, cf. with a lack of a red edge effect for 4-fluoro-N,N-dimethylaniline [67]. On the other hand, when the relaxation time of the molecules or segments (τr) of the polymer matrix is much longer than the NR fluorescence decay time τf = 3.87 ns [62] in PMMA

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Molecular structure of Nile red (NR).

Figure 2: Fluorescence (a) and absorption (b) spectra of NR in solvents of different polarity at 25 °C. The s...

Figure 3: Solvatochromic plot of the absorption (νa) and fluorescence (νf) maxima of NR in a series of solven...

Figure 4: Absorption (a) and fluorescence (a, b) spectra of NR in PMMA (350 kg/mol) film 500 nm thin at diffe...

Figure 5: Dependence of the fluorescence maximum (νf) of NR on the excitation wavelength (λe) in rigid PMMA m...

Figure 6: Absorption (a) and fluorescence (a, b) spectra of NR in ethyl acetate (EtOAc) at different excitati...
Self-assembled coordination thioether silver(I) macrocyclic complexes for homogeneous catalysis
- Zhen Cao,
- Aline Lacoudre,
- Cybille Rossy and
- Brigitte Bibal
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2465–2472, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.239
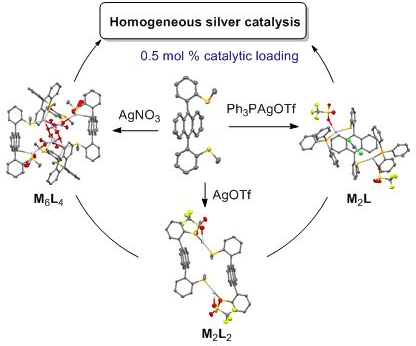
- nitrate complex was thus soluble in chlorinated solvents. In the presence of the bulky triphenylphosphine silver triflate salt, a monocoordination occurred between Ag(I) and each sulfur atom of ligand 1 leading to a discrete complex (syn-1)·(Ph3PAgOTf)2, as revealed by 1H NMR and X-ray (Figure 3). The

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Synthesis of ligand 1, as its syn-atropisomer.

Figure 1: X-ray structures of complex 1a, as two diastereoisomeric macrocycles (R,S-1)2·(AgOTf)2 with ligands...

Figure 2: X-ray structure of complex 1c, as a (R,S-1)4·(AgNO3)6 cage with three nitrate anions as coordinatin...

Figure 3: X-ray structure of complex 1d, as a racemic mixture of (R,R)- and (S,S)-(syn-1)·(PPh3AgOTf)2.

Figure 4: Variable temperature 1H NMR of complex 1a in CDCl3 (7 mM) from −30 °C to 60 °C.
Mechanochemical synthesis of hyper-crosslinked polymers: influences on their pore structure and adsorption behaviour for organic vapors
- Sven Grätz,
- Sebastian Zink,
- Hanna Kraffczyk,
- Marcus Rose and
- Lars Borchardt
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1154–1161, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.112
- suitable alternative in the synthesis of hyper-crosslinked polymers. By avoiding chlorinated solvents (typically 1,2-dichloroethane), the synthesis of this promising material can be undertaken in a greener, faster, and cheaper fashion. The obtained materials show surface areas as high as 1720 m2g−1 with a

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: A: Mechanochemical polymerization of BCMBP (4,4’-bis(chloromethyl)-1,1’-biphenyl) towards the porou...

Figure 2: A: IR spectra of the monomer BCMBP and NG-HCP showing a decrease of the C–Cl vibration after the re...

Figure 3: A: Evolution of pressure in the course of the reaction measured by the GTM system. The addition of ...

Figure 4: The correlation between the liquids’ boiling point and the SSA of the polymer. In general, a lower ...

Figure 5: Physisorption isotherms of benzene vapour at different temperatures on HCP synthesised classically ...

Figure 6: Physisorption isotherms of cyclohexane on mechanochemically synthesised HCP at temperatures 288, 29...
Extending mechanochemical porphyrin synthesis to bulkier aromatics: tetramesitylporphyrin
- Qiwen Su and
- Tamara D. Hamilton
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1149–1153, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.111

- porphyrins are synthesized through a four-fold acid-catalyzed condensation to form a porphyrinogen which is then oxidized (− 6H) to form the conjugated porphyrin product. Lindsey’s reaction takes place at room temperature and utilizes chlorinated solvents under optimized dilution conditions (10−2 M reactant

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: A) Porphyrin structure and labelling system. B) Substituents in the ortho-position of the group att...

Scheme 1: Steps leading to the formation of a porphyrin.

Scheme 2: Mechanochemical synthesis of tetramesitylporphyrin.
Synthesis of polydicyclopentadiene using the Cp2TiCl2/Et2AlCl catalytic system and thin-layer oxidation of the polymer in air
- Zhargolma B. Bazarova,
- Ludmila S. Soroka,
- Alex A. Lyapkov,
- Мekhman S. Yusubov and
- Francis Verpoort
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 733–745, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.69

- transformations occurring in thin layers of PDCPD during oxidation in air. Polymers obtained during the dicyclopentadiene polymerization under these conditions are well soluble in aromatic and chlorinated solvents, and from these solutions, smooth transparent films can be produced. However, the surface of PDCPD

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Absorption spectra in the UV and visible spectral region: 1) bis(cyclopentadienyl)titan dichloride (...

Figure 2: Absorption spectra in the visible spectral region: 1) Cp2TiCl2·AlEt2Cl (toluene, 10 mmol/L, Ti/Al r...

Figure 3: 1Н NMR spectra of tricyclopentadiene (a) and the interaction product between Cp2TiCl2 and AlEt2Cl w...

Scheme 1: Mechanism of alkylation of Cp2TiCl2.

Figure 4: Visible spectra of a mixture of Cp2TiCl2 and AlEt2Cl as function of time.

Figure 5: Thermometric curve of DCPD polymerization using the catalyst system based on Cp2TiCl2 (a) and its s...

Scheme 2: The structures formed as a result of the cationic polymerization of dicyclopentadiene.

Scheme 3: The units resulting from ROMP of dicyclopentadiene.

Scheme 4: Mechanism of ROMP dicyclopentadiene.

Figure 6: FTIR spectrum of PDCPD obtained in toluene with the catalyst system based on Cp2TiCl2 and AlEt2Cl.

Figure 7: 1Н NMR spectrum of PDCPD obtained with the catalytic system based on Cp2TiCl2 and AlEt2Cl.

Figure 8: GPC traces for two samples of DCPD polymers obtained at a concentration of Cp2TiCl2/AlEt2Cl complex...

Figure 9: IR spectra of cationic polymerized dicyclopentadiene taken after certain periods of time exposed to...

Figure 10: Correlation of intensities of vibrational bands at 1620 and 700 cm−1 and layer exposure time in air...

Figure 11: DSC exotherm for PDCPD subjected to air oxidation for 700 hours.

Figure 12: DSC exotherm for PDCPD subjected to unexposed film: 1) in air atmosphere; 2) in argon.

Scheme 5: Possible radical formation in the reaction (1).

Scheme 6: The first step of the chain propagation.

Figure 13: Dependence of intensities of adsorption bands at 1410 and 700 cm−1 and dwell time of the layer in a...

Figure 14: Semi-logarithmic kinetic curve of PDCPD oxidation in air (thin layer on silicon) with respect to in...

Figure 15: The distribution of oxygen concentration in the polymer layer: 1 – a layer of oxidized cross-linked...

Figure 16: Dependence of the ratio of adsorption bands at 1700 and 700 cm−1 on the exposure time of the layer ...

Figure 17: Infrared spectra (a) of products of cationic polymerization of DCPD, stabilized with an antioxidant...
Gold-catalyzed post-Ugi alkyne hydroarylation for the synthesis of 2-quinolones
- Xiaochen Du,
- Jianjun Huang,
- Anton A. Nechaev,
- Ruwei Yao,
- Jing Gong,
- Erik V. Van der Eycken,
- Olga P. Pereshivko and
- Vsevolod A. Peshkov
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2572–2579, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.234
- -dimethoxyaniline (6a). Next, the cycloisomerization of 7a was investigated in order to identify the optimal conditions. At first, we attempted two reactions using 5 mol % of the standard AuPPh3Cl/AgOTf precatalytic combination in conventional chlorinated solvents such as deuterated chloroform and dichloromethane
- ). Conducting the AuPPh3Cl/AgOTf-catalyzed reaction in trifluoroethanol (TFE) led to improved results producing 8a in up to 97% yield (Table 1, entry 6). Thus, this greener alternative [63] to chlorinated solvents was selected as the solvent of choice for the further exploration. Changing the silver counterpart

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Synthesis of 2-quinolones 2 through intramolecular Friedel–Crafts hydroarylation of N-aryl propargy...

Scheme 2: Strategy towards 2-quinolones 8 bearing a branched substituent on the nitrogen atom.

Figure 1: Scope of the protocol.
Asymmetric α-amination of 3-substituted oxindoles using chiral bifunctional phosphine catalysts
- Qiao-Wen Jin,
- Zhuo Chai,
- You-Ming Huang,
- Gang Zou and
- Gang Zhao
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 725–731, doi:10.3762/bjoc.12.72
- influence of solvents and reaction temperature on the reaction were investigated with the best catalyst (Table 2). The use of both polar solvents (ethyl ether, tetrahydrofuran, acetone, acetonitrile or ethyl alcohol) including other chlorinated solvents such as chloroform, 1,2-dichloroethane and 1,1,2

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: The mimetic activation mode of Mitsunobu reaction.

Scheme 2: Scale-up of the reaction and deprotection of the product.

Figure 1: The 31P NMR spectra research in CD2Cl2.

Scheme 3: Proposed transition-state model.
Copper-catalysed asymmetric allylic alkylation of alkylzirconocenes to racemic 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyrans
- Emeline Rideau and
- Stephen P. Fletcher
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2435–2443, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.264
- electron withdrawing counterions were found to provide the desired product, with CuClO4 giving the best ee (70% ee, Table 1, entry 3). A solvent screen lead us to the conclusion that chlorinated solvents are best (CH2Cl2 (70% ee) and CHCl3 (67% ee), Table 1, entries 7 and 10, respectively). Extensive

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Previously reported Cu-AAA of alkylzirconium reagents to racemic allyl chlorides [26] and this work.

Figure 1: DoE from 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-yl diethyl phosphate (2d). Conditions: 4-phenyl-1-butene (2.5 equiv...

Scheme 2: Scope of nucleophiles. Conditions: alkene (2.5 equiv), Cp2ZrHCl (2.0 equiv), 3-chloro-3,6-dihydro-2H...

Figure 2: Reaction kinetics as monitored by in situ 1H NMR spectroscopy from 3-chloro-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran (2a...

Figure 3: Reaction kinetics as monitored by in situ 1H NMR spectroscopy from 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-yl diethy...

Figure 4: Kinetic ee analysis using 2a. ee of reaction with 3-chloro-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran (2a) as measured by...

Figure 5: Kinetic ee analysis using 2d. ee of reaction with 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-yl diethyl phosphate (2d) ...
Hexacoordinate Ru-based olefin metathesis catalysts with pH-responsive N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) and N-donor ligands for ROMP reactions in non-aqueous, aqueous and emulsion conditions
- Shawna L. Balof,
- K. Owen Nix,
- Matthew S. Olliff,
- Sarah E. Roessler,
- Arpita Saha,
- Kevin B. Müller,
- Ulrich Behrens,
- Edward J. Valente and
- Hans-Jörg Schanz
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 1960–1972, doi:10.3762/bjoc.11.212
- , ether, THF and acetone. Chlorinated solvents such as CH2Cl2 and CHCl3 dramatically improve the complex solubility but have shown to result in significant degradation over a period of several hours. An NMR sample of complex 12 in CDCl3 exhibited approx. 10% decomposition over a 24 h period at room

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Hydrophilic and/or pH-responsive Ru–alkylidene complexes 1–7 for olefin metathesis.

Scheme 1: Synthesis of 2nd Grubbs-type generation complex 9.

Scheme 2: Synthesis of hexacoordinate, pH-responsive complexes 11 and 12.

Figure 2: ORTEP diagram for H2ITap(DMAP)2Cl2Ru=CH-SPh (12). The positions of the hydrogen atoms were calculat...

Scheme 3: ROMP reactions conducted under microemulsion conditions.

Scheme 4: Proposed formation of catalytic species 14 and 15 under emulsion ROMP conditions.

Figure 3: AFM image produced from COE/DCPD latex film. Measurement: AFM tapping at room temperature, material...
Site-selective covalent functionalization at interior carbon atoms and on the rim of circumtrindene, a C36H12 open geodesic polyarene
- Hee Yeon Cho,
- Ronald B. M. Ansems and
- Lawrence T. Scott
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 956–968, doi:10.3762/bjoc.10.94
- circumtrindene might also be brominated. Fullerenes are known to undergo bromine addition with elemental bromine in chlorinated solvents at room temperature [28]. To avoid the unwanted bromination at interior carbon atoms, the reaction conditions were carefully optimized (see Supporting Information File 1 for

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Prototypical open and closed geodesic polyarenes.

Figure 2: Planar vs pyramidalized π-system.

Figure 3: Selected examples of geodesic polyarenes synthesized by FVP.

Scheme 1: Covalent functionalization of fullerene C60 by the Bingel–Hirsch reaction and the Prato reaction.

Scheme 2: Fullerene-type chemistry at interior carbon atoms of corannulene (1) and diindenochrysene (10).

Figure 4: POAV angles of fullerene C60 (2), corannulene (1), and diindenochrysene (10).

Scheme 3: Synthesis of circumtrindene (6) by FVP.

Scheme 4: Synthetic route to 3,9,15-trichlorodecacyclene (12).

Figure 5: POAV angle and bond lengths of circumtrindene.

Scheme 5: Bingel–Hirsch reaction of circumtrindene (6).

Scheme 6: Proposed mechanism for the Bingel–Hirsch reaction of circumtrindene (6).

Scheme 7: Prato reaction of circumtrindene (6).

Figure 6: LUMO orbital map of circumtrindene (B3LYP/6-31G*). The darkest blue areas correspond to the regions...

Figure 7: Electrostatic potentials on the surfaces of circumtrindene (B3LPY/6-31G*).

Figure 8: Monoindeno- (25), diindeno- (26), and triindenocircumtrindene (27).

Figure 9: Two different types of rim carbon atoms on circumtrindene.

Scheme 8: Site-selective peripheral monobromination of circumtrindene.

Scheme 9: Suzuki coupling and ring-closing reactions toward indenocircumtrindene (25).

Scheme 10: Suzuki coupling to prepare compound 30.

Figure 10: Chemical shifts of ortho-methyl groups in 30 and 31.






