Search results
Search for "electrochemical" in Full Text gives 462 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology. Showing first 200.
Magnetism and magnetoresistance of single Ni–Cu alloy nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2345–2355, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.219

- University of Bucharest, Faculty of Physics, PO Box MG-11, 077125, Magurele-Bucharest, Romania 10.3762/bjnano.9.219 Abstract Arrays of magnetic Ni–Cu alloy nanowires with different compositions were prepared by a template-replication technique using electrochemical deposition into polycarbonate nanoporous
- purpose of all these specific methods is to have a good and simultaneous control of morphology, structure and composition in order to succeed in tailoring the magnetic properties of the nanowires. A very useful technique to fabricate nanowire arrays is electrochemical deposition inside nanoporous
- electrochemical replication, using as templates chemically etched polycarbonate membranes irradiated with swift heavy ions. Individual Ni–Cu alloy nanowires of different compositions have been contacted on interdigitated metallic electrodes by using electron beam lithography (EBL) and magnetoresistive
Lead-free hybrid perovskites for photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2209–2235, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.207

- sandwiched between ETL and HTL, the photo-electrochemical HP-based systems are explored as well, where an electron-shutting redox-couple is used for the charge exchange between the light-absorbing electrode and a counter electrode. For example, a solar cell based on a MASnI3−xBrx film coupled to a carbon
- stability [165]. Along with the chemical and photochemical stability, MABI retains perfect integrity during charging/discharging events. In particular, a MABI-based electrochemical capacitor retains around 85% of its initial maximal capacitance after more than ten thousand charge/discharge cycles [158]. A
Interaction-induced zero-energy pinning and quantum dot formation in Majorana nanowires
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2171–2180, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.203

- , respectively. This different behavior can be clearly seen in Figure 2c where the electrochemical potential at the center of the wire, given by VZ + μ − (L/2), is plotted as a function of the Zeeman splitting, both in the presence and absence of interactions. The effect of this peculiar evolution of the
Electrospun one-dimensional nanostructures: a new horizon for gas sensing materials
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2128–2170, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.202

- integration flexibility. To date, many different gas sensing technologies have been developed. The predominant approaches to utilization are based on changes in the electrical conductance, optical properties, electrochemical potential or resonant frequency of the device [12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21
Phosphorus monolayer doping (MLD) of silicon on insulator (SOI) substrates
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2106–2113, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.199

- necessary when carrying out phosphorus MLD. This was done using bulk silicon samples. Electrochemical capacitance–voltage (ECV) profiling is a technique that analyses the quantity of active dopant atoms present in a substrate as a function of the depth. Figure 2 shows that the application of a capping layer
- thermal annealing and cap removal to provide an n-type doped silicon layer. Electrochemical capacitance–voltage profile showing the impact of applying a SiO2 capping layer for the duration of the annealing process. Both samples were annealed at 1050 °C for 5 s (the inset shows the allyldiphenylphosphine
Localized photodeposition of catalysts using nanophotonic resonances in silicon photocathodes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2097–2105, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.198

- -electrochemical system. The tapering angle of the silicon nanowires as well as the excitation wavelength are used to control the location of the hot spots together with the deposition sites of the platinum catalyst. A combination of finite difference time domain (FDTD) simulations with scanning electron
- , known optical constants and broad spectral absorption range. In presence of a Pt-catalyst precursor (H2PtCl6) in a three-electrode photo-electrochemical system (Figure 1), photogenerated electrons reach the surface of the silicon nanowires, reducing the precursor to form metallic platinum nanoparticles
- -electrochemical performance [39][40][41]. The amorphous TiO2 layer was further annealed at 350 °C for 3 h to form crystalline anatase TiO2, which led to an improved performance. The final TiO2 layers were characterized with X-ray diffraction (XRD) (Figure S2, Supporting Information File 1) and ellipsometry
Metal-free catalysis based on nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials: a photoelectron spectroscopy point of view
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 2015–2031, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.191

- studies on the oxidation of oxalic acid on charcoal containing nitrogen and iron [7]. In 1966, activated carbon, heated at high temperatures in the presence of ammonia, was used in the cathode of a fuel cell showing an enhanced activity for the electrochemical reduction of oxygen [8]. However, a metal
- vCNTs, to randomly oriented N-CNTs, and, in particular, to commercially available platinum-loaded carbon (Vulcan XC-72R), as reported in Figure 1. The electrochemical mechanism for the ORR was the same for aligned and disordered CNTs. The improved electrocatalytic performance of vCNTs was associated
- -electron pathway with higher steady-state current with respect to commercial Pt–C electrode. The authors referred to a long-term operation stability and tolerance to poisoning effects, such as the introduction of methanol and CO in the air-saturated electrochemical cell (Figure 2). The response of N
A differential Hall effect measurement method with sub-nanometre resolution for active dopant concentration profiling in ultrathin doped Si1−xGex and Si layers
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1926–1939, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.184

- concentration measurements by SCM [14]. Finally, capacitance-based techniques such as SCM or electrochemical capacitance voltage (ECV) [15], provide reliable values of carrier concentrations only in the absence of additional electrically active defects, which can affect the CV signal [16]. In contrast
Synthesis of carbon nanowalls from a single-source metal-organic precursor
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1895–1905, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.181

- batteries, electrochemical sensors or fuel cells [3][9][10][11][12][13][14][15]. Due to the high aspect ratio and the sharp top edges of the CNWs, a possible application could also be seen as electron field emitters [16]. Depending on the chosen deposition parameters, CNWs can have superhydrophobic or
Synthesis of rare-earth metal and rare-earth metal-fluoride nanoparticles in ionic liquids and propylene carbonate
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1881–1894, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.180
- gain increasing importance in materials science and modern chemistry [1][2][3]. Special attention has been paid to nanoscaled rare-earth metal particles [4][5][6]. In addition to the oxido and nitrido compounds, the rare-earth fluorides have interesting photo physical and electrochemical properties. An
- that the use of FeF2 nanoparticles as electrode material leads to a significant increase in the performance of the batteries compared to the macroscopic LiFeF3 [55]. Therefore, we investigated the electrochemical properties of ErF3-NPs by galvanostatic charge/discharge profiles (Figure 5). Until now
- images were calibrated with Debye–Scherrer patterns recorded from a gold reference sample (S106, Plano GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany). Thermogravimetric analysis: TGA was performed with Netzsch TG 209 F3 Tarsus equipped with an Al crucible by using a heating rate of 10 K·min−1. Electrochemical measurements: The
Synthesis of hafnium nanoparticles and hafnium nanoparticle films by gas condensation and energetic deposition
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1868–1880, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.179

- demonstrate high catalytic activity during hydrogenation of levulinic acid [17], nickel NPs, which find application as electrochemical sensor [18], and cobalt NPs, which exhibit high magnetic anisotropy [19]. Recently, we have reported that hcp hafnium nanoparticles fabricated by inert-gas condensation, when
Improving the catalytic activity for hydrogen evolution of monolayered SnSe2(1−x)S2x by mechanical strain
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1820–1827, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.173

- non-noble metals and earth-abundant elements is a promising pathway for achieving practical electrochemical water splitting. In this work, the electronic properties and catalytic activity of monolayer SnSe2(1−x)S2x (x = 0–1) under compressive and tensile strain were investigated using density
- in recent decades to the development of inexpensive catalysts for the electrochemical HER. Some of the recent studies have focused on monolayer SnX2 (X = S, Se). Liu et al. [43] investigated SnS2 nanosheets regarding their electrochemical behaviour and electrocatalytic properties for HER by examining
Nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles as sulfur encapsulator for high-performance lithium/sulfur batteries
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1677–1685, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.159

- carbon nanotubes coated with zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO@NCNT) were prepared via a sol–gel route as sulfur encapsulator for lithium/sulfur (Li/S) batteries. The electrochemical properties of the S/ZnO@NCNT composite cathode were evaluated in Li/S batteries. It delivered an initial capacity of 1032
- of nucleation sites in NCNT allows ZnO to uniformly grow on its surface with a small size. Also, NCNT has a higher electrical conductivity due to its additional free electron pairs compared to CNT without nitrogen doping. The ZnO@NCNT composite showed excellent electrochemical properties in lithium
- conductivity and the ability of active nitrogen sites to enhance the electrochemical performances of Li/S batteries [13][16]. To the best of our knowledge, such uniquely structured S/ZnO@NCNT composites have been rarely reported as cathode material for Li/S battery in the literature. Here, we present a
Nanoscale electrochemical response of lithium-ion cathodes: a combined study using C-AFM and SIMS
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1623–1628, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.154

- strong and localized electric field. Second, the combination of C-AFM and SIMS is used to correlate electrical conductivity and local chemistry in different cathodes for application in ASB. Finally, a promising starting point towards quantitative electrochemical information starting from C-AFM is
- –electronic conductors, represents an interesting starting point to obtain local electrochemical information from the sample using C-AFM [6]. Indeed, the biased tip induces a strong electric field (localized under the tip) inside the material, thus triggering a field-induced ionic migration of the Li ions
- , using MnO2 and LMO as cathode model systems for ASB, we have demonstrated the use of combined scanning probe and beam analysis techniques to investigate electrical, structural and electrochemical properties at the nanoscale. C-AFM was used for comparing the local electrical conductivity of the two
Correlative electrochemical strain and scanning electron microscopy for local characterization of the solid state electrolyte Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1564–1572, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.148

- improvement of solid state electrolytes such as LATP is a better understanding of interfacial and ion transport properties on relevant length scales in the nanometer to micrometer range. Using common techniques, such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, only global information can be obtained. In this
- work, we employ multiple microscopy techniques to gain local chemical and structural information paired with local insights into the Li-ion conductivity based on electrochemical strain microscopy (ESM). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) have been applied
- discussed. We demonstrate that correlative microscopy is an adjuvant tool to gain local insights into interfacial properties of energy materials. Keywords: correlative microscopy; electrochemical strain microscopy (ESM); Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 (LATP); scanning electron microscopy (SEM); solid state
Sheet-on-belt branched TiO2(B)/rGO powders with enhanced photocatalytic activity
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1550–1557, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.146

- hence are of different sizes, and especially different grain sizes that would readily affect the band gaps. Song et al. reported that the composite of anatase TiO2 synthesized via two different routes resulted in enhanced charge separation and hence increased photo-electrochemical response and
Optical near-field mapping of plasmonic nanostructures prepared by nanosphere lithography
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1536–1543, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.144

- laser onto a gold tip. A schematic of the experimental setup can be found elsewhere [37]. The elastically backscattered signal detected by a PMT was studied here. To obtain a tip with a radius down to 10 nm and low surface roughness, the gold tips were fabricated by electrochemical etching. A 100 µm
Cathodoluminescence as a probe of the optical properties of resonant apertures in a metallic film
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1491–1500, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.140

- apertures. The high sensitivity of the resonant modes of the apertures to the refractive index of the surrounding media underpins significant potential in realizing highly efficient ultra-compact biological and chemical sensors [26][27][28][29][30][31], plasmonic electrochemical sensors [32] and as SERS
Cr(VI) remediation from aqueous environment through modified-TiO2-mediated photocatalytic reduction
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1448–1470, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.137

- six sections. The optical and electrochemical characteristics of modified TiO2 photocatalysts are discussed in the first section. In the second section, we have reviewed how carbon-based advanced materials like reduced graphene oxide (RGO), carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and carbon dots (CDs) improve the
- range of TiO2 by modification with metal sulfides. The enhancement in photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) over noble-metal-modified TiO2 is depicted in section five whereas section six includes the use of dye-sensitized TiO2 for photoreduction of Cr(VI). Optical and electrochemical characteristics of
- modified TiO2 photocatalysts The photocatalytic activity of a photocatalyst is characterized by its optical and electrochemical properties. Modifications of titania can hinder the recombination of charge carriers and extend the light absorption range, which are evident from optical and photoelectrochemical
Preparation and morphology-dependent wettability of porous alumina membranes
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1423–1436, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.135

- [10][11], and the development of new nanoporous composite materials based on PAA [12][13]. Both of these are commercially available. Porous silicon formed by electrochemical anodizing [14], zeolites [15], porous mica [16], nanoporous polymer glasses [17] and other materials [18] have also been studied
Nanoporous silicon nitride-based membranes of controlled pore size, shape and areal density: Fabrication as well as electrophoretic and molecular filtering characterization
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1390–1398, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.131

- increase is due to the fact that the nanopillars etched in SiOx are slightly conical. Thus, the electrochemical growth step for the NPs could be substituted or shortened by adjusting the thickness of the SiOx sacrificial layer. For smaller pore diameters, this enlargement can be minimized by using
Ag2WO4 nanorods decorated with AgI nanoparticles: Novel and efficient visible-light-driven photocatalysts for the degradation of water pollutants
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1308–1316, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.123

- −) scavenger) or ammonium oxalate (a hole radical (h+) scavenger) was introduced, the degradation rate of RhB was severely depressed. That is, •O2−, •OH, and h+ were generated in the 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4 mediated degradation system, but •O2− and h+ played a more crucial role in RhB degradation. Electrochemical
- RhB in the presence of 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. (a) The cycled photocatalytic degradation of RhB over 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4; (b) XRD patterns of the fresh and used 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. Active-species trapping tests over 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) Nyquist plots of AgI and 0.3AgI/Ag2WO4
Electrodeposition of reduced graphene oxide with chitosan based on the coordination deposition method
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1200–1210, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.111

- , which can then be used for electrochemical detection. Keywords: chitosan; coordination; electrodeposition; nanocomposite films; reduced graphene oxide; Introduction Graphene has attracted tremendous attention due to its large surface area, excellent mechanical strength, high electronic conductivity
- et al. reported that after electrodeposition in the graphene oxide/chitosan solution, graphene nanosheets could be electrodeposited onto the glassy carbon electrode through the electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide [24]. However, it has been reported that the electrochemically reduced graphene
- oxide contains a high amount of oxygen-containing groups, suggesting only the partial reduction of graphene oxide during the electrodeposition [25][26]. This approach can generate hydrogen bubbles during the electrochemical reduction process, introducing defects which limit the subsequent applications
Semi-automatic spray pyrolysis deposition of thin, transparent, titania films as blocking layers for dye-sensitized and perovskite solar cells
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 1135–1145, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.105

- acetylacetone), concentration (0.05 and 0.2 M) and subsequent post-calcination at 500 °C. The photo-electrochemical properties were evaluated in aqueous electrolyte solution under UV irradiation. The blocking properties were tested by cyclic voltammetry with a model redox probe with a simple one-electron
- ), solid state dye-sensitized solar cells (SSDSSCs) and perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are attractive alternatives to solid state photovoltaics at competitive cost. The general concept of a DSSC is based on a liquid junction photo-electrochemical cell with a nanocrystalline TiO2 photoanode that is
- prevent recombination on this surface [3][4][5]. Blocking layers (BLs) can be fabricated by spray pyrolysis [3][6], magnetron sputtering [7], electrochemical deposition [8] spin coating [9][10], dip coating [11] and atomic layer deposition (ALD) [3]. From the viewpoint of low-cost processing and easy
Cyclodextrin inhibits zinc corrosion by destabilizing point defect formation in the oxide layer
Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9, 936–944, doi:10.3762/bjnano.9.86
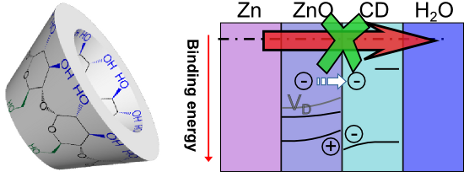
- . This work uses electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to show the cyclic oligosaccharide β-cyclodextrin (β-CD) to inhibit corrosion of zinc in 0.1M chloride with an inhibition efficiency of up to 85%. Only a monomolecular adsorption layer of β-CD is present on the surface of the oxide covered metal
- inhibitors [8][12][13]. Metallic zinc is industrially used for cathodic protection of steel [15]. In this work, the inhibition of zinc corrosion by β-CD was investigated electrochemically. Inhibition efficiencies were determined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). After exposure to chloride
- containing electrolyte, samples were analysed by angle-dependent X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ADXPS) combined with ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS). Results and Discussion Electrochemical measurements of the corrosion potential Ecorr displayed in Figure 1a show a cathodic shift by several








































































































































































































































