Search results
Search for "evolution" in Full Text gives 293 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Disposable cartridge concept for the on-demand synthesis of turbo Grignards, Knochel–Hauser amides, and magnesium alkoxides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1343–1356, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.115

- exothermic Grignard reaction done at 25 ºC was not fully dissipated by the heat exchanger (≈10 ºC increment). To better understand this exothermic process, we decided to measure the temperature evolution during the conversion of EtBr (0.5 M) at a 0.5 mL/min flow rate with no heat controller. Three
- coil reactor placed in the left reactor area. E) Example of a disposable cartridge. Temperature evolution measured with thermocouples along the column outer surface at three different points. Stratified bicomponent column (Diba Omnifit EZ Solvent Plus) composed of magnesium (chips/powder, 1:1) and
Activated carbon as catalyst support: precursors, preparation, modification and characterization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1188–1202, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.104

- ammonia due to the evolution of NH3 and HCN. Depending on the modification temperature, nitrogen is incorporated mainly to aromatic rings at higher temperatures, while less temperature-stable amide-like functionalities were formed at lower temperatures [129]. Composition of activated carbon Elemental
A smart deoxyribozyme-based fluorescent sensor for in vitro detection of androgen receptor mRNA
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1135–1141, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.100

- random sequence molecules, also known as SELEX (systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment), and was a holistic harpin [22]. In further work MGA was separated into two strands, and nucleic acid binding arms were added to each strand, allowing MGA to target a sequence of interest
Synthesis of esters of diaminotruxillic bis-amino acids by Pd-mediated photocycloaddition of analogs of the Kaede protein chromophore
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1111–1123, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.98
- spectra were measured on a Thermo Scientific Evolution 600BB spectrophotometer. Cinnamoylglycine (1) was prepared by the Schotten–Baumann method [49]. Irradiation setup for batch synthesis The irradiation setup consisted of a flask (100 mL) irradiated by a printed circuit board (PCB) formed by 24 LEDs of
Accelerating fragment-based library generation by coupling high-performance photoreactors with benchtop analysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 982–988, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.87
- collections. These are of high value to medicinal chemists to provide defined exit vectors and facilitate rational lead evolution [2][3][4][5][6][7]. Thus, we were interested in developing reliable synthetic methods and technologies to apply metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions to such scaffolds, which
Copper catalysis with redox-active ligands
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 858–870, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.77

- a different matter. The Arnold group has elegantly shown that through iterative mutagenesis “directed evolution” enzymes can be coaxed to perform unnatural transformations such as C–N bond forming aziridination, which has no biological counterpart [33]. While the exact structure of the mutant
Copper-catalyzed O-alkenylation of phosphonates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 611–615, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.56
- products. An acetal-protected aldehyde could also be used providing enol phosphonate 3g in 52% yield. In this case, prolonged reaction times led to partial evolution of 3g into enol ether 4. This transformation may be explained by an acid-mediated elimination of ethanol likely caused by trace formation of
Synthesis of 3-alkenylindoles through regioselective C–H alkenylation of indoles by a ruthenium nanocatalyst
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 140–148, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.16
- essentially zerovalent Ru nanoparticles promotes their catalytic ability towards several challenging reactions, such as CO oxidation [67][68] and hydrogen evolution [69]. Interestingly, pristine Ru(0) single crystals have been reported to perform poorly in these reactions when compared to the surface-oxidised
Potent hemithioindigo-based antimitotics photocontrol the microtubule cytoskeleton in cellulo
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 125–134, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.14

- neurons; the regulation and functioning of these processes is still not satisfactorily understood [1][2][3][4]. The MT cytoskeleton is a finely tuned complex system that is highly conserved through evolution. Direct genetic modifications of tubulin that affect its functions risk causing a diversity of
Bacterial terpene biosynthesis: challenges and opportunities for pathway engineering
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2889–2906, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.283

- during evolution. In contrast, the underlying mechanistic logic of terpene biosynthesis is based on repetitive electrophilic and nucleophilic functionalities in each oligomeric substrate, similar to nonmodular type II PKSs, coupled with conformational flexibility for enzyme-mediated juxtaposition of
- nature [39]. Therefore, evolution would likely favor organisms that can generate and retain chemical diversity at a low cost [38]. As a result, producing and “screening” a large number of specialized metabolites for potent TCs that can generate multiple products from simple building blocks is a huge
- reported [40]. In fact, different pathways have evolved in plants, fungi, and bacteria for this fascinating compound family in an extreme case of convergent evolution [41][42]. While the plant and fungal biosynthetic pathways are well studied [42], the bacterial pathway was studied to a lesser degree until
Emission and biosynthesis of volatile terpenoids from the plasmodial slime mold Physarum polycephalum
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2872–2880, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.281
- relatedness to bacterial TPSs. The biological role of the volatile terpenoids produced by the plasmodia of P. polycephalum is discussed. Keywords: amoebae; evolution; terpene synthases; volatiles; Introduction Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are used by many living organisms as chemical languages for
- ), suggesting two evolutionary origins of PpolyTPS genes. It is tempting to speculate that PpolyTPS2 and PpolyTPS3 may be derived from bacteria through horizontal gene transfer, which was recently demonstrated to have occurred from bacteria to fungi for the evolution of TPS genes [26]. It is also interesting to
Chiral terpene auxiliaries V: Synthesis of new chiral γ-hydroxyphosphine oxides derived from α-pinene
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2493–2499, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.242
- gas evolution ceased. Solvents were removed using a rotary evaporator and the resulting intermediate was dissolved in dichloromethane (6 mL). meta-Chloroperbenzoic acid (75%, 2.301 g, 10 mmol) was dissolved in dichloromethane (10 mL), cooled in a dry ice–acetone bath, and the intermediate solution was
Ultrafast processes triggered by one- and two-photon excitation of a photochromic and luminescent hydrazone
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2438–2446, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.236

- positive signal at <380 nm, where absorption of the E-isomer is expected, signals the occurrence of isomerization. This event is also associated to the aforementioned evolution in the visible region, clearly indicating a variation of the excited state electronic distribution. No further band-shape changes
- . The output of the global analysis retrieves the kinetic constants describing the evolution of the system and the associated spectral components, the so-called EADS (evolution associated difference spectra) which are shown in Figure 4b. As it can be noticed, the evolution occurring on the 0.6 ps
- an absorption band in the region where the E-isomer absorbs is indicative of the photoinduced Z/E isomerization event, which thus results to be an ultrafast process, as observed for other photoswitches – azobenzene in particular [32]. Upon this initial ultrafast evolution, the transient absorption
Excited state dynamics for visible-light sensitization of a photochromic benzil-subsituted phenoxyl-imidazolyl radical complex
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2369–2379, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.229

- (355 nm). The difference may affect the ratio of isomer A and isomer B at the photostationary state (PSS) and initial relaxation kinetics at sub-picosecond time scales. Benzil was used for a reference sample. Figure 3a shows the time evolution of the transient absorption spectra of benzil in benzene
- (Equation 2) convolved with Gaussian pulse. The detail of the SVD analyses are shown in Supporting Information File 1. The evolution associated spectra (EAS) thus obtained indicate the resolved transient absorption spectra into each component of the kinetic models. Because the time window of our
- biradical generated instantaneously, respectively. It indicates that the biradical was also formed by the direct excitation of the PIC unit with 400 nm light. The spectral evolution from EAS1 (160 fs, grey line in Figure 3d) to EAS2 (1.4 ps, red line in Figure 3d) shows the C–N bond cleavage of the PIC unit
Fluorinated azobenzenes as supramolecular halogen-bonding building blocks
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2013–2019, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.197
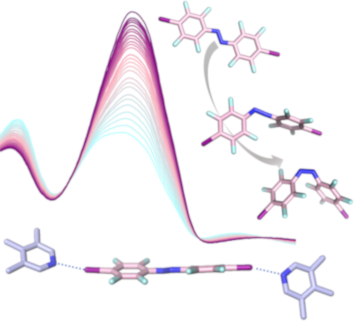
- most positive compared to that of A2 and A1. The evolution of the iodine potential follows our experimental observation with iodoethynylazobenzene A3 being the strongest halogen bond donor and A1 being the weakest, within this series [48]. For potential, reversible photochemical control of
Functional panchromatic BODIPY dyes with near-infrared absorption: design, synthesis, characterization and use in dye-sensitized solar cells
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1758–1768, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.169

- /EtOH 1:1 (v/v)). Photovoltaic parameters evolution with the increasing concentration of tBP in the electrolyte. Selected optical properties of compounds BOD-TTPA-alk and BOD-TTPA. Photovoltaic parameters of compounds BOD-TTPA-alk and BOD-TTPA (light source: AM1.5G at 100 mW·cm−2, electrolyte
Transient and intermediate carbocations in ruthenium tetroxide oxidation of saturated rings
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1552–1562, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.158

- , with P1, P2 and P3, respectively. A close inspection of the IRCs revealed a shoulder characteristic of a transient carbocation [23] which is more pronounced following the sequence R1 < R2 < R3. The preliminary analysis of the evolution of bonds along those IRCs further confirmed a high asynchronicity
- transient carbocation is supported by the disappearance of V(C1) and the trigonal planar geometry observed for C1 in the above indicated gap. The evolution of the electron population is in clear agreement with the development of a partial positive charge at C1 (+0.25 at point 100). The oxidation of
- tetrahydrothiophene (TS3). The IRC (black trace) and O–H (green trace), C–H (brown trace), and C–O (blue trace) distances are also given. The double red arrow indicates the delay between H transfer and C–O bond formation. ELF analysis for the oxidation of cyclopentane (R1). Left: evolution of the electron population
Borylation and rearrangement of alkynyloxiranes: a stereospecific route to substituted α-enynes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1416–1424, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.141
- in organic synthesis [1][2]. Such species can undergo different reactions, driven either by their carbanionic or carbenic behavior [3][4], thus leading to various products. In contrast, the transmetalation of lithiated oxiranes and the evolution of the resulting species have been less explored
Synthesis of non-racemic 4-nitro-2-sulfonylbutan-1-ones via Ni(II)-catalyzed asymmetric Michael reaction of β-ketosulfones
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1289–1297, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.127
- 8a or 9a. Оne of the stereoisomers can be formed directly during the reaction. To test this hypothesis, we decided to study the evolution of dr on the course of reaction by 1H NMR spectroscopy (Figure 3). The reaction of sulfone 5a with ω-nitrostyrene (6a) was chosen as the model reaction. Conversion
- the reaction was observed. Рharmacologically active sulfones. Structures of the ligands L1–L8. Evolution of the conversion of 5 and diastereomeric composition of the products of reaction of 5a with 6a in the presence of catalyst 7a (2 mol %) in chloroform-d. Time profile of epimerization and retro
Self-assembly behaviors of perylene- and naphthalene-crown macrocycle conjugates in aqueous medium
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1203–1209, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.117

- DLS measurement result showed that the size of aggregates of 2 formed in H2O/MeCN (v/v = 10:1) was centered at 576.8 nm. It should be noted that the aggregates formed by 1 and 2 with specific shapes were obtained immediately after the preparation of solutions, without days’ evolution process [77
Alkylation of lithiated dimethyl tartrate acetonide with unactivated alkyl halides and application to an asymmetric synthesis of the 2,8-dioxabicyclo[3.2.1]octane core of squalestatins/zaragozic acids
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1194–1202, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.116
- ][11]. Here, we report in detail the evolution of chemistry that provides an asymmetric entry to the tricarboxylate core of these natural products, with particular focus on tartrate alkylation methodology to establish the fully-substituted C-5 stereocentre (squalestatin numbering). Our studies in this
Phylogenomic analyses and distribution of terpene synthases among Streptomyces
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1181–1193, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.115

- /bjoc.15.115 Abstract Terpene synthases are widely distributed among microorganisms and have been mainly studied in members of the genus Streptomyces. However, little is known about the distribution and evolution of the genes for terpene synthases. Here, we performed whole-genome based phylogenetic
- analysis of this genus is discussed. Keywords: biosynthesis; evolution; geosmin; Streptomyces; terpenes; Introduction Streptomyces are soil bacteria that belong to the order of actinomycetales and are a rich source of natural products with broad biotechnological interest. Species of this genus have a
- available in the NCBI database and compared the distribution of terpene synthase genes among them. Furthermore, we studied whether phylogenetic trees calculated based on the three most abundant terpene synthases in Streptomyces represent the evolution of the Streptomyces species based on the whole genome
Synthesis of aryl cyclopropyl sulfides through copper-promoted S-cyclopropylation of thiophenols using cyclopropylboronic acid
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1162–1171, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.113
- using an encapsulated solvent purification system and were further dried over 4 Å molecular sieves. The evolution of reactions was monitored by analytical thin-layer chromatography using silica gel 60 F254 precoated plates. Flash chromatography was performed employing 230–400 mesh silica using the
Mechanochemical synthesis of hyper-crosslinked polymers: influences on their pore structure and adsorption behaviour for organic vapors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1154–1161, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.112
- a decrease of the C–Cl vibration after the reaction. B: Low pressure nitrogen isotherm of NG-HCP demonstrating the textural properties. A: Evolution of pressure in the course of the reaction measured by the GTM system. The addition of 1 mL of Et2O is sufficient to drastically reduce the released
Precious metal-free molecular machines for solar thermal energy storage
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1096–1106, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.106

- constants of metal complexes were determined and are in good agreement with the literature data for reference dyes. The temporal evolution of trans-to-cis isomerization was observed in a real-time regime. The dyes demonstrated a low intrinsic fluorescence of their Ba2+ complexes and high yield of E/Z
- characteristic changes in the absorption spectra of dye 4b–Ba2+ complex under optical excitation with λ = 488 nm and intensity of 14 mW cm−2. The temporal evolution of the absorption at specific wavelength of λabs = 500 nm is demonstrated in Figure 3b: during the first time interval from t1 = 10 s up to t2 = 180
- × 10−4 M) with Ba2+ (cM = 1 M) on the irradiation time. b) Temporal absorption evolution, measured at λabs = 500 nm, upon irradiation. Experimental conditions: Excitation wavelength λexc = 488 nm; excitation intensity 14 mW cm−2, solvent, ACN; pulse duration t = 180 s. UV–vis absorption spectra of dye








































































































































































































