Search results
Search for "host" in Full Text gives 510 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Synthesis and optoelectronic properties of benzoquinone-based donor–acceptor compounds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2914–2921, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.285
- photoluminescence quantum yield (ΦPL) of 3 is poor at 4%. We next investigated the solid-state PL behavior of 3 in a 10 wt %-doped thin film using PMMA as host matrix. The PL spectrum of 3 exhibited two bands, one at 550 nm, corresponding to the emission of 3 and a second high-energy band at 450 nm that was
- attributed to the PMMA host matrix [39]. The narrower emission profile of 3 in the solid state than in DCM solution could be due to the suppression of various nonradiative vibrational modes in the inert host matrix PMMA. Compound 3 showed a low ΦPL of 6% under nitrogen atmosphere. Time-resolved PL
Bacterial terpene biosynthesis: challenges and opportunities for pathway engineering
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2889–2906, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.283

- ubiquitous odiferous terpenes that overshadow characteristic terpene signals (branching methyl groups) in NMR experiments, render the targeted isolation of terpenes highly challenging. Therefore, heterologous expression in modified host organisms could be the method of choice in most studies. Understanding
- terpene skeleton produced natively or in the heterologous hosts (Figure 6a) [76]. In fact, it is occasionally observed that the same terpene cyclase generates different terpene skeletons dependent on the heterologous host in which it was expressed. While the exact reasons for the observed product
- ent-kaurenoic acid (27 and 28, respectively, Figure 7b) [41]. Characterization of CYPs is typically achieved by in vitro or in vivo studies. E. coli is the most popular host for obtaining proteins for in vitro studies, and proper selection of a redox system is usually the obstacle to reconstitute CYP
Preparation of anthracene-based tetraperimidine hexafluorophosphate and selective recognition of chromium(III) ions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2847–2855, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.278
- hydrogen bonds, namely C(3)–H(3A)···F(2) and C(17)–H(17A)···F(2) interactions (Supporting Information File 1, Figure S1b). Chemosensing of cations by 3 Compound 3 was employed as a host to study its ability to detect some cations through fluorescence and UV titrations in CH3CN/DMSO, 9:1, v/v at room
Photoreversible stretching of a BAPTA chelator marshalling Ca2+-binding in aqueous media
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2801–2811, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.273

- concentrations potentially allows greater control over certain biological functions. In order to permit remote regulation of Ca2+, a selective BAPTA-type synthetic receptor / host was integrated with a photoswitchable azobenzene motif, which upon photoirradiation would enhance (or diminish) the capacity to bind
- , as elucidated by the crystallographic structure of a 1:1 host–guest BAPTA system [2]. This moiety has been exploited in the development of various fluorescent supramolecular chemosensor systems and even molecular logic systems [3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11]. Equally, the incorporation of
- cis and trans-forms [33][34]. Herein we describe a BAPTA host molecule 1, with an azobenzene moiety integrated in the tether linking both aromatic rings, as illustrated in Figure 1. The principle goal of the current work, with a long-term view of interfacing biological systems, was the development of
A chiral self-sorting photoresponsive coordination cage based on overcrowded alkenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2767–2773, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.268

- between the three isomers. Two of the isomers were able to form host–guest complexes opening up new prospects toward stimuli-controlled substrate binding and release. Keywords: coordination cages; molecular motors; molecular switches; overcrowded alkene; palladium; Introduction Supramolecular
- metal centers has been used to control host–guest interactions [25][26][27][28], structural composition [29], and sol–gel transition [30]. However, dithienylethene undergoes a limited structural change upon photoisomerization and, up to now, photoswitchable ligands based on other types of photochromic
- formed revealing that a chiral self-sorting process takes place. In addition, two of the cage isomers can bind a tosylate anion in solution by formation of a host–guest complex. Results and Discussion Ligands Z-1 and E-1 (Scheme 1) were synthesized by a Suzuki cross-coupling reaction of 3
Chemical synthesis of the pentasaccharide repeating unit of the O-specific polysaccharide from Escherichia coli O132 in the form of its 2-aminoethyl glycoside
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2563–2568, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.249
- play a key role in determining and regulating the biology of these organisms [1] and act as the elicitor of the innate immune response [2]. As these polysaccharides can protect the bacteria concerned by killing the serum complements of the host system and can stop phagocytosis, they are extremely
Anion-driven encapsulation of cationic guests inside pyridine[4]arene dimers
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2486–2492, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.241

- and studied by multiple gas-phase techniques, ESI-QTOF-MS, IRMPD, and DT-IMMS experiments, as well as DFT calculations. The comparison of classical resorcinarenes with pyridinearenes by MS and NMR experiments reveals clear differences in their host–guest chemistry and implies that cation encapsulation
- synthesis of pyridine[4]arenes dates back to 2001 [4], their host–guest chemistry is still under-explored. Both macrocycles are concave and are known to form capsular assemblies via intermolecular hydrogen bonding [5][6]. Pyridine is significantly less electron-rich than benzene. Consequently, pyridinearene
- dimeric resorcin[4]arene and pyridine[4]arene capsules, we highlight here unique host–guest properties of pyridinearene capsules. In marked contrast to the corresponding resorcin[4]arene capsules, cation binding is clearly feasible, when anions bind in an exo-site and support cation encapsulation by
Reversible switching of arylazopyrazole within a metal–organic cage
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2398–2407, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.232

- found to be stabilized in their zwitterionic form when confined to iron oxide nanoparticles [24]. Similarly, the ability of anthracenes to photodimerize greatly depends on the curvature of their “host” nanoparticle [25]. Despite these advances, we are still far from achieving the ease and elegance, with
- ; rather, they suggest that 1 resides in the hydrophobic cavity of 2, interacting with its aromatic walls. Integration of the signals due to 1 and 2 confirmed that each molecule of the host encapsulates two molecules of the guest. The presence of a complex is also evident from the NOE spectrum, which shows
- multiple host–guest correlations (see Figure S6 in Supporting Information File 1 for a full-range spectrum). For example, E-1’s protons Hd at 6.22 ppm correlate both with the resonances at 7.78 ppm and at 7.57 ppm, which all originate from 2’s protons (H2 + H3 and H5 + H7, respectively). Similarly, the Ha
Current understanding and biotechnological application of the bacterial diterpene synthase CotB2
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2355–2368, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.228

- description of the bacterial TPS CotB2, we will therefore refer to the NSE motif only. Using host microorganisms, such as bacteria or baker’s yeast for the heterologous synthesis of terpenes increases the sustainability of bioactive terpene production by saving resources, as the production host can be fed
- have to be circumvented [83]. In that regard, there are different ways of enhancing E. coli host productivity. First, the general production pathway is usually genetically established. Choosing a plasmid-based production pathway has the advantage, that single genes can be exchanged or added quite
- rapidly [84]. Furthermore, decreasing the metabolic burden of the plasmid construct on the native host metabolism [85] can be achieved by using polycistronic operons to reduce the amount of plasmid in a cell. Additionally, computer aided fine-tuning [86] of transcription rates by promotor [24] and RBS [87
Isolation and biosynthesis of an unsaturated fatty acid with unusual methylation pattern from a coral-associated bacterium Microbulbifer sp.
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2327–2332, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.225

- . Compound 1 showed weak growth inhibition against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Keywords: biosynthesis; fatty acid; marine bacteria; methylation; Microbulbifer; Introduction Marine microbial symbionts are currently recognized as a reservoir of new bioactive compounds [1]. The most well-studied host animal is
- but are widely produced by many fungi and are thought to play an important role in the interaction between fungi and their host organisms. C9-Methylated sphingolipids are also found from some marine invertebrates such as sea anemone and starfish although their biological function is still unclear in
1,2,3-Triazolium macrocycles in supramolecular chemistry
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2142–2155, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.211
- -triazolium macrocycles; Review 1. Introduction Supramolecular chemistry – “The chemistry beyond the molecule” [1] – is an ever growing interdisciplinary area has emerged from the early host–guest chemistry to more elaborate bio-inspired supramolecular aggregates by exploiting various noncovalent
- imidazoles [8][9], polypyrroles [10][11], and indole moieties [12][13], as part of supramolecular receptors, triazole heterocycles containing macrocycles have recently been introduced as new host molecules for the selective recognition of ions, mechanically interlocked molecules (MIMs), supramolecular
- macrocycles are a class of steroid-based receptors which can host polar molecules in nonpolar solvents because of their amphiphilic nature. As a result, their design and synthesis has been a topic of substantial research interest in supramolecular chemistry [32][33]. Various synthetic methods have been
Multiple threading of a triple-calix[6]arene host
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2092–2104, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.207

- directed towards the study of multiple-threading processes of host systems bearing multiple-wheels (multivalent hosts). On this basis, interesting handcuff-like interpenetrated systems (Figure 1) have been reported to date in literature [10][11][12][13][14][15][16], which represent non-trivial
- designed the triple-calix[6]arene host 6 (Figure 2) bearing three calix[6]arene wheels symmetrically-linked to a central benzene unit. Now the question arises as to whether the triple-calix[6]arene system 6 is also capable to form pseudo[n]rotaxanes by multiple-threading with dialkylammonium axles. Results
- diffusion coefficient of 7.06 × 10−11 m2/s attributable to the 7+6 pseudo[2]rotaxane as TFPB− salt and significantly lower than that measured for the free triple-calix[6]arene host 6 of 3.02 × 10–10 m2/s. Through an 1H NMR quantitative analysis of a 1:1 mixture of 7+·TFPB– and 6 in CDCl3, using 1,1,2,2
Bipolenins K–N: New sesquiterpenoids from the fungal plant pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2020–2028, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.198
- fungi against plant hosts [12]. Well-known examples include the host-specific toxins victorin and T-toxin and other non-host-specific toxins such as the ophiobolins [11]. Bipolaris sorokiniana (syn. Cochliobolus sativus) has been identified as the causative agent of multiple diseases on wheat and barley
- and is a major threat to yield improvement and food security in Central Asia [13]. Recent genome sequencing of 35 Australian strains of B. sorokiniana identified a known proteinaceous necrotrophic effector, ToxA, which confers host-specific virulence proteins and is proposed to be acquired through
Synthesis and anion binding properties of phthalimide-containing corona[6]arenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1976–1983, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.193
- noncovalent interactions between anions and the tetrazine rings. Keywords: anion–π interactions; coronarenes; host–guest complexation; N-functionalized phthalimides; O6-corona[3]arene[3]tetrazines; Introduction Synthetic macrocycles [1][2] are always attractive and important because they are unique
- ability of 3a to bind various anion species in gas phase. To our delight, host molecule 3a co-crystalized with n-Bu4NX (X = Cl, Br) from diffusion of diethyl ether vapor into ethyl acetate solution at ambient temperature to give single crystals of the host–guest complexes (n-Bu4NX)3-3a (X = Cl, Br). X-ray
- crystallography then allowed us to understand the host–guest interactions at the molecular level. As illustrated in the molecular structures in Figure 4, above the centroid of each tetrazine ring there resided a chloride or a bromide. The distance of the anion to the centroid of tetrazine ranged from 3.060 Å to
Morphology-tunable and pH-responsive supramolecular self-assemblies based on AB2-type host–guest-conjugated amphiphilic molecules for controlled drug delivery
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1925–1932, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.188

- -responsive supramolecular self-assemblies have been constructed, the controlled drug delivery induced by morphology transitions of these supramolecular self-assemblies on the basis of host–guest-conjugated monomers (HGCMs) are few reported. In this paper, the self-assembly behaviors of AB2-type HGCMs, e.g
- varied morphology could inhibit cancer cell proliferation, indicating their potential application in the field of drug delivery. Keywords: β-cyclodextrin; controlled drug delivery; host–guest interaction; stimuli-responsive; supramolecular self-assemblies; Introduction Supramolecular self-assemblies
- based on noncovalent interactions with dynamic nature and reversible property have attracted increasing attention in the fields of biomedicine [1][2][3][4][5][6][7], smart materials [8][9][10], etc. As one common noncovalent interaction [11], host–guest interaction has been used to effectively create
Complexation of chiral amines by resorcin[4]arene sulfonic acids in polar media – circular dichroism and diffusion studies of chirality transfer and solvent dependence
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1913–1924, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.187
- a hydrophobic effect, while the other one has a more directional character, or application of multidentate interaction sites [3]. Macrocyclic compounds with persistent hydrophobic cavities constitute a fundamental class of scaffolds for the construction of supramolecular host–guest complexes in
- manifested in chirality transfer. We will also present a crucial and non-intuitive solvent dependence. RSAs (e.g., 1) can be considered as analogues of calix[4]arene sulfonic acids (CSAs) – the class of macrocycles widely studied in the context of various host–guest interactions, especially with various
- direct evidence that the complexes are tight ion-pairs with an ordered structure comes from the diastereotopic splitting of the CH2SO3− groups of 1 (insets in Figure 2a–g). Such splitting can only be present when chirality of the guest is transferred into the host and the effect is not averaged by
Nanopatterns of arylene–alkynylene squares on graphite: self-sorting and intercalation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1848–1855, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.180
- three TCB molecules). In addition, five TCB molecules intercalate into the intermolecular nanopore in a dense packing of two, one, and two molecules (cf. white dotted circle in Figure 2c). The observation of intercalated TCB molecules inspired us to investigate, whether the nanopores can also host
- , and lead to blurred regions as marked by arrow 3 in Figure 3a. In addition, nine of the 59 intraannular regions (i.e., 15%) in Figure 3a host a molecule of 2 (up to 17%, see Supporting Information File 1). Eight species of 2 (in Figure 3a) appear as bright features (with a slight central depression
- geometries and/or side chains pointing towards the pore interior translate into varying numbers of intercalated solvent molecules in the intraannular regions. In addition, the intermolecular pores are scalable by the lengths of the alkoxy side chains in a certain range. We showed that the nanopores host
Synthesis of a [6]rotaxane with singly threaded γ-cyclodextrins as a single stereoisomer
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1829–1837, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.177

- face with primary hydroxy groups and a wider secondary face with secondary hydroxy groups [6][7]. With the hydrophobic cavity and the hydrophilic hydroxy groups, CDs efficiently form host–guest complexes with different hydrophobic guests in aqueous medium [8][9]. Among the common CDs, γ-CD possesses a
- relatively large cavity size that could accommodate up to two aromatic guests to form 1:2 host–guest complexes, in contrast to the usual formation of 1:1 complex by α-CD and β-CD [10][11]. In addition to host–guest chemistry, the favourable binding of CDs to common organic scaffolds has also made CDs popular
- threaded through one γ-CD [34]. More recently, Yang and co-workers have described a rotaxane-based host that detects tryptophan which binds to the γ-CD cavity of the rotaxane [35]. As part of our program in the synthesis and application of complex, multicomponent interlocked molecules [37][38][39], we are
Complexation of 2,6-helic[6]arene and its derivatives with 1,1′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium salts and protonated 4,4'-bipyridinium salts: an acid–base controllable complexation
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1795–1804, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.173

- ; macrocycles; macrocyclic arene; Introduction Macrocyclic host molecules [1][2] play a significant role in host–guest chemistry. Compared with noncyclic molecules, the structures of macrocyclic hosts can greatly enhance the host–guest complexation ability through preorganization. Moreover, cyclic structures
- methenyl groups. They have been a kind of important macrocyclic host molecules during the last decades due to their unique structures and a wide range of applications in host–guest chemistry [13][14][15][16][17][18], self-assembly [19], biomedicine [20] and materials science [21][22]. The derivatives of
- macrocyclic arenes with diverse functional groups are also important for the development of various new host–guest supramolecular systems [23][24][25][26][27][28][29]. Helic[6]arenes [30], a new kind of macrocyclic arenes, are composed of 2,6-dihydroxy-substituted triptycene subunits bridged by methylene
Host–guest interactions in nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril: novel guest-dependent molecular recognition and stereoisomerism
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1705–1711, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.166
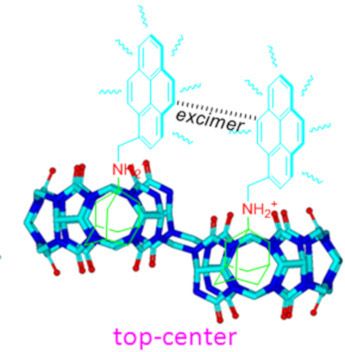
- ]. Keywords: fluorescent; host–guest interaction; macrocycles; molecular recognition; nor-seco-cucurbit[10]uril; pyrene; Introduction Host–guest interactions that trigger molecular recognition are a current topic of interest. For example, understanding the protein–ligand molecular recognition is of paramount
- importance in the study of enzymatic catalysis and allosteric regulation of cell signaling, as well as in the design of efficient drugs that utilize host–guest interactions [1]. Cucurbit[n]urils (Q[n]s or CB[n]s) [2][3] having been viewed to have high potential use in host–guest chemistry in aqueous solution
- guests in its cavity through host-stabilized charge-transfer or π–π interactions [14][15]. This novel property of Q[8] has been utilized as molecular container for biological substrates [16][17], as well as in the construction of various supramolecular assemblies with specific structures and properties
Synthesis, enantioseparation and photophysical properties of planar-chiral pillar[5]arene derivatives bearing fluorophore fragments
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1601–1611, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.164

- guest receptors [4][5]. Planar-chiral macrocyclic molecules are particularly interesting in the context of the host–guest complexation properties [6][7][8]. Pillararenes are typical examples of this type of compounds and have attracted considerable attention due to their facile chemical synthesis and
- quantum yield was significantly decreased to 46.4% compared with 78.2% for Py-6. We ascribed the decreased fluorescence of P5A-Py to the π–π stacking of the Py units caused by the high local concentration of perylene. For P5A-DPA, which also bears two DPA units in one macrocyclic host, the fluorescent
- of P5A-Py is 3.4 ns which is shorter than that of Py-6 (4.4 ns), demonstrating that grafting two Py units in close proximity in one host, opened a new route for nonradiative decay. This phenomenon further verified the occurrence of π–π stacking of the Py fragments in P5A-Py. The lifetime of P5A-DPA
Water inside β-cyclodextrin cavity: amount, stability and mechanism of binding
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1592–1600, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.163

- .15.163 Abstract Cyclodextrins (CDs) are native host systems with inherent ability to form inclusion complexes with various molecular entities, mostly hydrophobic substances. Host cyclodextrins are accommodative to water molecules as well and contain water in the native state. For β-cyclodextrin (β-CD
- ; hydration; macrocycles; thermodynamic characteristics; Introduction Cyclodextrins (CDs), a family of enzymatically modified starches, are widely used as host macrocycles in forming inclusion complexes with various molecular entities of interest to food industry, pharmacology, cosmetics, catalysis, and
- water and can displace (completely or partially) the hydration content of the host molecule [2]. Most of these complexation reactions take place in aqueous solutions, thus it is important to understand the mechanism and energetics of interactions between the water molecules and the components of the
2,3-Dibutoxynaphthalene-based tetralactam macrocycles for recognizing precious metal chloride complexes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1460–1467, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.146

- macrocycle, which make it conformationally adaptive to maximize the binding affinities. In addition, the macrocycle shows fluorescent quenching when adding the chloride metal complexes in its solution and may be used as a fluorescent sensor for the detection of these coordination complexes. Keywords: host
- distance: 2.21, 2.38 and 2.46 Å). C–H···π interactions (H···π distance: 2.75 and 2.83 Å) between the methyl group of CH3CN and the naphthalene panels of the host are also detected. This suggests that the 2.3-dibutoxynaphthalene tetralactam macrocycle, just like other tetralactam macrocycles, may use
- , hydrogen bonds are detected between the amide protons and H6 of 1 and the chloride ions of the guest (H···Cl distance: 2.48, 2.77 and 2.90 Å). Consequently, the electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonds are the main driving forces for the host–guest complex. It is noted that the four amide protons are
Reversible end-to-end assembly of selectively functionalized gold nanorods by light-responsive arylazopyrazole–cyclodextrin interaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1407–1415, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.140

- of gold nanorods (AuNR) by thiolated cyclodextrin (CD) host molecules. As a result of the complete removal of the precursor capping agent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) by a tetraethylene glycol derivative, competitive binding to the host cavity was prevented, and reversible, light-responsive
- assembly and disassembly of the AuNR could be induced by host–guest interaction of CD on the nanorods and a photoswitchable arylazopyrazole cross-linker in aqueous solution. The end-to-end assembly of AuNR could be effectively controlled by irradiation with UV and visible light, respectively, over four
- –organic hybrid nanomaterials. Keywords: cyclodextrins; gold nanorods; host–guest chemistry; light-responsive materials; molecular switches; self-assembly; Introduction Metallic nanomaterials have received intense and interdisciplinary interest due to their unique optical [1], electronic [2][3] and
Complexation of a guanidinium-modified calixarene with diverse dyes and investigation of the corresponding photophysical response
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1394–1406, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.139

- and potential applications according to the diverse photophysical responses are provided. Keywords: calixarene; host–guest complexation; luminescent dyes; macrocycles; photophysical properties; Introduction Fluorescence sensing represents a powerful detection methodology due to its low cost, ease of
- with carboxylated bipyridyl ligands (Ru(dcbpy)3), were screened as model guests on account of the desired strong host–guest binding affinity (Scheme 2). Fl, EY, RB, TPPS and AlPcS4 were employed as classical aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) dyes; 2,6-TNS and 1,8-ANS were selected as intramolecular
- with substrates, typically oxygen, to produce reactive oxygen species. The competitive complexation can not only be applied in diagnosis via the aforementioned IDA but also be engaged in therapy. We proposed a host–guest strategy for activatable phototheranostics termed biomarker displacement

























































































































































































































