Search results
Search for "reactivity" in Full Text gives 1429 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. Showing first 200.
Radical chemistry in polymer science: an overview and recent advances
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1580–1603, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.116
- used in post-polymerization modification, including chemical crosslinking of polymers and polymer surface modification. Radicals are powerful tools for post-polymerization processes because of their exceptional reactivity. In contrast to the previous sections, we set the topic of section 4 on the
- negative free energy of polymerization and the latter an adequate reactivity of the monomer, stability of the derived free radical, and a low proportion of side reactions. A slow rate of chain initiation, a fast rate of chain propagation, and a rapid rate of chain termination are key features of
- of precisely controlled, high-value polymeric materials. The extremely high reactivity of radical species enabled efficient polymer modifications and depolymerizations with applications in many aspects essential to the advancement of the human society. Since the dawn of polymer science, it has been
Morpholine-mediated defluorinative cycloaddition of gem-difluoroalkenes and organic azides
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1545–1554, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.111
- , organic azides, and morpholine. Terminal gem-difluoroalkenes exhibit unique reactivity toward nucleophiles. The two σ-withdrawing fluorine atoms at the α-position and the strong polar nature of the double bond make gem-difluoroalkenes susceptible to a nucleophilic attack that is followed by a β-fluoride
- -difluoroalkenes that subsequently undergoes a cycloaddition reaction. Results and Discussion While investigating 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions between organic azides and gem-difluoroalkenes to obtain the 4-fluoro-1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole regioisomers, we observed an interesting reactivity while
- been reported to facilitate the addition of azoles to gem-difluoroalkenes (Figure 1B) [9][33]. An elevated temperature (110 °C) was required along with 48 h reaction time (Table 1, entry 3 vs entry 4) due to the sluggish nature of the reaction and poor reactivity of the gem-difluoroalkenes. The
Synthesis of 5-arylidenerhodanines in L-proline-based deep eutectic solvent
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1537–1544, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.110
- increased to 99% when the reaction was run for 3 h. 2-Hydroxy-5-methoxybenzaldehyde in the reaction with rhodanine gave product 3e in a moderate 63% yield. The presence of an electron-withdrawing group such as a nitro did not seem to really decrease the reactivity as product 3f was obtained in 79% yield
- formation of the expected 5-benzylidenerhodanine 3i under the optimized conditions with a slightly lower yield (3i versus 3a). Finally, we also decided to investigate the reactivity of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Indeed, HMF is considered as one of the most promising biomass-derived platform chemicals
N-Sulfenylsuccinimide/phthalimide: an alternative sulfenylating reagent in organic transformations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1471–1502, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.106

- organosulfur chemistry, sulfenylating agents are an important key in C–S bond formation strategies. Among various organosulfur precursors, N-sulfenylsuccinimide/phthalimide derivatives have shown highly electrophilic reactivity for the asymmetric synthesis of many organic compounds. Hence, in this review
- reactivity than electron-withdrawing groups, and the thiolation occurred mainly at the para position to the hydroxy group in phenols. In 2016, the azidoarylthiation of various alkenes 9 by trimethylsilyl azide (10) and N-(organothio)succinimide 1 to the corresponding products containing ortho-sited azide and
- low reactivity of these phthalimides, 10 mol % of catalyst was required. Cross-coupling reaction of sulfoximines 44 with N‑(arylthio)succinimides 1 catalyzed by a nanomaterial containing hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) and γ-cyclodextrin-supported copper(II) acetate (h-BN@γ-CD@Cu(OAc)2) was developed
α-(Aminomethyl)acrylates as acceptors in radical–polar crossover 1,4-additions of dialkylzincs: insights into enolate formation and trapping
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1443–1451, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.103
- , 1,4-additions of dialkylzinc reagents have been reported with dehydroamino ester derivatives [13][14] and α-bromoacrylates [15], which both involve an SH2 at zinc of tertiary α-alkoxycarbonyl radicals (Scheme 2, top). Here, the key to unlock the reactivity is the presence of a Lewis-basic substituent
- . Mechanistic insights The last part of our work was devoted to gain mechanistic insight for the developed reaction protocols through several diagnostic experiments. Regarding the 1,4-addition process, the lower reactivity noted in the absence of air (Table 2, entry 5) represents already a strong indication for
- configuration of the major diastereomer of (RS)-14b. Air-promoted tandem 1,4-addition–aldol condensation reactions of Et2Zn with α-(aminomethyl)acrylates. Diagnostic experiments for a radical mechanism and for enolate formation. Diagnostic experiments with N-benzyl enoate 10. Reactivity manifolds for the air
Application of N-heterocyclic carbene–Cu(I) complexes as catalysts in organic synthesis: a review
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1408–1442, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.102
- heteroleptic Cu(I) complexes combining the malonic acid-derived anionic NHC and a neutral imidazol-2-ylidene were also obtained in a very selective manner (Scheme 12). As discussed later, many of these complexes were employed as catalysts. In 2015, Collins et al. [27] compared the stability and reactivity of
- . The hydrosilylation of aryl, alkyl, and cyclic ketones could be accomplished with excellent yields (Scheme 35) [48]. In 2011, Gawley and co-worker reported an excellent reactivity and enantioselectivity of a C2-symmetric NHC–Cu(I) complex for the catalytic hydrosilylation of a variety of carbonyl
- dichloromethane increased the reactivity, resulting in quantitative conversion, but toluene, acetonitrile, and tetrahydrofuran (THF), which had previously been reported to be extremely effective in the presence of copper salts, gave poor yields. In 2013, Navarro and co-worker [78] used [(NHC)Cu(I)]X (X = Cl, NHC
Visible-light-induced nickel-catalyzed α-hydroxytrifluoroethylation of alkyl carboxylic acids: Access to trifluoromethyl alkyl acyloins
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1372–1378, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.98
- reaction showed a good tolerance of a diverse range of functional groups, including methoxy (3b), methyl (3c), chloro (3d,i), fluoro (3f,g), and ethers (3i,l,p). Notably, aryl bromide (3e) was also tolerated in this protocol, probably due to the higher reactivity of the mixed anhydride formed between
Synthesis of ether lipids: natural compounds and analogues
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1299–1369, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.96
- was selectively alkylated on the primary alcohol to produce 20.2 via the use of dibutyltin oxide as selective reagent for the alkylation of diols [109]. For this reaction, CsF was added to increase the reactivity of the alkyl bromide, likely by a combined effect that includes the interaction of the
Non-noble metal-catalyzed cross-dehydrogenation coupling (CDC) involving ether α-C(sp3)–H to construct C–C bonds
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1259–1288, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.94
- significantly different reactivity and chemical selectivity from noble metals (Ru, Rh, Pd). Compared with noble metals, copper catalysts are cheaper and easier to obtain, making Cu more advantageous for industrial applications of C–H functionalization reactions. The Glaser–Hay reaction may be one of the oldest
- benzothiazole, in which benzothiazole compounds have higher reactivity and regioselectivity than thiazole. In 2014, Lei et al. successfully realized the copper-catalyzed oxidative alkenylation of simple ethers to construct allyl ethers in the presence of di-tert-butyl peroxide and KI (Scheme 10) [60]. The
- achieve the CDC of THF and phenol C(sp2)–H (Scheme 12) [62]. The role of Pd may be through the formation of a Pd(II) phenolic acid salt from phenol and Pd(OAc)2 to improve the reactivity of phenol. Subsequently, a more complex C(sp2)–H component was employed as a coupling substrate to functionalize the
Metal catalyst-free N-allylation/alkylation of imidazole and benzimidazole with Morita–Baylis–Hillman (MBH) alcohols and acetates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1251–1258, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.93
- precursors in nucleophilic allylic substitution reactions with amines, presumably due to the perceived poor leaving group ability and low reactivity of the hydroxy group. Interestingly, the direct nucleophilic substitution of the corresponding alcohols has drawn much attention because of the availability of
Acetaldehyde in the Enders triple cascade reaction via acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1243–1250, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.92
- because of its high reactivity. Herein, we report the Enders-type cascade reaction using acetaldehyde dimethyl acetal, as a masked form of acetaldehyde. This strategy directly converts acetaldehyde, nitroalkenes and enals into stereochemically dense cyclohexenals in good yield and excellent
- process. The ingenious crafting of the reaction lies in the selection of the reactivity of the different nucleophiles and electrophiles present in the mixture, both as reagents and as intermediates. First, the chiral aminocatalyst 1 activates the saturated aldehyde 2 via enamine intermediate A, which
- as a reagent has always been challenging. The low boiling point and high volatility pose a problem with its handling and safety. The small steric hindrance gives rise to a high reactivity both as an electrophile and as a pro-nucleophile, hampering chemoselectivity (further to side reactions such as
Selective construction of dispiro[indoline-3,2'-quinoline-3',3''-indoline] and dispiro[indoline-3,2'-pyrrole-3',3''-indoline] via three-component reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1234–1242, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.91
- different reactivity to that of the adducts of 3-ethoxycarbonylmethyleneoxindoles. For confirming the chemical structures of dispirooxindoles 4a–i, the single crystal structure of compound 4a was determined by X-ray diffraction (Figure 2). In Figure 2, the two oxindole scaffolds are in trans-position. The
Radical ligand transfer: a general strategy for radical functionalization
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1225–1233, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.90
- body’s own cytochrome P450 enzymes. These catalysts exhibit unique “radical rebound” reactivity at their heme active sites (Scheme 1) [12], a mechanism proposed by Groves and co-workers and heavily explored beginning in the 1970s [13][14]. This two-step functionalization sequence begins with HAT from an
- asymmetric RLT processes. We hope that this perspective provides a useful framework for understanding RLT reactivity and inspires new advances using this versatile and intriguing elementary step. Overview of the RLT mechanism in nature and in literature. I: The radical rebound mechanism in cytochrome P450
Enabling artificial photosynthesis systems with molecular recycling: A review of photo- and electrochemical methods for regenerating organic sacrificial electron donors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1198–1215, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.88
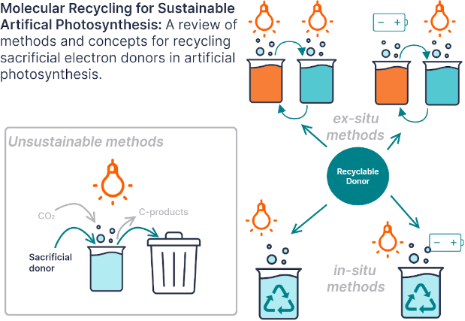
- as triethylamine, breakdown after oxidation which prevents regeneration [3][5]. Furthermore, there have also been studies where systems have been developed with sacrificial donors that interact and actually change the reactivity of the system [5][6]. Replacing these sacrificial donors becomes more
Cyanothioacetamides as a synthetic platform for the synthesis of aminopyrazole derivatives
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1191–1197, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.87
- (3)-thiocarbamoyl-NH-pyrazoles 5a–e were obtained with a yield of 68–78% (Scheme 2). These experiments allowed us to conclude that in the compounds 2a–e under study, the enamine group has a higher reactivity towards hydrazine than the thioamide one, which leads to the preservation of the thioamide
Exploring the role of halogen bonding in iodonium ylides: insights into unexpected reactivity and reaction control
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1171–1190, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.86

- elimination) more commonly associated with transition metal-mediated chemistry; however, halogen- or σ-hole bonding has recently emerged as a credible explanation for the diverse reactivity that iodonium ylides undergo. σ-Hole bonding theory offers a means to explain the occurrence of transition metal-free
- potential to alter the physical properties (e.g., stability, solubility, UV–vis absorption) of an ylide, as well as bias a Lewis base’s σ-hole selectivity through σ-hole blocking, which represent emerging avenues for tuning an ylide’s reactivity and improving its reaction outcomes. Review 1 Halogen bonding
- appreciation and understanding of σ-holes in iodonium ylides, many examples exist where inter- or intramolecular halogen bonding has been invoked to provide a meaningful explanation of unexpected reactivity, of reagent stability, or as a reaction control element. Examples of these include spontaneous
Selective and scalable oxygenation of heteroatoms using the elements of nature: air, water, and light
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1146–1154, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.82
- oxidation of tetrahydrothiophene). Therefore, we performed a control experiment in the presence of an additive with an aromatic moiety to determine its effect on the reactivity of a non-aromatic substrate. Surprisingly, and to the best of our knowledge, never reported before in literature, the addition of 1
Photoredox catalysis harvesting multiple photon or electrochemical energies
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1055–1145, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.81
- the most appropriate for a given reaction, scale and purpose of a project. Keywords: consecutive photoinduced electron transfer; electro-activated photoredox catalysis; photoelectrochemistry; photoredox catalysis; radical ions; Review 1 Introduction Owing to the unique reactivity patterns of free
- intermediate is proposed in conPET and PEC reactions (e.g., a photoexcited radical anion), yet different reactivity outcomes arise; the underlying reasons for such are discussed. Finally, we provide our perspective on current challenges and target areas for future exploration. 1.1 Multi-photon processes As
- efficiency and selectivity of the reactions (vide infra, conPET section). Electrolytes have the potential to be i) aqueous-separated and recovered in batch, or ii) decreased, even ultimately eliminated by flow reactors as an engineering control. Regarding purely the chemical reactivity and scope of
Copper-catalyzed N-arylation of amines with aryliodonium ylides in water
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1008–1014, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.76
- in oxidation, C–C, C–X bond formation, rearrangements, and halogenation reactions [23][24][25]. Due to the nontoxic nature, easier preparation, and handling of the hypervalent iodine reagents, many researchers are attracted to unravel the chemistry and reactivity of these reagents. Amongst different
Synthesis of tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridines via Pictet–Spengler reaction
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 991–997, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.74
- the condensation of easily accessibly 2-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)ethanamine with commercially available aromatic aldehydes followed by acid-catalyzed Pictet–Spengler cyclization. Using this approach, we synthesized a range of 4-substituted tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridines in reasonable yields. The reactivity
- . Reactivity of tetrahydrofuro[3,2-c]pyridine 4a. Optimization of reaction conditionsa. Supporting Information Supporting Information File 47: Experimental procedures, characterization data, copies of 1H and 13C NMR spectra, HRMS of new compounds, and X-ray crystallography data. Supporting Information File 48
The unique reactivity of 5,6-unsubstituted 1,4-dihydropyridine in the Huisgen 1,4-diploar cycloaddition and formal [2 + 2] cycloaddition
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 982–990, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.73
- ][28][29][30]. The 5,6-unsubstituted 1,4-dihydropyridines can be easily prepared from the three-component reaction of an arylamine, cinnamaldehyde, and methyl acetoacetate [31][32][33][34]. The unsubstituted C=C double bond in 5,6-unsubstituted 1,4-dihydropyridines exhibits high reactivity and could
- unprecedented synthetic reactivity of the electron-deficient alkynes, but also provides efficient synthetic methodologies for complex nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The potential application of this reaction in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry might be significant. Experimental General procedure for
Aromatic C–H bond functionalization through organocatalyzed asymmetric intermolecular aza-Friedel–Crafts reaction: a recent update
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 956–981, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.72
- reactivity of catalyst P5 initiated with the protonation of amidates 42 to generate intermediate 44 through ring cleavage. Then, the intermediate 44 was paired with the anionic conjugate base of catalyst P5 and acts as electrophile to facilitate the conjugate Friedel–Crafts reaction involving C3 of indole 4
Clauson–Kaas pyrrole synthesis using diverse catalysts: a transition from conventional to greener approach
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 928–955, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.71
- and co-workers [57] synthesized various N-substituted pyrrole derivatives 9 using the Clauson–Kaas reaction to study their structure–reactivity relationship (SRR). These compounds were synthesized in 15–90% yields from the reaction between various aliphatic and aromatic amines 8 and 2,5-DMTHF (2) in
- chemoselective procedure in which the iodine counterion and MeCN played key roles in the unique reactivity of this catalytic system. To optimize the reaction conditions, many catalysts, solvents, and temperatures were studied and finally, 10 mol % MgI2∙(OEt2)n as the catalyst, CH3CN as the solvent, and 80 °C
- reactivity of the aromatic amine depends on the electron density of the amino compounds. In addition, the authors also performed the reaction of aliphatic amines with 2,5-DMTHF (2), and found that aliphatic amines are inert in the presence of MgI2 etherate. The proposed mechanism shown in Scheme 9b suggests
Synthesis of aliphatic nitriles from cyclobutanone oxime mediated by sulfuryl fluoride (SO2F2)
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 901–908, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.68
- the [Cun] catalyst and intermediate V. The critical β-H elimination step occurs smoothly in the presence of excessive base to generate the final nitrile product. Due to the high reactivity of the intermediate fluorosulfonate I, the attempt of isolation or detecting the in situ generated intermediate I
Cyclodextrins as building blocks for new materials
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 889–891, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.66

- reactivity of their alcohol functions. This allows regioselective chemical modification at either the primary or secondary rim [13]. As a result, these molecular hosts can be specifically linked either covalently or noncovalently to a wide variety of ligands. CDs are a significant part of almost all areas of


































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































