Search results
Search for "cycloisomerization" in Full Text gives 65 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Pathway economy in cyclization of 1,n-enynes
- Hezhen Han,
- Wenjie Mao,
- Bin Lin,
- Maosheng Cheng,
- Lu Yang and
- Yongxiang Liu
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 2260–2282, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.173

- and co-workers achieved an innovative gold-catalyzed cascade cycloisomerization of 3-allyloxy-1,6-diynes to access cyclopropane- and cyclobutane-fused benzofurans/chromanols (Scheme 5) [12]. In this study, solvent polarity and trace water were identified as key parameters governing the reaction
- synthetic intermediates, and used to successfully modify diverse bioactive scaffolds via late-stage functionalization, collectively demonstrating the method’s synthetic utility. In 2025, the Das group developed a palladium-catalyzed cycloisomerization of 2-alkynylbenzoate-cyclohexadienone that enables
- derivatives 31 (Scheme 7, path b). This work provided a novel approach for constructing substituted naphthalene and indene frameworks via gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of 1,5-enynes. In 2016, Liu et al. achieved the stereoselective syntheses of furofuran and furopyran scaffolds from propargyl vinyl ethers

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Economical synthesis and pathway economy.

Scheme 2: Au(I)-catalyzed cascade cyclization paths of 1,5-enynes.

Scheme 3: Au(I)-catalyzed cyclization paths of 1,7-enynes.

Scheme 4: I2/TBHP-mediated radical cycloisomerization paths of 1,n-enyne.

Scheme 5: Au(I)-catalyzed cycloisomerization paths of 3-allyloxy-1,6-diynes.

Scheme 6: Pd(II)-catalyzed cycloisomerization paths of 2-alkynylbenzoate-cyclohexadienone.

Scheme 7: Stereoselective cyclization of 1,5-enynes.

Scheme 8: Substituent-controlled cycloisomerization of propargyl vinyl ethers.

Scheme 9: Au(I)-catalyzed pathway-controlled domino cyclization of 1,2-diphenylethynes.

Scheme 10: Au(I)-catalyzed tandem cyclo-isomerization of tryptamine-N-ethynylpropiolamide.

Scheme 11: Au(I)-catalyzed tunable cyclization of 1,6-cyclohexenylalkyne.

Scheme 12: Substituent-controlled 7-exo- and 8-endo-dig-selective cyclization of 2-propargylaminobiphenyl deri...

Scheme 13: BiCl3-catalyzed cycloisomerization of tryptamine-ynamide derivatives.

Scheme 14: Au(I)-mediated substituent-controlled cycloisomerization of 1,6-enynes.

Scheme 15: Ligand-controlled regioselective cyclization of 1,6-enynes.

Scheme 16: Ligand-dependent cycloisomerization of 1,7-enyne esters.

Scheme 17: Ligand-controlled cycloisomerization of 1,5-enynes.

Scheme 18: Ligand-controlled cyclization strategy of alkynylamide tethered alkylidenecyclopropanes.

Scheme 19: Ag(I)-mediated pathway-controlled cycloisomerization of tryptamine-ynamides.

Scheme 20: Gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of indoles with alkynes.

Scheme 21: Catalyst-dependent cycloisomerization of dienol silyl ethers.

Scheme 22: Cycloisomerization of aromatic enynes governed by catalyst.

Scheme 23: Catalyst-dependent 1,2-migration in cyclization of 1-(indol-2-yl)-3-alkyn-1-ols.

Scheme 24: Gold-catalyzed cycloisomerization of N-propargyl-N-vinyl sulfonamides.

Scheme 25: Gold(I)-mediated enantioselective cycloisomerizations of ortho-(alkynyl)styrenes.

Scheme 26: Catalyst-controlled intramolecular cyclization of 1,7-enynes.

Scheme 27: Brønsted acid-catalyzed cycloisomerizations of tryptamine ynamides.

Scheme 28: Catalyst-controlled cyclization of indolyl homopropargyl amides.

Scheme 29: Angle strain-dominated 6-endo-trig cyclization of propargyl vinyl ethers.

Scheme 30: Angle strain-controlled cycloisomerization of alkyn-tethered indoles.

Scheme 31: Geometrical isomeration-dependent cycloisomerization of 1,3-dien-5-ynes.

Scheme 32: Temperature-controlled cyclization of 1,7-enynes.

Scheme 33: Cycloisomerizations of n-(o-ethynylaryl)acrylamides through temperature modulation.

Scheme 34: Temperature-controlled boracyclization of biphenyl-embedded 1,3,5-trien-7-ynes.
Asymmetric total synthesis of tricyclic prostaglandin D2 metabolite methyl ester via oxidative radical cyclization
- Miao Xiao,
- Liuyang Pu,
- Qiaoli Shang,
- Lei Zhu and
- Jun Huang
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1964–1972, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.152
- the total syntheses of PGs via organocatalysis, and enyne cycloisomerization, respectively. Thus, from a strategic viewpoint, developing alternative synthetic approaches for the stereoselective construction of the highly substituted cyclopentanol core framework in compound 4 may advance the efficient

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Representative prostaglandins and general synthetic strategy toward PGDM methyl ester 4.

Scheme 2: Retrosynthetic analysis for the first generation synthesis of PGDM methyl ester 4.

Scheme 3: Synthesis of bicyclic ketal 25.

Scheme 4: Retrosynthetic analysis for the second-generation synthesis of tricyclic PGDM methyl ester 4.

Scheme 5: Asymmetric total synthesis of tricyclic-PGDM methyl ester 4.
Enantioselective desymmetrization strategy of prochiral 1,3-diols in natural product synthesis
- Lihua Wei,
- Rui Yang,
- Zhifeng Shi and
- Zhiqiang Ma
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1932–1963, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.151
- 25 with vinyl butanoate and PPL delivered monoester 26 in 92% yield (99% ee). The axial chirality was transferred to the C7’ stereocenter through a Ag(I)-catalyzed cycloisomerization of the allenol, constructing the dihydrofuran ring. Lipase-catalyzed ester hydrolysis provided allylic alcohol 27

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: General mechanism of a lipase-catalyzed esterification.

Scheme 2: Shishido’s synthesis of (−)-xanthorrhizol (4) and (+)-heliannuol D (8).

Scheme 3: Shishido’s synthesis of a) (−)-heliannuol A (15) and b) heliannuol G (20) and heliannuol H (21).

Scheme 4: Deska’s synthesis of hyperione A (30) and ent-hyperione B (31).

Scheme 5: Huang’s synthesis of (+)-brazilin (37).

Scheme 6: Shishido’s synthesis of (−)-heliannuol D (42) and (+)-heliannuol A (43).

Scheme 7: Chênevert’s synthesis of (S)-α-tocotrienol (49).

Scheme 8: Kita’s synthesis of monoester 53.

Scheme 9: Kita’s synthesis of fredericamycin A (60).

Scheme 10: Takabe’s synthesis of (E)-3,7-dimethyl-2-octene-1,8-diol (64).

Scheme 11: Takabe’s synthesis of (18S)-variabilin (70).

Scheme 12: Kawasaki’s synthesis of (S)-Rosaphen (74) and (R)-Rosaphen (75).

Scheme 13: Tokuyama’s synthesis of a) (−)-petrosin (84) and b) (+)-petrosin (86).

Scheme 14: Fukuyama’s synthesis of leustroducsin B (96).

Scheme 15: Nanda’s synthesis of a) fragment 100, b) fragment 106 and c) (−)-rasfonin (109).

Scheme 16: Davies’ synthesis of (+)-pilocarpine (115) and (+)-isopilocarpine (116).

Scheme 17: Ōmura’s synthesis of salinosporamide A (125).

Scheme 18: Kang’s synthesis of ʟ-cladinose (124) and its derivative.

Scheme 19: Kang’s preparation of fragment 139.

Scheme 20: Kang’s synthesis of azithromycin (149).

Scheme 21: Kang’s synthesis of (−)-dysiherbaine (156).

Scheme 22: Kang’s synthesis of (−)-kaitocephalin (166).

Scheme 23: Kang’s synthesis of laidlomycin (180).

Scheme 24: Snyder’s synthesis of arboridinine (190).

Scheme 25: Ma’s synthesis of (+)-alstrostine G (203).

Scheme 26: Trost’s synthesis of (−)-18-epi-peloruside A (215).

Scheme 27: Lindel’s synthesis of (–)-dihydroraputindole (223).

Scheme 28: Iwata’s synthesis of a) (−)-talaromycin B (232) and b) (+)-talaromycin A (235).

Scheme 29: Cook’s synthesis of a) (−)-vincamajinine (240) and b) (−)-11-methoxy-17-epivincamajine (245).

Scheme 30: Cook’s synthesis of (+)-dehydrovoachalotine (249) and voachalotine (250).

Scheme 31: Cook’s synthesis of a) (−)-12-methoxy-Nb-methylvoachalotine (257) and b) (+)-polyneuridine, macusin...

Scheme 32: Trauner’s synthesis of stephadiamine (273).

Scheme 33: Garg’s synthesis of (–)-ψ-akuammigine (285).

Scheme 34: Ding’s synthesis of (+)-18-benzoyldavisinol (293) and (+)-davisinol (294).
Transition-state aromaticity and its relationship with reactivity in pericyclic reactions
- Israel Fernández
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 1613–1626, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.125
- corresponding transition states is comparable). Thermal cycloisomerization of 1,3-hexadien-5-ynes (Hopf cyclization) Since the original report by Hopf and Musso in 1969 [80], the thermal cycloisomerization reactions of 1,3-haxedien-5-ynes have been widely applied to the synthesis of aromatic six-membered rings
- cycloisomerization reaction of 1,3-hexadien-5-yne. 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions between t-BuN3 and cyaphide complexes. LA-catalyzed Diels–Alder reactions between isoprene and methyl acrylate. Computed free activation energies (ΔG≠, in kcal/mol), synchronicity (Sy), and NICS(3, +1) values in the corresponding

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: (a) Diels–Alder cycloaddition reaction between butadiene and ethylene. (b) Gold(I)-catalyzed propar...

Figure 1: Transition states computed for the Diels–Alder cycloaddition reaction between isoprene and methyl a...

Figure 2: Comparative activation strain analyses (a) and energy decomposition analysis (b) of the Diels–Alder...

Figure 3: (a) Evolution of the NICS(3, +1) values along a z-axis perpendicular to the molecular plane of the ...

Figure 4: Comparative activation strain analyses (a) and energy decomposition analysis (b) of the carbonyl–en...

Figure 5: AICD (a) and EDDB (b) plots for the transition state involved in the DGRT between ethene and ethane....

Figure 6: Comparative activation strain analyses (a) and energy decomposition analysis (b) of the DGRT betwee...

Scheme 2: Representative cycloisomerization reaction of 1,3-hexadien-5-yne.

Figure 7: AICD plots of the transition states associated with the Hopf cyclization reactions involving cis-he...

Figure 8: Comparative activation strain analyses of the Hopf cyclization involving ene–ene–ynes E=CH–CH=CH–C≡...

Scheme 3: 1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition reactions between t-BuN3 and cyaphide complexes.

Figure 9: Evolution of the NICS(3, +1) values along a z-axis perpendicular to the molecular plane of the TSs ...

Figure 10: Comparative activation strain analyses (a) and energy decomposition analysis (b) of the 1,3-dipolar...
Recent total synthesis of natural products leveraging a strategy of enamide cyclization
- Chun-Yu Mi,
- Jia-Yuan Zhai and
- Xiao-Ming Zhang
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 999–1009, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.81
- cyclization modes that provide entries to various N-heterocycles, some of which serve as key structural motifs in natural alkaloids. This review highlights recent advancements in enamide-based cyclization reactions, including enamide–alkyne cycloisomerization, [3 + 2] annulation, and polycyclization, with a
- have attracted considerable attention due to their promise in the total synthesis of alkaloids [16]. Notably, these valuable compounds can be employed as efficient synthons in enamide–alkyne cycloisomerization, [n + m] cycloadditions, pericyclic reactions, and radical cyclizations. A comprehensive
- review of these advancements up until 2015 has already been documented [16]. In this review, recent breakthroughs of these enamide cyclizations will be surveyed from the viewpoint of natural product synthesis. Leveraging the enamide–alkyne cycloisomerization cyclizations, Lycopodium alkaloids

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Reactivity of enamides and enamide cyclizations.

Scheme 1: Total synthesis of (−)-dihydrolycopodine and (−)-lycopodine.

Scheme 2: Collective total synthesis of fawcettimine-type alkaloids.

Scheme 3: Total syntheses of cephalotaxine and cephalezomine H.

Scheme 4: Collective total syntheses of Cephalotaxus alkaloids.

Scheme 5: Asymmetric tandem cyclization/Pictet–Spengler reaction of tertiary enamides.

Scheme 6: Tandem cyclization/Pictet–Spengler reaction for the synthesis of chiral tetracyclic compounds.

Scheme 7: Total synthesis of (−)-cephalocyclidin A.
Formaldehyde surrogates in multicomponent reactions
- Cecilia I. Attorresi,
- Javier A. Ramírez and
- Bernhard Westermann
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2025, 21, 564–595, doi:10.3762/bjoc.21.45
- ). The alkyne reacts with the in situ-generated carbanion through a 5-endo-dig-cycloisomerization process to yield a nitrogen-containing five-membered heterocycle (Scheme 44). Examples in which the propargyl group is incorporated into the amine [106] or the carboxylic acid components [107] are known

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Features of the ideal reaction (redrawn from P. A. Wender et al. [1]).

Scheme 2: Some of the most popular MCRs with formaldehyde as the carbonyl component.

Scheme 3: Ugi reaction under a catalyzed electro-oxidation process using TEMPO (2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperid...

Scheme 4: Examples of different products obtained by MCRs in which DMSO serves as -SCH3 source.

Scheme 5: Mechanism of the decomposition of DMSO under acidic or thermal conditions. a) In situ generation of...

Scheme 6: Povarov multicomponent reaction to quinolines.

Scheme 7: Example of the Povarov reaction with formaldehyde with a julolidine derivative as main product.

Scheme 8: Povarov multicomponent reaction to quinoline derivatives I and II using DMSO as formaldehyde surrog...

Scheme 9: Example of a Povarov three-component reaction with change of catalyst, yielding regioisomer III. In...

Scheme 10: The Povarov three-component reactions carried out under acidic catalysis to afford quinoline regios...

Scheme 11: Different MCR routes involving DMSO to synthesize complex heterocycles such as diarylpyridines and ...

Scheme 12: Pyrazole synthesis by a three-component reaction using DMSO as a source of a C-1 unit.

Scheme 13: Three-component reactions for the synthesis of aliphatic heterocycles 13 and 14 using DMSO as a for...

Scheme 14: Proposed mechanism for the 3CR between homoallylic amines, disulfides, and DMSO.

Scheme 15: Mannich-type reaction using DMSO as formaldehyde surrogate.

Scheme 16: Mechanism for the 3CR-Mannich-type reaction between aryl ketone 18, saccharine (19), and DMSO. The ...

Scheme 17: Mannich-type reaction using DMSO as formaldehyde surrogate and under oxidative activation.

Scheme 18: Three-component reaction between an indazole, a carboxylic acid, and DMSO.

Scheme 19: Amine–aldehyde–alkyne (AAA) coupling reaction and plausible mechanism.

Scheme 20: AHA coupling for the synthesis of propargylamines using dihalomethanes as C1 building blocks.

Scheme 21: AHA coupling using CH2Cl2 as both solvent and methylene source.

Scheme 22: Examples of propargylamines synthesized under catalytic AHA protocols.

Scheme 23: Proposed mechanism for the synthesis of propargylamines using dichloromethane as a C1 source.

Scheme 24: Mechanism proposed for the generation of the aminal intermediate E by Buckley et al. [68].

Scheme 25: Pudovic and Kabachnik–Fields reactions for the synthesis of α-aminophosphonates.

Scheme 26: a) Abramov side reaction that generates α-hydroxy phosphonate as a byproduct during the Kabachnik-F...

Scheme 27: Catalyst-free three component reaction to afford α-amino phosphorus product 35 using 1,1-dihaloalka...

Scheme 28: a) Proposed mechanism for the three-component reaction of dichloromethane, amine and phosphorus com...

Scheme 29: Ugi-ammonia strategy using HMTA as a formaldehyde surrogate.

Scheme 30: Glyoxylate and its derivatives as C1 building blocks.

Scheme 31: The Groebke–Blackburn–Bienaymé multicomponent reaction (GBB) and its mechanism.

Scheme 32: a) Byproducts in the GBB multicomponent reaction (GBB) when formaldehyde is used as the carbonyl co...

Scheme 33: Possible regioisomers in the GBB multicomponent reaction when formaldehyde is used as the carbonyl ...

Scheme 34: The multicomponent GBB reaction yields 2-unsubstituted 3-aminoimidazo heterocycles 42a using MP-gly...

Scheme 35: GBB multicomponent reaction to 2-unsubstituted 3-amino imidazo heterocycles 42a using glyoxylic aci...

Scheme 36: GBB reaction using glyoxylic acid immobilized on silica as formaldehyde surrogate.

Scheme 37: Bioactive products synthesized by the GBB reaction using glyoxylic acid.

Scheme 38: van Leusen three-component reaction to imidazoles.

Scheme 39: Side reaction during the synthesis of imidazoles with formaldehyde as the carbonyl compound.

Scheme 40: Optimization of the van Leusen three component reaction to 1,4-disubstituted imidazoles 43 using gl...

Scheme 41: Application of the Sisko strategy [96] for the synthesis of CB1 receptor antagonist compounds [97].

Scheme 42: Side reaction, when NH4OH is used as amine component.

Scheme 43: Ugi-type adducts with the ester moiety and the acidic CH to be used for post-cyclization sequences.

Scheme 44: Ugi/cycloisomerization process to pyrrolones 51, butenolides 52, and pyrroline 53.

Scheme 45: Radical cyclization reactions from Ugi adducts promoted by TEMPO.

Scheme 46: Hydrolysis and decarboxylation reactions to products with incorporation of a C1 unit of ethyl glyox...

Scheme 47: One-step synthetic route to pyrrolones 60 using phenylglyoxal.

Scheme 48: Ugi-pseudo-Knoevenagel-pseudo-Dieckmann cascade sequence for the synthesis of fused heterocycles.

Scheme 49: Ugi-pseudo-Knoevenagel reaction from ethyl glyoxylate.
Solvent-dependent chemoselective synthesis of different isoquinolinones mediated by the hypervalent iodine(III) reagent PISA
- Ze-Nan Hu,
- Yan-Hui Wang,
- Jia-Bing Wu,
- Ze Chen,
- Dou Hong and
- Chi Zhang
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 1914–1921, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.167
- ) diacetate (PIDA) [22][23]. And more recently, Du and our group have developed a method for the chemoselective cycloisomerization of o-alkenylbenzamides to 3-arylisoquinolinones, using PhIO as oxidant in combination with a catalytic amount of trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate [24]. Although
- , isopropyl, cyclopropyl, phenyl, or hydrogen, respectively, the intramolecular amination smoothly gave the corresponding 4-substituted isoquinolinone products 2b,c,d–f in 51–94% yield. Notably, when 1c was used as the substrate, the cycloisomerization product 2c' was observed in 31% yield besides 2c in 51

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Selected natural products, pharmaceuticals, and biologically active compounds having an isoquinolin...

Scheme 1: Chemoselective and PISA-mediated, solvent-controlled synthesis of different isoquinolinone derivati...

Scheme 2: Substrate scope for the synthesis of 4-substituted isoquinolinones 2. Reaction conditions: 1 (0.3 m...

Scheme 3: Optimal reaction conditions for the synthesis of 3-substituted isoquinolinone 3a.

Scheme 4: Substrate scope for the synthesis of 3-substituted isoquinolinones 3. Reaction conditions: 1 (0.3 m...

Scheme 5: Control experiment to test for radical intermediates.

Scheme 6: Proposed mechanism for the reaction between 1a and PISA in anhydrous acetonitrile.

Scheme 7: Two other resonance structures of the intermediate 1CC.

Scheme 8: Proposed mechanism for the reaction between 1a and PISA in wet HFIP.
One-pot Ugi-azide and Heck reactions for the synthesis of heterocyclic systems containing tetrazole and 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline
- Jiawei Niu,
- Yuhui Wang,
- Shenghu Yan,
- Yue Zhang,
- Xiaoming Ma,
- Qiang Zhang and
- Wei Zhang
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 912–920, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.81
- oxidative cycloisomerization reactions for the synthesis of 2-tetrazolyl-substituted 3-acylpyrroles (Scheme 2C) [42]. The Ding group also reported sequential Ugi-azide/Staudinger/aza-Wittig/addition/Ag-catalyzed cyclization reactions for obtaining 12-tetrazolyl-substituted (E)-5H-quinazolino[3,2-a

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Representative bioactive tetrazole- and tetrahydroisoquinoline-containing compounds.

Scheme 1: The Ugi and Ugi-azide reactions.

Scheme 2: Ugi-azide and post-condensation reactions for the synthesis of various heterocyclic scaffolds.

Scheme 3: One-pot synthesis of tetrazolyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline.

Scheme 4: One-pot synthesis of tetrazolo-pyrazino[2,1-a]isoquinolin-6(5H)-ones 6.

Scheme 5: One-pot synthesis for tetrazolyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolines 8.

Scheme 6: Gram-scale two-step one-pot synthesis of 6c.

Figure 2: ORTEP diagrams of compound 6d (left) [CCDC: 2164364] and 8c (right) [CCDC: 2321622].
Synthetic study toward tridachiapyrone B
- Morgan Cormier,
- Florian Hernvann and
- Michaël De Paolis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1741–1748, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.183
- electrocyclization of compounds 1a and b [19][20][21][22]. Interestingly, Baldwin and Moses demonstrated the irradiation or sunlight-promoted cycloisomerization of a similar tetraenyl framework into the bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane core through a 6π-conrotatory stereocontrol [23][24]. To date, the known strategies to

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Routes to crispatene, photodeoxytridachione, aureothin, and tridachiapyrone B.

Scheme 2: Desymmetrization of 2.

Scheme 3: Addition of lithiocyclopentadiene to pyrone 2.

Scheme 4: Plan to reach 2,5-cyclohexadienone 5.

Scheme 5: Preparation of 2,5-cyclohexadienone 5.

Scheme 6: Attempts to perform the conjugate addition.

Scheme 7: Updated route to tridachiapyrone B.
Formal total synthesis of macarpine via a Au(I)-catalyzed 6-endo-dig cycloisomerization strategy
- Jiayue Fu,
- Bingbing Li,
- Zefang Zhou,
- Maosheng Cheng,
- Lu Yang and
- Yongxiang Liu
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1589–1595, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.169
- total synthesis of macarpine [12] is proposed via a Au(I)-catalyzed cycloisomerization reaction. Retrosynthetically, the target molecule macarpine (1) could be disconnected into naphthol 12 (Scheme 3), a key intermediate reported by Ishikawa in the total synthesis of macarpine. This intermediate could
- be synthesized from silyl enol ether compound 10 via the Au(I)-catalyzed cycloisomerization reaction developed by our group [15]. The compound 10 could be constructed by the Sonogashira coupling reaction from readily prepared iodoarene 8 [12][16] and ketone 5, which could be synthesized by using
- building blocks 5 and 8 in hand, ketone 9 was prepared via a palladium-catalyzed Sonogashira coupling reaction in a yield of 95%. The precursor 10 for the gold(I)-catalyzed [19][20][21][22][23][24] cycloisomerization was then synthesized by treating ketone 9 with sodium bis(trimethylsilyl)amide (NaHMDS

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Classification of benzo[c]phenanthridine alkaloids.

Scheme 2: Representative synthetic strategies for macarpine (1).

Scheme 3: Retrosynthetic analysis of marcarpine precursor 12 for a partial synthesis.

Scheme 4: Syntheses of precursors 5 and 8.

Scheme 5: Synthesis of enol silyl ether 10.

Scheme 6: Formal total synthesis of macarpine (1).
Supramolecular approaches to mediate chemical reactivity
- Pablo Ballester,
- Qi-Qiang Wang and
- Carmine Gaeta
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1463–1465, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.152

- whose geometry, in low-polarity solvents, is controlled by the 1,2,3-alternate conformation of the calix[6]arene skeleton. These catalysts can tune the selectivity of the catalytic cycloisomerization of 1,6-enynes in response to the relative orientation of the coordinated gold(I) atom with respect to
Vicinal ketoesters – key intermediates in the total synthesis of natural products
- Marc Paul Beller and
- Ulrich Koert
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1236–1248, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.129
- cycloisomerization of the α-ketoester 22, which can be described as a Friedel–Crafts-type reaction or an aldol reaction of an S,O-ketene acetal (Scheme 4). The required ketoester 22 was synthesized from sulfonylchromenone 20, accessible from dihydroxyacetophenone 19 and thiol 18 derived from known alcohol 17 [11][12
- ]. DMP oxidation of α-hydroxyester 21 and subsequent cycloisomerization led to the desired cyclization product 23 via transition state II in a dr of 5:1. Final deprotection gave preussochromone A (24). (−)-Preussochromone D A similar approach was chosen in the synthesis of the structurally related
- -diketoester. Synthesis of euphorikanin A (16) by intramolecular, nucleophilic addition [6]. Ketoester cycloisomerization for the synthesis of preussochromone A (24) [10]. Diastereoselective, intramolecular aldol reaction of an α-ketoester 28 in the synthesis of (−)-preussochromone D (30) [13][14]. Synthesis

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Structures of vicinal ketoesters and examples for their typical reactivity.

Scheme 2: Doyle’s diastereoselective intramolecular aldol addition of α,β-diketoester.

Scheme 3: Synthesis of euphorikanin A (16) by intramolecular, nucleophilic addition [6].

Scheme 4: Ketoester cycloisomerization for the synthesis of preussochromone A (24) [10].

Scheme 5: Diastereoselective, intramolecular aldol reaction of an α-ketoester 28 in the synthesis of (−)-preu...

Scheme 6: Synthesis of an α-ketoester through Riley oxidation and its use in an α-ketol rearrangement in the ...

Scheme 7: Azomethine imine cycloaddition towards the synthesis of the proposed structure of palau’amine (44) [19]....

Scheme 8: Intramolecular diastereoselective carbonyl-ene reaction of an α-ketoester in the synthesis of jatro...

Scheme 9: Grignard addition to an α-ketoester and subsequent Friedel–Crafts cyclization in the synthesis of (...

Scheme 10: Diastereoselective addition to an auxiliary modified α-ketoester in the formal synthesis of (+)-cam...

Scheme 11: Intramolecular photoreduction of an α-ketoester in the synthesis of (rac)-isoretronecanol (69) [26].

Scheme 12: α-Ketoester as nucleophile in a Tsuji–Trost reaction in the synthesis of (rac)-corynoxine (76) [27].

Scheme 13: Mannich reaction of an α-ketoester in the synthesis of (+)-gracilamine (83) [28].

Scheme 14: Enantioselective aldol reaction using an α-ketoester in the synthesis of (−)-irofulven (87) [29].

Scheme 15: Allylboration of a mesoxalic acid ester in the synthesis of (+)-awajanomycin (92) [30,31].

Scheme 16: Condensation of a diamine with mesoxolate in the synthesis of (−)-aplaminal (96) [32].

Scheme 17: Synthesis of mesoxalic ester amide 102 and its use in the synthesis of (rac)-cladoniamide G (103) [33].

Scheme 18: The thermodynamically controlled, intramolecular aldol addition of a vic-tricarbonyl compound in th...
Diametric calix[6]arene-based phosphine gold(I) cavitands
- Gabriele Giovanardi,
- Andrea Secchi,
- Arturo Arduini and
- Gianpiero Cera
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 190–196, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.21
- polarity solvents, of a novel class of diametric phosphine gold(I) cavitands characterized by a 1,2,3-alternate geometry. Preliminary catalytic studies were performed on a model cycloisomerization of 1,6-enynes as a function of the relative orientation of the bonded gold(I) nuclei with respect to the
- catalytic activity was demonstrated in promoting gold(I)-catalyzed cycloisomerization of 1,6-enynes, with ample scope and high regioselectivity. However, preliminary studies suggested that the catalytic event occurs outside the macrocyclic cavity. In order to get more insights on the role of the cavity to
- in controlling the reactivity of gold(I)-catalyzed transformations by means of supramolecular macrocycles, we choose a cycloisomerization of 1,6-enynes as a model reaction [36]. Substrate 1a was reacted in the presence of monomeric gold(I) catalyst A’(AuCl) (2 mol %), using AgSbF6 as the chloride

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Selected examples of: a) calix[4]arene-; b) resorcin[4]arene-; c) calix[6]arene-gold(I) macrocyclic...

Scheme 1: i) NH2NH2∙H2O, Pd/C in EtOH, 80 °C (quant.); ii) diphenylphosphinobenzoic acid, EDC∙HCl, DMAP (cat....

Figure 2: Stacked-plot, mid-field expanded region of the 1H NMR spectrum (400 MHz, 298 K) of A(AuCl)2, B(AuCl)...

Figure 3: Stacked plot 1H NMR (tetrachloroethane-d2) of A(AuCl)2 at variable temperature.

Scheme 2: Synthesis of the monomeric gold catalyst analogues A’,B’,C’(AuCl). Conditions: i) diphenylphosphino...
Iron-catalyzed domino coupling reactions of π-systems
- Austin Pounder and
- William Tam
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2848–2893, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.196

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Price comparison among iron and other transition metals used in catalysis.

Scheme 1: Typical modes of C–C bond formation.

Scheme 2: The components of an iron-catalyzed domino reaction.

Scheme 3: Iron-catalyzed tandem cyclization and cross-coupling reactions of iodoalkanes 1 with aryl Grignard ...

Scheme 4: Three component iron-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of vinyl cyclopropanes 14.

Scheme 5: Three-component iron-catalyzed dicarbofunctionalization of alkenes 21.

Scheme 6: Double carbomagnesiation of internal alkynes 31 with alkyl Grignard reagents 32.

Scheme 7: Iron-catalyzed cycloisomerization/cross-coupling of enyne derivatives 35 with alkyl Grignard reagen...

Scheme 8: Iron-catalyzed spirocyclization/cross-coupling cascade.

Scheme 9: Iron-catalyzed alkenylboration of alkenes 50.

Scheme 10: N-Alkyl–N-aryl acrylamide 60 CDC cyclization with C(sp3)–H bonds adjacent to a heteroatom.

Scheme 11: 1,2-Carboacylation of activated alkenes 60 with aldehydes 65 and alcohols 67.

Scheme 12: Iron-catalyzed dicarbonylation of activated alkenes 68 with alcohols 67.

Scheme 13: Iron-catalyzed cyanoalkylation/radical dearomatization of acrylamides 75.

Scheme 14: Synergistic photoredox/iron-catalyzed 1,2-dialkylation of alkenes 82 with common alkanes 83 and 1,3...

Scheme 15: Iron-catalyzed oxidative coupling/cyclization of phenol derivatives 86 and alkenes 87.

Scheme 16: Iron-catalyzed carbosulfonylation of activated alkenes 60.

Scheme 17: Iron-catalyzed oxidative spirocyclization of N-arylpropiolamides 91 with silanes 92 and tert-butyl ...

Scheme 18: Iron-catalyzed free radical cascade difunctionalization of unsaturated benzamides 94 with silanes 92...

Scheme 19: Iron-catalyzed cyclization of olefinic dicarbonyl compounds 97 and 100 with C(sp3)–H bonds.

Scheme 20: Radical difunctionalization of o-vinylanilides 102 with ketones and esters 103.

Scheme 21: Dehydrogenative 1,2-carboamination of alkenes 82 with alkyl nitriles 76 and amines 105.

Scheme 22: Iron-catalyzed intermolecular 1,2-difunctionalization of conjugated alkenes 107 with silanes 92 and...

Scheme 23: Four-component radical difunctionalization of chemically distinct alkenes 114/115 with aldehydes 65...

Scheme 24: Iron-catalyzed carbocarbonylation of activated alkenes 60 with carbazates 117.

Scheme 25: Iron-catalyzed radical 6-endo cyclization of dienes 119 with carbazates 117.

Scheme 26: Iron-catalyzed decarboxylative synthesis of functionalized oxindoles 130 with tert-butyl peresters ...

Scheme 27: Iron‑catalyzed decarboxylative alkylation/cyclization of cinnamamides 131/134.

Scheme 28: Iron-catalyzed carbochloromethylation of activated alkenes 60.

Scheme 29: Iron-catalyzed trifluoromethylation of dienes 142.

Scheme 30: Iron-catalyzed, silver-mediated arylalkylation of conjugated alkenes 115.

Scheme 31: Iron-catalyzed three-component carboazidation of conjugated alkenes 115 with alkanes 101/139b and t...

Scheme 32: Iron-catalyzed carboazidation of alkenes 82 and alkynes 160 with iodoalkanes 20 and trimethylsilyl ...

Scheme 33: Iron-catalyzed asymmetric carboazidation of styrene derivatives 115.

Scheme 34: Iron-catalyzed carboamination of conjugated alkenes 115 with alkyl diacyl peroxides 163 and acetoni...

Scheme 35: Iron-catalyzed carboamination using oxime esters 165 and arenes 166.

Scheme 36: Iron-catalyzed iminyl radical-triggered [5 + 2] and [5 + 1] annulation reactions with oxime esters ...

Scheme 37: Iron-catalyzed decarboxylative alkyl etherification of alkenes 108 with alcohols 67 and aliphatic a...

Scheme 38: Iron-catalyzed inter-/intramolecular alkylative cyclization of carboxylic acid and alcohol-tethered...

Scheme 39: Iron-catalyzed intermolecular trifluoromethyl-acyloxylation of styrene derivatives 115.

Scheme 40: Iron-catalyzed carboiodination of terminal alkenes and alkynes 180.

Scheme 41: Copper/iron-cocatalyzed cascade perfluoroalkylation/cyclization of 1,6-enynes 183/185.

Scheme 42: Iron-catalyzed stereoselective carbosilylation of internal alkynes 187.

Scheme 43: Synergistic photoredox/iron catalyzed difluoroalkylation–thiolation of alkenes 82.

Scheme 44: Iron-catalyzed three-component aminoazidation of alkenes 82.

Scheme 45: Iron-catalyzed intra-/intermolecular aminoazidation of alkenes 194.

Scheme 46: Stereoselective iron-catalyzed oxyazidation of enamides 196 using hypervalent iodine reagents 197.

Scheme 47: Iron-catalyzed aminooxygenation for the synthesis of unprotected amino alcohols 200.

Scheme 48: Iron-catalyzed intramolecular aminofluorination of alkenes 209.

Scheme 49: Iron-catalyzed intramolecular aminochlorination and aminobromination of alkenes 209.

Scheme 50: Iron-catalyzed intermolecular aminofluorination of alkenes 82.

Scheme 51: Iron-catalyzed aminochlorination of alkenes 82.

Scheme 52: Iron-catalyzed phosphinoylazidation of alkenes 108.

Scheme 53: Synergistic photoredox/iron-catalyzed three-component aminoselenation of trisubstituted alkenes 82.
Recent advances in the tandem annulation of 1,3-enynes to functionalized pyridine and pyrrole derivatives
- Yi Liu,
- Puying Luo,
- Yang Fu,
- Tianxin Hao,
- Xuan Liu,
- Qiuping Ding and
- Yiyuan Peng
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2462–2476, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.163
- release of a nitrogen molecule to form the desired product 46. In 2018, Ding and co-workers reported the synthesis of 2-tetrazolyl-substituted 3-acylpyrroles 53 via sequential Ugi-azide/Ag-catalyzed oxidative cycloisomerization reactions in good yield (Scheme 20) [64]. Firstly, The Ugi-azide reaction

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Ag/I2-mediated electrophilic annulation of 2-en-4-ynyl azides 1.

Scheme 2: The proposed mechanism of Ag-catalyzed aza-annulation.

Scheme 3: The proposed mechanism of I2-mediated aza-annulation.

Scheme 4: Copper-catalyzed amination of (E)-2-en-4-ynyl azides 1.

Scheme 5: The proposed mechanism of copper-catalyzed amination.

Scheme 6: The derivatization of sulfonated aminonicotinates.

Scheme 7: Copper-catalyzed chalcogenoamination of (E)-2-en-4-ynyl azides 1.

Scheme 8: The possible mechanism of chalcogenoamination.

Scheme 9: The derivatization of 5‑selenyl- and 5-sulfenyl-substituted nicotinates.

Scheme 10: The tandem reaction of nitriles, Reformatsky reagents, and 1,3-enynes.

Scheme 11: Nickel-catalyzed [4 + 2]-cycloaddition of 3-azetidinones with 1,3-enynes.

Scheme 12: Electrophilic iodocyclization of 2-nitro-1,3-enynes to pyrroles.

Scheme 13: Electrophilic halogenation of 2-trifluoromethyl-1,3-enynes to pyrroles.

Scheme 14: Copper-catalyzed cascade cyclization of 2-nitro-1,3-enynes with amines.

Scheme 15: Tandem cyclization of 2-nitro-1,3-enynes, Togni reagent II, and amines.

Scheme 16: Tandem cyclization of 2-nitro-1,3-enynes, TMSN3, and amines.

Scheme 17: Cascade cyclization of 6-hydroxyhex-2-en-4-ynals to pyrroles.

Scheme 18: Au/Ag-catalyzed oxidative aza-annulation of 1,3-enynyl azides.

Scheme 19: The plausible mechanism of Au/Ag-catalyzed oxidative aza-annulation.

Scheme 20: Synthesis of 2-tetrazolyl-substituted 3-acylpyrroles from enynals.

Scheme 21: CuH-catalyzed coupling reaction of 1,3-enynes and nitriles to pyrroles.

Scheme 22: The mechanism of CuH-catalyzed coupling of 1,3-enynes and nitriles to pyrroles.
Advances in mercury(II)-salt-mediated cyclization reactions of unsaturated bonds
- Sumana Mandal,
- Raju D. Chaudhari and
- Goutam Biswas
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2348–2376, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.153

- temperature. It was an example of cycloisomerization of 2-ethynylaniline derivatives utilizing mild reaction conditions (Scheme 50) [110]. Rong et al. had demonstrated the Hg(II)-salt-catalyzed enolate umpolung reaction for the efficient synthesis of various 3-indolinones and 3-coumaranones 174. They had
- difficult for organic chemists. Morimoto and co-workers were the first to disclose the Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed cycloisomerization of amino ynone to produce the azaspiro skeleton. Later, this methodology was successfully used for the synthesis of several spiroskeleton structures. Natural products such as
- -methylenepiperidine. a) Preparation of indole derivatives through cycloisomerization of 2-ethynylaniline and b) its mechanism. a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed synthesis of 3-indolinones and 3-coumaranones and b) simplified mechanism. a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed one pot cyclization of nitroalkyne and b) its plausible mechanism

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Schematic representation of Hg(II)-mediated addition to an unsaturated bond.

Scheme 2: First report of Hg(II)-mediated synthesis of 2,5-dioxane derivatives from allyl alcohol.

Scheme 3: Stepwise synthesis of 2,6-distubstituted dioxane derivatives.

Scheme 4: Cyclization of carbohydrate alkene precursor.

Scheme 5: Hg(II)-mediated synthesis of C-glucopyranosyl derivatives.

Scheme 6: Synthesis of C-glycosyl amino acid derivative using Hg(TFA)2.

Scheme 7: Hg(OAc)2-mediated synthesis of α-ᴅ-ribose derivative.

Scheme 8: Synthesis of β-ᴅ-arabinose derivative 18.

Scheme 9: Hg(OAc)2-mediated synthesis of tetrahydrofuran derivatives.

Scheme 10: Synthesis of Hg(TFA)2-mediated bicyclic nucleoside derivative.

Scheme 11: Synthesis of pyrrolidine and piperidine derivatives.

Scheme 12: HgCl2-mediated synthesis of diastereomeric pyrrolidine derivatives.

Scheme 13: HgCl2-mediated cyclization of alkenyl α-aminophosphonates.

Scheme 14: Cyclization of 4-cycloocten-1-ol with Hg(OAc)2 forming fused bicyclic products.

Scheme 15: trans-Amino alcohol formation through Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization.

Scheme 16: Hg(OAc)2-mediated 2-aza- or 2-oxa-bicyclic ring formations.

Scheme 17: Hg(II)-salt-induced cyclic peroxide formation.

Scheme 18: Hg(OAc)2-mediated formation of 1,2,4-trioxanes.

Scheme 19: Endocyclic enol ether derivative formation through Hg(II) salts.

Scheme 20: Synthesis of optically active cyclic alanine derivatives.

Scheme 21: Hg(II)-salt-mediated formation of tetrahydropyrimidin-4(1H)-one derivatives.

Scheme 22: Cyclization of ether derivatives to form stereoselective oxazolidine derivatives.

Scheme 23: Cyclization of amide derivatives induced by Hg(OAc)2.

Scheme 24: Hg(OAc)2/Hg(TFA)2-promoted cyclization of salicylamide-derived amidal auxiliary derivatives.

Scheme 25: Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization to form dihydrobenzopyrans.

Scheme 26: HgCl2-induced cyclization of acetylenic silyl enol ether derivatives.

Scheme 27: Synthesis of exocyclic and endocyclic enol ether derivatives.

Scheme 28: Cyclization of trans-acetylenic alcohol by treatment with HgCl2.

Scheme 29: Synthesis of benzofuran derivatives in presence of HgCl2.

Scheme 30: a) Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization of 4-hydroxy-2-alkyn-1-ones to furan derivatives and b) its mec...

Scheme 31: Cyclization of arylacetylenes to synthesize carbocyclic and heterocyclic derivatives.

Scheme 32: Hg(II)-salt-promoted cyclization–rearrangement to form heterocyclic compounds.

Scheme 33: a) HgCl2-mediated cyclization reaction of tethered alkyne dithioacetals; and b) proposed mechanism.

Scheme 34: Cyclization of aryl allenic ethers on treatment with Hg(OTf)2.

Scheme 35: Hg(TFA)2-mediated cyclization of allene.

Scheme 36: Hg(II)-catalyzed intramolecular trans-etherification reaction of 2-hydroxy-1-(γ-methoxyallyl)tetrah...

Scheme 37: a) Cyclization of alkene derivatives by catalytic Hg(OTf)2 salts and b) mechanism of cyclization.

Scheme 38: a) Synthesis of 1,4-dihydroquinoline derivatives by Hg(OTf)2 and b) plausible mechanism of formatio...

Scheme 39: Synthesis of Hg(II)-salt-catalyzed heteroaromatic derivatives.

Scheme 40: Hg(II)-salt-catalyzed synthesis of dihydropyranone derivatives.

Scheme 41: Hg(II)-salt-catalyzed cyclization of alkynoic acids.

Scheme 42: Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization of alkyne carboxylic acids and alcohol to furan, pyran, and spiroc...

Scheme 43: Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization of 1,4-dihydroxy-5-alkyne derivatives.

Scheme 44: Six-membered morpholine derivative formation by catalytic Hg(II)-salt-induced cyclization.

Scheme 45: Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed hydroxylative carbocyclization of 1,6-enyne.

Scheme 46: a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed hydroxylative carbocyclization of 1,6-enyne. b) Proposed mechanism.

Scheme 47: a) Synthesis of carbocyclic derivatives using a catalytic amount of Hg(II) salt. b) Proposed mechan...

Scheme 48: Cyclization of 1-alkyn-5-ones to 2-methylfuran derivatives.

Scheme 49: Hg(NO3)2-catalyzed synthesis of 2-methylenepiperidine.

Scheme 50: a) Preparation of indole derivatives through cycloisomerization of 2-ethynylaniline and b) its mech...

Scheme 51: a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed synthesis of 3-indolinones and 3-coumaranones and b) simplified mechanism.

Scheme 52: a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed one pot cyclization of nitroalkyne and b) its plausible mechanism.

Scheme 53: Synthesis of tricyclic heterocyclic scaffolds.

Scheme 54: HgCl2-mediated cyclization of 2-alkynylphenyl alkyl sulfoxide.

Scheme 55: a) Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed cyclization of allenes and alkynes. b) Proposed mechanism of cyclization.

Scheme 56: Stereoselective synthesis of tetrahydropyran derivatives.

Scheme 57: a) Hg(ClO4)2-catalyzed cyclization of α-allenol derivatives. b) Simplified mechanism.

Scheme 58: Hg(TFA)2-promoted cyclization of a γ-hydroxy alkene derivative.

Scheme 59: Synthesis Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclization of allyl alcohol for the construction of ventiloquinone ...

Scheme 60: Hg(OAc)2-mediated cyclization as a key step for the synthesis of hongconin.

Scheme 61: Examples of Hg(II)-salt-mediated cyclized ring formation in the syntheses of (±)-fastigilin C and (...

Scheme 62: Formal synthesis of (±)-thallusin.

Scheme 63: Total synthesis of hippuristanol and its analog.

Scheme 64: Total synthesis of solanoeclepin A.

Scheme 65: a) Synthesis of Hg(OTf)2-catalyzed azaspiro structure for the formation of natural products. b) Pro...
Methodologies for the synthesis of quaternary carbon centers via hydroalkylation of unactivated olefins: twenty years of advances
- Thiago S. Silva and
- Fernando Coelho
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1565–1590, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.112
- cycloisomerization of diolefins triggered by the MHAT process. Some challenges associated with the development of these reactions were the reversible nature of the HAT and the competition with linear isomerization and reductive pathways (Scheme 18) [72][73]. In 2014, the Shenvi group developed an olefin
- of this kind of reaction is the catalytic use of the hydride donor, in this case phenylsilane (PhSiH3), due to the regeneration of the active metal hydride species in the cycloisomerization mechanism pathway (Scheme 18). The lower cyclization constant for the six-membered ring formation, in

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Some examples of natural products and drugs containing quaternary carbon centers.

Scheme 1: Simplified mechanism for olefin hydrofunctionalization using an electrophilic transition metal as a...

Scheme 2: Selected examples of quaternary carbon centers formed by the intramolecular hydroalkylation of β-di...

Scheme 3: Control experiments and the proposed mechanism for the Pd(II)-catalyzed intermolecular hydroalkylat...

Scheme 4: Intermolecular olefin hydroalkylation of less reactive ketones under Pd(II) catalysis using HCl as ...

Scheme 5: A) Selected examples of Pd(II)-mediated quaternary carbon center synthesis by intermolecular hydroa...

Scheme 6: Selected examples of quaternary carbon center synthesis by gold(III) catalysis. This is the first r...

Scheme 7: Selected examples of inter- (A) and intramolecular (B) olefin hydroalkylations promoted by a silver...

Scheme 8: A) Intermolecular hydroalkylation of N-alkenyl β-ketoamides under Au(I) catalysis in the synthesis ...

Scheme 9: Asymmetric pyrrolidine synthesis through intramolecular hydroalkylation of α-substituted N-alkenyl ...

Scheme 10: Proposed mechanism for the chiral gold(I) complex promotion of the intermolecular olefin hydroalkyl...

Scheme 11: Selected examples of carbon quaternary center synthesis by gold and evidence of catalytic system pa...

Scheme 12: Synthesis of a spiro compound via an aza-Michael addition/olefin hydroalkylation cascade promoted b...

Scheme 13: A selected example of quaternary carbon center synthesis using an Fe(III) salt as a catalyst for th...

Scheme 14: Intermolecular hydroalkylation catalyzed by a cationic iridium complex (Fuji (2019) [47]).

Scheme 15: Generic example of an olefin hydrofunctionalization via MHAT (Shenvi (2016) [51]).

Scheme 16: The first examples of olefin hydrofunctionalization run under neutral conditions (Mukaiyama (1989) [56]...

Scheme 17: A) Aryl olefin dimerization catalyzed by vitamin B12 and triggered by HAT. B) Control experiment to...

Scheme 18: Generic example of MHAT diolefin cycloisomerization and possible competitive pathways. Shenvi (2014...

Scheme 19: Selected examples of the MHAT-promoted cycloisomerization reaction of unactivated olefins leading t...

Scheme 20: Regioselective carbocyclizations promoted by an MHAT process (Norton (2008) [76]).

Scheme 21: Selected examples of quaternary carbon centers synthetized via intra- (A) and intermolecular (B) MH...

Scheme 22: A) Proposed mechanism for the Fe(III)/PhSiH3-promoted radical conjugate addition between olefins an...

Scheme 23: Examples of cascade reactions triggered by HAT for the construction of trans-decalin backbone uniti...

Scheme 24: A) Selected examples of the MHAT-promoted radical conjugate addition between olefins and p-quinone ...

Scheme 25: A) MHAT triggered radical conjugate addition/E1cB/lactonization (in some cases) cascade between ole...

Scheme 26: A) Spirocyclization promoted by Fe(III) hydroalkylation of unactivated olefins. B) Simplified mecha...

Scheme 27: A) Selected examples of the construction of a carbon quaternary center by the MHAT-triggered radica...

Scheme 28: Hydromethylation of unactivated olefins under iron-mediated MHAT (Baran (2015) [95]).

Scheme 29: The hydroalkylation of unactivated olefins via iron-mediated reductive coupling with hydrazones (Br...

Scheme 30: Selected examples of the Co(II)-catalyzed bicyclization of dialkenylarenes through the olefin hydro...

Scheme 31: Proposed mechanism for the bicyclization of dialkenylarenes triggered by a MHAT process (Vanderwal ...

Scheme 32: Enantioconvergent cross-coupling between olefins and tertiary halides (Fu (2018) [108]).

Scheme 33: Proposed mechanism for the Ni-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between olefins and tertiary halide...

Scheme 34: Proposed catalytic cycles for a MHAT/Ni cross-coupling reaction between olefins and halides (Shenvi...

Scheme 35: Selected examples of the hydroalkylation of olefins by a dual catalytic Mn/Ni system (Shenvi (2019) ...

Scheme 36: A) Selected examples of quaternary carbon center synthesis by reductive atom transfer; TBC: 4-tert-...

Scheme 37: A) Selected examples of quaternary carbon centers synthetized by radical addition to unactivated ol...

Scheme 38: A) Selected examples of organophotocatalysis-mediated radical polyene cyclization via a PET process...

Scheme 39: A) Sc(OTf)3-mediated carbocyclization approach for the synthesis of vicinal quaternary carbon cente...

Scheme 40: Scope of the Lewis acid-catalyzed methallylation of electron-rich styrenes. Method A: B(C6F5)3 (5.0...

Scheme 41: The proposed mechanism for styrene methallylation (Oestreich (2019) [123]).
Synthesis of 1-indolyl-3,5,8-substituted γ-carbolines: one-pot solvent-free protocol and biological evaluation
- Premansh Dudhe,
- Mena Asha Krishnan,
- Kratika Yadav,
- Diptendu Roy,
- Krishnan Venkatasubbaiah,
- Biswarup Pathak and
- Venkatesh Chelvam
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1453–1463, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.101
- cycloisomerization/Pictet–Spengler cyclization of 2-(4-aminobut-1-yn-1-yl)aniline [16], the Ru and Rh-catalyzed [2 + 2 + 2] cycloadditions of yne-ynamides [17], and the Pd-catalyzed tandem coupling-cyclization [18] are significant works in the area (Scheme 1). However, the use of toxic and expensive metal catalysts

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Selected examples of compounds containing the γ-carboline core.

Scheme 1: The synthetic strategy of present work in comparison with previous reports.

Scheme 2: Series of synthesized 1-indolyl-3,5,8-substituted γ-carboline 3aa–ac, 3ba-ea and 1-indolyl-1,2-dihy...

Figure 2: Single-crystal XRD structure of 3ac (CCDC: 1897787).

Scheme 3: Plausible mechanism for the formation of 1,2-dihydro-γ-carboline derivative 3ga and 1-indolyl-3,5,8...

Figure 3: UV–vis absorption (left side) and emission (right side) spectra of 3ac measured in different solven...

Figure 4: Fluorescence decay profile of 3ac in DMSO (left side; λex 360 nm) and 10−5 M solutions of compound ...

Figure 5: Dose–response curves for (A) γ-carbolines 3ac, 3bc, 3ca, 3ga in the breast cancer cell line, MCF7 a...

Figure 6: Dose–response curve of γ-carbolines 3ac, 3bc, 3ca, 3ga in macrophage cell line, RAW264.7.

Figure 7: Laser scanning confocal microscopy studies (λex = 405 nm; collection range = 420–470 nm) for uptake...
Extension of the 5-alkynyluridine side chain via C–C-bond formation in modified organometallic nucleosides using the Nicholas reaction
- Renata Kaczmarek,
- Dariusz Korczyński,
- James R. Green and
- Roman Dembinski
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1–8, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.1
- only provide a biological impact but also create a synthetic handle for further functionalization/modification. Among others, alkynyl uridines undergo cycloisomerization to potent antiviral agents, furopyrimidines [13], related halofuropyrimidines [14], and can be converted into interstrand dimers [15
- , triethylamine, in DMF, and at room temperature – to avoid cycloisomerization to furopyrimidines (Scheme 1). The modified pyrimidine nucleoside scaffolds, propargyl acetate-substituted 2'-deoxyuridine (R = Ac, 2) and propargyl methyl ether-substituted uridine (R = Me, 3), were obtained in 87% and 61% yield

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Preparation of (2'-deoxy)-5-alkynyluridines 2 and 3, their dicobalt hexacarbonyl derivatives 4 and 5...

Figure 1: Structures of nucleosides 6 and 7, products of the Nicholas reaction.
Self-assembled coordination thioether silver(I) macrocyclic complexes for homogeneous catalysis
- Zhen Cao,
- Aline Lacoudre,
- Cybille Rossy and
- Brigitte Bibal
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2465–2472, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.239
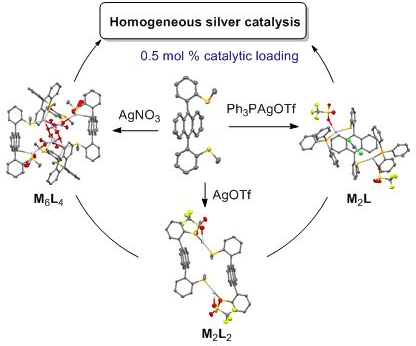
- of the two L2·(AgOTf)2 stereoisomers highlighted their different geometry. The catalytic activity of all silver(I) complexes was effective under homogeneous conditions in two tandem addition/cycloisomerization of alkynes using 0.5–1 mol % of catalytic loading. Keywords: coordination macrocycle
- candidates for directional metal coordination. Herein, a new syn-atropisomer of 9,10-DPA ortho-substituted by two thioethers is exploited as a ligand for silver(I) salts. The impact of this bis-thioether ligand on silver(I) homogeneous catalysis is evaluated in two tandem addition/cycloisomerization
- complexes 1a–d were evaluated as homogeneous catalysts in two tandem addition/cycloisomerization reactions using alkynes 2 and 3. 2-Alkynylbenzaldehyde 2 [58][59] was chosen as the first model substrate for a cyclization reaction in the presence of methanol as a second nucleophile. This tandem addition

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Synthesis of ligand 1, as its syn-atropisomer.

Figure 1: X-ray structures of complex 1a, as two diastereoisomeric macrocycles (R,S-1)2·(AgOTf)2 with ligands...

Figure 2: X-ray structure of complex 1c, as a (R,S-1)4·(AgNO3)6 cage with three nitrate anions as coordinatin...

Figure 3: X-ray structure of complex 1d, as a racemic mixture of (R,R)- and (S,S)-(syn-1)·(PPh3AgOTf)2.

Figure 4: Variable temperature 1H NMR of complex 1a in CDCl3 (7 mM) from −30 °C to 60 °C.
Recent advances on the transition-metal-catalyzed synthesis of imidazopyridines: an updated coverage
- Gagandeep Kour Reen,
- Ashok Kumar and
- Pratibha Sharma
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1612–1704, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.165

- ) complex 64, which on reductive elimination gave the final product 62 (Scheme 22). Also, Irina V. Rassokhina and others have employed Cu(OAc)2 for the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines under aerobic conditions (Scheme 23) [114]. They have performed aminomethylation and cycloisomerization of propiolates

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: Various drugs having IP nucleus.

Figure 2: Participation percentage of various TMs for the syntheses of IPs.

Scheme 1: CuI–NaHSO4·SiO2-catalyzed synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 2: Experimental examination of reaction conditions.

Scheme 3: One-pot tandem reaction for the synthesis of 2-haloimidazopyridines.

Scheme 4: Mechanistic scheme for the synthesis of 2-haloimidazopyridine.

Scheme 5: Copper-MOF-catalyzed three-component reaction (3-CR) for imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 6: Mechanism for copper-MOF-driven synthesis.

Scheme 7: Heterogeneous synthesis via titania-supported CuCl2.

Scheme 8: Mechanism involving oxidative C–H functionalization.

Scheme 9: Heterogeneous synthesis of IPs.

Scheme 10: One-pot regiospecific synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 11: Vinyl azide as an unprecedented substrate for imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 12: Radical pathway.

Scheme 13: Cu(I)-catalyzed transannulation approach for imidazo[1,5-a]pyridines.

Scheme 14: Plausible radical pathway for the synthesis of imidazo[1,5-a]pyridines.

Scheme 15: A solvent-free domino reaction for imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 16: Cu-NPs-mediated synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 17: CuI-catalyzed synthesis of isoxazolylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 18: Functionalization of 4-bromo derivative via Sonogashira coupling reaction.

Scheme 19: A plausible reaction pathway.

Scheme 20: Cu(I)-catalyzed intramolecular oxidative C–H amidation reaction.

Scheme 21: One-pot synthetic reaction for imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine.

Scheme 22: Plausible reaction mechanism.

Scheme 23: Cu(OAc)2-promoted synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 24: Mechanism for aminomethylation/cycloisomerization of propiolates with imines.

Scheme 25: Three-component synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Figure 3: Scope of pyridin-2(1H)-ones and acetophenones.

Scheme 26: CuO NPS-promoted A3 coupling reaction.

Scheme 27: Cu(II)-catalyzed C–N bond formation reaction.

Scheme 28: Mechanism involving Chan–Lam/Ullmann coupling.

Scheme 29: Synthesis of formyl-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 30: A tandem sp3 C–H amination reaction.

Scheme 31: Probable mechanistic approach.

Scheme 32: Dual catalytic system for imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 33: Tentative mechanism.

Scheme 34: CuO/CuAl2O4/ᴅ-glucose-promoted 3-CCR.

Scheme 35: A tandem CuOx/OMS-2-based synthetic strategy.

Figure 4: Biomimetic catalytic oxidation in the presence of electron-transfer mediators (ETMs).

Scheme 36: Control experiment.

Scheme 37: Copper-catalyzed C(sp3)–H aminatin reaction.

Scheme 38: Reaction of secondary amines.

Scheme 39: Probable mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 40: Coupling reaction of α-azidoketones.

Scheme 41: Probable pathway.

Scheme 42: Probable mechanism with free energy calculations.

Scheme 43: MCR for cyanated IP synthesis.

Scheme 44: Substrate scope for the reaction.

Scheme 45: Reaction mechanism.

Scheme 46: Probable mechanistic pathway for Cu/ZnAl2O4-catalyzed reaction.

Scheme 47: Copper-catalyzed double oxidative C–H amination reaction.

Scheme 48: Application towards different coupling reactions.

Scheme 49: Reaction mechanism.

Scheme 50: Condensation–cyclization approach for the synthesis of 1,3-diarylated imidazo[1,5-a]pyridines.

Scheme 51: Optimized reaction conditions.

Scheme 52: One-pot 2-CR.

Scheme 53: One-pot 3-CR without the isolation of chalcone.

Scheme 54: Copper–Pybox-catalyzed cyclization reaction.

Scheme 55: Mechanistic pathway catalyzed by Cu–Pybox complex.

Scheme 56: Cu(II)-promoted C(sp3)-H amination reaction.

Scheme 57: Wider substrate applicability for the reaction.

Scheme 58: Plausible reaction mechanism.

Scheme 59: CuI assisted C–N cross-coupling reaction.

Scheme 60: Probable reaction mechanism involving sp3 C–H amination.

Scheme 61: One-pot MCR-catalyzed by CoFe2O4/CNT-Cu.

Scheme 62: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 63: Synthetic scheme for 3-nitroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 64: Plausible mechanism for CuBr-catalyzed reaction.

Scheme 65: Regioselective synthesis of halo-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 66: Synthesis of 2-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 67: Synthesis of diarylated compounds.

Scheme 68: CuBr2-mediated one-pot two-component oxidative coupling reaction.

Scheme 69: Decarboxylative cyclization route to synthesize 1,3-diarylimidazo[1,5-a]pyridines.

Scheme 70: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 71: C–H functionalization reaction of enamines to produce diversified heterocycles.

Scheme 72: A plausible mechanism.

Scheme 73: CuI-promoted aerobic oxidative cyclization reaction of ketoxime acetates and pyridines.

Scheme 74: CuI-catalyzed pathway for the formation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine.

Scheme 75: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 76: Mechanistic rationale for the synthesis of products.

Scheme 77: Copper-catalyzed synthesis of vinyloxy-IP.

Scheme 78: Regioselective product formation with propiolates.

Scheme 79: Proposed mechanism for vinyloxy-IP formation.

Scheme 80: Regioselective synthesis of 3-hetero-substituted imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines with different reaction su...

Scheme 81: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 82: CuI-mediated synthesis of 3-formylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 83: Radical pathway for 3-formylated IP synthesis.

Scheme 84: Pd-catalyzed urea-cyclization reaction for IPs.

Scheme 85: Pd-catalyzed one-pot-tandem amination and intramolecular amidation reaction.

Figure 5: Scope of aniline nucleophiles.

Scheme 86: Pd–Cu-catalyzed Sonogashira coupling reaction.

Scheme 87: One-pot amide coupling reaction for the synthesis of imidazo[4,5-b]pyridines.

Scheme 88: Urea cyclization reaction for the synthesis of two series of pyridines.

Scheme 89: Amidation reaction for the synthesis of imidazo[4,5-b]pyridines.

Figure 6: Amide scope.

Scheme 90: Pd NPs-catalyzed 3-component reaction for the synthesis of 2,3-diarylated IPs.

Scheme 91: Plausible mechanistic pathway for Pd NPs-catalyzed MCR.

Scheme 92: Synthesis of chromenoannulated imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 93: Mechanism for the synthesis of chromeno-annulated IPs.

Scheme 94: Zinc oxide NRs-catalyzed synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]azines/diazines.

Scheme 95: Zinc oxide-catalyzed isocyanide based GBB reaction.

Scheme 96: Reaction pathway for ZnO-catalyzed GBB reaction.

Scheme 97: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 98: ZnO NRs-catalyzed MCR for the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]azines.

Scheme 99: Ugi type GBB three-component reaction.

Scheme 100: Magnetic NPs-catalyzed synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 101: Regioselective synthesis of 2-alkoxyimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines catalyzed by Fe-SBA-15.

Scheme 102: Plausible mechanistic pathway for the synthesis of 2-alkoxyimidazopyridine.

Scheme 103: Iron-catalyzed synthetic approach.

Scheme 104: Iron-catalyzed aminooxygenation reaction.

Scheme 105: Mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 106: Rh(III)-catalyzed double C–H activation of 2-substituted imidazoles and alkynes.

Scheme 107: Plausible reaction mechanism.

Scheme 108: Rh(III)-catalyzed non-aromatic C(sp2)–H bond activation–functionalization for the synthesis of imid...

Scheme 109: Reactivity and selectivity of different substrates.

Scheme 110: Rh-catalyzed direct C–H alkynylation by Li et al.

Scheme 111: Suggested radical mechanism.

Scheme 112: Scandium(III)triflate-catalyzed one-pot reaction and its mechanism for the synthesis of benzimidazo...

Scheme 113: RuCl3-assisted Ugi-type Groebke–Blackburn condensation reaction.

Scheme 114: C-3 aroylation via Ru-catalyzed two-component reaction.

Scheme 115: Regioselective synthetic mechanism.

Scheme 116: La(III)-catalyzed one-pot GBB reaction.

Scheme 117: Mechanistic approach for the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 118: Synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine using LaMnO3 NPs under neat conditions.

Scheme 119: Mechanistic approach.

Scheme 120: One-pot 3-CR for regioselective synthesis of 2-alkoxy-3-arylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 121: Formation of two possible products under optimization of the catalysts.

Scheme 122: Mechanistic strategy for NiFe2O4-catalyzed reaction.

Scheme 123: Two-component reaction for synthesizing imidazodipyridiniums.

Scheme 124: Mechanistic scheme for the synthesis of imidazodipyridiniums.

Scheme 125: CuI-catalyzed arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 126: Mechanism for arylation reaction.

Scheme 127: Cupric acetate-catalyzed double carbonylation approach.

Scheme 128: Radical mechanism for double carbonylation of IP.

Scheme 129: C–S bond formation reaction catalyzed by cupric acetate.

Scheme 130: Cupric acetate-catalyzed C-3 formylation approach.

Scheme 131: Control experiments for signifying the role of DMSO and oxygen.

Scheme 132: Mechanism pathway.

Scheme 133: Copper bromide-catalyzed CDC reaction.

Scheme 134: Extension of the substrate scope.

Scheme 135: Plausible radical pathway.

Scheme 136: Transannulation reaction for the synthesis of imidazo[1,5-a]pyridines.

Scheme 137: Plausible reaction pathway for denitrogenative transannulation.

Scheme 138: Cupric acetate-catalyzed C-3 carbonylation reaction.

Scheme 139: Plausible mechanism for regioselective C-3 carbonylation.

Scheme 140: Alkynylation reaction at C-2 of 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridines.

Scheme 141: Two-way mechanism for C-2 alkynylation of 3H-imidazo[4,5-b]pyridines.

Scheme 142: Palladium-catalyzed SCCR approach.

Scheme 143: Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki coupling reaction.

Scheme 144: Reaction mechanism.

Scheme 145: A phosphine free palladium-catalyzed synthesis of C-3 arylated imidazopyridines.

Scheme 146: Palladium-mediated Buchwald–Hartwig cross-coupling reaction.

Figure 7: Structure of the ligands optimized.

Scheme 147: Palladium acetate-catalyzed direct arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 148: Palladium acetate-catalyzed mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 149: Palladium acetate-catalyzed regioselective arylation reported by Liu and Zhan.

Scheme 150: Mechanism for selective C-3 arylation of IP.

Scheme 151: Pd(II)-catalyzed alkenylation reaction with styrenes.

Scheme 152: Pd(II)-catalyzed alkenylation reaction with acrylates.

Scheme 153: A two way mechanism.

Scheme 154: Double C–H activation reaction catalyzed by Pd(OAc)2.

Scheme 155: Probable mechanism.

Scheme 156: Palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative coupling.

Scheme 157: Mechanistic cycle for decarboxylative arylation reaction.

Scheme 158: Ligand-free approach for arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-3-carboxylic acids.

Scheme 159: Mechanism for ligandless arylation reaction.

Scheme 160: NHC-Pd(II) complex assisted arylation reaction.

Scheme 161: C-3 arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines with aryl bromides catalyzed by Pd(OAc)2.

Scheme 162: Pd(II)-catalyzed C-3 arylations with aryl tosylates and mesylates.

Scheme 163: CDC reaction for the synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 164: Plausible reaction mechanism for Pd(OAc)2-catalyzed synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 165: Pd-catalyzed C–H amination reaction.

Scheme 166: Mechanism for C–H amination reaction.

Scheme 167: One-pot synthesis for 3,6-di- or 2,3,6-tri(hetero)arylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines.

Scheme 168: C–H/C–H cross-coupling reaction of IPs and azoles catalyzed by Pd(II).

Scheme 169: Mechanistic cycle.

Scheme 170: Rh-catalyzed C–H arylation reaction.

Scheme 171: Mechanistic pathway for C–H arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine.

Scheme 172: Rh(III)-catalyzed double C–H activation of 2-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and alkynes.

Scheme 173: Rh(III)-catalyzed mechanistic pathway.

Scheme 174: Rh(III)-mediated oxidative coupling reaction.

Scheme 175: Reactions showing functionalization of the product obtained by the group of Kotla.

Scheme 176: Mechanism for Rh(III)-catalyzed oxidative coupling reaction.

Scheme 177: Rh(III)-catalyzed C–H activation reaction.

Scheme 178: Mechanistic cycle.

Scheme 179: Annulation reactions of 2-arylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridines and alkynes.

Scheme 180: Two-way reaction mechanism for annulations reaction.

Scheme 181: [RuCl2(p-cymene)]2-catalyzed C–C bond formation reaction.

Scheme 182: Reported reaction mechanism.

Scheme 183: Fe(III) catalyzed C-3 formylation approach.

Scheme 184: SET mechanism-catalyzed by Fe(III).

Scheme 185: Ni(dpp)Cl2-catalyzed KTC coupling.

Scheme 186: Pd-catalyzed SM coupling.

Scheme 187: Vanadium-catalyzed coupling of IP and NMO.

Scheme 188: Mechanistic cycle.

Scheme 189: Selective C3/C5–H bond functionalizations by mono and bimetallic systems.

Scheme 190: rGO-Ni@Pd-catalyzed C–H bond arylation of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine.

Scheme 191: Mechanistic pathway for heterogeneously catalyzed arylation reaction.

Scheme 192: Zinc triflate-catalyzed coupling reaction of substituted propargyl alcohols.
Stereodivergent approach in the protected glycal synthesis of L-vancosamine, L-saccharosamine, L-daunosamine and L-ristosamine involving a ring-closing metathesis step
- Pierre-Antoine Nocquet,
- Aurélie Macé,
- Frédéric Legros,
- Jacques Lebreton,
- Gilles Dujardin,
- Sylvain Collet,
- Arnaud Martel,
- Bertrand Carboni and
- François Carreaux
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2949–2955, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.274
- protected 3-aminoglycals from non-carbohydrate precursors. Most of them used a common methodology for the construction of the pyranosyl glycal ring which is based on a cycloisomerization reaction of chiral homopropargylic alcohols [7][8][9][10]. In some cases, the strategy used for the preparation of the

Graphical Abstract

Figure 1: N,N-Dimethyl-L-vancosamine as substructure of kidamycin and pluramycin.

Figure 2: Glycals as relevant scaffolds for constructing aryl C-glycosidic linkage.

Figure 3: Strategy including a ring-closing metathesis of vinyl ethers as key step for the preparation of sev...

Scheme 1: Evans aldol reaction for the preparation of diastereomeric compounds 13a and 13b.

Scheme 2: Alternative preparation of 13b based on a diastereoselective allylboration.

Scheme 3: O-Vinylation-ring-closing metathesis sequence for access to 3-amino glycals.

Scheme 4: Synthesis of key intermediate 23 for the C-3 unbranched amino glycals preparation.

Scheme 5: Access to diastereoisomeric compounds 3 and 4 from 23.
Gold-catalyzed post-Ugi alkyne hydroarylation for the synthesis of 2-quinolones
- Xiaochen Du,
- Jianjun Huang,
- Anton A. Nechaev,
- Ruwei Yao,
- Jing Gong,
- Erik V. Van der Eycken,
- Olga P. Pereshivko and
- Vsevolod A. Peshkov
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2572–2579, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.234
- -dimethoxyaniline (6a). Next, the cycloisomerization of 7a was investigated in order to identify the optimal conditions. At first, we attempted two reactions using 5 mol % of the standard AuPPh3Cl/AgOTf precatalytic combination in conventional chlorinated solvents such as deuterated chloroform and dichloromethane

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: Synthesis of 2-quinolones 2 through intramolecular Friedel–Crafts hydroarylation of N-aryl propargy...

Scheme 2: Strategy towards 2-quinolones 8 bearing a branched substituent on the nitrogen atom.

Figure 1: Scope of the protocol.
Cobalt bis(acetylacetonate)–tert-butyl hydroperoxide–triethylsilane: a general reagent combination for the Markovnikov-selective hydrofunctionalization of alkenes by hydrogen atom transfer
- Xiaoshen Ma and
- Seth B. Herzon
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2018, 14, 2259–2265, doi:10.3762/bjoc.14.201
- developed (e.g., reductive coupling [22][23][24][25][26][27][28], formal hydromethylation [29], cycloisomerization [8][30][31], hydrooximation [32], hydroheteroarylation [28][33][34][35], hydroarylation [36][37][38], and cross-coupling [37]). Many of these transformations have found applications in

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: General mechanism of alkene hydrofunctionalization via HAT.

Scheme 2: Reduction of the alkenyl chloride 1 by HAT.

Scheme 3: Substrate scope of alkyl-aryl azo compound synthesis via HAT. Conditions: alkene (0.250 mmol), diaz...
Is the tungsten(IV) complex (NEt4)2[WO(mnt)2] a functional analogue of acetylene hydratase?
- Matthias Schreyer and
- Lukas Hintermann
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2017, 13, 2332–2339, doi:10.3762/bjoc.13.230
- cycloisomerization of alkynols, in which the alcohol adds to the alkyne [19]. The reaction of [W(CO)5(THF)] with ortho-ethynylacetophenone and excess water gives 1,2-diacetylbenzene via neighboring group attack to complexed alkyne, and hydrolysis [20]. The latter pathway represents the π-activation pathway of alkyne
- hydration (Scheme 2a), whereas alkynol cycloisomerization proceeds via rearrangement to a tungsten vinylidene complex and addition of the alcohol hydroxy group to the vinylidene α-carbon [18]. The vinylidene mechanism is related to that of ruthenium-catalyzed anti-Markovnikov hydration of terminal alkynes

Graphical Abstract

Scheme 1: a) Acetylene hydratase catalyzes the hydration of acetylene to ethanal. b) Currently favored key-st...

Scheme 2: a) π-Activation pathway in Markovnikov selective alkyne hydration, e.g., with mercury catalysts. b)...

Scheme 3: a) Synthesis of complex (NEt4)2[WO(mnt)2] (1) [29]. b) Attempted catalytic hydration reaction with a te...

Scheme 4: a) Unexpected isolation of acetone 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (10) from an attempted catalytic hydr...

Figure 1: Frequency of reported melting points for acetaldehyde 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (9) from the Reaxy...

Figure 2: Experimental setup for the study of catalytic acetylene hydration. Red arrows indicate the directio...

Figure 3: Identification of ethyne (2) in the reaction solution by coupling pattern analysis of 13C-satellite...






