Search results
Search for "modification" in Full Text gives 782 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Facile access to pyridinium-based bent aromatic amphiphiles: nonionic surface modification of nanocarbons in water
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 32–40, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.5
- )2–Y (Y = OCH3, OH, and imidazole)). The new amphiphiles quantitatively self-assemble into ≈2 nm-sized aromatic micelles in water independent of the side-chain. Importantly, efficient water-solubilization and nonionic surface modification of various nanocarbons (e.g., fullerene C60, carbon nanotubes
- ., graphitic carbon nitride) in the form of 10–30 nm-sized stacks is also demonstrated using the present amphiphiles. Keywords: aromatic micelle; nanocarbon; nonionic surface modification; pyridinium; water-solubilization; Introduction Nanocarbons, such as fullerenes, graphenes, and carbon nanotubes, are
- of the side-chain present. Importantly, efficient water-solubilization and nonionic surface modification of nanocarbons (i.e., fullerene C60 (C60), single/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (s/m-CNT), and graphene nanoplatelets (GN)) can be achieved through noncovalent encircling with the present
Studying specificity in protein–glycosaminoglycan recognition with umbrella sampling
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1933–1946, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.144

- structural analysis of GAGs is extremely difficult due to their complex pattern of modification such as epimerization and sulfation [29]. In addition, GAGs’ high flexibility and periodicity render these molecules profoundly challenging to analyze using experimental techniques only [30][31]. Thus
Biphenylene-containing polycyclic conjugated compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1895–1911, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.141
- presence of two reduction potentials commonly observed in azaacenes, suggesting that the modification did not alter this characteristic feature. For compound 58a, λmax was observed at 600 nm, and λmax,em was at 614 nm. On the other hand, for compound 58b, λmax was found at 606 nm, and λmax,em occurred at
Anion–π catalysis on carbon allotropes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1881–1894, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.140

- introduced explicitly in 2019 [13]. Already in the presence of pristine SWCNTs 2, the ability of TEA 23 to catalyze enolate addition with 4 increased to A/D48/23 = 1.2 for a virtual catalytic complex 48 between the two (Figure 8). Covalent modification of SWCNTs with tertiary amines as in 49 further
- . This is not surprising because virtual complexes 52 and 48 are not expected to exist to an appreciable extent. With covalent modification, MWCNTs 53 with A/D53/23 = 7.3 outperformed the corresponding SWCNTs 49 with A/D49/23 = 2.0 clearly. This significant increase in activity was consistent with the
N-Boc-α-diazo glutarimide as efficient reagent for assembling N-heterocycle-glutarimide diads via Rh(II)-catalyzed N–H insertion reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1841–1848, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.136
- circumstances, considerably impacting their pharmacological utility [19][20], Moreover, the conventional CRBN recruiters restrict structural modification options necessary to maintain satisfactory affinity for the E3-ligase [21][22][23][24]. These limitations underscore the relevance of expanding the chemical
- N–H bond of tetrazoles and 1,2,4-triazole was realized for the first time. This transformation can serve as a powerful tool to carry out N-modification of these heterocycles. Despite all our efforts, it was not possible to obtain N–H insertion products with N-heterocycles containing an α-carbonyl
- the preparation of modified glutarimides with a wide range of aromatic and aliphatic NH-heterocycles under mild conditions in moderate to high yields. It is shown that electron-rich substrates tend to give C–H insertion products. The N-modification of tetrazoles and 1,2,4-triazoles using a
Substituent-controlled construction of A4B2-hexaphyrins and A3B-porphyrins: a mechanistic evaluation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1832–1840, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.135
- been reported involving the use of A3-bilanes [30][31] or dipyrromethane–dicarbinols [32], the modification of A4-porphyrins [33], or the reaction of pyrrole with different aldehydes [34]. In the present work, the applied synthetic method provided the A3B-porphyrins in a single-step reaction from
Recent advancements in iodide/phosphine-mediated photoredox radical reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1785–1803, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.131
- of mild reaction conditions allowed for the application of this method in the modification of complex natural products or pharmaceuticals. Moreover, this photoinduced decarboxylative approach demonstrated the potential for broader utilization in the construction of diverse C(sp3)–N and C(sp3)–X bonds
Unprecedented synthesis of a 14-membered hexaazamacrocycle
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1728–1740, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.126
- , in contrast to pure imidate 4. Pyrazolopyrimidine 8 was prepared by the reaction of 4 with N2H4∙H2O in EtOH according to our modification of the described procedure [40] using room temperature (without pre-cooling), a lower excess of N2H4∙H2O (1.6 equiv instead of 5 equiv) and a shorter reaction time
- -standard approach [44]. 3-[(Ethoxymethylene)amino]-1-methyl-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile (4): Imidate 4 was prepared according to the literature method [43]. Our modification of the method is provided below in details. A solution of aminopyrazole 3 [42] (9.044 g, 74.10 mmol) in HC(OEt)3 (145 mL) was stirred
Effects of the aldehyde-derived ring substituent on the properties of two new bioinspired trimethoxybenzoylhydrazones: methyl vs nitro groups
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1713–1727, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.125

- derived from 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid hydrazide, a modification inspired by mescaline, the active principle of the hallucinogenic cactus peyote, which could result in a greater BBB penetration [36]. In this study, however, the structural modifications in the compound did not seem to significantly
Quinoxaline derivatives as attractive electron-transporting materials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1694–1712, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.124

- modification, the study by Zhou et al. showcases the importance of solvent choice and annealing techniques in optimizing the performance of all-PSCs using Qx9 and Qx10. While both polymers served as donors in all-PSC devices, the study primarily focused on side chain engineering of the electron-deficient Qx
- unit. The combination of thermal annealing treatment and the use of THF as a non-halogenated solvent led to improvements in photovoltaic performance and charge carrier transport. Additionally, the impact of side chain modification on device characteristics, such as lower HOMO and higher circuit voltage
- enhanced electron hopping and reduced geminate recombination. Qx12 and Qx13 achieved remarkable PCEs of 13.31% and 16.64%, respectively, with PBDB-TF donor in OSC devices [28]. Zhu et al. reported a modification in Qx13 by incorporating an imide-functionalized Qx moiety in its core and end-capping groups
A series of perylene diimide cathode interlayer materials for green solvent processing in conventional organic photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1620–1629, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.119

- the previously reported N-annulated PDI (PDIN-H) and nitrile functionalized N-annulated PDI (CN-PDIN-H) compounds (Figure 1c) as the scaffolds for modification [18]. The PDIN-H scaffold was modified by N-functionalization with a benzyl (PDIN-B) or pentafluorobenzyl group (PDIN-FB). Similarly, the CN
Radical chemistry in polymer science: an overview and recent advances
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1580–1603, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.116
- past century, new knowledge on radical chemistry has both promoted and been generated from the emergence of polymer synthesis and modification techniques. In this review, we discuss radical chemistry in polymer science from four interconnected aspects. We begin with radical polymerization, the most
- employed technique for industrial production of polymeric materials, and other polymer synthesis involving a radical process. Post-polymerization modification, including polymer crosslinking and polymer surface modification, is the key process that introduces functionality and practicality to polymeric
- constantly acquire new inspirations from organic chemists. Dialogues on radical chemistry between the two communities will deepen the understanding of the two fields and benefit the humanity. Keywords: crosslinking; polymer surface modification; post-polymerization modification; radical chemistry; radical
Synthesis of 5-arylidenerhodanines in L-proline-based deep eutectic solvent
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1537–1544, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.110
- Stephanie Hesse Université de Lorraine, LCP-A2MC, F-57000, Metz, France 10.3762/bjoc.19.110 Abstract Rhodanines and their derivatives are known to have many pharmacological activities that can be modulated through different functionalization sites. One of the most studied modification in those
Synthesis and biological evaluation of Argemone mexicana-inspired antimicrobials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1511–1524, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.108
- effects of each modification. It was found that the acetone adduct B9 and the partially reduced variant B10 were more potent, while the fully reduced variant B11 was significantly less active (Table 2). These results suggested the activity of B1 could be similarly altered by the same modifications to the
- structural modification, this was chosen as the path towards enhancing the activity of B1. As shown in Scheme 5, we reduced B1 to produce B14, which was then screened against our panel of microbial organisms (Table 2). We were very pleased with the results of B14, representing a near universal improvement
- desired derivatives. Unexpected oxidation side-product B2, B4, and B6 were also isolated from certain reaction mixtures. Direct modification of the original berberine structure. Preparation of non-cyclic charged variants of B1. Partial reduction of compound B1 to B14. Synthesis of the substituted 2
Application of N-heterocyclic carbene–Cu(I) complexes as catalysts in organic synthesis: a review
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1408–1442, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.102
- or carbon–heteroatom double bond, resulting in the formation of a new carbon–silicon (C–Si) or heteroatom–Si (X–Si) bond (Scheme 34). This reaction is widely used in the synthesis of organosilicon compounds and in the modification of surfaces with silicon-containing molecules. NHC–Cu complexes have
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- with biomembranes via supramolecular interactions with the lipids and proteins that are embedded in these membranes. We can hypothesis that their mechanism of action occurs via a direct interaction with membrane proteins or by a modification of the biophysical properties of the membranes. It must be
- solubility of the salt. 1.2 Analogues of PAF with modification on sn-1 position PAF is characterized by a C16 or C18 saturated lipid chain at the sn-1 position. A first analogue, reported by Hirth et al. in 1983, consisted in replacing this saturated lipid chains by the mono-unsaturated oleyl ((Z)-octadec-9
- installation of the phosphocholine moiety (67%) followed by the deprotection of the secondary alcohol (100%) and its acetylation (53%) produced 13.6. Wissner et al. also reported the incorporation of a gem-dimethyl substituent on the glycerol backbone [97]. One illustration of this structural modification is
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
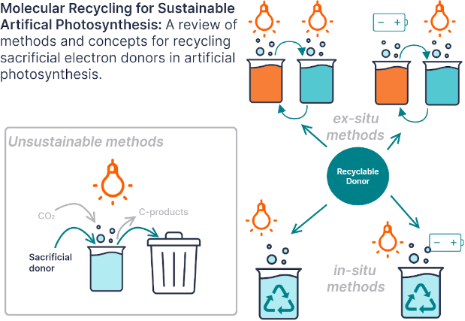
- mediators that can be recycled photo- and electrochemically [45][49]. As illustrated in Figure 5, structural modification of the benzimidazole core alters the redox behavior and allows tuning of the oxidation potential. The benzimidazoles shown all have enough reducing power to reductively quench Ru(bpy)3
Exploring the role of halogen bonding in iodonium ylides: insights into unexpected reactivity and reaction control
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1171–1190, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.86

- hard fluoride interacts with the stronger σ-hole. Structural modification of the β-dicarbonyl auxiliary has led to improved outcomes, due to increased ylide stability rather than decreasing activation energies of the fluorination reaction. There are, however, other conflicting pieces of evidence that
Photoredox catalysis harvesting multiple photon or electrochemical energies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1055–1145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.81
The effect of dark states on the intersystem crossing and thermally activated delayed fluorescence of naphthalimide-phenothiazine dyads
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1028–1046, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.79

- not changed by the unique molecular structure modification method [51]. This approach is useful for studying molecules showing complicated, entangled photophysical processes upon photoexcitation, for instance the electron donor–acceptor type of TADF emitters [44][46]. Recently, we reported NI-PTZ
Photoredox catalysis enabling decarboxylative radical cyclization of γ,γ-dimethylallyltryptophan (DMAT) derivatives: formal synthesis of 6,7-secoagroclavine
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 918–927, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.70
- ][32][33], modification of biomacromolecules [34], and relatively complex pharmaceutical agents [35][36][37][38]. Photocatalysis tremendously enriches the synthetic compound library, providing a precious alternative to directly modify abundant natural substrates, including biomass, which usually
- selectively targeted by photoredox catalysis to enable unprecedented modification of the amino acid. In this context, it is worth mentioning that the single-electron oxidation of the indole moiety in tryptophan provides the radical cation, which enables selective C-radical generation at the weaker benzylic
Intermediates and shunt products of massiliachelin biosynthesis in Massilia sp. NR 4-1
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 909–917, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.69
- fulfill specific functions, ranging from the selection and linkage of building blocks to their chemical modification. A plausible scenario for the formation of compounds 1–6 involves the enzymatic machinery for massiliachelin biosynthesis, namely the protein RS02200 [18]. According to our proposal (Figure
Cyclodextrins as building blocks for new materials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 889–891, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.66

- reactivity of their alcohol functions. This allows regioselective chemical modification at either the primary or secondary rim [13]. As a result, these molecular hosts can be specifically linked either covalently or noncovalently to a wide variety of ligands. CDs are a significant part of almost all areas of
Eschenmoser coupling reactions starting from primary thioamides. When do they work and when not?
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 808–819, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.61
- observed in both MeCN and DMF which was in equilibrium with the starting compounds in a ratio of approximately 1:2. The addition of a base or any thiophile always caused only the decomposition to a complex mixture of products in which no ECR product was detected. Next, we performed modification of the
Facile access to 3-sulfonylquinolines via Knoevenagel condensation/aza-Wittig reaction cascade involving ortho-azidobenzaldehydes and β-ketosulfonamides and sulfones
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 800–807, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.60
- modification of various substrates, such as 3-bromoquinolines [52][53][54][55], quinoline-3-boronic acids [56], and diazonium salts [57]. When considering general methods for the quinoline core formation, aromatic ortho-substituted carbonyl compounds attract attention as decent and easily available reagents
































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































