Search results
Search for "cation" in Full Text gives 659 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Recent developments in photoredox-catalyzed remote ortho and para C–H bond functionalizations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 248–280, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.26

- takes place for the generation of the S-centered radical 57. The reactive aryl radical 58 is obtained by the cyclization of the sulfur-based radical 57. Simultaneously, photocatalyst 11 is regenerated from Ru(I) photocatalyst 51 and Co(III) complex 56. Additionally, the Co(I) complex 54 and the cation
- , followed by the reduction of 72 to PhCO2− along with the generation of the radical 73, which further attacks the electron-richest position of 70. Next, the reactive cation species 75 is generated via an SET mechanism. In the end, PhCO2− abstracts a proton, which yields the benzoyloxylated product 71, as
- catalyst for the oxidation of the arenes. The reaction is initiated by the oxidation of 100 through the excited photocatalyst to generate the arene radical cation 102. Here, P(OEt)3 acts as a nucleophile, capturing the radical cation of 102 and generating 103. Concomitant to the reduction of the Co(III
The use of isoxazoline and isoxazole scaffolding in the design of novel thiourea and amide liquid-crystalline compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 175–184, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.20
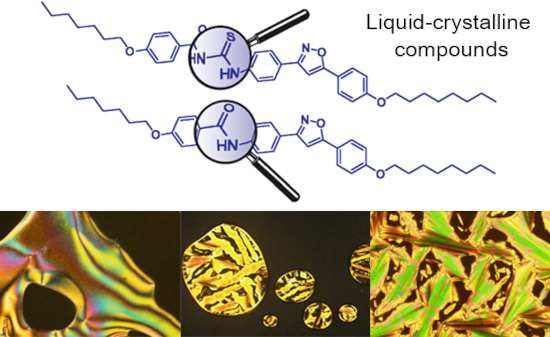
- the thiocyanate salt, following the same experimental protocol. However, when a cyanate salt was used, only the amides 19–22 were isolated as the main products. The target ureas were not obtained, according to Scheme 3, part A. To test the hypothesis of intermediate formation of acyl cation [ArCO
The reaction of arylmethyl isocyanides and arylmethylamines with xanthate esters: a facile and unexpected synthesis of carbamothioates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 159–167, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.18
- amount of NaH (Table 1, method A, entry 8, cf. entry 1) but 2 equivalents in the other solvents suggested that the latter scenarios (a and b) were less likely and that the methylthiolate was perhaps countered by the sodium cation from sodium hydride. Further work on this and other isocyanide-mediated
Understanding the role of active site residues in CotB2 catalysis using a cluster model
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 50–59, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.7

- isotope labeling experiments combined with QM calculations. Intermediate G forms via a 1,5-hydride shift from C6 to C10 to generate a homoallylic cation, and the formation of intermediate H occurs due to cyclization to yield a cyclopropyl ring. Intermediate I forms due to isomeric formation of a
- cyclopropylcarbinyl cation, as shown by isotope labeling [41]. QM calculations support this unusual 1,3-alkyl shift that interconverts H and I [38][39]. Finally, the cyclopropyl ring opens by virtue of a nucleophilic water attack, and cyclooctat-9-en-7-ol is formed. Although gas phase calculations shed light on the
- site model energies. All interaction distances are provided in Table 1, which provided the basis for the following categorization of interactions as π–cation, dipole–cation, and charge–cation. Note, that no attempts to quantify the individual pairwise interactions were made. Carbocation A was
Extension of the 5-alkynyluridine side chain via C–C-bond formation in modified organometallic nucleosides using the Nicholas reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1–8, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.1
- hexacarbonyl complexes; Nicholas reaction; nucleosides; propargyl cation; Introduction Nucleoside analogs are molecules of high pharmacological interest for the treatment of various conditions, especially cancer and viral diseases [1][2][3][4][5]. The substitution at C-5 of the uracil nucleobase provides a
- functionalization by way of propargyl dicobalt cation chemistry. Nucleoside modifications are considerably challenging due to the presence of reactive functional groups. Since numerous uridine C-5 modifications play an important role in biochemistry, we considered exploration of pertinent methods development
Synthesis and characterization of bis(4-amino-2-bromo-6-methoxy)azobenzene derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 3000–3008, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.296
- elevated pKa of 1 has been attributed to resonance stabilization of the azonium cation together with intramolecular H-bonding between the azonium proton and methoxy groups in ortho-position to the azo double bond [10]. Since the azonium ion 1 forms under physiological conditions, i.e., at neutral pH value
SnCl4-catalyzed solvent-free acetolysis of 2,7-anhydrosialic acid derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2990–2999, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.295
- bond of the positively charged intermediate 17 rapidly undergoes bond cleavage to generate the sialyl cation 18, which is then attacked by nucleophile 16 from the β-face to provide the desired acetolysis product 20 and the original SnCl4 species. On the other hand, abstraction of hydrogen H-3 by the
- the sialyl cation could also have affected cleavage of the ring [12][13][14]. To further test the scope of the optimized ring-opening conditions, disaccharides 29, 33, and 37, bearing a 2,7-anhydro-Neu5N3 unit, have been synthesized based on our reported procedure [6] and were examined as substrates
Regioselectivity of glycosylation reactions of galactose acceptors: an experimental and theoretical study
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2982–2989, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.294

- between the ground-state molecule and the radical cation (fa) [41], a direct calculation of the frontier molecular orbitals (fb) [42] was carried out. For simplicity, analogs of acceptors 1α/β and 2α/β, where benzoyl and benzyl groups were replaced by acetyl and methyl moieties, respectively, were used
Synthesis and optoelectronic properties of benzoquinone-based donor–acceptor compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2914–2921, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.285
- derivatives (3 and 4) showed irreversible oxidation waves, which is a function of the electrochemically unstable carbazole-based radical cation that can subsequently undergo dimerization [34]. The oxidation waves shifted cathodically upon increasing the donor strength from carbazole (3 and 4) to diphenylamine
Bacterial terpene biosynthesis: challenges and opportunities for pathway engineering
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2889–2906, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.283

- the leaving pyrophosphate group and the nucleophilic alkenes in proximity to initiate the C–C-bond forming, carbocation-mediated cascade reactions [10]. The hydrophobic binding pocket stabilizes the reaction intermediates and tames the propagation of carbocations through cation–π and other
Palladium-catalyzed synthesis and nucleotide pyrophosphatase inhibition of benzo[4,5]furo[3,2-b]indoles
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2830–2839, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.276
- . However, the zinc–metal interaction was exhibited by the substituted phenyl moiety on the indole ring. The oxygen atom of the furan ring of dual inhibitor 6e showed a single hydrogen bond with Phe548. Asp423 was found to be involved in two π–cation bindings with the indole ring, whereas π–π stacked, π–π T
- = 254 nm). Column chromatography was performed on Fluka silica gel 60 (0.063–0.200 mm, 70–320 mesh) on a glass column. For the cation exchange column dowex 50WX8 H+ was used. Melting points (mp) were determined by the instrument Elektrothermal. 1H and 13C NMR spectra («Mercury-300 Varian» 300 MHz with
Photoreversible stretching of a BAPTA chelator marshalling Ca2+-binding in aqueous media
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2801–2811, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.273

- molecules, since the 1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) scaffold was first described by Tsien, it has been widely used in biological systems and has given rise to a wealth of derivatives [1]. Key to the wide interest in this cation binder are its high specificity for Ca2+ ions
- EDTA) such that photoswitching would enhance or lower Ca2+ binding based on the state of the adjacent photoswitch. Photogeneration of a positive charge proximal to the BAPTA site is undoubtedly the most robust approach to provoke calcium cation release, while diminishing electron density on the
A review of asymmetric synthetic organic electrochemistry and electrocatalysis: concepts, applications, recent developments and future directions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2710–2746, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.264

- reduction of pyruvic acid (36) using this electrode in a two compartment cell separated by a cation exchange membrane resulted in the production of ᴅ-alanine (37) with almost 100% ee (Scheme 15). As per the proposed mechanism, the imino acid 36A produced from the reaction of acid with NH4OH, gets oxidized
- resulted in the corresponding coupling products 108 in moderate yields and good enantioselectivities. After detailed electrochemical analysis, the authors proposed that the reaction proceeds through the intermediacy of radical cation 111, generated via anodic oxidation of enamine 110 (Scheme 37). The same
- 115 with moderate enantioselectivity (Scheme 38). As shown in Scheme 39, the mechanism involved initial formation of radical cation 117 via anodic oxidation of enamine 116 (obtained from the condensation of 114 and 105'), which then coupled with xanthene radical 119 (Scheme 39). Finally, hydrolysis of
Unexpected one-pot formation of the 1H-6a,8a-epiminotricyclopenta[a,c,e][8]annulene system from cyclopentanone, ammonia and dimethyl fumarate. Synthesis of highly strained polycyclic nitroxide and EPR study
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2664–2670, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.259
- assignment was based on the single-crystal X-ray analysis (Figure 4) and a possible mechanism for this hydroxylation is shown in Scheme 4. Oxidation of amines with peracids is known to proceed through oxoammonium cation formation [12]. The close proximity of this reactive group to the allyl hydrogen results
Acid-catalyzed rearrangements in arenes: interconversions in the quaterphenyl series
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2655–2663, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.258
- 1,2-phenyl shifts, while Figure 2 shows those for a 1,2-biphenyl shifts. In each case, the energy reference is arbitrarily chosen as the linear ipso cation 12c or 12d for phenyl or biphenyl shift, respectively. Predicted barriers for rearrangements of ipso cations are all in the range of 9–22 kcal/mol
- . Common to both potential energy surfaces are the lowest energy non-ipso carbocations 12a–17a which lie at the bottom on the energy scale. It is noteworthy that m,p' cation 13a is the lowest energy species predicted by our calculations. In each diagram, double-headed vertical arrows show the energy
- that m,m'-quaterphenyl 14 might be favored at equilibrium was unsupported by experiment, which instead showed the m,p' isomer 13 to be preferred. A comparison of 5a, the lowest energy cation from terphenyl rearrangements, with 13a, the corresponding cation for quaterphenyls, provides a simple
Arylisoquinoline-derived organoboron dyes with a triaryl skeleton show dual fluorescence
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2612–2622, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.254

- dye 18 is insensitive to oxygen and was tentatively attributed to the formation of a pyrene-based radical cation, resulting from photoionization [46]. Interaction with fluoride anions The presence of the boronic acid ester moiety does not only contribute to significant changes in the fluorescence
Synthetic terpenoids in the world of fragrances: Iso E Super® is the showcase
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2590–2602, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.252
- yield a new cation, which in turn is nucleophilically trapped by the carbinol moiety. The resulting tetrahydrofuran 59 is chemically stable and this observation was used as rationale for the erosion of the isomeric ratio observed during prolonged reaction times. In the same piece of work Fráter et al
A new approach to silicon rhodamines by Suzuki–Miyaura coupling – scope and limitations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2569–2576, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.250

- optimizations of the reaction conditions could lead to the silicon rhodamine 22 in moderate yields, an inseparable impurity of the cationic fluorophore was detected. After identifying this impurity as the tetraphenylphosphonium cation, we exchanged the triphenylphosphine ligand of the catalyst with dppf (1,1
- explored the substrate scope of the Suzuki–Miyaura coupling by screening commercially available boronic acids (Scheme 4, Table 2). Hereby, PdCl2(dppf) was also tested in order to suppress the formation of the inseparable phosphonium cation species. At first, we investigated the use of 3-boronobenzoic acid
Formation of alkyne-bridged ferrocenophanes using ring-closing alkyne metathesis on 1,1’-diacetylenic ferrocenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2534–2543, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.246

- ≡CH (n = 2, 3), DMAP, NEt3, DCM, 0 °C to rt; b) 2 mol % MoF6, MS 5Å, toluene, rt. Top: Oxidation of ferrocenophane 2a to the corresponding ferrocenium cation 4 with Ag(SbF6) in DCM solution; bottom: upon reaction of 2a with Ag(SbF6) in THF the formation of coordination polymer 5 is observed
Anion-driven encapsulation of cationic guests inside pyridine[4]arene dimers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2486–2492, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.241

- and studied by multiple gas-phase techniques, ESI-QTOF-MS, IRMPD, and DT-IMMS experiments, as well as DFT calculations. The comparison of classical resorcinarenes with pyridinearenes by MS and NMR experiments reveals clear differences in their host–guest chemistry and implies that cation encapsulation
- in pyridine[4]arene is an anion-driven process. Keywords: cation binding; DFT calculations; ion mobility mass spectrometry; macrocycles; pyridinearenes; resorcinarenes; Introduction Resorcinarenes and their derivatives are known for the molecular recognition properties of their self-assembled
- dimeric resorcin[4]arene and pyridine[4]arene capsules, we highlight here unique host–guest properties of pyridinearene capsules. In marked contrast to the corresponding resorcin[4]arene capsules, cation binding is clearly feasible, when anions bind in an exo-site and support cation encapsulation by
Experimental and computational electrochemistry of quinazolinespirohexadienone molecular switches – differential electrochromic vs photochromic behavior
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2473–2485, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.240
- substrates [11][12][13][14][15], or vinylcarbazole or alkoxystyrene derivatives for radical cation cylcloaddition and polymerization reactions [16][17][18][19][20]). We thus proposed the replacement of the naphthalene in 1a with a more electron-deficient quinoline ring. Due to the saturated spirocyclic
Self-assembled coordination thioether silver(I) macrocyclic complexes for homogeneous catalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2465–2472, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.239
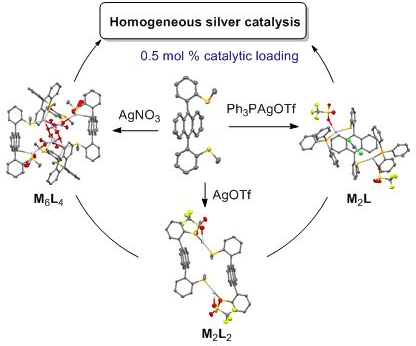
- ; homogeneous catalysis; prochiral; silver complex; thioether ligand; Introduction Since the early advances in the late eighties [1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10], silver(I) catalysis has been widely exploited based on the versatile redox and soft Lewis acid properties of this coinage metal cation. Silver
- )–1 ligands). The X-ray diffraction of monocrystals 1a revealed the formation of (R,S–1)2·(AgOTf)2 macrocycles driven by silver(I) coordination (Figure 1). The two ligands are facing through the coordination of one syn-thioether group to the same silver cation. Two different crystals were isolated and
- highlighted the two possible arrangements of the ligands that led to different diastereoisomeric macrocycles (Figure 1a,b). In Figure 1a, each silver cation was coordinated to two sulfur atoms with the same configuration (named head-to-head coordination mode for ligands) meanwhile in Figure 1b, each Ag(I
Sugar-derived oxazolone pseudotetrapeptide as γ-turn inducer and anion-selective transporter
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2419–2427, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.234

- cation and anion transport across lipid bilayer membranes plays a crucial role in various biological processes [31][32]. Amongst these, the transport of anions is useful in regulating intracellular pH, membrane potential, cell volume, and fluid transport [33]. Any dysfunction in these processes led to
- value of 1.26 indicated that one molecule of 2a is involved in the formation of the active transporter. The promising ion transport activity of 2a encouraged us to explore its cation and anion selectivity study by varying either cations (for MCl, M+ = Li+, Na+, K+, Rb+, and Cs+) or anions (for NaA, A
- cation in an overall transport process (Figure 8C). Finally, to evaluate the mechanism of ion transport, the transport of Cl– using compound 2a (20 µM) was monitored in the presence and absence of valinomycin (a selective K+ transporter, 1 μM). There was a significant increase in the transport rate of 2a
Current understanding and biotechnological application of the bacterial diterpene synthase CotB2
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2355–2368, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.228

- . Cyclization is initiated by cleavage of the GGDP diphosphate moiety. After two consecutive cyclization reactions, a dolabellatrienyl cation (A) is generated, stabilized by π-cation interactions with W186 (Scheme 2 and Figure 7). Whereas mutation of this residue to amino acids with aromatic character mainly
- lead to different migration of the double bound and different hydroxylation pattern (Table 2 and Scheme 1). An exchange to leucine drastically changes the product to cembrane A (7) and 3,7,18-dolabellatriene 12 (Table 2 and Scheme 1) [36]. The cation migrates via a 1,5 hydride shift, as shown by
Synthesis of a dihalogenated pyridinyl silicon rhodamine for mitochondrial imaging by a halogen dance rearrangement
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2333–2343, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.226

- . Lipophilic cations such as the phosphonium cation or rhodamines are known to accumulate selectively within the mitochondria, driven by the mitochondrial plasma membrane potential [39][40]. Thereby, the high lipophilicity facilitates the diffusion through the lipid bilayers of the cell and mitochondrial


































































































































































































































































































































