Search results
Search for "mechanisms" in Full Text gives 574 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Benzoimidazolium-derived dimeric and hydride n-dopants for organic electron-transport materials: impact of substitution on structures, electrochemistry, and reactivity
- Swagat K. Mohapatra,
- Khaled Al Kurdi,
- Samik Jhulki,
- Georgii Bogdanov,
- John Bacsa,
- Maxwell Conte,
- Tatiana V. Timofeeva,
- Seth R. Marder and
- Stephen Barlow
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1651–1663, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.121

- by various quinone derivatives [63]. For both mechanisms, the first steps are typically rate determining and thus, in general, the rate law is: where k1 and k2 are rate constants for the first steps of the “cleavage first” and “ET-first” pathways respectively, k1 being negligible in the case of
- the rise in VII•– absorption is neither zero-order nor first-order in VII, consistent with both mechanisms contributing, as previously demonstrated by more extensive investigations in the case of 1c2, 1d2, and (RhCp*Cp)2 [14][61]. Thus, the Y = alkyl derivative (1h2, “ET-first” only) appears to be
- more strongly bonded than its Y = aryl counterparts (1b2, 1g2, both mechanisms), consistent with previous DFT calculations for 1b2 and 1e2 (ΔUdiss = 163 and 210 kJ mol–1, respectively) and with the expected impact of the different Y substituents on monomer radical stability. In addition, the reaction

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: DMBI+, DMBI-H, and (DMBI)2 derivatives discussed in this work (new compounds in red).

Scheme 1: Synthesis of DMBI-H and (DMBI)2 derivatives and structures of side products.

Figure 2: Crystallographically characterized molecules related to DMBI dimers.

Figure 3: Molecular structures from the single crystal structures of 1b2 (two crystallographically inequivale...

Figure 4: Molecular structures from the single crystal structures of 1bH (upper left), 1gH (upper right), 1hH...

Figure 5: Structures of the cations from the single crystal structures of 1g+I− (left), 1h+PF6− (center), and ...

Figure 6: Cyclic voltammograms (50 mV s−1, THF, 0.1 M Bu4NPF6) of 1g+PF6–, 1gH, and 1g2, in each case contain...

Figure 7: Acceptors used to examine reactivity of DMBI-H and (DMBI)2 derivatives.

Figure 8: a) Temporal evolution of the absorbance at 1030 nm, corresponding to an absorption maximum of VI•–,...
Sulfur-containing spiroketals from Breynia disticha and evaluations of their anti-inflammatory effect
- Ken-ichi Nakashima,
- Naohito Abe,
- Masayoshi Oyama,
- Hiroko Murata and
- Makoto Inoue
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1604–1614, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.117
- Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats [12]. However, the molecular mechanisms of these anti-inflammatory effects have not been investigated. In our ongoing search for bioactive natural products, we have isolated three new spiroketals – breynin J (1), epibreynin J (2), and probreynogenin (3) – and

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Structures of compounds 1–7.

Figure 2: Key HMBC (red arrows), H2BC (black bold lines), and COSY (blue bold lines) correlations in 1 and 2.

Figure 3: a) Simplified model structures 1′ and 2′ for GIAO and TD-DFT calculations. b) Comparison of experim...

Figure 4: Key HMBC (red arrows), H2BC (black bold lines), and COSY (blue bold lines) correlations in compound...

Figure 5: Comparison of experimental (black solid line) and calculated (red dashed line) ECD spectra of 3.

Figure 6: Anti-inflammatory effects of isolated sulfur-containing compounds. mRNA levels of a) IL-1β, b) IL-6...
Radical chemistry in polymer science: an overview and recent advances
- Zixiao Wang,
- Feichen Cui,
- Yang Sui and
- Jiajun Yan
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1580–1603, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.116
- considered to have two mechanisms, degenerative transfer and reversible termination, which are comparable to RAFT and NMP, respectively (Scheme 7) [70]. Iodine transfer polymerization (ITP) is also a commonly used degenerate chain-transfer method. Its origin can be traced back to the 1970s [71] and it is
- using benzophenone. Depolymerization mechanism of common photoresists. (a) A possible mechanism of radiation decomposition of poly(methyl methacrylate). (b) A proposed mechanism of simultaneous radical/cationic decomposition of poly(olefin sulfone) upon radiation [197]. Proposed mechanisms of

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Oxidation of catechol and subsequent cross-linking. Scheme 1 redrawn from [3].

Scheme 2: (A) Structure of typical urushiol in Chinese lacquer, and (B) schematic process of laccase-catalyze...

Scheme 3: A) Primary amino acid sequence of mfp-1, mfp-3, and mfp-5 (Y: DOPA, K: lysine). B) Scheme showing e...

Scheme 4: Activation–deactivation equilibrium in nitroxide-mediated polymerizations. Bicomponent initiating s...

Scheme 5: Mechanism of a transition metal complex-mediated ATRP. Scheme 5 redrawn from [14].

Scheme 6: Mechanism of RAFT polymerization. Scheme 6 redrawn from [68].

Scheme 7: Degenerative transfer (a) and reversible termination (b) mechanism of OMRP. Scheme 7 redrawn from [70].

Scheme 8: Simplified mechanism of a RITP. Scheme 8 redrawn from [21].

Scheme 9: (A) Structures of π-conjugated conductive polymers. (B) Examples of conductive polymer synthesis vi...

Scheme 10: Possible regiochemical couplings in PATs. Scheme 10 redrawn from [79].

Scheme 11: General thiol-ene photopolymerization process. Scheme 11 redrawn from [81].

Scheme 12: (a) Three generations of Grubbs catalysts. (b) Proposed mechanism for photo-ROMP via a reductive qu...

Scheme 13: Pyrylium and thiopyrylium salts studied by Boydston et al. Scheme 13 redrawn from [91].

Scheme 14: A general illustration of post-polymerization modification by thiol–ene chemistry.

Scheme 15: Introduction of functionalities by nitroxide radical coupling of HO-TEMPO derivatives.

Scheme 16: Chemical reaction process scheme of DCP-induced crosslinking of LDPE. Scheme 16 redrawn from [126].

Scheme 17: A probable mechanism of radical-induced hydrosilylation.

Scheme 18: Polymer surface modification by homolytic dediazonation of diazonium salts.

Scheme 19: Photoinduced polymer surface modification or surface grafting using benzophenone.

Scheme 20: Depolymerization mechanism of common photoresists. (a) A possible mechanism of radiation decomposit...

Scheme 21: Proposed mechanisms of photooxidative depolymerization of polystyrene. (a) Scheme 21a was reprinted with perm...
Unraveling the role of prenyl side-chain interactions in stabilizing the secondary carbocation in the biosynthesis of variexenol B
- Moe Nakano,
- Rintaro Gemma and
- Hajime Sato
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1503–1510, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.107

- . Several terpene cyclizations with an exomethylene group are known, such as with caryolene and crotinsulidane diterpenoids, and the reaction mechanisms have been analyzed [27][28][29][30]. It would be interesting to see how the exomethylene group reacts in the cyclization of variexenol B. In this study, we
- follow similar reaction mechanisms, however, when comparing path a and path b, the most striking energy difference is in the step from IM2a/b to IM3a/b (Figure 2B). The energy barrier of this step is 6.3 kcal/mol for path a, whereas 13.6 kcal/mol for path b, with a difference of 7.3 kcal/mol. Although

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Proposed biosynthetic pathway for variexenol B.

Figure 1: (A) Results of DFT evaluation of the whole pathway of variexenol B without cation–π interaction. (B...

Figure 2: (A) Results of the DFT evaluation of the whole pathway of variexenol B including cation–π interacti...

Figure 3: (A) A representative example of the evolution of key bond lengths in the conversion of path a. (B) ...
N-Sulfenylsuccinimide/phthalimide: an alternative sulfenylating reagent in organic transformations
- Fatemeh Doraghi,
- Seyedeh Pegah Aledavoud,
- Mehdi Ghanbarlou,
- Bagher Larijani and
- Mohammad Mahdavi
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1471–1502, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.106

- is no need to use a metal catalyst, base, or additive. N-(Sulfenyl)succinimide/phthalimide acted as an active electrophilic sulfur source, acted in the reaction mechanisms. However, mechanistic studies need further exploration to define a valid reaction pathway. Therefore, we believe that the use of

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Sulfur-containing bioactive molecules.

Scheme 2: Scandium-catalyzed synthesis of thiosulfonates.

Scheme 3: Palladium-catalyzed aryl(alkyl)thiolation of unactivated arenes.

Scheme 4: Catalytic cycle for Pd-catalyzed aryl(alkyl)thiolation of unactivated arenes.

Scheme 5: Iron- or boron-catalyzed C–H arylthiation of substituted phenols.

Scheme 6: Iron-catalyzed azidoalkylthiation of alkenes.

Scheme 7: Plausible mechanism for iron-catalyzed azidoalkylthiation of alkenes.

Scheme 8: BF3·Et2O‑mediated electrophilic cyclization of aryl alkynoates.

Scheme 9: Tentative mechanism for BF3·Et2O‑mediated electrophilic cyclization of aryl alkynoates.

Scheme 10: Construction of 6-substituted benzo[b]thiophenes.

Scheme 11: Plausible mechanism for construction of 6-substituted benzo[b]thiophenes.

Scheme 12: AlCl3‑catalyzed cyclization of N‑arylpropynamides with N‑sulfanylsuccinimides.

Scheme 13: Synthetic utility of AlCl3‑catalyzed cyclization of N‑arylpropynamides with N‑sulfanylsuccinimides.

Scheme 14: Sulfenoamination of alkenes with sulfonamides and N-sulfanylsuccinimides.

Scheme 15: Lewis acid/Brønsted acid controlled Pd-catalyzed functionalization of aryl C(sp2)–H bonds.

Scheme 16: Possible mechanism for Lewis acid/Brønsted acid controlled Pd-catalyzed functionalization of aryl C...

Scheme 17: FeCl3-catalyzed carbosulfenylation of unactivated alkenes.

Scheme 18: Copper-catalyzed electrophilic thiolation of organozinc halides.

Scheme 19: h-BN@Copper(II) nanomaterial catalyzed cross-coupling reaction of sulfoximines and N‑(arylthio)succ...

Scheme 20: AlCl3‑mediated cyclization and sulfenylation of 2‑alkyn-1-one O‑methyloximes.

Scheme 21: Lewis acid-promoted 2-substituted cyclopropane 1,1-dicarboxylates with sulfonamides and N-(arylthio...

Scheme 22: Lewis acid-mediated cyclization of β,γ-unsaturated oximes and hydrazones with N-(arylthio/seleno)su...

Scheme 23: Credible pathway for Lewis acid-mediated cyclization of β,γ-unsaturated oximes with N-(arylthio)suc...

Scheme 24: Synthesis of 4-chalcogenyl pyrazoles via chalcogenation/cyclization of α,β-alkynic hydrazones.

Scheme 25: Controllable synthesis of 3-thiolated pyrroles and pyrrolines.

Scheme 26: Possible mechanism for controllable synthesis of 3-thiolated pyrroles and pyrrolines.

Scheme 27: Co-catalyzed C2-sulfenylation and C2,C3-disulfenylation of indole derivatives.

Scheme 28: Plausible catalytic cycle for Co-catalyzed C2-sulfenylation and C2,C3-disulfenylation of indoles.

Scheme 29: C–H thioarylation of electron-rich arenes by iron(III) triflimide catalysis.

Scheme 30: Difunctionalization of alkynyl bromides with thiosulfonates and N-arylthio succinimides.·

Scheme 31: Suggested mechanism for difunctionalization of alkynyl bromides with thiosulfonates and N-arylthio ...

Scheme 32: Synthesis of thioesters, acyl disulfides, ketones, and amides by N-thiohydroxy succinimide esters.

Scheme 33: Proposed mechanism for metal-catalyzed selective acylation and acylthiolation.

Scheme 34: AlCl3-catalyzed synthesis of 3,4-bisthiolated pyrroles.

Scheme 35: α-Sulfenylation of aldehydes and ketones.

Scheme 36: Acid-catalyzed sulfetherification of unsaturated alcohols.

Scheme 37: Enantioselective sulfenylation of β-keto phosphonates.

Scheme 38: Organocatalyzed sulfenylation of 3‑substituted oxindoles.

Scheme 39: Sulfenylation and chlorination of β-ketoesters.

Scheme 40: Intramolecular sulfenoamination of olefins.

Scheme 41: Plausible mechanism for intramolecular sulfenoamination of olefins.

Scheme 42: α-Sulfenylation of 5H-oxazol-4-ones.

Scheme 43: Metal-free C–H sulfenylation of electron-rich arenes.

Scheme 44: TFA-promoted C–H sulfenylation indoles.

Scheme 45: Proposed mechanism for TFA-promoted C–H sulfenylation indoles.

Scheme 46: Organocatalyzed sulfenylation and selenenylation of 3-pyrrolyloxindoles.

Scheme 47: Organocatalyzed sulfenylation of S-based nucleophiles.

Scheme 48: Conjugate Lewis base Brønsted acid-catalyzed sulfenylation of N-heterocycles.

Scheme 49: Mechanism for activation of N-sulfanylsuccinimide by conjugate Lewis base Brønsted acid catalyst.

Scheme 50: Sulfenylation of deconjugated butyrolactams.

Scheme 51: Intramolecular sulfenofunctionalization of alkenes with phenols.

Scheme 52: Organocatalytic 1,3-difunctionalizations of Morita–Baylis–Hillman carbonates.

Scheme 53: Organocatalytic sulfenylation of β‑naphthols.

Scheme 54: Acid-promoted oxychalcogenation of o‑vinylanilides with N‑(arylthio/arylseleno)succinimides.

Scheme 55: Lewis base/Brønsted acid dual-catalytic C–H sulfenylation of aryls.

Scheme 56: Lewis base-catalyzed sulfenoamidation of alkenes.

Scheme 57: Cyclization of allylic amide using a Brønsted acid and tetrabutylammonium chloride.

Scheme 58: Catalytic electrophilic thiocarbocyclization of allenes with N-thiosuccinimides.

Scheme 59: Suggested mechanism for electrophilic thiocarbocyclization of allenes with N-thiosuccinimides.

Scheme 60: Chiral chalcogenide-catalyzed enantioselective hydrothiolation of alkenes.

Scheme 61: Proposed mechanism for chalcogenide-catalyzed enantioselective hydrothiolation of alkenes.

Scheme 62: Organocatalytic sulfenylation for synthesis a diheteroatom-bearing tetrasubstituted carbon centre.

Scheme 63: Thiolative cyclization of yne-ynamides.

Scheme 64: Synthesis of alkynyl and acyl disulfides from reaction of thiols with N-alkynylthio phthalimides.

Scheme 65: Oxysulfenylation of alkenes with 1-(arylthio)pyrrolidine-2,5-diones and alcohols.

Scheme 66: Arylthiolation of arylamines with (arylthio)-pyrrolidine-2,5-diones.

Scheme 67: Catalyst-free isothiocyanatoalkylthiation of styrenes.

Scheme 68: Sulfenylation of (E)-β-chlorovinyl ketones toward 3,4-dimercaptofurans.

Scheme 69: HCl-promoted intermolecular 1, 2-thiofunctionalization of aromatic alkenes.

Scheme 70: Possible mechanism for HCl-promoted 1,2-thiofunctionalization of aromatic alkenes.

Scheme 71: Coupling reaction of diazo compounds with N-sulfenylsuccinimides.

Scheme 72: Multicomponent reactions of disulfides with isocyanides and other nucleophiles.

Scheme 73: α-Sulfenylation and β-sulfenylation of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
Cyclization of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichlorobut-2-en-1-ones into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones in triflic acid
- Vladislav A. Sokolov,
- Andrei A. Golushko,
- Irina A. Boyarskaya and
- Aleksander V. Vasilyev
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1460–1470, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.105
- mechanisms for the cyclization of compounds 1 and 2 into indanones 3 in TfOH (Scheme 7). Protonation of the carbonyl oxygen of enone 2 gives rise to cation B which is followed by cyclization into indanone 3 through mesomeric form B'. The hydroxy ketone 1 is protonated at the oxygen atoms leading to cation A
- -4,4,4-trichlorobut-2-en-1-ones 2 into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones 3 in TfOH. Cyclization of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichloro-3-hydroxybutan-1-ones 1 into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones 3 in TfOH. Plausible mechanisms for the cyclization of compounds 1 and 2 into indanones 3 in TfOH. Transformations of hydroxy

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Generation of O-protonated and O,C-diprotonated species from substituted conjugated enones under su...

Scheme 2: Synthesis of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichloro-3-hydroxybutan-1-ones 1a–o by condensation of acetophenones wit...

Scheme 3: Synthesis of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichloro-3-hydroxybutan-1-ones 1p–v by acylation of electron-donating ar...

Scheme 4: Synthesis of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichlorobut-2-en-1-ones 2 by dehydration of hydroxy ketones 1.

Scheme 5: Cyclization of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichlorobut-2-en-1-ones 2 into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones 3 in TfOH....

Scheme 6: Cyclization of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichloro-3-hydroxybutan-1-ones 1 into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones 3 ...

Scheme 7: Plausible mechanisms for the cyclization of compounds 1 and 2 into indanones 3 in TfOH.
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
- Marco Antônio G. B. Gomes,
- Alicia Bauduin,
- Chloé Le Roux,
- Romain Fouinneteau,
- Wilfried Berthe,
- Mathieu Berchel,
- Hélène Couthon and
- Paul-Alain Jaffrès
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- modulation of membrane proteins that represent a pertinent strategy for some diseases like cancers. Beside the use of synthetic ether lipids for the prevention or the treatment of cancers via different mechanisms, it must be noted that some synthetic ether lipids (e.g., Ino-C2-PAF) have also the ability to

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Chemical structure of some natural ether lipids (ELs).

Figure 2: Synthesis of lyso-PAF and PAF from 1-O-alkylglycerol [64].

Figure 3: Synthesis of lyso-PAF from 1,3-benzylideneglycerol 3.1 [69].

Figure 4: A) Synthesis of the two enantiomers of octadecylglycerol (4.6 and 4.10) from ᴅ-mannitol (4.1); B) s...

Figure 5: Four-step synthesis of PAF 5.6 from (S)-glycidol [73].

Figure 6: Synthesis of 1-O-alkylglycerol A) from solketal, B) from ᴅ- or ʟ-tartaric acid and the intermediate ...

Figure 7: Synthesis of EL building blocks starting from substituted glycidol 7.1a–c [82].

Figure 8: Synthesis of PAF 8.5 by using phosphoramidite 8.2 [86].

Figure 9: Synthesis of oleyl-PAF 9.7 from ʟ-serine [88].

Figure 10: Synthesis of racemic analogues of lyso-PAF 10.8 and PAF 10.9 featuring a phenyl group between the g...

Figure 11: Synthesis of racemic deoxy-lyso-PAF 11.7 and deoxy-PAF 11.8 [91].

Figure 12: Synthesis of racemic thio-PAF 12.8 [93].

Figure 13: Racemic synthesis of 13.6 to illustrate the modification of the glycerol backbone by adding a methy...

Figure 14: Racemic synthesis of 14.5 as an illustration of the introduction of methyl substituents on the glyc...

Figure 15: Synthesis of functionalized sn-2-acyl chains of PC-EL; A) Steglich esterification or acylation reac...

Figure 16: Synthesis of racemic mc-PAF (16.3), a carbamate analogue of PAF [102].

Figure 17: A) Synthesis of (R)-17.2 and (S)-17.6 starting from (S)-solketal (17.1); B) synthesis of N3-PAF (17...

Figure 18: Modification of the phosphocholine polar head to produce PAF analogues [81].

Figure 19: Racemic PAF analogues 19.3 and 19.5 characterized by the absence of the phosphate group [107].

Figure 20: Synthesis of PIP3-PAF (20.7) [108].

Figure 21: Large-scale synthesis of C18-edelfosine (21.8) [116].

Figure 22: Synthesis of C16-edelfosine (22.10) starting from isopropylidene-ʟ-glyceric acid methyl ester (22.1...

Figure 23: Phosphocholine moiety installation by the use of chlorophosphite 23.2 as key reagent [119].

Figure 24: Synthesis of rac-1-alkyl-2-O-methylglycerol (AMG) [120].

Figure 25: Synthesis of stereocontrolled 1-alkyl-2-O-methyl glycerol 25.9 (AMG) from dimethyl ᴅ-tartrate [81].

Figure 26: A) Racemic synthesis of thioether 26.4 [129,130], B) structure of sulfone analogue 26.5 [129].

Figure 27: Stereocontrolled synthesis of C18-edelfosine thioether analogue 27.8 [118].

Figure 28: Synthesis of thioether 28.4 that include a thiophosphate function [134].

Figure 29: Synthesis of ammonium thioether 29.4 and 29.6 [135].

Figure 30: Synthesis of the N-methylamino analogue of edelfosine 30.6 (BN52211) [138].

Figure 31: Synthesis of 1-desoxy analogues of edelfosine; A) with a saturated alkyl chain; B) synthesis of the...

Figure 32: Stereocontrolled synthesis of edelfosine analogue (S)-32.8 featuring a C18:1 lipid chain [142].

Figure 33: Synthesis of edelfosine analogues with modulation of the lipid chain; A) illustration with the synt...

Figure 34: Synthesis of phospholipid featuring a carbamate function to link the lipid chain to the glycerol un...

Figure 35: Synthesis of sesquiterpene conjugates of phospho glycero ether lipids [148].

Figure 36: Racemic synthesis of methyl-substituted glycerol analogues 36.7 and 36.10: A) synthesis of diether ...

Figure 37: Racemic synthesis of ilmofosine (37.6) [155,156].

Figure 38: A) Stereoselective synthesis of 38.5 via a stereoselective hydroboration reaction; B) synthesis of ...

Figure 39: Racemic synthesis of SRI62-834 (39.6) featuring a spiro-tetrahydrofurane heterocycle in position 2 ...

Figure 40: Racemic synthesis of edelfosine analogue 40.5 featuring an imidazole moiety in sn-2 position [160].

Figure 41: Racemic synthesis of fluorine-functionalized EL: A) Synthesis of 41.6 and B) synthesis of 41.8 [161-163].

Figure 42: A) Synthesis of the β-keto-ester 42.6 that also features a decyl linker between the phosphate and t...

Figure 43: Synthesis of phosphonate-based ether lipids; A) edelfosine phosphonate analogue 43.7 and B) thioeth...

Figure 44: Enantioselective synthesis of phosphonates 44.3 and 44.4 [171].

Figure 45: Racemic synthesis of phosphinate-based ether lipid 45.10 [172].

Figure 46: Racemic synthesis of edelfosine arsonium analogue 46.5 [173].

Figure 47: Synthesis of edelfosine dimethylammonium analogue 47.2 [118].

Figure 48: Synthesis of rac-C18-edelfosine methylammonium analogue 48.4 [176].

Figure 49: A) Synthesis of edelfosine N-methylpyrrolidinium analogue 49.2 or N-methylmorpholinium analogue 49.3...

Figure 50: A) Synthesis of edelfosine’s analogue 50.4 with a PE polar group; B) illustration of a pyridinium d...

Figure 51: A) Synthesis of 51.4 featuring a thiazolium cationic moiety; B) synthesis of thiazolium-based EL 51...

Figure 52: Synthesis of cationic ether lipids 52.3, 52.4 and 52.6 [135,183].

Figure 53: Synthesis of cationic carbamate ether lipid 53.5 [184].

Figure 54: Synthesis of cationic sulfonamide 54.5 [185].

Figure 55: Chemical structure of ONO-6240 (55.1) and SRI-63-119 (55.2).

Figure 56: Synthesis of non-ionic ether lipids 56.2–56.9 [188].

Figure 57: Synthesis of ether lipid conjugated to foscarnet 57.6 [189].

Figure 58: A) Synthesis of ether lipid conjugated to arabinofuranosylcytosine; B) synthesis of AZT conjugated ...

Figure 59: Synthesis of quercetin conjugate to edelfosine [191].

Figure 60: Synthesis of 60.8 (Glc-PAF) [194].

Figure 61: A) Synthesis of amino ether lipid 61.7 functionalized with a rhamnose unit and its amide analogue 6...

Figure 62: A) Synthesis of glucose ether lipid 62.4; B) structure of ether lipid 62.5 possessing a maltose uni...

Figure 63: A) Synthesis of glucuronic methyl ester 63.8; B) structure of cellobiose 63.9 and maltose 63.10 ana...

Figure 64: A) Synthesis of maltosyl glycerolipid 64.7; B) structure of lactose analogue 64.8 prepared followin...

Figure 65: A) Asymmetric synthesis of the aglycone moiety starting from allyl 4-methoxyphenyl ether; B) glycos...

Figure 66: A) Synthesis of ohmline possessing a lactose moiety. B) Structure of other glyco glycero lipids pre...

Figure 67: A) Synthesis of lactose-glycerol ether lipid 67.5; B) analogues possessing a maltose (67.6) or meli...

Figure 68: Synthesis of digalactosyl EL 68.6, A) by using trityl, benzyl and acetyl protecting groups, B) by u...

Figure 69: A) Synthesis of α-ohmline; B) structure of disaccharide ether lipids prepared by using similar meth...

Figure 70: Synthesis of lactose ether lipid 70.3 and its analogue 70.6 featuring a carbamate function as linke...

Figure 71: Synthesis of rhamnopyranoside diether 71.4 [196].

Figure 72: Synthesis of 1-O-hexadecyl-2-O-methyl-3-S-(α-ᴅ-1'-thioglucopyranosyl)-sn-glycerol (72.5) [225].

Figure 73: A) Preparation of lipid intermediate 73.4; B) synthesis of 2-desoxy-C-glycoside 73.10 [226].

Figure 74: Synthesis of galactose-pyridinium salt 74.3 [228].

Figure 75: Synthesis of myo-inositol derivative Ino-C2-PAF (75.10) [230].

Figure 76: A) Synthesis of myo-inositol phosphate building block 76.7; B) synthesis of myo-inositolphosphate d...

Figure 77: A) Synthesis of phosphatidyl-3-desoxy-inositol 77.4; B) synthesis of phosphono-3-desoxyinositol 77.9...

Figure 78: A) Structure of diether phosphatidyl-myo-inositol-3,4-diphosphate 78.1; B) synthesis of phosphatidy...

Figure 79: A) Synthesis of diether-phosphatidyl derivative 79.4 featuring a hydroxymethyl group in place of a ...

Figure 80: Synthesis of Glc-amine-PAF [78].

Figure 81: Synthesis of glucosamine ether lipid 81.4 and its analogues functionalized in position 3 of the ami...

Figure 82: Synthesis of fully deprotected aminoglucoside ether lipid 82.5 [246].

Figure 83: Synthesis of C-aminoglycoside 83.12 using Ramberg–Bäcklund rearrangement as a key step [250].

Figure 84: A) List of the most important glyco lipids and amino glyco lipids included in the study of Arthur a...

Figure 85: Synthesis of mannosamine ether lipid 85.6 [254].

Figure 86: A) Synthesis of glucosamine ether lipids with a non-natural ʟ-glucosamine moiety; B) synthesis of e...

Figure 87: A) Structure of the most efficient anticancer agents 87.1–87.4 featuring a diamino glyco ether lipi...

Figure 88: A) Synthesis of diamino glyco ether lipid 87.4; B) synthesis of bis-glycosylated ether lipid 88.10 [256]....

Figure 89: Synthesis of triamino ether lipid 89.4 [260].

Figure 90: Synthesis of chlorambucil conjugate 90.7 [261].

Figure 91: Three main methods for the preparation of glycerol ether lipid 91.3; A) from solketal and via a tri...

Figure 92: Four different methods for the installation of the phosphocholine polar head group; A) method using...

Figure 93: Illustration of two methods for the installation of saccharides or aminosaccharides; A) O-glycosyla...
Non-noble metal-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenation coupling (CDC) involving ether α-C(sp3)–H to construct C–C bonds
- Hui Yu and
- Feng Xu
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1259–1288, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.94
- Cu-catalyzed oxidative coupling reactions [43]. However, due to complex mechanisms, Cu-catalyzed C–H functionalization reactions developed only slowly in the last decade. Since recently the Cu-catalyzed oxidative coupling has emerged as a powerful synthetic strategy due to the development of CDC
- metal-triggered oxidation of the ether substrate to obtain the corresponding radical or oxonium ion as the key intermediate to obtain the final coupling product. Subsequently, some novel Co-catalyzed coupling mechanisms have been proposed. In 2016, Lu et al. reported that the Co/TBHP catalyst oxidation

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Research progress of coupling reactions and active compounds containing α-C(sp3)-functionalized eth...

Scheme 2: Transition-metal-catalyzed CDC pathways.

Scheme 3: CDC of active methylene compounds in the α-C(sp3) position of ethers.

Scheme 4: InCl3/Cu(OTf)2/NHPI co-catalyzed CDC reaction.

Scheme 5: CDC of cyclic benzyl ethers with aldehydes.

Scheme 6: Cu-catalyzed CDC of (a) unactivated C(sp3)–H ethers with simple ketones and (b) double C(sp3)−H fun...

Scheme 7: Cu-catalyzed CDC of C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H bonds.

Scheme 8: Cu-catalyzed synthesis of chiral 2-substituted tetrahydropyrans.

Scheme 9: CDC of thiazole with cyclic ethers.

Scheme 10: Cu(I)-catalyzed oxidative alkenylation of simple ethers.

Scheme 11: Cross-dehydrogenation coupling of isochroman C(sp3)–H bonds with anisole C(sp2)–H bonds.

Scheme 12: Pd(OAc)2/Cu(OTf)2-catalyzed arylation of α-C(sp3)–H bonds of ethers.

Scheme 13: Cu-catalyzed C(sp3)–H/C(sp2)–H activation strategies to construct C(sp3)–C(sp2) bonds.

Scheme 14: Cu(I)-catalyzed C(sp2)–H alkylation.

Scheme 15: Cu-catalyzed C(sp3)–H/C(sp)–H activation to construct C(sp3)–C(sp) bonds (H2BIP: 2,6-bis(benzimidaz...

Scheme 16: Fe-catalyzed CDC reaction pathways.

Scheme 17: Fe2(CO)9-catalyzed functionalization of C–H bonds.

Scheme 18: Ligand-promoted Fe-catalyzed CDC reaction of N-methylaniline with ethers.

Scheme 19: Fe-catalyzed CDC of C(sp3)–H/C(sp3)–H bonds.

Scheme 20: Fe-catalyzed hydroalkylation of α,β-unsaturated ketones with ethers.

Scheme 21: Solvent-free Fe(NO3)3-catalyzed CDC of C(sp3)–H/C(sp2)–H bonds.

Scheme 22: Alkylation of disulfide compounds to afford tetrasubstituted alkenes.

Scheme 23: Fe-catalyzed formation of 1,1-bis-indolylmethane derivatives.

Scheme 24: Alkylation of coumarins and flavonoids.

Scheme 25: Direct CDC α-arylation of azoles with ethers.

Scheme 26: CDC of terminal alkynes with C(sp3)–H bonds adjacent to oxygen, sulfur or nitrogen atoms.

Scheme 27: Alkylation of terminal alkynes.

Scheme 28: Co-catalyzed functionalization of glycine esters.

Scheme 29: Co-catalyzed construction of C(sp2)–C(sp3) bonds.

Scheme 30: Co-catalyzed CDC of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines with isochroman.

Scheme 31: Co-catalyzed C–H alkylation of (benz)oxazoles with ethers.

Scheme 32: Cobalt-catalyzed CDC between unactivated C(sp2)–H and C(sp3)–H bonds.

Scheme 33: MnO2-catalyzed CDC of the inactive C(sp3)-H.

Scheme 34: Oxidative cross-coupling of ethers with enamides.

Scheme 35: Ni(II)-catalyzed CDC of indoles with 1,4-dioxane.

Scheme 36: Chemo- and regioselective ortho- or para-alkylation of pyridines.

Scheme 37: Asymmetric CDC of 3,6-dihydro-2H-pyrans with aldehydes.

Scheme 38: CDC of heterocyclic aromatics with ethers.

Scheme 39: Indium-catalyzed alkylation of DHPs with 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds.

Scheme 40: Rare earth-metal-catalyzed CDC reaction.

Scheme 41: Visible-light-driven CDC of cycloalkanes with benzazoles.

Scheme 42: Photoinduced alkylation of quinoline with cyclic ethers.

Scheme 43: Photocatalyzed CDC reactions between α-C(sp3)–H bonds of ethers and C(sp2)–H bonds of aromatics.
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
- Grace A. Lowe
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
- photosynthesis research not only because they occur in biological photosynthesis but also because the PCET can circumvent unstable one electron-reduced intermediates. This makes PCET mechanisms well-suited for complex multielectron reactions required to transfer electrons and protons from water onto carbon

Graphical Abstract

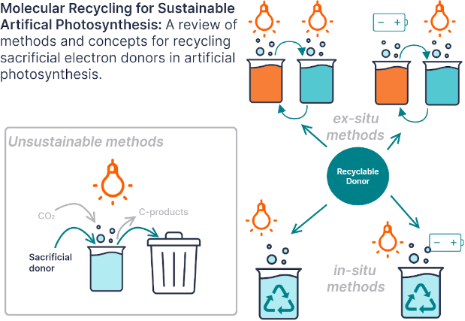
Figure 1: Diagram comparing the two reaction pathways for sacrificial electron donors (SD) in photocatalyzed ...

Figure 2: Diagram showing water-splitting systems developed by Girault, Scanlon, and co-workers that employ i...

Figure 3: Diagram illustrating the transfer of electrons in a photocatalytic particulate suspensions Z-scheme...

Figure 4: A. Structures of the molecules represented in part B. The numbers in brackets correspond to the com...

Figure 5: A. Structures of the molecules represented in part B. The numbers in brackets correspond to the com...
Exploring the role of halogen bonding in iodonium ylides: insights into unexpected reactivity and reaction control
- Carlee A. Montgomery and
- Graham K. Murphy
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1171–1190, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.86

- provides an overview of the reactions of iodonium ylides in which halogen bonding has been invoked. Herein, we summarize key discoveries and mechanistic proposals from the early iodonium ylide literature that invoked halogen bonding-type mechanisms, as well as recent reports of reactions between iodonium
- cyclopropane 22a. Interestingly, Hadjiarapoglou also revisited their investigation of iodonium ylide cycloadditions and their associated mechanisms [120], using diphenylketene as a new reaction partner with dimedone iodonium ylide 6 (analogous to earlier work reported by Koser in 1975 [9]). Investigations by
- , their scope has recently expanded to include X–H insertions based on single electron transfer (SET) mechanisms, cycloadditions based on blue LED photochemistry and radiofluorinations of unactivated arene motifs. In these reports, mechanistic proposals commonly treat the hypervalent iodine atom as being

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Generic representation of halogen bonding.

Figure 2: Quantitative evaluation of σ-holes in monovalent iodine-containing compounds; and, qualitative mole...

Figure 3: Quantitative evaluation of σ-holes in hypervalent iodine-containing molecules; and, qualitative MEP...

Figure 4: Quantitative evaluation of σ-holes in iodonium ylides; and, qualitative MEP map of I-12 from −0.083...

Scheme 1: Outline of possible reaction pathways between iodonium ylides and Lewis basic nucleophiles (top); a...

Scheme 2: Metal-free cyclopropanations of iodonium ylides, either as intermolecular (a) or intramolecular pro...

Figure 5: Zwitterionic mechanism for intramolecular cyclopropanation of iodonium ylides (left); and, stepwise...

Scheme 3: Metal-free intramolecular cyclopropanation of iodonium ylides.

Figure 6: Concerted cycloaddition pathway for the metal-free, intramolecular cyclopropanation of iodonium yli...

Scheme 4: Reaction of ylide 6 with diphenylketene to form lactone 24 and 25.

Figure 7: Nucleophilic (top) and electrophilic (bottom) addition pathways proposed by Koser and Hadjiarapoglo...

Scheme 5: Indoline synthesis from acyclic iodonium ylide 31 and tertiary amines.

Scheme 6: N-Heterocycle synthesis from acyclic iodonium ylide 31 and secondary amines.

Figure 8: Proposed mechanism for the formation of 33a from iodonium ylides and amines, involving an initial h...

Scheme 7: Indoline synthesis from acyclic iodonium ylides 39 and tertiary amines under blue light photocataly...

Scheme 8: Metal-free cycloproponation of iodonium ylides under blue LED irradiation. aUsing trans-β-methylsty...

Figure 9: Proposed mechanism of the cyclopropanation between iodonium ylides and alkenes under blue LED irrad...

Scheme 9: Formal C–H alkylation of iodonium ylides by nucleophilic heterocycles under blue LED irradiation.

Figure 10: Proposed mechanism of the formal C–H insertion of pyrrole under blue LED irradiation.

Scheme 10: X–H insertions between iodonium ylides and carboxylic acids, phenols and thiophenols.

Figure 11: Mechanistic proposal for the X–H insertion reactions of iodonium ylides.

Scheme 11: Radiofluorination of biphenyl using iodonium ylides 54a–e derived from various β-dicarbonyl auxilia...

Scheme 12: Radiofluorination of arenes using spirocycle-derived iodonium ylides 56.

Scheme 13: Radiofluorination of arenes using SPIAd-derived iodonium ylides 58.

Figure 12: Calculated reaction coordinate for the radiofluorination of iodonium ylide 60.

Scheme 14: Radiofluorination of iodonium ylides possessing various ortho- and para-substituents on the iodoare...

Figure 13: Difference in Gibbs activation energy for ortho- or para-anisyl derived iodonium ylides 63a and 63b....

Figure 14: Proposed equilibration of intermediates to transit between 64a (the initial adduct formed between 6...

Scheme 15: Comparison of 31 and ortho-methoxy iodonium ylide 39 in rhodium-catalyzed cyclopropanation and cycl...

Figure 15: X-ray crystal structure of dimeric 39 [6], (CCDC# 893474) [143,144].

Scheme 16: Enaminone synthesis using diazonium and iodonium ylides.

Figure 16: Transition state calculations for enaminone synthesis from iodonium ylides and thioamides.

Scheme 17: The reaction between ylides 73a–f and N-methylpyrrole under 365 nm UV irradiation.

Figure 17: Crystal structures of 76c (top) and 76e (bottom) [101], (CCDC# 2104180 & 2104181) [143,144].
Photoredox catalysis harvesting multiple photon or electrochemical energies
- Mattia Lepori,
- Simon Schmid and
- Joshua P. Barham
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1055–1145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.81

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Oxidative and reductive activations of organic compounds harvesting photoredox catalysis.

Figure 2: General catalytic cycles of radical ion conPET (left) and radical ion e-PRC (right).

Figure 3: “Beginner’s guide”: comparison between advantages, capacities, and prospectives of conPET and PEC.

Figure 4: A) conPET reductive dehalogenation of aryl halides with PDI. B) Reductive C–H arylation with pyrrol...

Figure 5: A) Chromoselective mono- and disubstitution or polybrominated pyrimidines with pyrroles. B) Sequent...

Figure 6: A) Synthesis of pyrrolo[1,2-a]quinolines. B) Synthesis of ullazines.

Figure 7: A) Reductive phosphorylation of aryl halides via conPET. B) Selected examples from the substrate sc...

Figure 8: A) Reductive dehalogenation of aryl halides via conPET and selected examples from the substrate sco...

Figure 9: A) Reductive C–H arylation of aryl halides via conPET (top) and selected examples from the substrat...

Figure 10: A) Reductive hydrodehalogenation of aryl halides with Mes-Acr-BF4. B) Selected examples from the su...

Figure 11: A) Reductive hydrodechlorination of aryl chlorides with 4-DPAIPN. B) Proposed formation of CO2•−. C...

Figure 12: A) Reductive conPET borylation with 3CzEPAIPN (top) and selected examples from the substrate scope ...

Figure 13: Scale-up of conPET phosphorylation with 3CzEPAIPN.

Figure 14: A) Borylation of 1d. B) Characteristics and structure of PC1 with green and red parts showing the l...

Figure 15: A) Reductive C–H arylation scope with polysulfide conPET (top) and selected examples from the subst...

Figure 16: Scale-up of A) C–H arylation and B) dehaloborylation with polysulfide photocatalysis in continuous-...

Figure 17: A) Formation of [Ir1]0 and [Ir2]0 upon PET between [Ir1]+ and Et3N. B) Mechanism of multi-photon ta...

Figure 18: A) Reductive hydrodehalogenation of aryl halides via multi-photon tandem photocatalysis. B) Selecte...

Figure 19: A) Carbonylative amidation of aryl halides in continuous flow. B) Selected examples from the substr...

Figure 20: A) General scheme for reductive (RQ) and oxidative quenching (OQ) protocols using [FeIII(btz)3](PF6)...

Figure 21: A) Carbonylative amidation of alkyl iodides with [IrIII(ppy)2(dtbbpy)]PF6. B) Selected examples fro...

Figure 22: A) Carboxylative C–N bond cleavage in cyclic amines. B) Selected examples from the substrate scope....

Figure 23: A) Formal reduction of alkenes to alkanes via transfer hydrogenation. B) Selected examples from the...

Figure 24: A) Birch-type reduction of benzenes with PMP-BPI. B) Selected examples from the substrate scope (sc...

Figure 25: Proposed mechanism of the OH− mediated conPET Birch-type reduction of benzene via generation of sol...

Figure 26: Reductive detosylation of N-tosylated amides with Mes-Acr-BF4. B) Selected examples from the substr...

Figure 27: A) Reductive detosylation of N-tosyl amides by dual PRC. B) Selected examples from the substrate sc...

Figure 28: A) Mechanism of the dual PRC based on PET between [Cu(dap)2]+ and DCA. B) Mechanism of the dual PRC...

Figure 29: A) N–O bond cleavage in Weinreb amides with anthracene. B) N–O bond cleavage in Weinreb amides rely...

Figure 30: A) Pentafluorosulfanylation and fluoride elimination. B) Mechanism of the pentafluorosulfanylation ...

Figure 31: A) α-Alkoxypentafluorosulfanylation (top) and selected examples from the substrate scope (bottom). ...

Figure 32: A) Oxidative amination of arenes with azoles catalyzed by N-Ph PTZ. B) Selected examples from the s...

Figure 33: A) C(sp3)–H bond activation by HAT via chloride oxidation by *N-Ph PTZ•+. B) Proposed mechanism for...

Figure 34: A) Recycling e-PRC C–H azolation of electron-rich arenes with pyrazoles using Mes-Acr+ as a photoca...

Figure 35: A) Radical ion e-PRC direct oxidation of unactivated arenes using TAC+ as an electro-activated phot...

Figure 36: A) Radical ion e-PRC direct oxidation of unactivated arenes using TPA as an electro-activated photo...

Figure 37: Proposed mechanism (top) and mode of preassembly (bottom).

Figure 38: A) Possible preassemblies of reactive (left) vs unreactive (right) arenes. B) Calculated spin densi...

Figure 39: A) Recycling e-PRC C(sp2 )–H acetoxylation of arenes using DDQ as a photocatalyst. B) Proposed cata...

Figure 40: Gram scale hydroxylation of benzene in a recirculated flow setup.

Figure 41: A) Radical ion e-PRC vicinal diamination of alkylarenes using TAC+ as an electro-activated photocat...

Figure 42: A) Sequential oxygenation of multiple adjacent C–H bonds under radical ion e-PRC using TAC+ as an e...

Figure 43: A) Enantioselective recycling e-PRC cyanation of benzylic C–H bonds using ADQS as photocatalyst. B)...

Figure 44: Proposed tandem mechanism by Xu and co-workers.

Figure 45: A) Enantioselective recycling e-PRC decarboxylative cyanation using Cu(acac)2, Ce(OTf)3 and a box l...

Figure 46: A) Enantioselective recycling e-PRC benzylic cyanation using Cu(MeCN)4BF4, box ligand and anthraqui...

Figure 47: A) Radical ion e-PRC acetoxyhydroxylation of aryl olefins using TAC+ as an electro-activated photoc...

Figure 48: Selected examples from the substrate scope.

Figure 49: Photoelectrochemical acetoxyhydroxylation in a recirculated flow setup.

Figure 50: A) Radical ion e-PRC aminooxygenation of aryl olefins using TAC+ as an electro-activated photocatal...

Figure 51: A) Recycling e-PRC C–H alkylation of heteroarenes with organic trifluoroborates using Mes-Acr+ as p...

Figure 52: A) Recycling e-PRC decarboxylative C–H alkylation of heteroarenes using CeCl3·7H2O as catalyst. B) ...

Figure 53: A) Recycling e-PRC decarboxylative C–H alkylation of heteroarenes using Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2·6H2O as cata...

Figure 54: A) Recycling e-PRC C–H alkylation of heteroarenes with alkyl oxalates and 4CzIPN as photocatalyst. ...

Figure 55: A) Recycling e-PRC decarboxylative C–H carbamoylation of heteroarenes using 4CzIPN as photocatalyst...

Figure 56: A) Photoelectrochemical HAT-mediated hydrocarbon activation via the chlorine radical. B) Proposed m...

Figure 57: A) Selected examples from the substrate scope. B) Gram and decagram scale semi-continuous flow PEC ...

Figure 58: A) Photoelectrochemical HAT-mediated dehydrogenative coupling of benzothiazoles with aliphatic C–H ...

Figure 59: A) Photoelectrochemical HAT activation of ethers using electro-activated TAC+ as photocatalyst. B) ...

Figure 60: Selected examples from the substrate scope.

Figure 61: A) Photoelectrochemical HAT-mediated synthesis of alkylated benzimidazo-fused isoquinolinones using...

Figure 62: A) Decoupled photoelectrochemical cerium-catalyzed oxydichlorination of alkynes using CeCl3 as cata...

Figure 63: Proposed decoupled photoelectrochemical mechanism.

Figure 64: A) Decoupled photoelectrochemical ring-opening bromination of tertiary cycloalkanols using MgBr2 as...

Figure 65: A) Recycling e-PRC ring-opening functionalization of cycloalkanols using CeCl3 as catalyst. B) Prop...

Figure 66: Selected examples from the substrate scope of the PEC ring-opening functionalization.

Figure 67: A) Radical ion e-PRC reduction of chloro- and bromoarenes using DCA as catalyst and various accepto...

Figure 68: A) Screening of different phthalimide derivatives as catalyst for the e-PRC reduction of aryl halid...

Figure 69: Screening of different organic catalysts for the e-PRC reduction of trialkylanilium salts.

Figure 70: A) e-PRC reduction of phosphonated phenols and anilinium salts. B) Selected examples from the subst...

Figure 71: A) ConPET and e-PRC reduction of 4-bromobenzonitrile using a naphthalene diimide (NDI) precatalyst ...

Figure 72: A) Radical ion e-PRC reduction of phosphinated aliphatic alcohols with n-BuO-NpMI as catalyst. B) C...

Figure 73: Selected examples from the substrate scope.

Figure 74: A) Recycling e-PRC reductive dimerization of benzylic chlorides using a [Cu2] catalyst. B) Proposed...

Figure 75: A) Decoupled photoelectrochemical C–H alkylation of heteroarenes through deamination of Katritzky s...

Figure 76: Proposed mechanism by Chen and co-workers.
The effect of dark states on the intersystem crossing and thermally activated delayed fluorescence of naphthalimide-phenothiazine dyads
- Liyuan Cao,
- Xi Liu,
- Xue Zhang,
- Jianzhang Zhao,
- Fabiao Yu and
- Yan Wan
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1028–1046, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.79

- intersystem crossing (rISC) is slow, without coupling with an approximate 3LE state. These studies are useful for an in-depth understanding of the photophysical mechanisms of the TADF emitters, as well as for molecular structure design of new electron donor–acceptor TADF emitters. Keywords: charge-transfer
- [38][39][40][41][42][43][44] and, more recently, time-resolved electron paramagnetic resonance (TREPR) spectroscopy [33][39][44][45][46] were also applied to study TADF mechanisms, but the examples are limited. Therefore, much room is left for studies of the photophysical mechanism of the TADF
- state energy), while keeping other factors intact to a large extent (e.g., the LE state energy). This is an important advantage for the study of complicated photophysical mechanisms involved in TADF processes. The syntheses of the dyads are based on the known derivatization chemistry of NI and PTZ

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Synthesis of the compounds. Conditions: (a) 4-fluoroaniline, acetic acid, N2, reflux, 7 h, yield: 7...

Figure 1: UV–vis absorption spectra of (a) NI-PTZ-F, NI-PTZ-Ph, NI-PTZ-CH3, NI-PTZ-OCH3, and NI-PTZ-C5 and (b...

Figure 2: Fluorescence spectra of the dyads. (a) NI-PTZ-F, (b) NI-PTZ-Ph, (c) NI-PTZ-CH3, (d) NI-PTZ-OCH3, (e...

Figure 3: Fluorescence spectra of the dyads. (a) NI-PTZ-F, (b) NI-PTZ-Ph, (c) NI-PTZ-CH3, (d) NI-PTZ-OCH3, (e...

Figure 4: Fluorescence lifetime of (a) NI-PTZ-F; (b) NI-PTZ-Ph; (c) NI-PTZ-CH3; (d) NI-PTZ-OCH3 (λem = 610 nm...

Figure 5: Cyclic voltammograms of the compounds. (a) NI-PTZ-F; NI-PTZ-Ph; NI-PTZ-CH3; NI-PTZ-OCH3; NI-PTZ-C5 ...

Figure 6: Thermogravimetric analysis curves of NI-PTZ-F, NI-PTZ-Ph, NI-PTZ-CH3, NI-PTZ-OCH3, NI-PTZ-F-O, and ...

Figure 7: Femtosecond transient absorption spectra of NI-PTZ-F. (a) Transient absorption spectra and (b) the ...

Figure 8: Nanosecond transient absorption spectra of NI-PTZ-F in deaerated solvents of (a) HEX (c = 2.0 × 10−5...

Figure 9: Nanosecond transient absorption spectra of (a) NI-PTZ-F-O (c = 4.0 × 10−5 M), (b) NI-PTZ-Ph-O (c = ...

Figure 10: Optimized ground state geometry of (a) NI-PTZ-F, (b) NI-PTZ-Ph, (c) NI-PTZ-CH3, (d) NI-PTZ-OCH3, (e...

Figure 11: Spin density surfaces of the dyads in the T1 state (gas phase) of (a) NI-PTZ-F, (b) NI-PTZ-Ph, (c) ...

Figure 12: Selected frontier molecular orbitals of NI-PTZ-F, NI-PTZ-Ph, NI-PTZ-C5, NI-PTZ-F-O, NI-PTZ-Ph-O, an...

Scheme 2: Simplified Jablonski diagram of (a) NI-PTZ-F and (b) NI-PTZ-F-O. The 1LE state (1[NI–PTZ–F–O]*) ene...
Intermediates and shunt products of massiliachelin biosynthesis in Massilia sp. NR 4-1
- Till Steinmetz,
- Blaise Kimbadi Lombe and
- Markus Nett
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 909–917, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.69
- into the cell through membrane receptors and transporters. Eventually, the bound metal is released through reductive or hydrolytic mechanisms [2]. In the past years, β-proteobacteria have received increasing attention as producers of siderophores with interesting chemical features. For instance
- underlie discrete regulation mechanisms, which explains their context-dependent production [27]. The examples of P. aeruginosa and B. anthracis suggest that siderophore biosynthesis sometimes requires specific triggers beyond iron deficiency, which may not be met under laboratory conditions. The six

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Selected siderophores from β-proteobacteria.

Figure 2: Chemical structures of compounds 1–6 isolated in this study and of the structurally related siderop...

Figure 3: 1H,1H-COSY and selected 1H,13C-HMBC correlations in 1.

Figure 4: Proposed origin of the isolated compounds 1–6 as well as massiliachelin (7). Domain notation of the...
Light-responsive rotaxane-based materials: inducing motion in the solid state
- Adrian Saura-Sanmartin
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 873–880, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.64

- Photoresponsive rotaxane discrete crystals A complete understanding of the crystallization mechanisms accompanied by a rational design can lead to the obtention of crystalline molecular materials which allow the dynamics of the counterparts to take place [35][36][37]. Indeed, the motion of the cyclic counterparts

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: a) Chemical structure of pseudorotaxanes 1; and (b) single-crystal X-ray structure of rotaxane 1a (R...

Figure 2: (a) Chemical structure of polyrotaxane 2; and (b) cartoon representation of the light-triggered deg...

Figure 3: a) Chemical structures of rotaxanes (E)-3 and (Z)-3; b) stick representation of the solid structure...

Figure 4: Stick representations of the solid structures of: (a) U-CB[8]-MPyVB showing an interlocked ligand c...
Pyridine C(sp2)–H bond functionalization under transition-metal and rare earth metal catalysis
- Haritha Sindhe,
- Malladi Mounika Reddy,
- Karthikeyan Rajkumar,
- Akshay Kamble,
- Amardeep Singh,
- Anand Kumar and
- Satyasheel Sharma
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 820–863, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.62
- the mechanisms involved. Keywords: C–H functionalization; heterocycles; pyridine; rare earth metal; transition-metal-catalyzed; Introduction Pyridine, one of the most important azaheterocyclic scaffolds, is found in a diverse range of bioactive natural products, pharmaceuticals, and functional

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Representative examples of bioactive natural products and FDA-approved drugs containing a pyridine ...

Scheme 1: Classical and traditional methods for the synthesis of functionalized pyridines.

Scheme 2: Rare earth metal (Ln)-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 3: Pd-catalyzed C–H alkylation of pyridine N-oxide.

Scheme 4: CuI-catalyzed C–H alkylation of N-iminopyridinium ylides with tosylhydrazones (A) and a plausible r...

Scheme 5: Zirconium complex-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 6: Rare earth metal-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation with nonpolar unsaturated substrates.

Scheme 7: Heterobimetallic Rh–Al complex-catalyzed ortho-C–H monoalkylation of pyridines.

Scheme 8: Mono(phosphinoamido)-rare earth complex-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 9: Rhodium-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation with acrylates and acrylamides.

Scheme 10: Ni–Al bimetallic system-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 11: Iridium-catalyzed pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 12: para-C(sp2)–H Alkylation of pyridines with alkenes.

Scheme 13: Enantioselective pyridine C–H alkylation.

Scheme 14: Pd-catalyzed C2-olefination of pyridines.

Scheme 15: Ru-catalyzed C-6 (C-2)-propenylation of 2-arylated pyridines.

Scheme 16: C–H addition of allenes to pyridines catalyzed by half-sandwich Sc metal complex.

Scheme 17: Pd-catalyzed stereodivergent synthesis of alkenylated pyridines.

Scheme 18: Pd-catalyzed ligand-promoted selective C3-olefination of pyridines.

Scheme 19: Mono-N-protected amino acids in Pd-catalyzed C3-alkenylation of pyridines.

Scheme 20: Amide-directed and rhodium-catalyzed C3-alkenylation of pyridines.

Scheme 21: Bimetallic Ni–Al-catalyzed para-selective alkenylation of pyridine.

Scheme 22: Arylboronic ester-assisted pyridine direct C–H arylation.

Scheme 23: Pd-catalyzed C–H arylation/benzylation with toluene.

Scheme 24: Pd-catalyzed pyridine C–H arylation with potassium aryl- and heteroaryltrifluoroborates.

Scheme 25: Transient activator strategy in pyridine C–H biarylation.

Scheme 26: Ligand-promoted C3-arylation of pyridine.

Scheme 27: Pd-catalyzed arylation of nicotinic and isonicotinic acids.

Scheme 28: Iron-catalyzed and imine-directed C–H arylation of pyridines.

Scheme 29: Pd–(bipy-6-OH) cooperative system-mediated direct pyridine C3-arylation.

Scheme 30: Pd-catalyzed pyridine N-oxide C–H arylation with heteroarylcarboxylic acids.

Scheme 31: Pd-catalyzed C–H cross-coupling of pyridine N-oxides with five-membered heterocycles.

Scheme 32: Cu-catalyzed dehydrative biaryl coupling of azine(pyridine) N-oxides and oxazoles.

Scheme 33: Rh(III)-catalyzed cross dehydrogenative C3-heteroarylation of pyridines.

Scheme 34: Pd-catalyzed C3-selective arylation of pyridines.

Scheme 35: Rhodium-catalyzed oxidative C–H annulation of pyridines to quinolines.

Scheme 36: Rhodium-catalyzed and NHC-directed C–H annulation of pyridine.

Scheme 37: Ni/NHC-catalyzed regio- and enantioselective C–H cyclization of pyridines.

Scheme 38: Rare earth metal-catalyzed intramolecular C–H cyclization of pyridine to azaindolines.

Scheme 39: Rh-catalyzed alkenylation of bipyridine with terminal silylacetylenes.

Scheme 40: Rollover cyclometallation in Rh-catalyzed pyridine C–H functionalization.

Scheme 41: Rollover pathway in Rh-catalyzed C–H functionalization of N,N,N-tridentate chelating compounds.

Scheme 42: Pd-catalyzed rollover pathway in bipyridine-6-carboxamides C–H arylation.

Scheme 43: Rh-catalyzed C3-acylmethylation of bipyridine-6-carboxamides with sulfoxonium ylides.

Scheme 44: Rh-catalyzed C–H functionalization of bipyridines with alkynes.

Scheme 45: Rh-catalyzed C–H acylmethylation and annulation of bipyridine with sulfoxonium ylides.

Scheme 46: Iridium-catalyzed C4-borylation of pyridines.

Scheme 47: C3-Borylation of pyridines.

Scheme 48: Pd-catalyzed regioselective synthesis of silylated dihydropyridines.
Synthesis of substituted 8H-benzo[h]pyrano[2,3-f]quinazolin-8-ones via photochemical 6π-electrocyclization of pyrimidines containing an allomaltol fragment
- Constantine V. Milyutin,
- Andrey N. Komogortsev,
- Boris V. Lichitsky,
- Mikhail E. Minyaev and
- Valeriya G. Melekhina
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 778–788, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.58
- of the methanol molecule occurs only for intermediate A and is not observed for product 11. It is important to emphasize that earlier, when discussing the mechanisms of the 6π-electrocyclization of various terarylenes accompanied by subsequent elimination of small molecules, we assumed a [1,9]-H

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Photochemical behavior of terarylenes containing an allomaltol fragment.

Scheme 2: Synthesis of starting compounds 9. Reaction conditions: 13 (1 mmol), NH2CN (14, 3 mmol, 0.13 g), Et...

Scheme 3: Proposed mechanism for the formation of compounds 9.

Scheme 4: Synthesis of methylated derivatives 10. Reaction conditions: 9 (1 mmol), MeI (3 mmol, 0.43 g), K2CO3...

Figure 1: 1H NMR monitoring of the photoreaction of compound 10a under UV irradiation (365 nm) in DMSO-d6 sol...

Figure 2: The crystal structure of compound 11a (one of two polymorph modifications; p = 50%), CCDC 2248033.

Scheme 5: Photochemical synthesis of compounds 11 and 12.

Scheme 6: Proposed mechanism for the studied photoreaction.

Scheme 7: Synthesis of compounds 11g–j starting from pyrimidines 9. Reaction conditions: 9 (0.5 mmol), DMF (1...

Figure 3: One of crystallographically unique molecules of 11g (p = 50%), CCDC 2248035.

Scheme 8: Synthesis of photoproducts 12. Reaction conditions: method A) 10 (0.5 mmol), DMF (15 mL) irradiatio...
Bromination of endo-7-norbornene derivatives revisited: failure of a computational NMR method in elucidating the configuration of an organic structure
- Demet Demirci Gültekin,
- Arif Daştan,
- Yavuz Taşkesenligil,
- Cavit Kazaz,
- Yunus Zorlu and
- Metin Balci
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 764–770, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.56
- have developed a machine learning-augmented DFT method for computational NMR, DU8ML, for fast and ‘accurate’ computational approaches [2]. They applied this computational method to a number of previously published organic compounds and claimed to have revised some structures and proposed new mechanisms

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Bromination of endo-7-bromonorbornene.

Figure 1: Structure 6 (our assignment) and structure 7 revised by Novitskiy and Kutateladze.

Figure 2: W or M orientaition in norbornane and the corresponding coupling constants.

Figure 3: The determined structure 6 by NMR experiments and the proposed structure 7 by computional NMR.

Figure 4: The normal and expanded 1H NMR spectra of compound 6.

Figure 5: γ-Gauche effects caused by bromine atoms in 3, 5, and 6.

Figure 6: NOE-Diff experiment. Double resonance experiment. Irradiation at the resonance frequency of protons...

Figure 7: NOE-Diff experiment. Irradiation at the resonance frequency of proton H7 (4.23 ppm).

Scheme 2: Our mechanism suggested for the formation of 6 [4].

Scheme 3: The mechanism suggested by Novitskiy and Kutateladze for the formation of 7 [3].

Figure 8: A) Molecular structure of the compound 6 with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability ...
Transition-metal-catalyzed domino reactions of strained bicyclic alkenes
- Austin Pounder,
- Eric Neufeld,
- Peter Myler and
- William Tam
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 487–540, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.38
- propagate further. A subsequent migratory insertion into a second azaspirotricyclic alkene furnishes 183. Finally, the anion from the catalyst attacks 183 causing a ring opening, forming the final product 178d and regenerating the Rh(I) catalyst. Keeping with other mechanisms, the Rh(I) may also undergo an

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Ring-strain energies of homobicyclic and heterobicyclic alkenes in kcal mol−1. a) [2.2.1]-Bicyclic ...

Figure 2: a) Exo and endo face descriptions of bicyclic alkenes. b) Reactivity comparisons for different β-at...

Scheme 1: Ni-catalyzed ring-opening/cyclization cascade of heterobicyclic alkenes 1 with alkyl propiolates 2 ...

Scheme 2: Ni-catalyzed ring-opening/cyclization cascade of heterobicyclic alkenes 8 with β-iodo-(Z)-propenoat...

Scheme 3: Ni-catalyzed two- and three-component difunctionalizations of norbornene derivatives 15 with alkyne...

Scheme 4: Ni-catalyzed intermolecular three-component difunctionalization of oxabicyclic alkenes 1 with alkyn...

Scheme 5: Ni-catalyzed intermolecular three-component carboacylation of norbornene derivatives 15.

Scheme 6: Photoredox/Ni dual-catalyzed coupling of 4-alkyl-1,4-dihydropyridines 31 with heterobicyclic alkene...

Scheme 7: Photoredox/Ni dual-catalyzed coupling of α-amino radicals with heterobicyclic alkenes 30.

Scheme 8: Cu-catalyzed rearrangement/allylic alkylation of 2,3-diazabicyclo[2.2.1]heptenes 47 with Grignard r...

Scheme 9: Cu-catalyzed aminoboration of bicyclic alkenes 1 with bis(pinacolato)diboron (B2pin2) (53) and O-be...

Scheme 10: Cu-catalyzed borylalkynylation of oxabenzonorbornadiene (30b) with B2pin2 (53) and bromoalkynes 62.

Scheme 11: Cu-catalyzed borylacylation of bicyclic alkenes 1.

Scheme 12: Cu-catalyzed diastereoselective 1,2-difunctionalization of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 for the synthe...

Scheme 13: Fe-catalyzed carbozincation of heterobicyclic alkenes 1 with arylzinc reagents 74.

Scheme 14: Co-catalyzed addition of arylzinc reagents of norbornene derivatives 15.

Scheme 15: Co-catalyzed ring-opening/dehydration of oxabicyclic alkenes 30 via C–H activation of arenes.

Scheme 16: Co-catalyzed [3 + 2] annulation/ring-opening/dehydration domino reaction of oxabicyclic alkenes 1 w...

Scheme 17: Co-catalyzed enantioselective carboamination of bicyclic alkenes 1 via C–H functionalization.

Scheme 18: Ru-catalyzed cyclization of oxabenzonorbornene derivatives with propargylic alcohols for the synthe...

Scheme 19: Ru-catalyzed coupling of oxabenzonorbornene derivatives 30 with propargylic alcohols and ethers 106...

Scheme 20: Ru-catalyzed ring-opening/dehydration of oxabicyclic alkenes via the C–H activation of anilides.

Scheme 21: Ru-catalyzed of azabenzonorbornadiene derivatives with arylamides.

Scheme 22: Rh-catalyzed cyclization of bicyclic alkenes with arylboronate esters 118.

Scheme 23: Rh-catalyzed cyclization of bicyclic alkenes with dienyl- and heteroaromatic boronate esters.

Scheme 24: Rh-catalyzed domino lactonization of doubly bridgehead-substituted oxabicyclic alkenes with seconda...

Scheme 25: Rh-catalyzed domino carboannulation of diazabicyclic alkenes with 2-cyanophenylboronic acid and 2-f...

Scheme 26: Rh-catalyzed synthesis of oxazolidinone scaffolds 147 through a domino ARO/cyclization of oxabicycl...

Scheme 27: Rh-catalyzed oxidative coupling of salicylaldehyde derivatives 151 with diazabicyclic alkenes 130a.

Scheme 28: Rh-catalyzed reaction of O-acetyl ketoximes with bicyclic alkenes for the synthesis of isoquinoline...

Scheme 29: Rh-catalyzed domino coupling reaction of 2-phenylpyridines 165 with oxa- and azabicyclic alkenes 30....

Scheme 30: Rh-catalyzed domino dehydrative naphthylation of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 with N-sulfonyl 2-aminob...

Scheme 31: Rh-catalyzed domino dehydrative naphthylation of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 with arylphosphine deriv...

Scheme 32: Rh-catalyzed domino ring-opening coupling reaction of azaspirotricyclic alkenes using arylboronic a...

Scheme 33: Tandem Rh(III)/Sc(III)-catalyzed domino reaction of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 with alkynols 184 dir...

Scheme 34: Rh-catalyzed asymmetric domino cyclization and addition reaction of 1,6-enynes 194 and oxa/azabenzo...

Scheme 35: Rh/Zn-catalyzed domino ARO/cyclization of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 with phosphorus ylides 201.

Scheme 36: Rh-catalyzed domino ring opening/lactonization of oxabenzonorbornadienes 30 with 2-nitrobenzenesulf...

Scheme 37: Rh-catalyzed domino C–C/C–N bond formation of azabenzonorbornadienes 30 with aryl-2H-indazoles 210.

Scheme 38: Rh/Pd-catalyzed domino synthesis of indole derivatives with 2-(phenylethynyl)anilines 212 and oxabe...

Scheme 39: Rh-catalyzed domino carborhodation of heterobicyclic alkenes 30 with B2pin2 (53).

Scheme 40: Rh-catalyzed three-component 1,2-carboamidation reaction of bicyclic alkenes 30 with aromatic and h...

Scheme 41: Pd-catalyzed diarylation and dialkenylation reactions of norbornene derivatives.

Scheme 42: Three-component Pd-catalyzed arylalkynylation reactions of bicyclic alkenes.

Scheme 43: Three-component Pd-catalyzed arylalkynylation reactions of norbornene and DFT mechanistic study.

Scheme 44: Pd-catalyzed three-component coupling N-tosylhydrazones 236, aryl halides 66, and norbornene (15a).

Scheme 45: Pd-catalyzed arylboration and allylboration of bicyclic alkenes.

Scheme 46: Pd-catalyzed, three-component annulation of aryl iodides 66, alkenyl bromides 241, and bicyclic alk...

Scheme 47: Pd-catalyzed double insertion/annulation reaction for synthesizing tetrasubstituted olefins.

Scheme 48: Pd-catalyzed aminocyclopropanation of bicyclic alkenes 1 with 5-iodopent-4-enylamine derivatives 249...

Scheme 49: Pd-catalyzed, three-component coupling of alkynyl bromides 62 and norbornene derivatives 15 with el...

Scheme 50: Pd-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization/ring-opening reaction of heterobicyclic alkenes 30 with 2-i...

Scheme 51: Pd-catalyzed dimer- and trimerization of oxabenzonorbornadiene derivatives 30 with anhydrides 268.

Scheme 52: Pd-catalyzed Catellani-type annulation and retro-Diels–Alder of norbornadiene 15b yielding fused xa...

Scheme 53: Pd-catalyzed hydroarylation and heteroannulation of urea-derived bicyclic alkenes 158 and aryl iodi...

Scheme 54: Access to fused 8-membered sulfoximine heterocycles 284/285 via Pd-catalyzed Catellani annulation c...

Scheme 55: Pd-catalyzed 2,2-bifunctionalization of bicyclic alkenes 1 generating spirobicyclic xanthone deriva...

Scheme 56: Pd-catalyzed Catellani-type annulation and retro-Diels–Alder of norbornadiene (15b) producing subst...

Scheme 57: Pd-catalyzed [2 + 2 + 1] annulation furnishing bicyclic-fused indanes 281 and 283.

Scheme 58: Pd-catalyzed ring-opening/ring-closing cascade of diazabicyclic alkenes 130a.

Scheme 59: Pd-NHC-catalyzed cyclopentannulation of diazabicyclic alkenes 130a.

Scheme 60: Pd-catalyzed annulation cascade generating diazabicyclic-fused indanones 292 and indanols 294.

Scheme 61: Pd-catalyzed skeletal rearrangement of spirotricyclic alkenes 176 towards large polycyclic benzofur...

Scheme 62: Pd-catalyzed oxidative annulation of aromatic enamides 298 and diazabicyclic alkenes 130a.

Scheme 63: Accessing 3,4,5-trisubstituted cyclopentenes 300, 301, 302 via the Pd-catalyzed domino reaction of ...

Scheme 64: Palladacycle-catalyzed ring-expansion/cyclization domino reactions of terminal alkynes and bicyclic...

Scheme 65: Pd-catalyzed carboesterification of norbornene (15a) with alkynes, furnishing α-methylene γ-lactone...
Transition-metal-catalyzed C–H bond activation as a sustainable strategy for the synthesis of fluorinated molecules: an overview
- Louis Monsigny,
- Floriane Doche and
- Tatiana Besset
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 448–473, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.35
- amide derived from 8-aminoquinoline 13e (Scheme 6, 13 examples, up to 75% yield). In this study, two mechanisms were reported. The first one suggested that a palladacycle C is formed after the irreversible chelation of the 2-phenylpyridine substrate with palladium, which is the rate-determining step

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Transition-metal-catalyzed C–XRF bond formation by C–H bond activation: an overview.

Scheme 2: Cu(OAc)2-promoted mono- and ditrifluoromethylthiolation of benzamide derivatives derived from 8-ami...

Scheme 3: Trifluoromethylthiolation of azacalix[1]arene[3]pyridines using copper salts and a nucleophilic SCF3...

Scheme 4: Working hypothesis for the palladium-catalyzed C–H trifluoromethylthiolation reaction.

Scheme 5: Trifluoromethylthiolation of 2-arylpyridine derivatives and analogs by means of palladium-catalyzed...

Scheme 6: C(sp2)–SCF3 bond formation by Pd-catalyzed C–H bond activation using AgSCF3 and Selectfluor® as rep...

Scheme 7: Palladium-catalyzed ortho-trifluoromethylthiolation of 2-arylpyridine derivatives reported by the g...

Scheme 8: Palladium-catalyzed ortho-trifluoromethylthiolation of 2-arylpyridine and analogs reported by Anbar...

Scheme 9: Mono- and ditrifluoromethylthiolation of benzamide derivatives derived from 8-aminoquinoline using ...

Scheme 10: Regioselective Cp*Rh(III)-catalyzed directed trifluoromethylthiolation reported by the group of Li [123]...

Scheme 11: Cp*Co(III)-catalyzed ortho-trifluoromethylthiolation of 2-phenylpyridine and 2-phenylpyrimidine der...

Scheme 12: Cp*Co(III)-catalyzed ortho-trifluoromethylthiolation of 2-phenylpyridine and 6-phenylpurine derivat...

Scheme 13: Diastereoselective trifluoromethylthiolation of acrylamide derivatives derived from 8-aminoquinolin...

Scheme 14: C(sp3)–SCF3 bond formation on aliphatic amide derivatives derived from 8-aminoquinoline by palladiu...

Scheme 15: Regio- and diastereoselective difluoromethylthiolation of acrylamides under palladium catalysis rep...

Scheme 16: Palladium-catalyzed (ethoxycarbonyl)difluoromethylthiolation reaction of 2-(hetero)aryl and 2-(α-ar...

Scheme 17: Pd(II)-catalyzed trifluoromethylselenolation of benzamides derived from 5-methoxy-8-aminoquinoline ...

Scheme 18: Pd(II)-catalyzed trifluoromethylselenolation of acrylamide derivatives derived from 5-methoxy-8-ami...

Scheme 19: Transition-metal-catalyzed dehydrogenative 2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation of (hetero)aromatic derivati...

Scheme 20: Pd(II)-catalyzed ortho-2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation of N-sulfonylbenzamides reported by the group of...

Scheme 21: Pd(II)-catalyzed selective 2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation and other fluoroalkoxylations of naphthalene...

Scheme 22: Pd(II)-catalyzed selective ortho-2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation of benzaldehyde derivatives by means o...

Scheme 23: Pd(II)-catalyzed selective ortho-2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation (and other fluoroalkoxylations) of ben...

Scheme 24: Pd(II)-catalyzed selective 2,2,2-trifluoroethoxylation of aliphatic amides using a bidentate direct...
Asymmetric synthesis of a stereopentade fragment toward latrunculins
- Benjamin Joyeux,
- Antoine Gamet,
- Nicolas Casaretto and
- Bastien Nay
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 428–433, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.32
- presence of DIPEA, performed well in the aldol reaction to furnish product 21 in 55% yield with a good dr of 91:9 (Scheme 3). The stereocontrol of the reaction could be envisaged through two principal mechanisms. A remote stereocontrol by the nucleophile could first be expected [29], through a 1,5-anti

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Structure of latrunculins (the red dots show the natural product stereopentade).

Figure 2: General strategy for latrunculin cycle disconnections (left), previous works towards linear precurs...

Scheme 1: Synthesis of fragment 15 from (+)-β-citronellene (10).

Scheme 2: Synthesis of fragment 8 from ʟ-cysteine ethyl ester hydrochloride (16).

Scheme 3: Synthesis of fragment 21 through a stereoselective aldol reaction.

Scheme 4: 1,3-Anti-diastereoselective reduction of 21 with PNBz transposition, and final determination of the...
Group 13 exchange and transborylation in catalysis
- Dominic R. Willcox and
- Stephen P. Thomas
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 325–348, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.28
- ). Thomas and Gunanathan independently reported the borane-catalysed double hydroboration of nitriles using either Me2S·BH3 or H-B-9-BBN, respectively, as the catalyst and HBpin as the turnover reagent (Scheme 9) [72][73]. Both reports proposed similar mechanisms for the Me2S·BH3- and H-B-9-BBN-catalysed
- species 93, followed by Al‒O/B‒H exchange with HBpin to give the alkoxy boronic ester 94 and regenerate the aluminium hydride 92 (Scheme 23). Several aluminium hydride compounds have been reported as competent carbonyl hydroboration catalysts, with proposed mechanisms similar to Roesky’s initial report

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Group 13 exchange.

Scheme 2: Borane-catalysed hydroboration of alkynes and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 3: a) Borane-catalysed hydroboration of alkenes and the proposed mechanism. b) H-B-9-BBN-catalysed dou...

Scheme 4: a) Amine-borane-catalysed C‒H borylation of heterocycles and the proposed mechanism. b) Benzoic aci...

Scheme 5: Bis(pentafluorophenyl)borane-catalysed dimerisation of allenes and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 6: Alkoxide-promoted hydroboration of heterocycles and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 7: Borane-catalysed reduction of indoles and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 8: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed hydrocyanation of enones and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 9: Borane-catalysed hydroboration of nitriles and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 10: Myrtanylborane-catalysed asymmetric reduction of propargylic ketones and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 11: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed C–F esterification of alkyl fluorides and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 12: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed 1,4-hydroboration of enones and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 13: Boric acid-promoted reduction of esters, lactones, and carbonates and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 14: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed reductive aldol-type reaction and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 15: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed diastereoselective allylation of ketones and the Ph-BBD-catalysed enantioselect...

Scheme 16: H-B-9-BBN-catalysed C–F arylation of benzyl fluorides and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 17: Borane-catalysed S‒H borylation of thiols and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 18: Borane-catalysed hydroalumination of alkenes and allenes.

Scheme 19: a) Aluminium-catalysed hydroboration of alkynes and example catalysts. b) Deprotonation mechanistic...

Scheme 20: Aluminium-catalysed hydroboration of alkenes and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 21: Aluminium-catalysed C–H borylation of terminal alkynes and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 22: Aluminium-catalysed dehydrocoupling of amines, alcohols, and thiols with H-B-9-BBN or HBpin and the...

Scheme 23: Aluminium-catalysed hydroboration of unsaturated compounds and the general reaction mechanism.

Scheme 24: a) Gallium-catalysed asymmetric hydroboration of ketones and the proposed mechanism. b) Gallium-cat...

Scheme 25: Gallium(I)-catalysed allylation/propargylation of acetals and aminals and the proposed mechanism.

Scheme 26: Indium(I)-catalysed allylation/propargylation of acetals, aminals, and alkyl ethers.

Scheme 27: Iron–indium cocatalysed double hydroboration of nitriles and the proposed mechanism.

Figure 1: a) The number of reports for a given group 13 exchange in catalysis. b) Average free energy barrier...
Germacrene B – a central intermediate in sesquiterpene biosynthesis
- Houchao Xu and
- Jeroen S. Dickschat
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 186–203, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.18
- ) The reprotonation of 1 at C-4 potentially leads to four stereoisomers of cation K, B) reprotonation at C-10 can result in four stereoisomers of L. The sesquiterpenes derived from cations K1, K2 and K4. A) Mechanisms of formation for compounds 53–56, B) pyrolysis of 58 to 53. The sesquiterpenes derived
- from cations L1–L4. A) Mechanisms of formation for compounds 54, 56, 59 and 60, B) dehydration of 61 to 56, C) oxidation of 56 to 62, D) dehydration of 63 to 60 and 64 (no yields were given in the original reports for the synthetic transformations shown in this Scheme).

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Possible cyclisation modes of FPP.

Scheme 2: Structures of germacrene B (1), germacrene A (2) and hedycaryol (3).

Scheme 3: The chemistry of germacrene B (1). A) Synthesis from germacrone (4), B) the four conformers of 1 es...

Scheme 4: The chemistry of germacrene B (1). A) Cyclisation of 1 to 9 and 10 upon treatment with alumina, B) ...

Scheme 5: Possible cyclisation reactions upon reprotonation of 1. A) Cyclisations to eudesmane sesquiterpenes...

Scheme 6: Cyclisation modes for 1 to the eudesmane skeleton. A) The reprotonation of 1 at C-1 potentially lea...

Scheme 7: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I1. WMR = Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement.

Scheme 8: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I1. A) Pyrolysis of 23 to yield 9 and 10, B) deprotonation–r...

Scheme 9: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I1. A) Acid-catalysed conversion of 18 into 26, B) conversio...

Scheme 10: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I1. A) Formation of 20 by pyrolysis of 33, B) acid-catalysed...

Scheme 11: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I2. WMR = Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement.

Scheme 12: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I2. A) Acid catalysed conversion of 41 into 38, B) dehydrati...

Scheme 13: The sesquiterpenes derived from cation I3. WMR = Wagner–Meerwein rearrangement.

Scheme 14: Cyclisation modes for 1 to the guaiane skeleton. A) The reprotonation of 1 at C-4 potentially leads...

Scheme 15: The sesquiterpenes derived from cations K1, K2 and K4. A) Mechanisms of formation for compounds 53–...

Scheme 16: The sesquiterpenes derived from cations L1–L4. A) Mechanisms of formation for compounds 54, 56, 59 ...
Total synthesis of insect sex pheromones: recent improvements based on iron-mediated cross-coupling chemistry
- Eric Gayon,
- Guillaume Lefèvre,
- Olivier Guerret,
- Adrien Tintar and
- Pablo Chourreu
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 158–166, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.15

- mechanisms to help regulate/balance the populations of harmful species rather than eradicating them) based on the use of insect pheromones [2][3][4][5] is an eco-friendly solution for the protection of a wide range of crops and plants against pests. Indeed, those chemical mediators, which are emitted by

Scheme 1: Structure of the (8E,10Z)-tetradecadienal (1, sex pheromone of the horse-chestnut leaf miner) and r...

Scheme 2: a) Alkyl–vinyl seminal cross-coupling reaction by Kochi; b) improved procedure described by Cahiez.

Scheme 3: Iron-catalyzed cross-coupling of n-OctMgCl with a 1-butadienyl phosphate.

Scheme 4: Synthesis of several insect sex pheromones (a) red bollworm moth, b) European grapevine moth, c) ho...

Scheme 5: Cross-coupling of alkyl Grignard reagents with a) alkenyl or b) aryl halides involving EtOMgCl as a...

Scheme 6: Total synthesis of codling moth sex pheromone 4 using an iron-mediated cross-coupling between an α,...
Insight into oral amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles for colorectal cancer: comprehensive mathematical model of drug release kinetic studies and antitumoral efficacy in 3D spheroid colon tumors
- Sedat Ünal,
- Gamze Varan,
- Juan M. Benito,
- Yeşim Aktaş and
- Erem Bilensoy
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 139–157, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.14

- assessments of this topic [9]. Release kinetics study The in vitro release profiles of CPT-loaded amphiphilic cyclodextrin nanoparticles were fitted with a variety of kinetic models, and the release mechanisms, which are illuminating markers for novel drug delivery systems, were mathematically investigated
- two different colon tumors to differ from each other is the origin of the cells. The genome-transcriptome mapping investigation revealed that despite having two separate origins, the CT26 cell has characteristics similar to human primary colorectal cancers in terms of drug resistance mechanisms, gene
- discovered that inhibiting E-cadherins, which are adhesion molecules that provide intracellular connection, increases the sensitivity of 3D colon cancer tumors to 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, vinblastine, and etoposide [67]. In the literature, uptake mechanisms of nanoparticles and free drugs in 2D and 3D

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: In vitro release profile of CPT from nanoparticle formulations (n = 3, ± SD).

Figure 2: Results for release kinetics obtained automatically by the DDSolver software for SGF release medium...

Figure 3: Results for release kinetics obtained automatically by the DDSolver software for SIF release medium...

Figure 4: Results for release kinetics obtained automatically by the DDSolver software for SCoF release mediu...

Figure 5: Anticancer effect of blank or CPT-loaded CD nanoparticles and camptothecin solution against 2D CT26...

Figure 6: Live/dead analysis of CT26 and HT29 cells using double staining with calcein AM and ethidium homodi...

Figure 7: Murine (CT26) and human (HT29) colon cancer spheroid was formed by scaffold-based method, and the m...

Figure 8: Anticancer effect of blank or drug-loaded cyclodextrin nanoparticles and CPT solution against 3D CT...

Figure 9: Chemical structures of 6-O-capro-β-CD, poly-β-CD-C6, and chitosan.
Organophosphorus chemistry: from model to application
- György Keglevich
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 89–90, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.8

- chemistry and beyond. Quantum chemical calculations are a great support for organic chemists when exploring structures, reactivities, and mechanisms. In this thematic issue, the Diels–Alder cycloaddition of 2-phosphaindolizine, 1-aza-2-phosphaindolizine, 3-aza-2-phosphaindolizine, and 1,3-diaza-2






