Search results
Search for "carbon" in Full Text gives 1887 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Tying a knot between crown ethers and porphyrins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1630–1650, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.120

- cations), forming coordination compounds wherein the central ion acquires a square planar [14], square pyramidal [15], or an octahedral coordination environment [16]. On the opposite side, crown ethers are cyclic molecules composed of carbon and oxygen atoms forming the macrocycle. Depending on the size
- another group of hybrid macrocycles in which the dipyrrin is connected to oligo(ethylene glycol) through carbon–carbon bonds [68]. In 2022, our group demonstrated the synthesis and reactivity of crownphyrins – hybrid macrocycles wherein the dipyrrin segment links with the crown ether part through the
- with Zn(II) was crucial to achieving the final strapping reaction, affording 11. The presence of the diaza-crown-6 caps resulted in the meso-bridge carbon atoms being slightly pulled out of the porphyrin plane, causing 11 to adopt a ruffled conformation. The penta-coordinated Zn(II) contained an
A series of perylene diimide cathode interlayer materials for green solvent processing in conventional organic photovoltaics
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1620–1629, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.119

- Organic photovoltaic (OPV) devices for energy harvesting or light recycling are of interest due to their low cost, fabrication via layer-by-layer printing, flexibility, and low carbon footprint [1][2]. Due to the processability of organic materials used in OPVs, the large-scale manufacturing of such
Sulfur-containing spiroketals from Breynia disticha and evaluations of their anti-inflammatory effect
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1604–1614, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.117
- = 7.8 Hz, 1H, H-1′), which corresponded to the carbon at δC 103.2 (C-1′). Furthermore, the 1D-TOCSY experiment involving irradiation at δH 2.52 (br d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H, H-5′′) resulted in the excitement of resonances at δH 3.32 (m, 3H, H-2′′, 3′′, 4′′, overlapping) and 3.50 (br s, 2H, H2-6′′) as well as
- an anomeric proton resonance at δH 4.30 (d, J = 7.3 Hz, 1H, H-1′′), which corresponded to the carbon at δC 104.5 (C-1′′). Based on the H2BC correlations of H-1′′/C-2′′ and H-5′′/C-4′′, the signals at δC 82.9 and 69.3 were assigned to C-2′′ and C-4′′, respectively, and that at δC 85.5 was assigned to
- C-3′′. The HSQC, 1D-TOCSY, and HSQC-TOCSY spectra also revealed a series of carbon signals corresponding to ʟ-rhamnose at δC 17.9, 70.5, 72.0, 72.1, 73.7, and 103.3. The remaining five carbon signals [an anomeric methine at δC 111.9 (C-1′′′′), a methine at δC 77.5 (C-2′′′′), two methylenes at δC
Radical chemistry in polymer science: an overview and recent advances
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1580–1603, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.116
- carbon-centered radical to another thiol group (propagation 2), and biradical termination between either carbon-centered or thiyl radicals (termination). Polymerization by thiol–ene coupling is a step-growth polymerization, which means it can produce polymers with no theoretical upper-limited molecular
- blending compatibilizers [211]. Radical depolymerization capability can be incorporated at synthesis. Wang et al. introduced photodegradability to polyolefins by copolymerization of carbon monoxide [212]. Nevertheless, radical depolymerization is an essential tool to tackle the problem of polymer wastes
Secondary metabolites of Diaporthe cameroonensis, isolated from the Cameroonian medicinal plant Trema guineensis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1555–1561, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.112
- peaks with their respective carbon signals at δC 122.0, 28.8, 16.6, 8.1, and 7.1, respectively (Figure S5 in Supporting Information File 1). In the HMBC spectrum, key correlations were observed between the olefinic proton signal (δH 7.12) and six carbon signals including three deshielded ones at δC
- 2.09 with the carbon signals at δC 165.6, 122.0, and 120.3, and the second one at δH 2.02 with the carbon signals at δC 169.2, 165.6, and 106.2 (Figure 2). These findings clearly indicated the presence of the 1,3-dimethylbenzene moiety linked to a side chain containing an ethyl group and a ketone group
- . Furthermore, the ethyl group was attached to a hemiketal group (δC 106.1) as evidenced by the HMBC cross-peaks observed between the methylene proton signals at δH 1.75 with the carbon signals at δC 196.1, 106.1, and 7.1, and also between the methyl proton signals at δH 0.75 with the carbon signals at δC 106.1
N-Sulfenylsuccinimide/phthalimide: an alternative sulfenylating reagent in organic transformations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1471–1502, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.106

- exo ratio was either related to the electron density of the alkene or the steric effect of a substituent. The tether lengths could affect the cyclization. For example, the two-carbon-tethered substrate completely showed endo selectivity, while the four-carbon-tethered substrate exclusively led to
- azlactone 146 skeletons. The presence of two heteroatom-bearing tetrasubstituted chiral carbon centers in a one-step fashion, avoiding the use of the heavy metal catalysts, and the performance of the reaction at ambient temperature are the prominent features of the protocol. Sahoo and co-workers found that
- of polarized ketene-N,O-acetal to the alkyne β-carbon and trapping of the sulfonium cation at the alkyne-α-carbon afforded 5-(arylthio)-3,6-dihydropyridin-2(1H)-one 148. The coordination of a sulfonium electrophile to the C–C triple bond of 1-I occurred through cyclopropyl intermediate 1-I. The
Cyclization of 1-aryl-4,4,4-trichlorobut-2-en-1-ones into 3-trichloromethylindan-1-ones in triflic acid
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1460–1470, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.105
- form of the starting compound [Cl3CCH=CHC(=OH+)Me]. The presence of two strong electron-withdrawing substituents, the trichloromethyl group (CCl3) and a protonated carbonyl (C(OH+)Me), at the carbon–carbon double bond makes this O-protonated species electrophilic enough to react with arenes (Scheme 1a
- to the 13C NMR spectra, the largest downfield shift was observed for the carbonyl carbon С1, with ∆δ = 17.7–21.1 ppm, showing a substantial degree of protonation of the carbonyl group in TfOH. The tendencies are the same for the protonation of enones 2a,c,d,m leading to cations Ba,c,d,m (Table 2
- -protonated forms B is substantially delocalized from the carbonyl group to vinyl carbon C3. For fluorophenyl-substituted compounds and cations 1d and Ad, 2d and Bd, also a large downfield shift of the corresponding fluorine signals is observed in the 19F NMR spectra (∆δ = 25.3–25.7 ppm), which shows a
α-(Aminomethyl)acrylates as acceptors in radical–polar crossover 1,4-additions of dialkylzincs: insights into enolate formation and trapping
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1443–1451, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.103
- thus the sense of chiral induction for the 1,4-addition reactions reported in Table 2. Tandem 1,4-addition–aldol condensation reactions We then went on to consider tandem 1,4-addition–aldol condensation reactions (Scheme 6), which offer the interesting prospect of generating an all-carbon quaternary
- chiral induction. It should be mentioned here that our attempts to trap the intermediate enolate with a carbon electrophile other than carbonyl acceptors (i.e., iodomethane) were not successful and protodemetalation of the enolate outcompeted methylation. Conclusion In conclusion, we have demonstrated
- view, the reported protocols are relevant as they offer a new, direct and modular route to enantioenriched α-mono- and α,α-disubstituted β-amino acids (β2-amino acids and β2,2-amino acids), with, for the latter, the noteworthy stereocontrolled construction of an all-carbon quaternary stereocenter
Application of N-heterocyclic carbene–Cu(I) complexes as catalysts in organic synthesis: a review
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1408–1442, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.102
- Nosheen Beig Varsha Goyal Raj K. Bansal Department of Chemistry, The IIS (deemed to be University), Jaipur, 302 020, India 10.3762/bjoc.19.102 Abstract N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are a special type of carbenes in which the carbene carbon atom is part of the nitrogen heterocyclic ring. Due to
- addition; [3 + 2] cycloaddition reaction; hydrosilylation reaction; N-heterocyclic carbenes; NHC–Cu complexes; NHC–Cu complexes as catalyst; Introduction N-Heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs) are a neutral species having the carbene carbon atom as a part of the nitrogen heterocyclic ring. The transient
- reaction of the carbene 1,3-dimesitylimidazol-2-ylidene (7a) with carbon tetrachloride in THF (Scheme 4) [5]. Structure of N-heterocyclic carbenes N-Heterocyclic carbenes contain at least one nitrogen atom and there may be another nitrogen atom or a sulfur atom present in the heterocycle. A general
One-pot nucleophilic substitution–double click reactions of biazides leading to functionalized bis(1,2,3-triazole) derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1399–1407, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.101
- on carbon and provided the expected (propyloxy)methyl-substituted aminopyran 22 in 81% yield (Scheme 7, reaction 1). The reductive removal of the N-benzyl group and the cleavage of the N–O bond occurred apparently without problems. With the second model compound, 1,2,3-triazole 23, which is almost
- -triazole) 21. It turned out that the hydrogenolysis of this compound was very capricious and (in part) depended on the batch of palladium on carbon used. In most cases, incomplete consumption of starting material was observed, even after long reaction time. The best result is depicted in Scheme 8 (reaction
- compounds, but the sample again contains unknown impurities, which are probably due to additional bond cleavage events. Compound 25 contains four bonds of heteroatoms to carbon atoms which have benzylic character and are possibly attacked under the reaction conditions, in particular, considering the long
Consecutive four-component synthesis of trisubstituted 3-iodoindoles by an alkynylation–cyclization–iodination–alkylation sequence
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1379–1385, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.99
- protective gas atmosphere, leads to slow decomposition. Therefore, storage at low temperature in a dark vial is strongly recommended. Upon using 2,4-dibromoaniline (1c) as the substrate and an excess of phenylacetylene (2a), both carbon–bromine bonds are transformed in the alkynylation step affording the
- summary the indole anion intermediate resulting from a one-pot alkynylation–cyclization sequence, which has been previously shown to be efficiently trapped by carbon electrophiles to give N-substituted indoles in a consecutive three-component synthesis, can be selectively iodinated in the 3-position with
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- (PAF), by an acetyl group (R2 = CH3) [1]. The asymmetric carbon of the glycerol (sn-2 position) features a R configuration. The last substituent attached to the glycerol unit is a polar head group mostly constituted by a phosphatidylethanolamine group (PE) or a phosphocholine moiety (PC). ELs with
- produces the diester 4.12 with an inversion of the configuration of the chiral carbon atom. Then, 4.12 was hydrolyzed in the presence of KOH to produce 4.10. The installation of the phosphocholine group was achieved following two schemes: a) Starting from the diol 4.10 (Figure 4C), tritylation and
- either sn-1 and sn-2 positions or sn-2 and sn-3 positions [97]. The incorporation of one methylene unit is shown in Figure 13 as an illustration of all these possibilities. But-3-en-1-ol (13.1) was alkylated with bromohexadecane to produce the ether 13.2. The epoxidation of the carbon–carbon double bond
Organic thermally activated delayed fluorescence material with strained benzoguanidine donor
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1289–1298, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.95
- the plane of the central benzene ring. In both molecules in the asymmetric unit, the benzoguanidine moiety bound to the benzene carbon neighboring two nitrile groups, is orientated in the opposing projection about the plane of the benzene ring to the remaining benzoguanidine moieties (Figure 2b
- ). Unlike monoclinic, the triclinic form of 4BGIPN possesses two donor moieties pointing down at C1 and C3 carbon atoms while donor moieties at C2 and C5 are pointed up (Figure 2c). Several possible 4BGIPN rotational isomers are demonstrated in Figure 2e, however, not isolated in this work. Compound 4BGIPN
- (CV) was performed using a three-electrode configuration consisting of a glassy carbon macrodisk working electrode (GCE) (diameter of 3 mm; BASi, Indiana, U.S.A.) combined with a Pt wire counter electrode (99.99%; GoodFellow, Cambridge, U.K.) and an Ag wire pseudoreference electrode (99.99
Non-noble metal-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenation coupling (CDC) involving ether α-C(sp3)–H to construct C–C bonds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1259–1288, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.94
- oxidative olefination of simple ethers might undergo the following three successive steps: (1) the formation of an α-carbon-centered radical A from simple ethers, (2) addition of the α-carbon-centered radical to olefins generating radical B. This step is one of the classical transformations of radicals and
- [74][75][76][77], which can directly activate inert C–H bonds to construct C–C bonds. Fe-catalyzed CDC reactions mainly follow the mechanism shown in Scheme 16. An oxidant abstracts a hydrogen from the C–H bond to generate a carbon-centered radical A. Then, through a single-electron transfer (SET
- the reaction mechanism supported by DFT calculations and concluded that FeF2 plays an important redox role in assisting the cleavage of oxidants and the oxidation of carbon radicals to cationic intermediates of oxygen. CDC reactions between C(sp3)–H/C(sp)–H bonds catalyzed by iron have been reported
Metal catalyst-free N-allylation/alkylation of imidazole and benzimidazole with Morita–Baylis–Hillman (MBH) alcohols and acetates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1251–1258, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.93
- various nucleophiles, including C- and heteronucleophiles, such as compounds bearing –OH, –SH, and –NH groups [4][5][6][7]. Among them, the carbon–nitrogen bond formation through N-nucleophilic substitution reactions plays a central role for the synthesis of numerous compounds exhibiting various
Acetaldehyde in the Enders triple cascade reaction via acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1243–1250, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.92
- last step involves the enamine intermediate which drives an intramolecular aldol condensation to form the final product 5. In this elegant cascade process, catalyst 1 promotes three consecutive carbon–carbon bond forming steps generating four stereogenic centers with high diastereoselectivity and
- aldehydes other than acetaldehyde generates higher control [11]. It was previously shown that the first stereogenic center formed in the presented cascade process is formed with high control [17]. Therefore, the second carbon–carbon bond forming step, i.e., the organocatalyzed Michael addition of the
Selective construction of dispiro[indoline-3,2'-quinoline-3',3''-indoline] and dispiro[indoline-3,2'-pyrrole-3',3''-indoline] via three-component reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1234–1242, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.91
- structures of the obtained dispiro compounds 3a–m were fully characterized by IR, HRMS, 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Because of the three chiral carbon atoms in the product, several diastereomers might be formed in the reaction. However, TLC monitoring and 1H NMR spectra of the crude products clearly
Radical ligand transfer: a general strategy for radical functionalization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1225–1233, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.90
- paradigm by Groves and Kochi, many groups have adopted and characterized new ways of using RLT to form valuable carbon–heteroatom bonds from a diverse pool of simple starting materials. RLT has been especially present in modern catalysis, where complexes of earth abundant iron and manganese have been
- simplified manganese salen complex I, allowing for the identity of the carbon–heteroatom bond to be controlled based on added nucleophile and enabling C–Cl, C–N, and C–S bonds to be formed directly while completely suppressing traditional ATRA products [9]. In mechanistic studies, rearrangement products
- diamines with excellent functional group compatibility (Scheme 3) [10][39]. In both reports, it is proposed that photoinduced LMCT of an in-situ generated Fe(III) azide species furnishes an azido radical, compatible with unactivated alkene addition. These steps provide the reactive carbon-centered radical
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
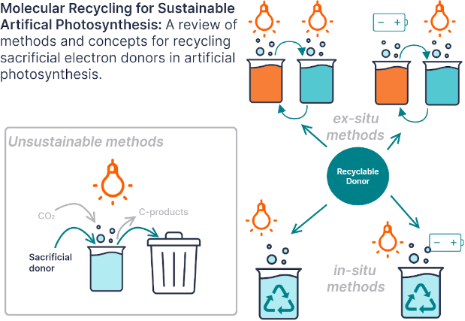
- artificial photosynthesis. Systems for photocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction are optimized using sacrificial electron donors. One strategy for coupling carbon dioxide reduction and water oxidation to achieve artificial photosynthesis is to use a redox mediator, or recyclable electron donor. This review
- discovery and creation of incredible chemical systems and materials. The ultimate goal is to harness energy from the sun and use it to transfer electrons and protons from water onto carbon dioxide and create molecules to replace fossil fuels [1][2]. However, when developing the components of artificial
- cycle to reduce and fixate carbon dioxide [7]. Quite sensibly, many research groups investigating artificial photosynthesis develop components and systems for water splitting and carbon dioxide reduction separately before they or others seek to combine them. This modular approach is hugely beneficial
Cyanothioacetamides as a synthetic platform for the synthesis of aminopyrazole derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1191–1197, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.87
- the data given in the current work. The formation of 3,5-diaminopyrazoles 4a–c occurs, presumably, as a result of a sequential attack of electrophilic carbon atoms of the cyano- and thioamide groups of thioamides 1a–c by nucleophilic nitrogen atoms of hydrazine (3a) and is accompanied by the
Exploring the role of halogen bonding in iodonium ylides: insights into unexpected reactivity and reaction control
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1171–1190, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.86

- pathway was operative, producing halogen-bonded adducts 28/28’ which could cyclize on the acylium at either carbon or oxygen, to eventually produce 24 and 25 after reductive elimination of iodobenzene (Figure 7, bottom). Based on these initial results and their corresponding mechanistic proposals, iodine
- ]. They disclosed a reaction between acyclic iodonium ylides (e.g., 31/ I-10) and tertiary amines 32, which produced indoline rings 33 by forging two new C–C bonds between the ylidic carbon and unactivated positions on the amine (Scheme 5). In 2020, they disclosed a more complex variant of this reaction
Two new lanostanoid glycosides isolated from a Kenyan polypore Fomitopsis carnea
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1161–1169, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.84
- unsaturation in its structure. The 1H, 13C NMR, and HSQC spectral data of compound 1 (Table 1) revealed the presence of forty-three carbon resonances sorted into eight methyl, fourteen methylenes (one olefinic), ten methine and eleven unprotonated carbon atoms. This includes three carbonyl carbons at δC 177.4
- (C-21), 175.0 (C-5'), and 172.4 (C-1') as well as four olefinic carbon signals at δC 156.7 (C-24), 136.3 (C-9), 135.2 (C-8), and 107.4 (C-31). The 1H and 13C NMR spectral data of compound 1 (Table 1) also revealed the presence of a sugar moiety through the presence of the characteristic anomeric
- proton resonance at δH 5.49 (d, J = 8.1, H-1'') which was directly correlated to the carbon at δC 95.7 (C-1'') in the HSQC spectrum. The 1H,1H COSY spectrum of compound 1 (Figure 2) revealed an extended spin system over four aliphatic methines and ending with one aliphatic methylene. By comparing the 1H
Photoredox catalysis harvesting multiple photon or electrochemical energies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1055–1145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.81
- SCE (1c) were readily reduced and dehalogenated products obtained in excellent yields (70–92%) (Figure 11A). Sodium formate was found to be a more efficient terminal reductant than trialkylamines which the authors attributed to the formation of a carbon dioxide radical anion (CO2•−) upon oxidation of
- interconnected photocatalytic cycles as the hydrodehalogenation, an aryl radical 2• is formed via successive PET and C(sp2)–X bond cleavage (Figure 17B). Carbon monoxide, introduced to the reaction mixture by a tube-in-tube reactor, traps the aryl radical to generate the acyl radical 23 (Figure 17B
Synthesis of imidazo[4,5-e][1,3]thiazino[2,3-c][1,2,4]triazines via a base-induced rearrangement of functionalized imidazo[4,5-e]thiazolo[2,3-c][1,2,4]triazines
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1047–1054, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.80
- closer location in structures 5 (Figure 3). In the downfield region of the 13C NMR spectra registered without proton decoupling for isomeric acids 4a and 5a, the carbon atom doublets of the carboxyl groups, carbonyl groups of thiazole (for 4a) or thiazine (for 5a) cycles, as well as multiplets of
The effect of dark states on the intersystem crossing and thermally activated delayed fluorescence of naphthalimide-phenothiazine dyads
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1028–1046, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.79

- -purged saturated solutions containing 0.10 M Bu4NPF6 as a supporting electrolyte, a platinum electrode as counter electrode, a glassy carbon electrode as working electrode, and the Ag/AgNO3 (0.1 M in ACN) couple as the reference electrode. Ferrocenium/ferrocene (Fc+/Fc) redox couple was used as an













































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































