Search results
Search for "supramolecular" in Full Text gives 501 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of immunostimulating mannosylated desmuramyl peptides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1805–1814, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.174
- , a powerful supramolecular nanoparticle carrier for targeted drug delivery [38]. Previous research suggested a design of mannosylated desmuramyl peptides with adamantane at the C-terminus in order to facilitate the incorporation into the hydrophobic layer of the cavity because of the minor steric
Complexation of 2,6-helic[6]arene and its derivatives with 1,1′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium salts and protonated 4,4'-bipyridinium salts: an acid–base controllable complexation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1795–1804, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.173

- macrocyclic arenes with diverse functional groups are also important for the development of various new host–guest supramolecular systems [23][24][25][26][27][28][29]. Helic[6]arenes [30], a new kind of macrocyclic arenes, are composed of 2,6-dihydroxy-substituted triptycene subunits bridged by methylene
- groups. They have exhibited wide potential applications in supramolecular chemistry [31][32][33][34][35][36] for their unique structures and electron-rich cavities. In this paper, we report the complexation between 2,6-helic[6]arene and its four derivatives with 1,1′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium and
Host–guest interactions in nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril: novel guest-dependent molecular recognition and stereoisomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1705–1711, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.166
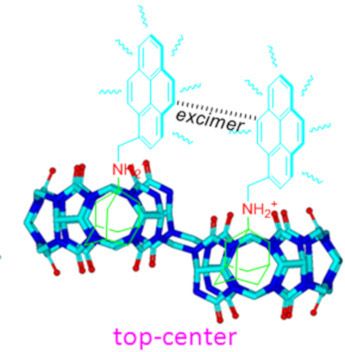
- Xiaodong Zhang Wei Wu Zhu Tao Xin-Long Ni Key Laboratory of Macrocyclic and Supramolecular Chemistry of Guizhou Province, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China 10.3762/bjoc.15.166 Abstract The unique monomer and excimer fluorescence emissions of pyrene were first exploited as distinctly
- guests in its cavity through host-stabilized charge-transfer or π–π interactions [14][15]. This novel property of Q[8] has been utilized as molecular container for biological substrates [16][17], as well as in the construction of various supramolecular assemblies with specific structures and properties
- adamantaneammonium (ADA) or alkylammonium ions into the cavity, forming a ternary complex. The novel binding capacity of NS-CB[10] has been utilized to form supramolecular polymers [24][25][26] and polymer nanoparticles [27]. More importantly, Isaacs et al. discovered that when the unsymmetrical guest ADA molecules
Synthesis, enantioseparation and photophysical properties of planar-chiral pillar[5]arene derivatives bearing fluorophore fragments
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1601–1611, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.164

- : aggregation; circular dichroism; chirality; click chemistry; macrocycles; pillar[5]arenes; Introduction Planar-chiral compounds are structurally appealing and potentially applicable in various functional materials such as chiral discriminators [1][2], chiral polymers, supramolecular sensors [3] and chiral
- center and therefore chirality transfer is non-effective [43]. Supramolecular assembly usually leads to different photophysical properties than homogeneous solutions. We have demonstrated that solvents play a critical role in chiral recognition and chiral photoreactions [44][45][46][47][48][49][50][51
- adding water into the THF solution. This work presented a new strategy for achieving versatile planar chiral hosts, and these hosts will have potential applications in various fields such as supramolecular sensing, host–guest recognition and triplet–triplet annihilation upconversion. Experimental General
Water inside β-cyclodextrin cavity: amount, stability and mechanism of binding
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1592–1600, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.163

- supramolecular host–guest structures. The water content of CDs has been a subject of numerous investigations. The data (both experimental and theoretical) are scattered and, still, no consensus has been reached on the number and position of water molecules, and the energetics of the hydration/dehydration of
An azobenzene container showing a definite folding – synthesis and structural investigation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1534–1544, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.156
- Abdulselam Adam Saber Mehrparvar Gebhard Haberhauer Institut für Organische Chemie, Universität Duisburg-Essen, Universitätsstr. 7, D-45117 Essen, Germany 10.3762/bjoc.15.156 Abstract The combination of photo-switchable units with macrocycles is a very interesting field in supramolecular
- the high dispersion energy in the compact cis,cis-isomer. Keywords: azobenzene; macrocycles; molecular switch; Introduction In supramolecular chemistry rigid scaffolds are required to arrange different recognition units in predefined distances and spatial orientation to each other [1]. One example
- organoammonium ions [10], and biomolecules [11][12][13][14][15][16][17]. Furthermore, modified Lissoclinum cyclopeptides were used for the construction of novel tubular and cage structures [18][19], as prototypes for mimicking multiple loops of proteins [20] and for homochiral supramolecular polymerization [21
Mechanochemistry II
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1521–1522, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.154

- find contributions from renowned global experts in the field of mechanochemistry spanning areas from organic mechanochemistry, supramolecular mechanochemistry to polymer mechanochemistry. Moreover, findings reported in this current thematic issue also contribute to the expansion of synthetic chemistry
A heteroditopic macrocycle as organocatalytic nanoreactor for pyrroloacridinone synthesis in water
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1505–1514, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.152
- supramolecular assemblies like molecular rotors (pseudorotaxane, rotaxane, catenane), molecular switches, molecular shuttles, etc. [32][33][34][35][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43]. Furthermore, macrocycles have been applied in the area of ion–ion pair recognition and heterometallic complex formation [44][45][46
2,3-Dibutoxynaphthalene-based tetralactam macrocycles for recognizing precious metal chloride complexes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1460–1467, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.146

- –guest chemistry; macrocycles; molecular recognition; precious metal chloride complexes; Introduction Macrocyclic receptors are the major workhorses in supramolecular chemistry. Design and synthesis of new macrocyclic receptors with new properties is always attractive but is also challenging [1
Introduction of an isoxazoline unit to the β-position of porphyrin via regioselective 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1434–1440, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.143

- enantiomers of 3a is present, which assembled to a dimeric structure with the fifth chelation of a Zn2+ ion by the carbonyl group of the other molecule. The self-dimerization property of 3a may be utilized in supramolecular chemistry [50][51][52][53]. Experimental 1: Porphyrin phosphonium salt 1 was prepared
Reversible end-to-end assembly of selectively functionalized gold nanorods by light-responsive arylazopyrazole–cyclodextrin interaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1407–1415, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.140

- aggregates can be realized more or less efficiently through various approaches based on supramolecular interactions like metal–metal and π–π interactions [11], DNA mediated [12] or by host–guest chemistry [13]. Most of these approaches require selective functionalization of the ends of the AuNR and take
- the complete surface because of its cell toxicity [17], hence strategies for replacing this coating are desirable. Host–guest chemistry is a supramolecular interaction that is tailor-made for self-assembly due to its lock–key mechanism and has been applied in our and other groups to various
- azobenzenes leading due to the superior photophysical properties to fully reversible supramolecular systems, which showed limited feasibility with azobenzenes [20][38][39]. Herein, we present the application of a light-responsive CD–AAP host–guest system for the reversible end-to-end assembly of AuNR. The
Complexation of a guanidinium-modified calixarene with diverse dyes and investigation of the corresponding photophysical response
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1394–1406, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.139

- -consuming syntheses. Alternatively, supramolecular chemistry provides a non-covalent approach to achieve fluorescence sensing [2]. An elegant supramolecular strategy, named indicator displacement assay (IDA), was established and popularized by Anslyn and co-workers (Scheme 1a) [3][4]. The complexation of a
- observable signal. Subsequent to IDA, Nau and co-workers conceptualized a novel approach towards enzyme assays, termed supramolecular tandem assay (STA) (Scheme 1b) [5]. STA is envisaged as a time-resolved version of IDA and the key idea is that the competitor is not added, but rather created during the
- fluorophores through supramolecular encapsulation using artificial macrocyclic hosts has always been an active research area [10][11][12]. The complexes of macrocycles with luminescent dyes not only act as reporter pairs for sensing [13][14][15], but also offer various applications in bioimaging [16][17
Selective detection of DABCO using a supramolecular interconversion as fluorescence reporter
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1371–1378, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.137
- -component rectangle [Cu4(1)2(2)2]4+ and the four-component sandwich complex [Cu2(1)(2)(4)]2+ is triggered by inclusion and release of DABCO (4). The fully reversible and clean switching between two multicomponent supramolecular architectures can be monitored by fluorescence changes at the zinc porphyrin
- sites. The structural changes are accompanied by a huge spatial contraction/expansion of the zinc porphyrin–zinc porphyrin distances that change from 31.2/38.8 Å to 6.6 Å and back. The supramolecular interconversion was used for the highly selective detection of DABCO in a mixture of other similar
- compounds. Keywords: copper; detection; fluorescence; interconversion; macrocycles; self-assembly; self-sorting; zinc porphyrin; Introduction Since dynamic multicomponent supramolecular structures are nowadays abundant [1][2], the weak intercomponent binding [3][4][5][6][7][8][9] is often instrumentalized
Efficient resolution of racemic crown-shaped cyclotriveratrylene derivatives and isolation and characterization of the intermediate saddle isomer
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1339–1346, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.133

- ; cyclotriveratrylenes; HPLC; macrocycles; racemization; saddle isomer; Introduction Cyclotriveratrylenes (CTVs) [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] are cyclic bowl-shaped molecules and belong to the most studied concave host molecules in supramolecular chemistry besides, e.g., calixarenes and resorcinarenes [9], cyclodextrins
- ][28]. Due to our interest in dissymmetric [29][30][31][32][33][34][35][36] and concave molecular building blocks [37] and their implementation in supramolecular architectures like (allosteric) receptors [38][39][40][41][42][43][44] or metallosupramolecular helicates and cages [45][46][47][48][49][50
Host–guest interactions between p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene and p-sulfonatothiacalix[4]arene and group IA, IIA and f-block metal cations: a DFT/SMD study
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1321–1330, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.131

- cations (La3+) a supramolecular approach with explicit solvent treatment has been applied in the study of the effect of metal hydration on the complexation process. The La3+ binding to the p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene host molecule (now in the metal’s second coordination shell) is still exergonic as evidenced
- formation reactions. Keywords: complex formation; DFT; group IA; IIA and f-block metal cations; macrocycles; p-sulfonatocalix[4]arene; p-sulfonatothiacalix[4]arene; Introduction If macrocycles are pillars of the supramolecular chemistry, then calixarenes (“calix” = vase + “arene”) are the 3rd pillar after
- metal hydration (i.e., explicit solvent treatment method) on the complexation process was studied here by employing a supramolecular approach for one representative of the metal species from the series, La3+ cation. A hydration number of 9 and initial tricapped trigonal prismatic arrangement of the
Bambusuril analogs based on alternating glycoluril and xylylene units
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1268–1274, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.124

- Tomas Lizal Vladimir Sindelar Department of Chemistry and RECETOX, Masaryk University, Kamenice 5, 625 00 Brno, Czech Republic 10.3762/bjoc.15.124 Abstract The glycoluril monomer is a popular building block in supramolecular chemistry as it is used for the synthesis of versatile host molecules
- ; supramolecular chemistry; Introduction Macrocycles consisting of urea building blocks play an important role in supramolecular chemistry [1]. Urea N–H motifs provide macrocycles with the ability to act as anion receptors due to the stabilizing effect of N–H···anion hydrogen bonding [2][3][4]. Furthermore, the
N-doped carbon dots covalently functionalized with pillar[5]arenes for Fe3+ sensing
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1262–1267, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.123

- units, the newly constructed fluorescent CCDs could recognize Fe3+ with high selectivity. Therefore, such CCDs can potentially serve as a promising chemical sensor for Fe3+ ions. Keywords: chemical sensor; CN-dots; fluorescence; ion recognition; supramolecular chemistry; Findings Carbon dots (C-dots
- macrocyclic compounds, especially new macrocyclic arenes, have become one of the research hotspots in supramolecular chemistry [11][12][13][14]. Among them pillarenes as a relatively new family of pillar-shaped members discovered a decade ago have played a key role due to their unique conformations
- , symmetrical structures, superior host–guest properties, supramolecular assembly characteristics, and versatile functionalities [11][15][16]. Carboxylatopillar[5]arene (CP[5]) is one of the most popular functional pillarenes that has been exploited in many research areas, especially in sensing and detection
Steroid diversification by multicomponent reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1236–1256, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.121
- supramolecular chemistry applications. Keywords: conjugation; heterocycles; macrocycles; multicomponent reactions; steroids; Review 1 Introduction The utilization of multicomponent reactions (MCRs) [1] for the derivatization of biomolecules has continuously grown over the last years. These diversity-oriented
- in the pursuit of medicinal and supramolecular chemistry applications. Despite some review articles have described selected examples of MCRs used to modify and to macrocyclize steroidal compounds [12][13], to our knowledge there is no review exclusively dedicated to covering the applications of MCRs
- synthetic program towards steroid-based supramolecular receptors [28]. There, steroidal diamines and diisocyanides derived from bile acids were employed in a procedure known as MiBs, i.e., multiple multicomponent macrocyclization including bifunctional building blocks. In a series of subsequent reports
Understanding the unexpected effect of frequency on the kinetics of a covalent reaction under ball-milling conditions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1226–1235, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.120

- for a wide range of different syntheses and chemical reactions of inorganic [8][9] and organic [10][11] compounds. Even supramolecular architectures such as co-crystals and metal-organic frameworks [4][12][13][14], cages [15] and rotaxanes [16] could be formed mechanochemically. Crucially, the
- mechanisms and driving forces which underpin mechanochemical transformations and supramolecular reactions remain poorly understood and are subject to considerable debate [2][4][7][8][14][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24][25]. The future successful academic and industrial application of these methods depends on
- their dependence on the milling frequency. Furthermore, they each exhibit sizeable induction periods, far greater than most reported kinetic profiles of multi-phase mechanochemical non-covalent supramolecular chemical reactions [28][45]. The notable exceptions are similar synthetic reactions, which
Self-assembly behaviors of perylene- and naphthalene-crown macrocycle conjugates in aqueous medium
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1203–1209, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.117

- -assemblies have been recognized as a type of exciting nanomaterials with tremendous potential for research and commercial applications [1][2][3][4][5][6]. Thanks to the development of supramolecular chemistry, the ordered structures could be obtained through programmed self-assembly coupled with covalent
- chemical synthesis [7]. In fact, supramolecular technology has shown great importance in various kinds of functional materials, including natural protein complexes [8][9][10], hydrogels [11][12][13], carbon-based materials [14][15][16][17], self-healing materials [18][19][20][21][22][23], and composite
- materials [24][25][26]. Moreover, several new proof-of-concept applications of supramolecular assemblies are also of increasing interest, specifically in the fields of energy generation and storage [27], water treatment and environmental remediation [28][29], and healthcare and biomedical engineering [30
Design of a double-decker coordination cage revisited to make new cages and exemplify ligand isomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1129–1140, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.109

- : anion binding; double-decker cage; ligand isomerism; macrocycles; palladium; self-assembly; supramolecular; Introduction Coordination-driven self-assembly is a convenient strategy for the construction of supramolecules of desired dimensions via simple synthetic procedures. Well-defined metal–ligand
Molecular recognition using tetralactam macrocycles with parallel aromatic sidewalls
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1086–1095, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.105
- Dong-Hao Li Bradley D. Smith Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Notre Dame, 236 Nieuwland Science Hall, Notre Dame, Indiana 46556, United States 10.3762/bjoc.15.105 Abstract This review summarizes the supramolecular properties of tetralactam macrocycles that have parallel
- aromatic sidewalls and four NH residues directed into the macrocyclic cavity. These macrocycles are versatile hosts for a large number of different guest structures in water and organic solvents, and they are well-suited for a range of supramolecular applications. The macrocyclic cavity contains a mixture
- selectivity. In organic solvents, the supramolecular factors are reversed; the polar NH groups drive high affinity and the aromatic surfaces provide the secondary interactions. In addition to an amphiphilic cavity, macrocyclic tetralactams exhibit conformational flexibility, and the combination of properties
Fabrication, characterization and adsorption properties of cucurbit[7]uril-functionalized polycaprolactone electrospun nanofibrous membranes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 992–999, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.97

- engineering [6], energy storage [7], biosensors [8], catalysis [9], and environmental engineering [10]. Various supramolecular host molecules such as cyclodextrins (CDs), calix[n]arenes, and pillar[n]arenes can form host–guest inclusion complexes (ICs) with numerous compounds due to their unique cavity
- present in the molecular structure. Combined with merits of host molecules and electrospun nanofibers, the supramolecular host functionalized nanofibers have been widely reported in recent years as efficient molecular filters and absorbent for the removal of hazardous chemicals or polluting substances. A
- [20] and supramolecular polymer nanofibers based on pillar[5]arene [21] also were prepared by the electrospinning technique. Cucurbit[n]urils (CB[n]s, n = 5–8, 10) are a family of pumpkin-shaped cyclic host molecules containing a hydrophobic cavity surrounded by two identical hydrophilic portals [22
Catalytic asymmetric oxo-Diels–Alder reactions with chiral atropisomeric biphenyl diols
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 955–962, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.92
- formation of a supramolecular structure whereas that of 6, containing additional CF3 substituents, shows the formation of a monomeric structure. Diols 1–6 were found to be active organocatalysts in oxo-Diels–Alder reactions in which 2 recorded a 72% ee with trimethylacetaldehyde as a substrate. Keywords
- supramolecular helices or dimers through intermolecular hydrogen bonding of two axially chiral biphenyl hybrid diols (1 and 2 in Scheme 1) which contain point chirality at the side arms and axial chirality at the biphenyl backbone [37]. We envisage the structural similarity and the ability of our scaffold to
- ; inter- D(OH···O): 1.822(3) Å] led to an enantiomerically pure infinite helical supramolecular structure. In contrast, only a dimeric structure was observed for the corresponding racemic mixture [39]. In our case, atropisomerization from (M)-(S,S) to (P)-(S,S) was not observed in solution. For catalyst 4
Halogen bonding and host–guest chemistry between N-alkylammonium resorcinarene halides, diiodoperfluorobutane and neutral guests
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 947–954, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.91

- guest inclusion in solution. Keywords: capsule; dimeric assemblies; halogen bonding; host–guest chemistry; resorcinarene salts; X-ray crystallography; Introduction The construction of specific supramolecular assemblies based on the directional non-covalent bonding has been a central goal of
- supramolecular chemistry and materials science [1][2][3]. New systems both help us to better understand the nature and impetus behind the self-assembly of these fascinating systems, while also providing new materials that can provide the basis for a wide number of applications [4][5]. Halogen bonding (XB), as a



















































































































































































































