Search results
Search for "HPLC" in Full Text gives 750 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Pigmentosins from Gibellula sp. as antibiofilm agents and a new glycosylated asperfuran from Cordyceps javanica
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2968–2981, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.293

- metabolite profiles using analytical HPLC coupled with diode array detection and mass spectrometry (HPLC–DAD–MS) revealed that the production of pigmentosin B (2) was apparently specific for Gibellula sp., while the glycoasperfuran 3 was specific for C. javanica. Keywords: antibiofilm agents; natural
- elucidation Gibellula sp. was cultivated in liquid yeast, malt, and glucose (YMG) medium and extracted as described in the Experimental section. The extracts were purified by HPLC to give pigmentosin A (1) and pigmentosin B (2). Using a similar procedure, compounds 3–6 were obtained from the liquid culture of
- the secondary metabolite production among species of Cordycipitaceae, HPLC–UV–vis profiles of all fungal isolates were generated and compared to each other. This revealed that the individual species possessed unique secondary metabolite profiles. Pigmentosins A (1) and B (2) were detected in all
Two new aromatic polyketides from a sponge-derived Fusarium
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2941–2947, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.289

- . collected in Karimunjawa National Park, Indonesia. This fungus produces a violet pigment in the mycelium and secretes pink to red pigments into the broth medium. Comprehensive chemospectroscopic analysis of the culture extract using HPLC/UV led to the isolation of two new aromatic polyketides, karimunones A
- database. HPLC/UV-guided purification of the secondary metabolites from this strain led to the isolation of two new polyketides, karimunones A (1) and B (2), together with five known compounds (3–7, Figure 1). Compound 1 was obtained as a red powder. TOF-HRESIMS analysis gave a deprotonated molecule [M − H
- to dryness. The residual solid (53 mg) was applied to the preparative HPLC (Cosmosil Cholester Packed Column, 10 × 250 mm, Nacalai Tesque) using a linear gradient of 40 to 70% MeCN in 0.1% HCO2H over 25 min at a flow rate of 4 mL/min, yielding karimunone A (1, 7.3 mg, tR 15.6 min) and B (2, 4.2 mg
Automated glycan assembly of arabinomannan oligosaccharides from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2936–2940, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.288

- -step purification and global deprotection [25]. Linear α-(1,6)-hexamannoside 4 was synthesized using six coupling cycles and 6.5 equiv of mannose building block (BB) 1. No deletion sequences were observed and the crude product was purified using normal-phase HPLC to obtain hexamannoside 4 in 55% yield
- methanolysis, followed by Pd/C-catalyzed hydrogenolysis of the carboxybenzyl group and the benzyl ethers. Mannosides 4–6 were deprotected and purified using reversed-phase HPLC to obtain fully deprotected mannosides 10–12 (Figure 2). For the arabinomannosides 7–9, the acid-labile arabinose chain was cleaved
- reaction conditions allowed for the synthesis of larger oligosaccharides. The resulting oligosaccharides will be used to study the substructure-specific antibody recognition of arabinomannans. HPLC chromatograms of crude dodecamer 9. a) Results obtained with AGA procedure A. b) Results obtained with AGA
Chemical synthesis of tripeptide thioesters for the biotechnological incorporation into the myxobacterial secondary metabolite argyrin via mutasynthesis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2922–2929, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.286
- kinetics under the standard conditions in the cultivation medium. The HPLC–MS analysis revealed a rather rapid degradation of the analysed mutasynthon, as after only 2 h of incubation time the majority was degraded and after 4 h of incubation almost complete degradation of the compound was observed
- phosphopantetheinyl arm of the peptide carrier protein (CP). Analysis of mutasynthon 14 obtained via the convergent synthetic route by HPLC on a HILIC stationary phase and UV detection (A) and mass spectrometry (B). Synthesis of tripeptide thioesters. Reagents and conditions: (a) SOCl2, EtOH, 78 °C; (b) IBCF, NMM
Skeletocutins M–Q: biologically active compounds from the fruiting bodies of the basidiomycete Skeletocutis sp. collected in Africa
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2782–2789, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.270
- of secondary metabolites for later comparison with herbarium specimens of other species by HPLC–diode array detection (HPLC–DAD)–MS. Surprisingly, we detected further members of the skeletocutin family that were not present in the cultures. The current paper is dedicated to the description of their
- isolation as well as biological and physicochemical characterization. Results and Discussion The fruiting bodies of the fungal specimen MUCL56074 were extracted with acetone and subsequently purified via preparative HPLC, which led to the isolation of five previously undescribed secondary metabolites, 1–5
- information NMR spectra were recorded with a Bruker 500 MHz spectrometer at frequencies of 500.130 (1H NMR) and 125.758 MHz (13C NMR). HRESIMS spectra were recorded after purification with an Agilent 1200 series HPLC–UV system (column size: 2.1 mm⋅50 mm, packing: 1.7 µm, Waters ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18 sorbent
Nanangenines: drimane sesquiterpenoids as the dominant metabolite cohort of a novel Australian fungus, Aspergillus nanangensis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2631–2643, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.256

- coverage of the grains. Extraction of the grains with acetone, followed by partitioning of the aqueous residue with EtOAc and defatting with hexane, provided an enriched extract of non-polar secondary metabolites. Fractionation by reversed-phase preparative HPLC (Figures S1 and S2 in Supporting Information
- × 10 mm quartz cuvette. Analytical HPLC was performed on a gradient Shimadzu VP HPLC system equipped with a Shimadzu SPD-M10A VP diode array detector and an LC-10AT VP gradient chromatograph. Preparative HPLC was performed on a gradient Shimadzu HPLC system comprising two LC-8A preparative liquid pumps
- series HPLC equipped with an Agilent 6130 Infinity series single quadrupole mass detector in both positive and negative ion modes. High-resolution electrospray ionisation mass spectra (HRESIMS) were obtained on a Bruker Apex Qe 7T Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance mass spectrometer equipped with
Arylisoquinoline-derived organoboron dyes with a triaryl skeleton show dual fluorescence
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2612–2622, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.254

- undertaken at 80 °C in C6D6 using a screw-cap NMR tube. Although significant changes were registered, a complete coalescence of the signals was not observed. The chiral HPLC analysis (see HPLC traces in Supporting Information File 1) demonstrated the high purity of compounds 16–19. The sharp peaks and
- fluoroboronate complexes, HPLC traces for the dyes 16–19. Acknowledgements Funding by the Spanish Ministry of Economy, Industry, and Competitiveness (CTQ2014-54729-C2-1-P for U.P., CTQ2013-48164-C2-1-P and CTQ2013-48164-C2-2-P for A.R., Ramón y Cajal contracts RYC-2013-12585 for A.R. and RYC-2015-17737 for I.V
Safe and highly efficient adaptation of potentially explosive azide chemistry involved in the synthesis of Tamiflu using continuous-flow technology
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2577–2589, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.251
- NaN3, 50 °C and 12 s affording full conversion (HPLC) towards the desired azide 5 in 91% isolated yield. Unlike all literature procedures [9][19][20], side product 5a was not detected using our procedure at 50 °C and 12 s residence time. The use of green solvents, excellent selectivities, safe handling
- conversion (HPLC) and 89% isolated yield. In batch, good yields (66–95%) were attained at reaction times between 3 h and 15 h at temperatures around 90 °C [9][19][20][23]. Our flow procedure was therefore more efficient than all the reported batch procedures. Continuous flow allowed for higher reaction
- in a continuous-flow system using NaN3 as the azidating agent. Optimum conditions for this reaction were found to be NaN3 (3 equiv), 190 °C and 45 s residence time affording full conversion (HPLC) towards azide 7 in 89% isolated yield. The use of NaN3 (2 equiv) was accompanied by a 15% decrease in
A new approach to silicon rhodamines by Suzuki–Miyaura coupling – scope and limitations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2569–2576, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.250

- catalyst, different substituted boroxines were assessed to explore the scope of the Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction. Conclusions: A number of silicon rhodamines were synthesized under the optimized conditions in up to 91% yield without the necessity of HPLC purification. Moreover, silicon rhodamines
- '-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene). Remarkably, not only the yield was increased with PdCl2(dppf) from 49% to 67%, even the dye 22 was obtained with high purity after column chromatography without the necessity of further HPLC purification (Table 1, entry 8). Exploration of substrate scope Next we
- catalytic system with ligands suitable for coupling of multisubstituted aryls is under current investigation. In conclusion, several silicon rhodamines could be synthesized under the optimized conditions, without the necessity of HPLC purification, in up to 91% yield whereby the free acids are directly
Synthesis of novel sulfide-based cyclic peptidomimetic analogues to solonamides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2544–2551, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.247
- cocktail afforded the resin-free linear peptidomimetics 8. The SN2’ macrocyclization step was performed immediately after the cleavage procedure to avoid the oxidative disulfide dimerization observed when preparative HPLC purification of the resin-free linear peptidomimetics 8 was tried. Thus, a 1 mM
- after preparative HPLC purification and lyophilization. The overall yield for this 11-step synthesis ranged from 7% to 15% for almost all solonamide analogues 9, based on the initial resin’s molarity. The exception relays on those containing ᴅ-Ala and ʟ-Leu amino acid residues sequentially attached to
A toolbox of molecular photoswitches to modulate the CXCR3 chemokine receptor with light
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2509–2523, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.244

- advanced intermediate 28b (Scheme 3), which was subjected to an aromatic nucleophilic substitution with potassium phthalimide prepared in situ from 29 and K2CO3. Presumably due to the alkaline medium, the phthalimide ring was partially opened as detected by HPLC–MS. Upon attempted re-closing under reflux
In search of visible-light photoresponsive peptide nucleic acids (PNAs) for reversible control of DNA hybridization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2500–2508, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.243

- compatible with the standard TFA/m-cresol/H2O (90:5:5) acidolysis yielding the photoswitchable PNA conjugates. These and all further studied PNAs in this work (Table 2) were purified by reversed-phase (RP) HPLC and fully characterized. Analogous compounds lacking the photoswitch were used as controls. First
- room temperature in the dark according to UV–vis measurements (Figure 2 and Figure S32, Supporting Information File 1). The thermal relaxation of the cis-PNA12(oF4Azo) (3) was slow even at high temperatures (Figures S27 and S28, Supporting Information File 1). Furthermore, RP-HPLC chromatograms of its
Experimental and computational electrochemistry of quinazolinespirohexadienone molecular switches – differential electrochromic vs photochromic behavior
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2473–2485, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.240
- (4) as we had previously surmised [21]. Finally, we have been able to rationalize these results computationally on the basis of bond lengths, bond orders, and molecular orbital occupancy. Experimental Materials Acetonitrile was of the highest HPLC grade (used as received or dispensed through a
Excited state dynamics for visible-light sensitization of a photochromic benzil-subsituted phenoxyl-imidazolyl radical complex
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2369–2379, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.229

- chromatography (HPLC), and each isomer was characterized by steady-state absorption spectra and time-dependent density functional theory (TDDFT) calculations as shown below. Figure 1 shows the steady-state absorption spectra of the two isomers of Benzil-PIC and PIC in benzene at 298 K. While the absorption of
- purified by silica gel column chromatography (AcOEt/hexane 2:3) to give the desired product as a yellow powder, 42 mg (0.081 mmol, 58%). Two structural isomers were separated by HPLC (eluent: CH3CN/H2O 7:3). 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) (isomer A) δ 8.01 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.97–7.94 (m, 2H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.6
Mono- and bithiophene-substituted diarylethene photoswitches with emissive open or closed forms
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2344–2354, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.227

- details). The progress of the reaction leading to monoiodide 4 was monitored by HPLC. Despite incomplete conversion, the formation of diiodide 5 could not be fully suppressed. The Rf values of 3 (TLC [SiO2, hexane]: Rf = 0.17), monoiodide 4 (Rf = 0.19), and diiodide 5 (Rf = 0.20) were very similar, and
- DAE 4 could not be isolated by column chromatography on regular silica gel. Instead, monoiodide 4 was obtained in 14% yield as colorless solid after preparative HPLC on a reversed phase (C18) column and lyophilization. The constitution and structure of 4 was confirmed by HRMS, 1H and 19F NMR
- ” indicates oxidized benzothiophene units, and “Th1”/ “Th2” specify the number of thiophene units in the side chain. The coupling products were isolated via preparative HPLC in yields ranging from 21% to 75%. While in all cases the open forms of the diarylethenes were isolated, small amounts of SyOTh1 in its
Synthesis of a dihalogenated pyridinyl silicon rhodamine for mitochondrial imaging by a halogen dance rearrangement
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2333–2343, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.226

- coexistence of 19 and its lithiated analogue. Using high excess of 19 could force the reaction to completeness leading to the dihalogenated pyridinyl silicon rhodamine in 85% yield without any monohalogenated byproduct and no necessity of HPLC purification. Although 15 can be coupled or further functionalized
- rearrangement. By our optimized procedure, we have obtained the dye 15 at high yield and without the necessity of HPLC purification. The chlorine atom in 2’-position can potentially be used to introduce the PET radionuclide fluorine-18 while the bromine atom serves as a constraint against rotation around the
Isolation and biosynthesis of an unsaturated fatty acid with unusual methylation pattern from a coral-associated bacterium Microbulbifer sp.
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2327–2332, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.225

- the whole culture broth was extracted with 1-butanol. The extract was consecutively fractionated by normal- and reversed-phase column chromatographies, followed by HPLC purification on a C18 column to yield compound 1. The molecular formula of 1 was determined to be C11H18O2 with three degrees of
- EtOAc. The organic layer was dried over anhydrous Na2SO4, filtered, and concentrated to give a semi-pure material (21 mg). Final purification was achieved by preparative HPLC (Cosmosil Cholester 5 µm, 10 × 250 mm, 4 mL/min, UV detection at 254 nm) with an isocratic elution of MeCN/0.1% HCO2H solution
Isolation of fungi using the diffusion chamber device FIND technology
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2191–2203, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.216
- chemically diverse secondary metabolites in the major VLC fraction 3. Detailed HRESIMS investigation was thus performed with VLC fraction 3, which showed prominent m/z values for metabolites with molecular weights of 248 and 250 Da. Subsequent repeated fractionation of VLC fraction 3 by RP-HPLC resulted in
- -Elmer Spectrum BX FTIR instruments, respectively. All NMR spectra were recorded in MeOH-d4 using a Bruker Avance 300 DPX spectrometer. Spectra were referenced to residual solvent signals with resonances at δH/C 3.35/49.0. HRESIMS were recorded on a LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometer. HPLC was performed on a
- Waters HPLC system equipped with a 1525µ binary pump, a 2998 PDA detector, Breeze 2 software and a Rheodyne 7725i injection system. A Macherey-Nagel Nucleoshell C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm; 5 µm), Nucleodur PolarTec column (250 mm × 4.6 mm; 5 µm), Pyramid C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm; 5 µm) and Phenomenex
Azologization and repurposing of a hetero-stilbene-based kinase inhibitor: towards the design of photoswitchable sirtuin inhibitors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2170–2183, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.214

- UV irradiation of 365 nm. The photoisomerization could be reversed by exposure to visible light, i.e. 452 nm, albeit the PSS at 452 nm still comprised about 25% of (Z)-11 as determined by HPLC analysis using UV–vis detection at the isosbestic points (Table 2). Light of 500 nm could also reverse
- apparatus from Büchi and are uncorrected. High accuracy mass spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu LCMS-IT-TOF using ESI ionization. Purity of final compounds was determined by HPLC with DAD (applying the 100% method at 220 nm). Preparative and analytical HPLC were performed using Shimadzu devices CBM-20A, LC
Characterization of two new degradation products of atorvastatin calcium formed upon treatment with strong acids
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2085–2091, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.206

- were not characterized in this [6] and several other reports, which only determined the downsizing of the atorvastatin peak in HPLC after treatment with acid [7][8][9][10]. The most prominent decomposition product upon acidic treatment, compound 2, results from lactonization of the 3,5
- anhydrous acid conditions, the entire carboxanilide residue was removed to give the (S)-configured 4-unsubstituted pyrrole 7, as exemplified by a typical CH resonance at 6.20 ppm in the 1H NMR spectrum. This structure was further confirmed by X-ray data (see Figure 2 and Supporting Information File 1). HPLC
- method for the detection of the novel impurities In order to provide a convenient method for including our new findings into quality control of atorvastatin batches, we worked out an isocratic HPLC protocol, which prettily separates the four artefacts 2, 3, 6 and 7 from atorvastatin (1). This method uses
α-Photooxygenation of chiral aldehydes with singlet oxygen
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2076–2084, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.205
- its rather simple structure diol 6 was not previously reported in the literature. The ratio of stereoisomers 6 was determined by HPLC analysis while the absolute configuration of the newly created stereocenter was established using a chiroptical spectroscopic method. Samples of stereoisomers syn-6 and
- P-2000 polarimeter. The enantiomeric purity of diols was determined by chiral-phase HPLC analysis on Daicel Chiralpak ID (250 mm × 4.6 mm inside diameter) using a hexane/iPrOH mixture as a mobile phase. Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) was performed using Merck Silica Gel GF254, 0.20 mm thickness
- ); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δC 140.8, 140.0, 129.1, 128.4, 128.3, 128.0, 126.7, 125.8, 75.3, 65.0, 51.4, 38.7; HRESIMS m/z: [M + Na]+ calcd for C16H18O2Na, 265.1204; found, 265,1198. HPLC analysis on Daicel Chiralpak ID (250 mm × 4.6 mm inside diameter) using a hexane/AcOEt, 80:20 (v/v) as a mobile phase
Genome mining in Trichoderma viride J1-030: discovery and identification of novel sesquiterpene synthase and its products
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2052–2058, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.202

- efficiently enriched via an abundant FPP supply. Detection and characterisation of Tvi09626 products By semi-preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), we purified compound 1 and compound 2 (23.1 mg and 13.2 mg, respectively). The structures of the two new compounds were characterised by 1D
Bipolenins K–N: New sesquiterpenoids from the fungal plant pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2020–2028, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.198
- chromatographed repeatedly with silica gel and RP-HPLC to afford four new sativene-type sesquiterpenoids, bipolenins K–N (1–4), along with eight previously reported compounds (5–12), which were identified as sativene-type sesquiterpenoids prehelminthosporol lactone (5) [1], helminthosporic acid (6) [1
- (Phenomenex, 2.6 µm, 2.1 × 100 mm), and semi-preparative C18 (Grace, 5 µm, 10 × 250 mm) were used. All solvents used for extraction were analytical grade, and solvents for HPLC were HPLC grade. Biological material The fungal strain B. sorokiniana BRIP10943 was obtained from Queensland Plant Pathology
- a light-yellow crude extract (205 mg), which was fractionated on a Reveleris flash chromatography (Grace) using gradient mode of H2O/MeOH equipped with the flash cartridge, UV and evaporative light scattering detector. The resulting fractions were further purified by RP-HPLC on gradient mode of H2O
Isolation and characterisation of irinans, androstane-type withanolides from Physalis peruviana L.
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2003–2012, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.196

- /MeOH (3:1) and divided into fractions soluble in petroleum ether, chloroform, and n-butanol, respectively. The chloroform fraction was further separated by flash chromatography on a C18 stationary phase, resulting in three major subfractions F1–F3. Final purification by preparative HPLC followed by NMR
- noted formation of small quantities of irinan A (2) when performing the reaction at 70 °C (Figure 4B and Figure S21 in Supporting Information File 1). The identity of irinan A (2) was verified by isolation of the corresponding compound by preparative HPLC (4% yield) followed by NMR analysis. This result
- exclude that unidentified impurities, which could not be removed by repeated preparative HPLC, obscure the true EC50 values of irinans. We conclude that irinans possess potent antiproliferative activity, that is however reduced compared to 4ß-hydroxywithanolide E (1). Our results demonstrate the
Archangelolide: A sesquiterpene lactone with immunobiological potential from Laserpitium archangelica
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1933–1944, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.189
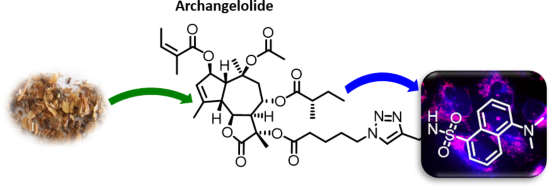
- 2) and HRMS (Supporting Information File 1, section 3). All compounds were re-purified on a short silica column prior to testing and afterwards lyophilized from tert-butanol. The substances were analyzed by HPLC proving a purity of ≥95% (Supporting Information File 1, section 4). Fluorescent











































































































































































































